[Go类库分享]Go template模版库
[Go类库分享]Go template模版库
官方地址:https://pkg.go.dev/text/template
文章所含代码Github地址:https://github.com/ziyifast/ziyifast-code_instruction/tree/main/go-demo/go-template

1. 概述
Go的template库主要包含两类,一类是html/template、另一类是text/template,其中html/template主要用于生成展示前端页面。本文主要会介绍text/template。
Go 的 text/template 包提供了一个强大的模板引擎,用于生成文本输出。它通过将数据应用于模板来工作,模板中包含特殊标记(称为"动作"),用于控制文档生成过程。
Go template 语言特点:
Go template 的设计使其成为流程编排和动态逻辑构建的理想选择。
- 声明式编程范式:通过模板定义处理逻辑,而非硬编码在程序中
- 动态性:运行时可以修改模板而无需重新编译和部署
- 安全性:内置沙箱机制,防止恶意代码执行
- 丰富的控制结构:支持条件判断、循环、变量定义等
模板执行流程:
- 解析模板: template.New().Parse()
- 注册函数: Funcs()
- 执行模板: Execute()
- 输出结果: 写入指定的 io.Writer
注意:函数必须在解析模板之前注册,否则模板中无法使用这些函数。
2. 基本语法
2.1 基本结构
// 模板中的基本动作由双大括号 {{}} 包围
{{.}} // 当前上下文
{{.FieldName}} // 访问结构体字段
{{.MethodName}} // 调用方法
{{$variable}} // 访问变量
案例:
// 基础使用
func case_basic_use() {type Person struct {Name stringAge int}tmpl := `姓名: {{.Name}}, 年龄: {{.Age}}`t := template.Must(template.New("example").Parse(tmpl))person := Person{Name: "张三", Age: 30}err := t.Execute(os.Stdout, person)if err != nil {panic(err)}
}
2.2 注释
{{/* 这是一个注释 */}}
案例:
// 包含注释
func case_comment_use() {tmpl := `{{/* 这是一个注释 */}}
Hello, {{.Name}}!
{{/* 另一个注释 */}}`t := template.Must(template.New("example").Parse(tmpl))err := t.Execute(os.Stdout, map[string]string{"Name": "世界"})if err != nil {panic(err)}
}
2.3 输出值
{{.}} // 输出当前上下文
{{.Field}} // 输出结构体字段
{{.Method}} // 输出方法返回值
{{index .Array 0}} // 输出数组第一个元素
{{.Map.key}} // 输出map的值
案例:
// 获取结构体属性
func case_get_field() {type Data struct {Name stringHobbies []stringInfo map[string]string}data := Data{Name: "张三",Hobbies: []string{"读书", "游泳", "跑步"},Info: map[string]string{"city": "北京", "job": "工程师"},}tmpl := `姓名: {{.Name}}
第一个爱好: {{index .Hobbies 0}}
城市: {{.Info.city}}`t := template.Must(template.New("example").Parse(tmpl))err := t.Execute(os.Stdout, data)if err != nil {panic(err)}
}
2.4 控制结构
比较判断
- eq: 等于 (==)
- ne: 不等于 (!=)
- lt: 小于 (<)
- le: 小于等于 (<=)
- gt: 大于 (>)
- ge: 大于等于 (>=)
代码案例:
func case_comparison() {user := map[string]interface{}{"name": "curry","age": 20,}//比较判断//- eq: 等于 (==)//- ne: 不等于 (!=)//- lt: 小于 (<)//- le: 小于等于 (<=)//- gt: 大于 (>)//- ge: 大于等于 (>=)tmpl := `{{if ge .age 18}} 已成年{{else}}未成年{{end}}`t := template.Must(template.New("example").Parse(tmpl))err := t.Execute(os.Stdout, user)if err != nil {panic(err)}
}
条件判断
{{if .Condition}}Content when condition is true
{{else if .OtherCondition}}Other content
{{else}}Content when condition is false
{{end}}
案例:
// 条件判断
func case_condition() {data := map[string]interface{}{"Age": 25,"Name": "张三","Active": true,}tmpl := `{{if .Active}}
用户 {{.Name}} 处于活跃状态
{{else}}
