Python基于Django的微博舆情可视化系统 关键词/用户ID/评论分析 大数据项目(建议收藏)✅
博主介绍:✌全网粉丝50W+,前互联网大厂软件研发、集结硕博英豪成立软件开发工作室,专注于计算机相关专业项目实战6年之久,累计开发项目作品上万套。凭借丰富的经验与专业实力,已帮助成千上万的学生顺利毕业,选择我们,就是选择放心、选择安心毕业✌
> 🍅想要获取完整文章或者源码,或者代做,拉到文章底部即可与我联系了。🍅点击查看作者主页,了解更多项目!
🍅感兴趣的可以先收藏起来,点赞、关注不迷路,大家在毕设选题,项目以及论文编写等相关问题都可以给我留言咨询,希望帮助同学们顺利毕业 。🍅
1、毕业设计:2026年计算机专业毕业设计选题汇总(建议收藏)✅
2、最全计算机专业毕业设计选题大全(建议收藏)✅
1、项目介绍
技术栈:Python语言、Django框架、MySQL数据库、Echarts可视化、requests爬虫技术、数据分析、地图分析、后台管理、关键词搜索分析、用户ID分析、微博评论分析、微博文章分析、情感分析
研究背景:微博日活过亿,高校与企业亟需实时掌握网络口碑与突发事件。利用requests爬虫对接微博移动端接口,可低成本获取文章、评论、用户地域等结构化数据;结合SnowNLP情感分析与Echarts多维可视化,实现“关键词-用户-内容-情感”一站式洞察,为舆情应对提供量化依据。
