【Linux】基础IO(1)
1. 理解“文件”
1.1 狭义理解
1.2 广义理解
1.3 文件操作的归类认知
1.4 系统角度
2. 回顾C文件接口文件
2.1 打开文件
#include<stdio.h>int main(){FILE* fp = fopen("newfile", "w");if(!fp) printf("fopen error\n");fclose(fp); return 0;}
fopen函数用于打开文件,第一个参数是文件名,第二个参数是打开模式- 打开模式 "w" 表示以写入方式打开,如果文件不存在则创建,如果存在则清空原有内容
- 函数返回
FILE*类型的文件指针,作为后续文件操作的句柄 - 必须检查返回值,如果为
NULL表示打开失败(可能是权限问题等)
2.2 写文件
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>int main()
{FILE* fp = fopen("newfile", "w");if(!fp) printf("fopen error\n");const char* msg = "hello Linux!\n";int count = 5;while(count--){fwrite(msg, strlen(msg), 1, fp);}fclose(fp);return 0;
}fwrite函数原型:size_t fwrite(const void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb, FILE *stream)- 这里表示每次写入 1 个大小为
strlen(msg)的元素(即整个字符串) - 循环 5 次,所以会将 "hello Linux!\n" 写入文件 5 次
2.3 读文件
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>int main()
{FILE* fp = fopen("newfile", "r");if(!fp){printf("fopen error!\n");return 1;}char buf[1024];const char* msg = "hello Linux!\n";while(1){size_t s = fread(buf, 1, strlen(msg), fp);if(s > 0){buf[s] = 0;printf("%s", buf);}if(feof(fp))break;}fclose(fp);return 0;
}fread函数原型:size_t fread(void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb, FILE *stream)- 这里每次读取
strlen(msg)个大小为 1 的元素(即与写入的字符串长度相同) feof(fp)用于检查是否到达文件末尾- 读取到内容后手动添加字符串结束符
\0,因为fread不会自动添加
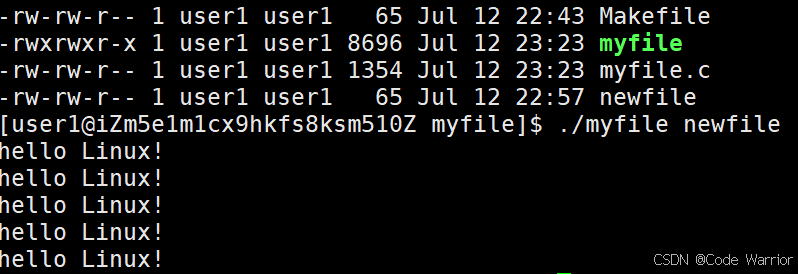
稍作修改,简单实现cat命令
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{if (argc != 2){printf("argv error!\n");return 1;}FILE* fp = fopen(argv[1], "r");if (!fp) {printf("fopen error!\n");return 2;}char buf[1024];while (1) {int s = fread(buf, 1, sizeof(buf), fp);if (s > 0) {buf[s] = 0;printf("%s", buf);}if (feof(fp)) {break;}}fclose(fp);return 0;
}
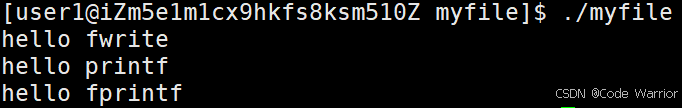
2.4 输出信息到显示器,你有哪些方法
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{const char* msg = "hello fwrite\n";fwrite(msg, strlen(msg), 1, stdout);printf("hello printf\n");fprintf(stdout, "hello fprintf\n");return 0;
}
2.5 stdin & stdout & stderr
- stdin:标准输入(键盘),行缓冲
- stdout:标准输出(屏幕),行缓冲(遇
\n刷新) - stderr:标准错误(屏幕),无缓冲(立即输出)
#include <stdio.h>
extern FILE *stdin;
extern FILE *stdout;
extern FILE *stderr;2.6 打开文件的方式
r Open text file for reading.The stream is positioned at the beginning of the file.
r+ Open for reading and writing.The stream is positioned at the beginning of the file.
w Truncate file to zero length or create text file for writing.The stream is positioned at the beginning of the file.
w+ Open for reading and writing.The file is created if it does not exist, otherwise it is truncated.The stream is positioned at the beginning of the file.
a Open for appending (writing at end of file).The file is created if it does not exist.The stream is positioned at the end of the file.
a+ Open for reading and appending (writing at end of file).The file is created if it does not exist.The initial file position for reading is at the beginning of the file,but output is always appended to the end of the file.
r:打开文本文件用于读取。流定位在文件开头(文件必须存在)。r+:打开文本文件用于读写。流定位在文件开头(文件必须存在)。w:创建文本文件用于写入,若文件已存在则截断为零长度。流定位在文件开头。w+:打开文本文件用于读写,若文件不存在则创建,若已存在则截断。流定位在文件开头。a:打开文件用于追加(在文件末尾写入),若文件不存在则创建。流定位在文件末尾。a+:打开文件用于读取和追加,若文件不存在则创建。读取的初始位置在文件开头,但输出始终追加到文件末尾。