用户 {{.Name}} 处于非活跃状态
{{end}}
{{if gt .Age 18}}
用户已成年
{{else}}
用户未成年
{{end}}`t := template.Must(template.New("example").Parse(tmpl))err := t.Execute(os.Stdout, data)if err != nil {panic(err)}
}
循环
{{range .Items}}{{.}} // 当前元素
{{end}}{{range $index, $element := .Items}}{{$index}}: {{$element}}
{{end}}// 使用 else 处理空情况
{{range .Items}}{{.}}
{{else}}No items found
{{end}}
案例:
// 循环
func case5_loop() {data := map[string][]string{"Fruits": {"苹果", "香蕉", "橙子"},}tmpl := `水果列表:
{{range .Fruits}}
- {{.}}
{{end}}带索引的列表:
{{range $index, $fruit := .Fruits}}
{{add $index 1}}. {{$fruit}}
{{end}}空列表处理:
{{range .Vegetables}}
- {{.}}
{{else}}
没有蔬菜
{{end}}`funcMap := template.FuncMap{"add": func(a, b int) int { return a + b },}t := template.Must(template.New("example").Funcs(funcMap).Parse(tmpl))err := t.Execute(os.Stdout, data)if err != nil {panic(err)}
}
定义变量
{{$name := .UserName}}
{{$count := len .Items}}
案例:
// 定义变量
func case_define_variable() {data := map[string]interface{}{"Items": []string{"item1", "item2", "item3"},"Name": "张三",}tmpl := `{{$name := .Name}}
{{$count := len .Items}}
用户: {{$name}}
项目数量: {{$count}}{{range $index, $item := .Items}}
项目 {{$index}}: {{$item}}
{{end}}`t := template.Must(template.New("example").Parse(tmpl))err := t.Execute(os.Stdout, data)if err != nil {panic(err)}
}
2.5 函数和管道
Go 模板支持函数调用和管道操作:
// 内置函数
{{printf "Hello, %s!" .Name}}
{{len .Items}}
{{index .Map "key"}}// 管道操作
{{.Name | printf "%s"}}
{{.Value | multiply 2 | add 10}}
案例:
// 管道
func case_pipe() {data := map[string]interface{}{"Name": "zhangsan","Text": "hello world","Items": []string{"item1", "item2", "item3"},}funcMap := template.FuncMap{"upper": strings.ToUpper,"join": func(sep string, s []string) string {return strings.Join(s, sep)},}tmpl := `原始名称: {{.Name}}
大写名称: {{.Name | upper}}
项目数量: {{len .Items}}
项目连接: {{join "," .Items}}格式化: {{printf "Hello %s, you have %d items" .Name (len .Items)}}`t := template.Must(template.New("example").Funcs(funcMap).Parse(tmpl))err := t.Execute(os.Stdout, data)if err != nil {panic(err)}
}
2.6 错误处理
我们可以自定义一个函数,当不满足条件时,我们可以抛出自己的业务错误。
package mainimport ("fmt""os""text/template"
)// 错误结构
type BusinessError struct {Code intMessage string
}func (e BusinessError) Error() string {return fmt.Sprintf("[%d] %s", e.Code, e.Message)
}// 在模板中抛出错误的核心函数
func throwError(code int, message string) (interface{}, error) {return nil, BusinessError{Code: code,Message: message,}
}func main() {tmpl := `
{{/* 条件性抛出错误 */}}
{{$age := 15}}
{{ if gt $age 18}}已成年
{{else}}{{throwError 1001 "年龄不满足"}}
{{end}}