研究意义:系统全程本地运行,保障数据合规与隐私;模块化设计支持替换算法或数据源,适合作为“数据科学”“Web开发”课程实践与毕业设计模板,推动大数据情感计算在高校教学与品牌管理中的落地应用。
2、项目界面
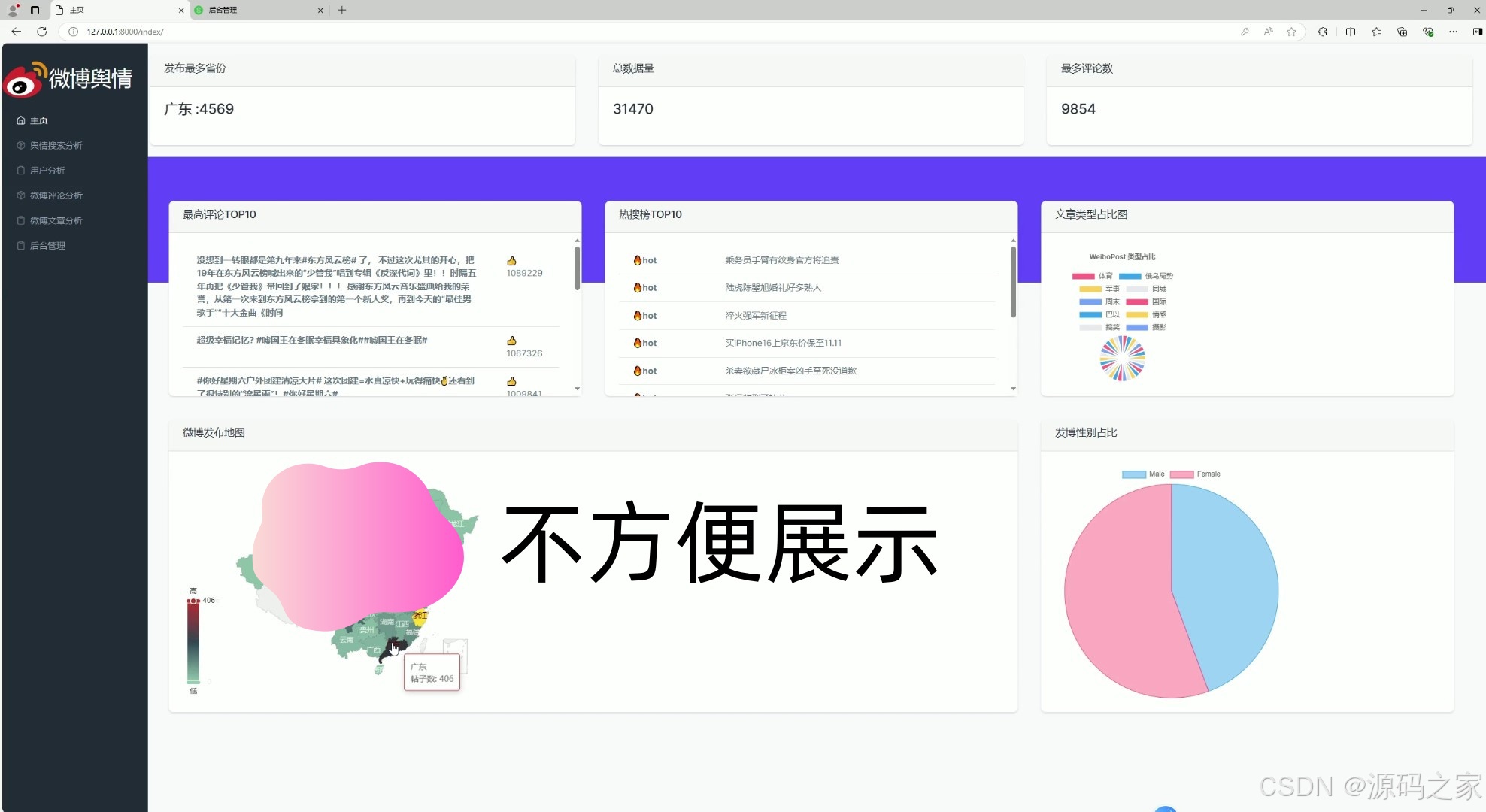
(1)首页
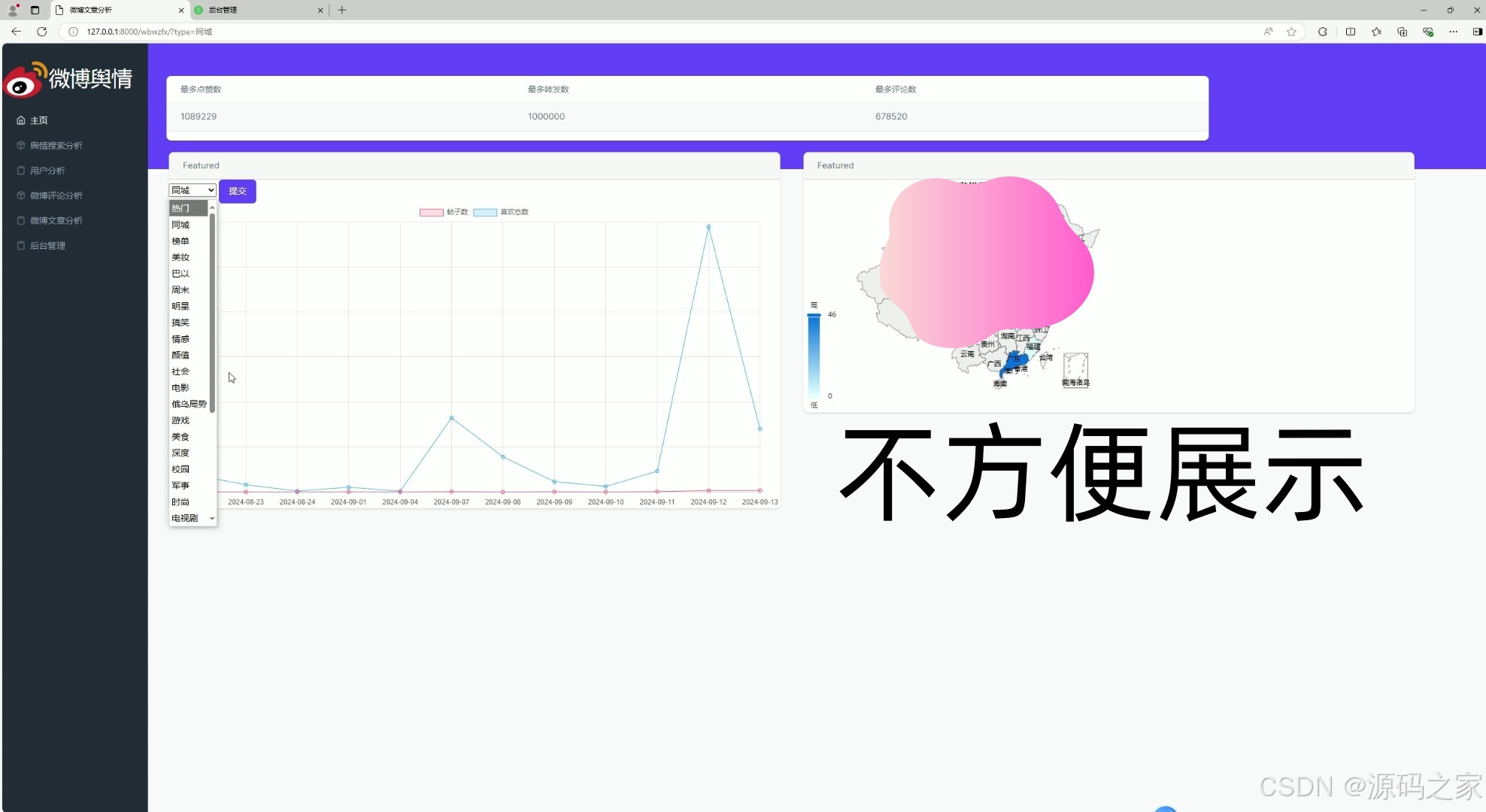
(2)微博文章分析
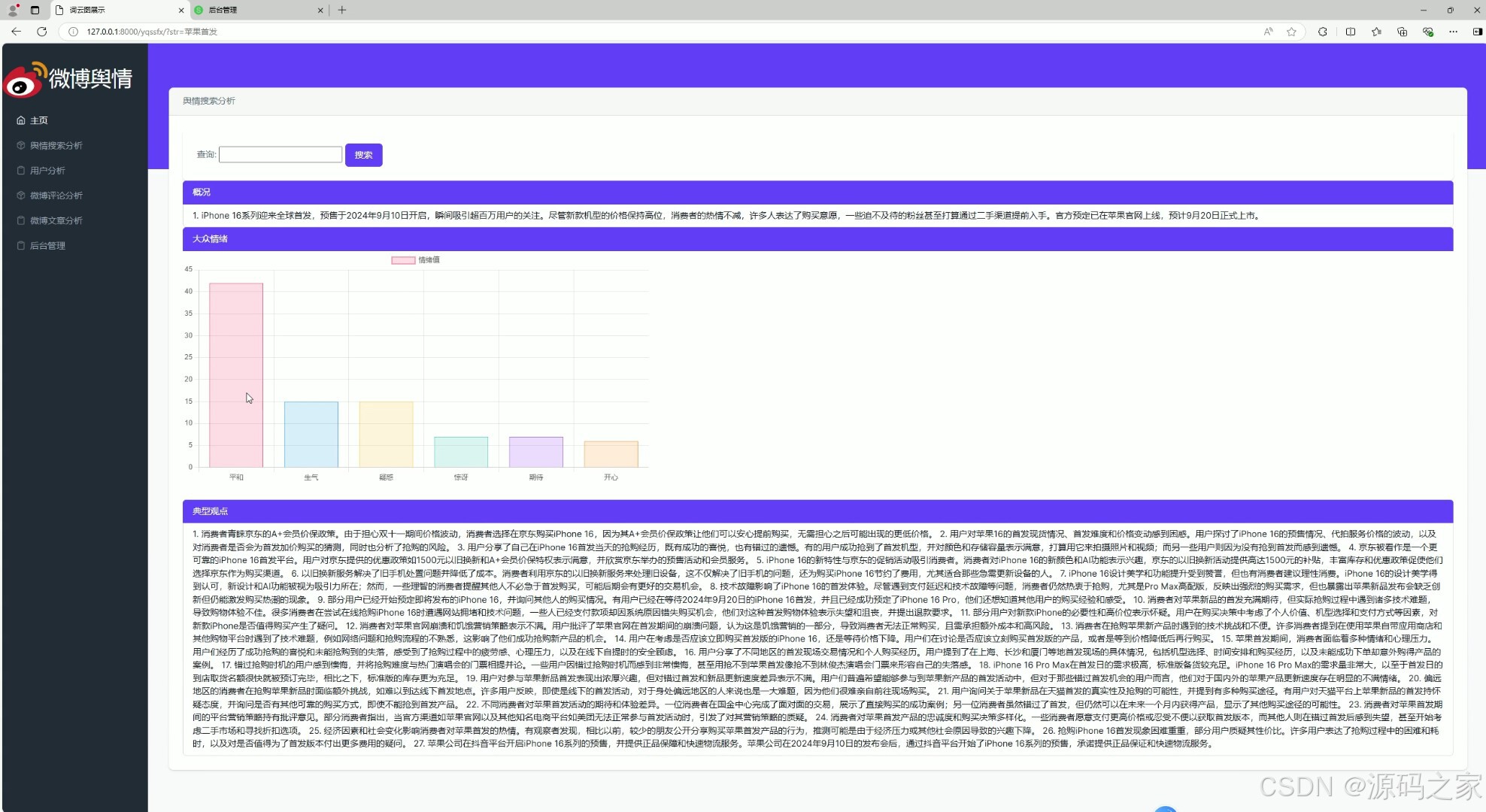
(3)舆情搜索分析
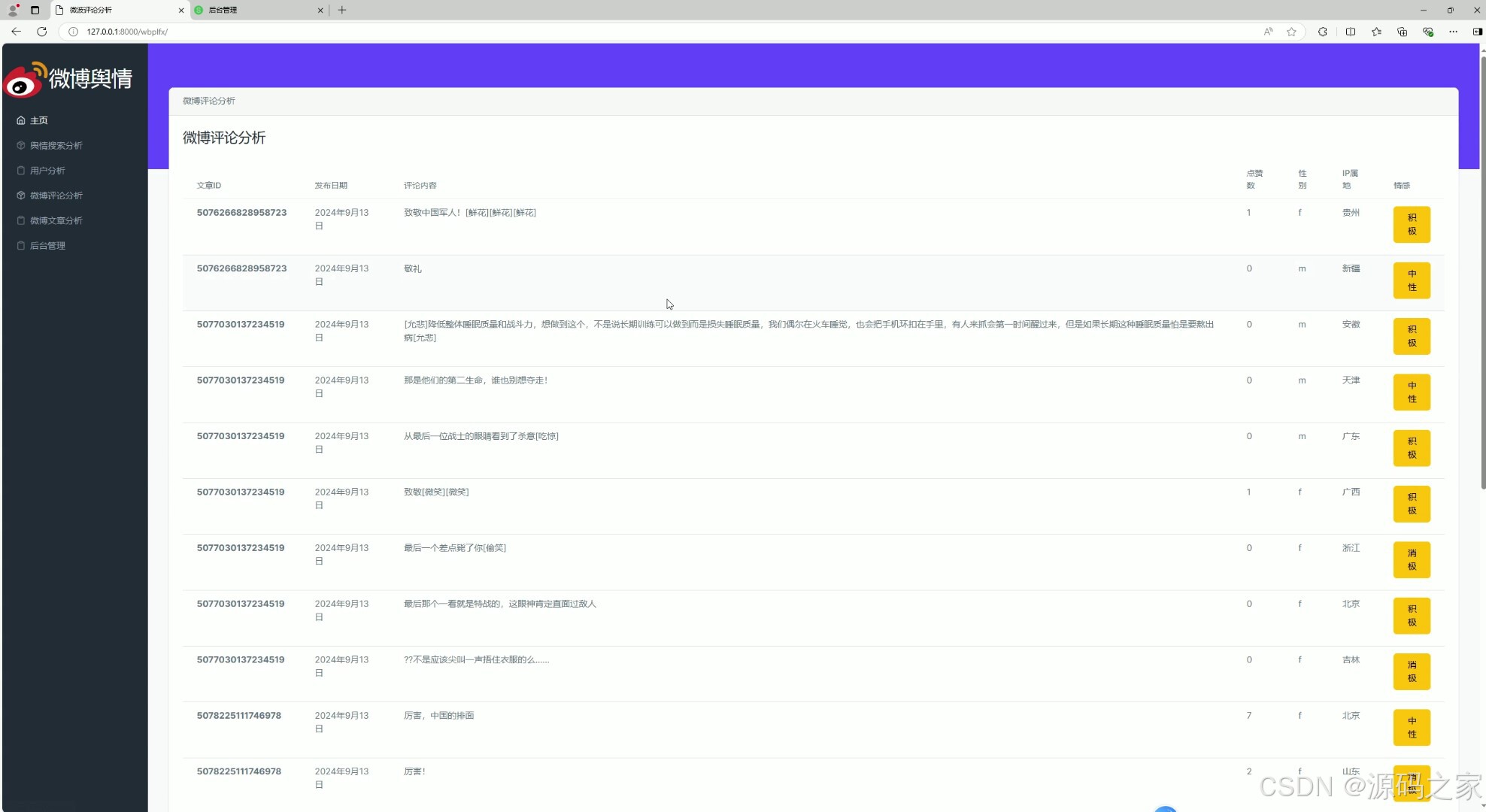