`funcMap := template.FuncMap{"throwError": throwError,}parsedTmpl, err := template.New("simple_error").Funcs(funcMap).Parse(tmpl)if err != nil {fmt.Printf("模板解析错误: %v\n", err)return}err = parsedTmpl.Execute(os.Stdout, nil)if err != nil {fmt.Printf("执行模板错误: %v\n", err)}
}
效果:

3. 高级功能
3.1 自定义函数
要向模板中添加自定义函数,需要使用 Funcs 方法:
// 自定义函数
func case_custom_function() {funcMap := template.FuncMap{"formatTime": formatTime,"multiply": multiply,"upper": strings.ToUpper,}data := map[string]interface{}{"Name": "张三","Time": time.Now(),"Price": 100,"Quantity": 3,}tmpl := `用户: {{.Name | upper}}
当前时间: {{.Time | formatTime}}
商品总价: {{multiply .Price .Quantity}} 元`t := template.Must(template.New("example").Funcs(funcMap).Parse(tmpl))err := t.Execute(os.Stdout, data)if err != nil {panic(err)}
}func formatTime(t time.Time) string {return t.Format("2006-01-02 15:04:05")
}func multiply(a, b int) int {return a * b
}
3.2 模板嵌套
主要用于展示固定结构的页面,比如:html/template会用来展示固定前端页面,text/template会用来展示邮件、消息模版等。
// 模版嵌套
func case_template_nesting() {tmpl := `
{{define "header"}}
================================
{{.Title}}
================================
{{end}}{{define "content"}}
用户信息:
姓名: {{.User.Name}}
邮箱: {{.User.Email}}
{{end}}{{define "footer"}}
--------------------------------
报告生成时间: {{.Time}}
--------------------------------
{{end}}{{template "header" .}}
{{template "content" .}}
{{template "footer" .}}`data := map[string]interface{}{"Title": "用户报告","User": map[string]string{"Name": "张三","Email": "zhangsan@example.com",},"Time": "2023-01-01 12:00:00",}t := template.Must(template.New("example").Parse(tmpl))err := t.Execute(os.Stdout, data)if err != nil {panic(err)}
}
3.3 去除空行
有些时候我们想要去除模版中的换行、空白符等,这个时候就需要使用类似{{- -}}语法来去除。
Go模板提供空白符控制功能,用于精确控制输出格式:
- {{- : 去除标记左侧的空白符(包括空格、制表符、换行符)
- -}} : 去除标记右侧的空白符
- {{- -}} : 去除标记两侧的空白符
TIPS:如果后续脚本需要在业务上频繁使用,那么为了编写方便,我们也可以进行适配,比如通过前置处理器的方式,自动添加{{ }},让用户编写时,更关注流程,减少因编写格式带来的时间损耗。
// 移除空行
// {{-:去除左侧的空白符(包括空格、制表符和换行符)
// -}}:去除右侧的空白符
// {{- -}}:去除两侧的空白符
func case_remove_empty_line() {//不去除空行的模版tmpl := `
{{range .Lines}}
{{.}}
{{end}}`//去除空行的模版tmpl = `
{{- range .Lines -}}
{{- . -}}
{{- end -}}`data := map[string]interface{}{"Lines": []string{"", "line1", "", "line2", ""},}t := template.Must(template.New("example").Parse(tmpl))err := t.Execute(os.Stdout, data)if err != nil {panic(err)}
}
4. 实战应用:服务编排
go的这种模版语言,包含流程处理、函数定义等,很适合用来做流程编排,动态构建一些简单逻辑,避免频繁调整代码、发版等,比如在处理消息队列的消息时,就很适合,可以用来配合消息总线+数据处理,实现下游服务只用关心自己需要的结构,将整个解析逻辑放在脚本服务编排里。这种架构的优势:
- 解耦性:下游服务只需关注自己的数据结构
- 灵活性:通过修改模板即可调整处理逻辑
- 可维护性:业务逻辑集中管理,无需频繁发版
- 可观测性:模板执行过程可以被完整记录和追踪
整体流程:
[消息生产者] → [消息队列] → [模板编排引擎] → [下游服务]↓[模板配置中心]
这里主要给大家演示最核心的部分,服务编排,其他部分大家可根据文中代码自行补充实现:
package mainimport ("encoding/json""fmt""log""net/http""os""text/template""time"
)// 服务响应结构
type ServiceResponse struct {Data interface{} `json:"data"`
}// 用户信息
type User struct {ID string `json:"id"`Name string `json:"name"`Email string `json:"email"`Level string `json:"level"`Region string `json:"region"`Language string `json:"language"`
}// 订单信息
type Order struct {ID string `json:"id"`Amount float64 `json:"amount"`Status string `json:"status"`Currency string `json:"currency"`Items []OrderItem `json:"items"`Metadata map[string]string `json:"metadata"`CreatedAt string `json:"created_at"`CustomerID string `json:"customer_id"`
}// 订单项
type OrderItem struct {ProductID string `json:"product_id"`ProductName string `json:"product_name"`Quantity int `json:"quantity"`Price float64 `json:"price"`
}// 支付信息
type Payment struct {ID string `json:"id"`OrderID string `json:"order_id"`Method string `json:"method"`Status string `json:"status"`Amount float64 `json:"amount"`Currency string `json:"currency"`CreatedAt string `json:"created_at"`Transaction string `json:"transaction_id"`
}// 库存信息
type Inventory struct {ProductID string `json:"product_id"`Stock int `json:"stock"`Reserved int `json:"reserved"`
}// 通知配置
type NotificationConfig struct {Channels []string `json:"channels"`Template string `json:"template"`
}// 模拟数据
var (users = map[string]User{"cust_12345": {ID: "cust_12345", Name: "张三", Email: "zhangsan@example.com", Level: "VIP", Region: "CN", Language: "zh-CN"},"cust_67890": {ID: "cust_67890", Name: "李四", Email: "lisi@example.com", Level: "普通", Region: "US", Language: "en-US"},}orders = map[string]Order{"ord_001": {ID: "ord_001",Amount: 299.99,Status: "completed",Currency: "CNY",CreatedAt: "2023-01-01T10:30:00Z",CustomerID: "cust_12345",Items: []OrderItem{{ProductID: "prod_001", ProductName: "iPhone 14", Quantity: 1, Price: 299.99},},Metadata: map[string]string{"source": "web","promo": "NEWYEAR2023",},},"ord_002": {ID: "ord_002",Amount: 199.50,Status: "processing",Currency: "CNY",CreatedAt: "2023-01-02T14:15:00Z",CustomerID: "cust_12345",Items: []OrderItem{{ProductID: "prod_002", ProductName: "AirPods", Quantity: 1, Price: 199.50},},Metadata: map[string]string{"source": "mobile",},},}payments = map[string]Payment{"pay_001": {ID: "pay_001", OrderID: "ord_001", Method: "credit_card", Status: "success", Amount: 299.99, Currency: "CNY", CreatedAt: "2023-01-01T10:30:00Z", Transaction: "txn_abc123"},"pay_002": {ID: "pay_002", OrderID: "ord_002", Method: "alipay", Status: "pending", Amount: 199.50, Currency: "CNY", CreatedAt: "2023-01-02T14:15:00Z", Transaction: "txn_def456"},}inventories = map[string]Inventory{"prod_001": {ProductID: "prod_001", Stock: 100, Reserved: 10},"prod_002": {ProductID: "prod_002", Stock: 50, Reserved: 5},}notificationConfigs = map[string]NotificationConfig{"order_completed": {Channels: []string{"email", "sms"}, Template: "order_completion"},"order_processing": {Channels: []string{"email"}, Template: "order_processing"},}
)// 模拟用户服务
func userHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {userID := r.URL.Query().Get("id")if userID == "" {http.Error(w, "缺少用户ID参数", http.StatusBadRequest)return}user, exists := users[userID]if !exists {http.Error(w, "用户不存在", http.StatusNotFound)return}response := ServiceResponse{Data: user}w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(response)
}// 模拟订单服务
func orderHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {orderID := r.URL.Query().Get("id")if orderID == "" {http.Error(w, "缺少订单ID参数", http.StatusBadRequest)return}order, exists := orders[orderID]if !exists {http.Error(w, "订单不存在", http.StatusNotFound)return}response := ServiceResponse{Data: order}w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(response)
}// 模拟支付服务
func paymentHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {orderID := r.URL.Query().Get("order_id")if orderID == "" {http.Error(w, "缺少订单ID参数", http.StatusBadRequest)return}// 查找与订单关联的支付信息var payment *Paymentfor _, p := range payments {if p.OrderID == orderID {payment = &pbreak}}if payment == nil {http.Error(w, "支付信息不存在", http.StatusNotFound)return}response := ServiceResponse{Data: *payment}w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(response)
}// 模拟库存服务
func inventoryHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {productID := r.URL.Query().Get("product_id")if productID == "" {http.Error(w, "缺少产品ID参数", http.StatusBadRequest)return}inventory, exists := inventories[productID]if !exists {http.Error(w, "库存信息不存在", http.StatusNotFound)return}response := ServiceResponse{Data: inventory}w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(response)
}// 模拟通知配置服务
func notificationConfigHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {eventType := r.URL.Query().Get("event_type")if eventType == "" {http.Error(w, "缺少事件类型参数", http.StatusBadRequest)return}config, exists := notificationConfigs[eventType]if !exists {// 返回默认配置config = NotificationConfig{Channels: []string{"email"}, Template: "default"}}response := ServiceResponse{Data: config}w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(response)
}// 启动模拟服务
func startMockServices() {http.HandleFunc("/users", userHandler)http.HandleFunc("/orders", orderHandler)http.HandleFunc("/payments", paymentHandler)http.HandleFunc("/inventory", inventoryHandler)http.HandleFunc("/notification-config", notificationConfigHandler)fmt.Println("模拟服务已启动在 :8080 端口")fmt.Println("用户服务: http://localhost:8080/users?id=cust_12345")fmt.Println("订单服务: http://localhost:8080/orders?id=ord_001")fmt.Println("支付服务: http://localhost:8080/payments?order_id=ord_001")fmt.Println("库存服务: http://localhost:8080/inventory?product_id=prod_001")fmt.Println("通知配置服务: http://localhost:8080/notification-config?event_type=order_completed")fmt.Println()go func() {log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil))}()// 等待服务启动time.Sleep(100 * time.Millisecond)
}// 自定义函数:调用用户服务
func getUserService(userID string) (map[string]interface{}, error) {resp, err := http.Get("http://localhost:8080/users?id=" + userID)if err != nil {return nil, err}defer resp.Body.Close()var result ServiceResponseif err := json.NewDecoder(resp.Body).Decode(&result); err != nil {return nil, err}// 转换为 map[string]interface{}userData, ok := result.Data.(map[string]interface{})if !ok {return nil, fmt.Errorf("用户数据格式错误")}return userData, nil
}// 自定义函数:调用订单服务
func getOrderService(orderID string) (map[string]interface{}, error) {resp, err := http.Get("http://localhost:8080/orders?id=" + orderID)if err != nil {return nil, err}defer resp.Body.Close()var result ServiceResponseif err := json.NewDecoder(resp.Body).Decode(&result); err != nil {return nil, err}// 转换为 map[string]interface{}orderData, ok := result.Data.(map[string]interface{})if !ok {return nil, fmt.Errorf("订单数据格式错误")}return orderData, nil
}// 自定义函数:调用支付服务
func getPaymentService(orderID string) (map[string]interface{}, error) {resp, err := http.Get("http://localhost:8080/payments?order_id=" + orderID)if err != nil {return nil, err}defer resp.Body.Close()var result ServiceResponseif err := json.NewDecoder(resp.Body).Decode(&result); err != nil {return nil, err}// 转换为 map[string]interface{}paymentData, ok := result.Data.(map[string]interface{})if !ok {return nil, fmt.Errorf("支付数据格式错误")}return paymentData, nil
}// 自定义函数:调用库存服务
func getInventoryService(productID string) (map[string]interface{}, error) {resp, err := http.Get("http://localhost:8080/inventory?product_id=" + productID)if err != nil {return nil, err}defer resp.Body.Close()var result ServiceResponseif err := json.NewDecoder(resp.Body).Decode(&result); err != nil {return nil, err}// 转换为 map[string]interface{}inventoryData, ok := result.Data.(map[string]interface{})if !ok {return nil, fmt.Errorf("库存数据格式错误")}return inventoryData, nil
}// 自定义函数:获取通知配置
func getNotificationConfig(eventType string) (map[string]interface{}, error) {resp, err := http.Get("http://localhost:8080/notification-config?event_type=" + eventType)if err != nil {return nil, err}defer resp.Body.Close()var result ServiceResponseif err := json.NewDecoder(resp.Body).Decode(&result); err != nil {return nil, err}// 转换为 map[string]interface{}configData, ok := result.Data.(map[string]interface{})if !ok {return nil, fmt.Errorf("通知配置数据格式错误")}return configData, nil
}// 自定义函数:格式化货币
func formatCurrency(amount float64, currency string) string {switch currency {case "CNY":return fmt.Sprintf("¥%.2f", amount)case "USD":return fmt.Sprintf("$%.2f", amount)default:return fmt.Sprintf("%.2f %s", amount, currency)}
}// 自定义函数:获取订单状态描述
func getOrderStatusDescription(status string) string {statusMap := map[string]string{"completed": "已完成","processing": "处理中","cancelled": "已取消","pending": "待处理",}if desc, ok := statusMap[status]; ok {return desc}return status
}// 辅助函数:加法
func add(a, b int) int {return a + b
}// 辅助函数:乘法
func multiply(a, b float64) float64 {return a * b
}// 辅助函数:连接字符串
func join(sep string, s []interface{}) string {if len(s) == 0 {return ""}result := fmt.Sprintf("%v", s[0])for _, item := range s[1:] {result += sep + fmt.Sprintf("%v", item)}return result
}// 辅助函数:转换为JSON
func toJson(v interface{}) string {b, _ := json.Marshal(v)return string(b)
}func main() {// 启动模拟服务startMockServices()// 定义所有函数funcMap := template.FuncMap{"getUser": getUserService,"getOrder": getOrderService,"getPayment": getPaymentService,"getInventory": getInventoryService,"getNotificationConfig": getNotificationConfig,"formatCurrency": formatCurrency,"getOrderStatus": getOrderStatusDescription,"add": add,"multiply": multiply,"join": join,"toJson": toJson,}// 创建复杂的业务流程编排模板tmplText := `
{{/* 获取订单信息 */}}
{{$order := getOrder "ord_001"}}
{{$customer := getUser $order.customer_id}}订单处理报告
================================
订单ID: {{$order.id}}
订单状态: {{getOrderStatus $order.status}}
创建时间: {{$order.created_at}}
订单金额: {{formatCurrency $order.amount $order.currency}}客户信息:姓名: {{$customer.name}}邮箱: {{$customer.email}}等级: {{$customer.level}}地区: {{$customer.region}}订单项目:
{{range $index, $item := $order.items}}{{$index | add 1}}. {{$item.product_name}}产品ID: {{$item.product_id}}数量: {{$item.quantity}}单价: {{formatCurrency $item.price $order.currency}}小计: {{formatCurrency (multiply $item.quantity $item.price) $order.currency}}
{{end}}{{/* 获取支付信息 */}}
{{$payment := getPayment $order.id}}
支付信息:支付ID: {{$payment.id}}支付方式: {{$payment.method}}支付状态: {{$payment.status}}交易号: {{$payment.transaction_id}}支付时间: {{$payment.created_at}}{{/* 检查库存信息 */}}
{{$inventoryIssues := false}}
库存检查:
{{range $item := $order.items}}{{$inventory := getInventory $item.product_id}}产品 {{$item.product_name}}:可用库存: {{$inventory.stock}}已预留: {{$inventory.reserved}}{{if lt $inventory.stock $item.quantity}}警告: 库存不足!{{$inventoryIssues = true}}{{end}}
{{end}}{{/* 获取通知配置 */}}
{{$notificationConfig := getNotificationConfig (printf "order_%s" $order.status)}}
通知配置:渠道: {{join ", " $notificationConfig.channels}}模板: {{$notificationConfig.template}}{{/* 业务决策 */}}
{{if eq $order.status "completed"}}{{if eq $payment.status "success"}}{{if not $inventoryIssues}}
处理结论: 订单处理成功,可以进行发货准备{{else}}
处理结论: 订单支付成功但库存不足,请人工处理{{end}}{{else}}
处理结论: 订单状态异常,请检查支付状态{{end}}
{{else if eq $order.status "processing"}}
处理结论: 订单正在处理中,等待后续状态更新
{{else}}
处理结论: 订单状态{{$order.status}},按相应流程处理
{{end}}{{/* 生成下游服务调用 */}}
下游服务调用:
{{if eq $order.status "completed"}}1. 发货服务: prepareShipment({{toJson $order}})2. 通知服务: sendNotification({{toJson $notificationConfig}}, {{$customer.email}})3. 积分服务: addPoints({{$customer.id}}, {{$order.amount}})
{{end}}
`// 创建模板并添加所有函数tmpl := template.Must(template.New("business_process").Funcs(funcMap).Parse(tmplText))// 执行模板fmt.Println("开始执行业务流程编排...")fmt.Println("========================")err := tmpl.Execute(os.Stdout, nil)if err != nil {log.Fatal("执行模板错误: ", err)}
}
运行效果:
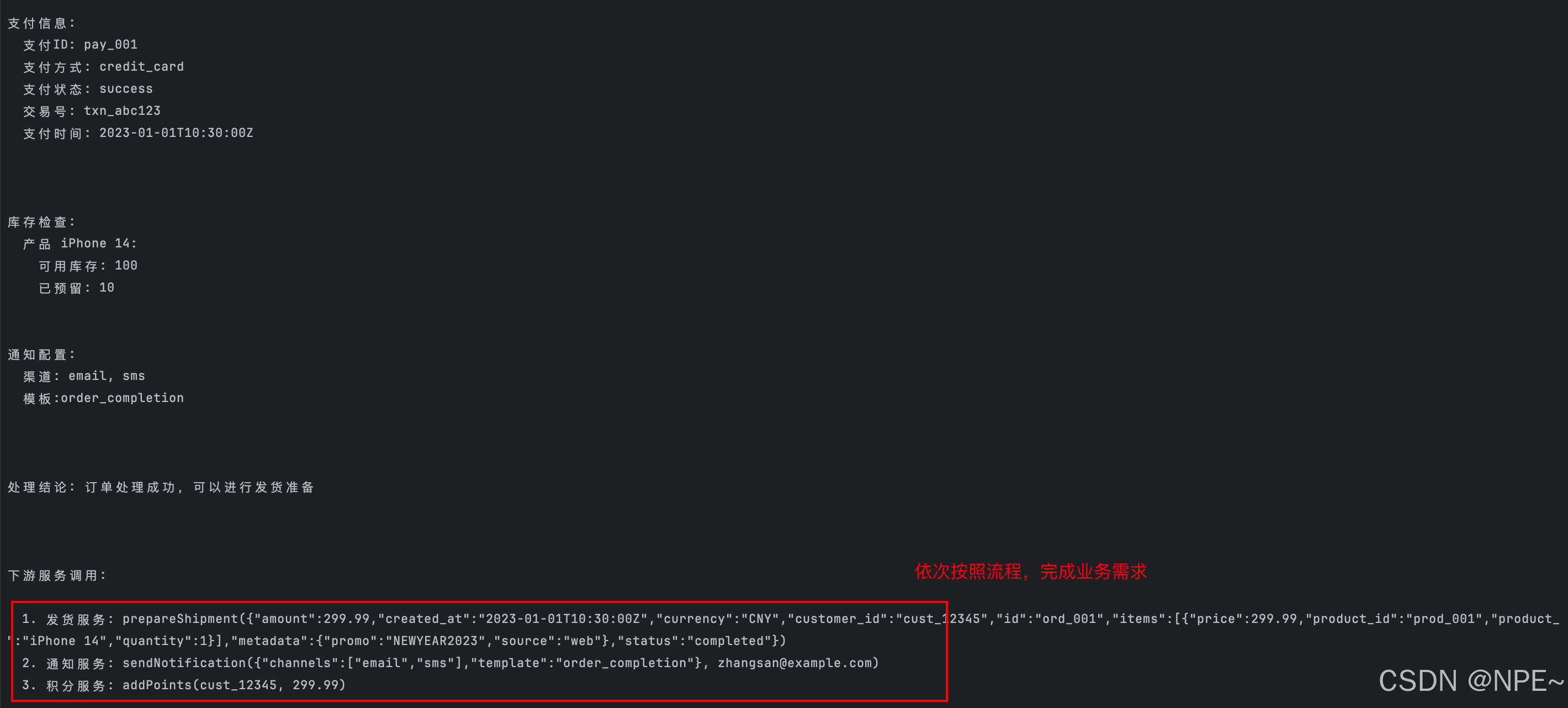
5. 拓展
与go expr混合使用
Go expr可以放在每个节点,控制是否需要条件执行、不执行、循环执行(迭代)等。go template关注每个节点自身的逻辑。
- Go expr教程地址
通用流程编排:
- Go template:基于Go标准库构建,主要承担业务逻辑表达、数据处理和文本生成功能
- Go expr:作为轻量级表达式引擎,用于DAG节点的条件判断、路由决策和循环控制(满足什么样的条件才执行该节点等)
职责分工:
- Go template:关注节点内部的业务逻辑实现和数据处理
- Go expr:专注条件判断和流程控制逻辑
应用场景:
- 节点执行条件判断:customer.level == ‘VIP’ && order.amount > 1000
- 边路由条件:result.status == ‘success’
- 循环控制条件:loop.index < array.length
- 数据验证:input.field != null && input.field.length > 0
DAG概念
DAG(Directed Acyclic Graph):有向无环图,是工作流编排的核心数据结构。
与传统流程控制的区别:
- 传统流程:通常是线性的或简单的分支结构
- DAG流程:支持复杂的多分支、汇聚、并行等结构
1. DAG的基本特征:
- 有向性:节点之间的连接有明确的方向性
- 无环性:不存在从某个节点出发经过若干条边后能回到该节点的路径
- 节点:代表工作流中的任务或决策点
- 边:表示节点间的依赖关系和执行流向
2. 在流程编排中的应用:
- 节点(Nodes):对应工作流中的各个步骤(任务、决策、循环等)
- 边(Edges):定义执行顺序和依赖关系
- 入度:指向某个节点的边的数量,入度为0的节点是起始节点
- 出度:从某个节点指出的边的数量,出度为0的节点是结束节点
3. DAG的优势:
- 清晰的依赖关系:明确表达任务间的前后依赖
- 并行执行:无依赖关系的节点可以并行执行
- 易于分析:可以进行拓扑排序,确定执行顺序
- 避免循环依赖:防止工作流陷入无限循环
- 可视化友好:便于图形化展示和理解
4. 实际应用场景
电商订单处理:
- 订单验证 → 库存检查 → 支付处理 → 发货通知
- VIP客户特殊处理流程
数据ETL管道:
- 数据提取 → 数据转换 → 数据验证 → 数据加载
- 异常数据重试机制
审批流程:
- 提交申请 → 多级审批 → 结果通知
- 条件性审批路径
消息处理(消息总线):
- 消息接收 → 内容解析 → 业务处理 → 结果分发
- 基于消息类型的路由处理
流程编排最佳实践
可以通过go template + go expr + DAG实现整体流程编排。
1. 模板设计:
- 保持模板简洁,复杂逻辑封装在Go函数中
- 合理使用模板缓存提高性能
- 统一错误处理机制
2. 表达式使用:
- 表达式应尽量简单明确
- 避免在表达式中进行复杂计算
- 合理使用表达式缓存
3. DAG设计:
- 避免过度复杂的节点依赖关系
- 合理划分节点粒度
- 考虑并行执行的可能性
- 性能优化:
- 实施模板和表达式缓存
- 监控执行性能
- 优化节点执行顺序
参考文档:
- https://pkg.go.dev/text/template