(4)微博评论分析
(5)用户分析
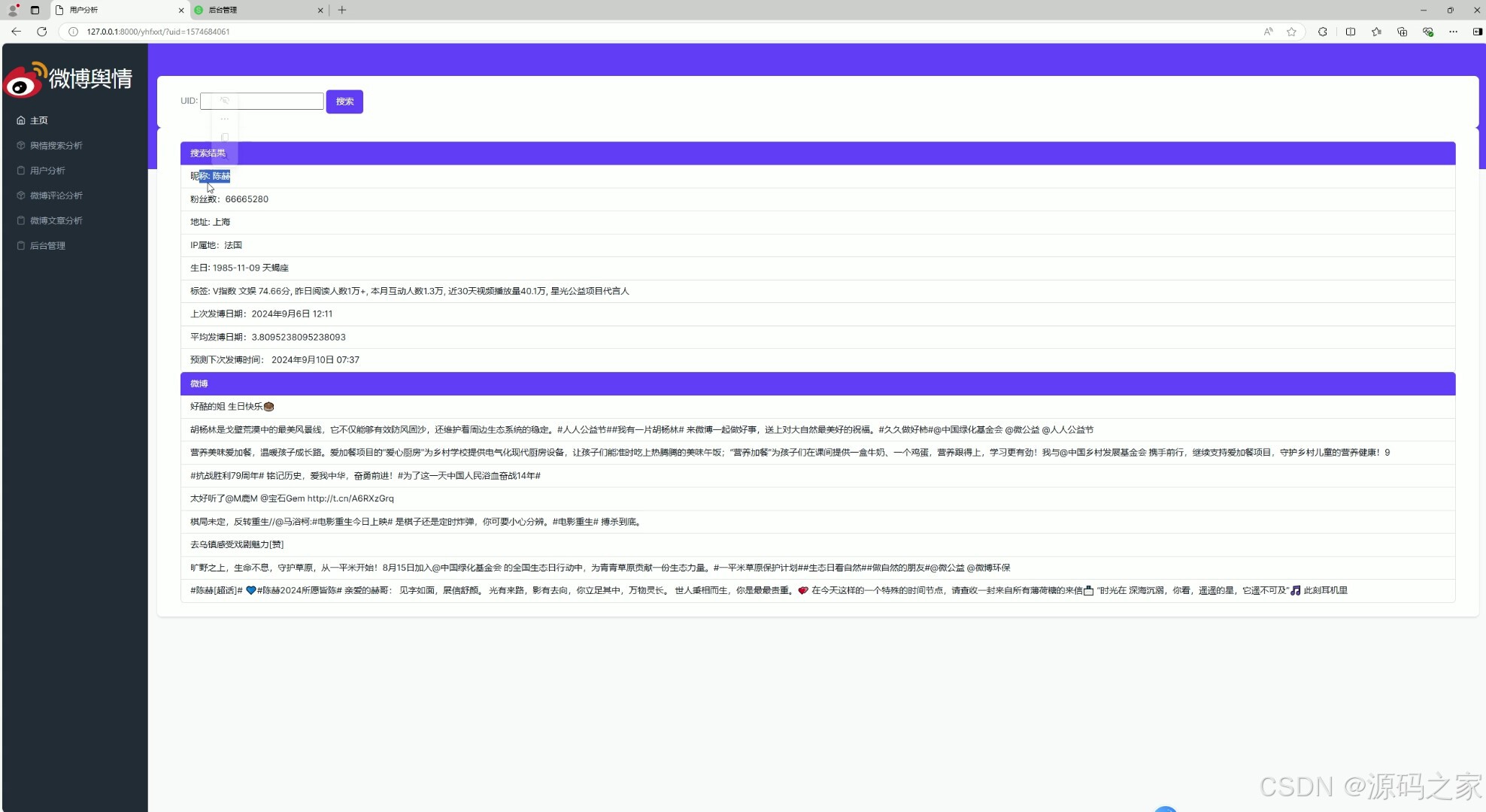
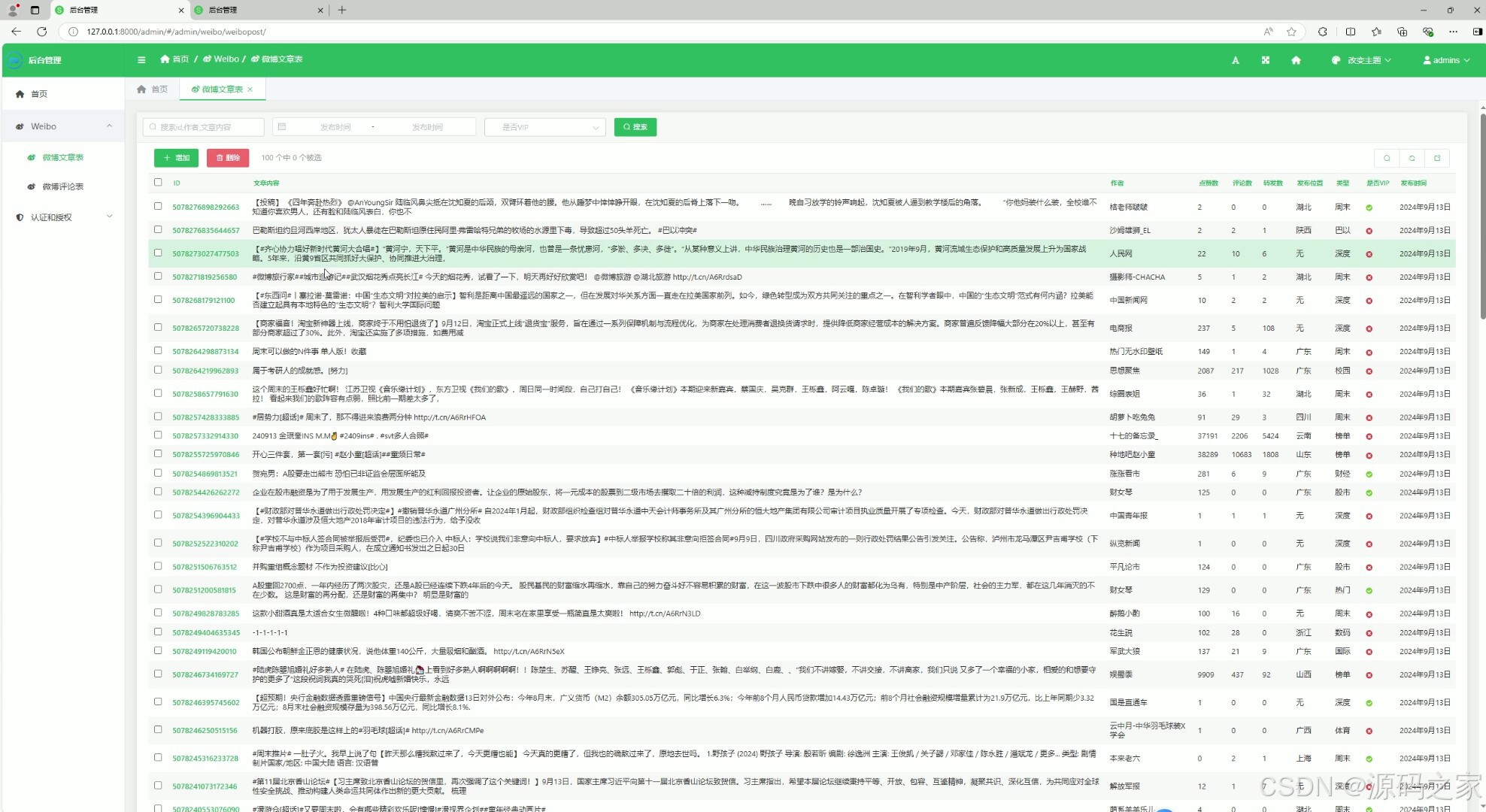
(6)后台数据管理
(7)注册登录
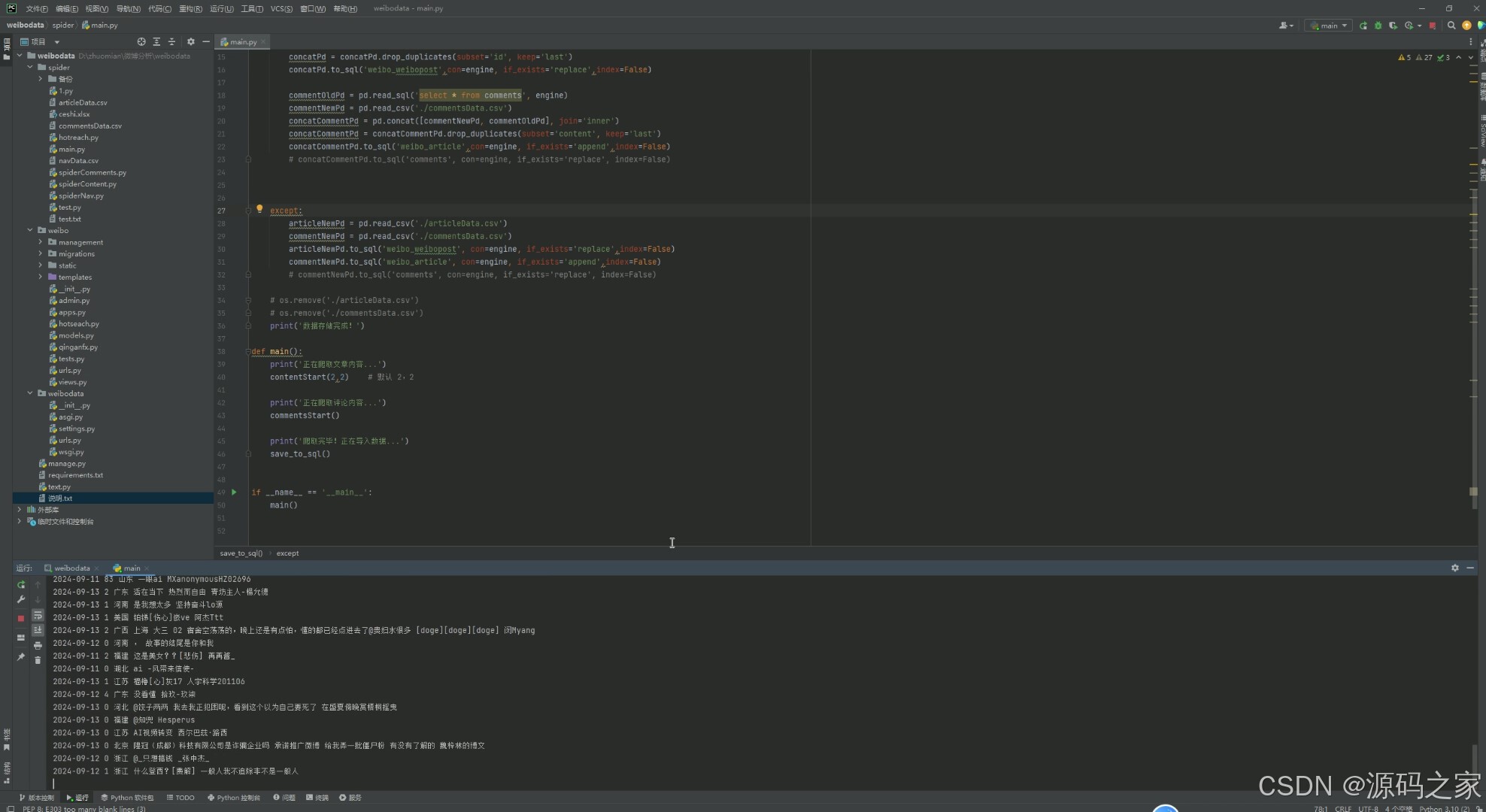
(8)数据采集
3、项目说明
社交媒体的兴起使微博成为信息扩散主阵地。本研究基于Django构建“采集-存储-分析-可视化”一体化平台,通过requests爬虫定时抓取微博文章、评论与用户地域数据,经SnowNLP完成情感极性判断,利用Echarts生成地图热力、词云、趋势折线等多维图表,实现关键词搜索、用户ID追踪、评论情感占比等交互分析。后台管理支持数据清洗、敏感词过滤、增量入库与Excel导出,全程本地运行,保障数据隐私。系统模块化设计便于替换算法或接入其他数据源,适合高校与企业快速部署,也为“数据挖掘”“Web开发”课程提供开箱即用的教学与毕业设计模板。
4、核心代码
from django.contrib.auth.forms import UserCreationForm
from django.contrib import messages
from django.contrib.auth import authenticate, login
from django.shortcuts import render, redirect
from .models import WeiboPost
from .hotseach import hs,yonghu,yuqin
from django.http import JsonResponse
from .models import WeiboPost,Article
from django.db.models import Count,Max,F,Sum
import json
from django.core.paginator import Paginator
from snownlp import SnowNLP
from django.db.models.functions import ExtractDay, ExtractHour, ExtractMinute
from django.db.models.functions import TruncDaydef wbwzfx(request):selected_type = request.GET.get('type', None)types = WeiboPost.objects.values_list('type', flat=True).distinct()if selected_type:data = WeiboPost.objects.filter(type=selected_type) \.annotate(day=TruncDay('created_at')) \.values('day') \.annotate(count=Count('id'), total_likes=Sum('likeNum')) \.order_by('day')province_data = WeiboPost.objects.filter(type=selected_type) \.values('region') \.annotate(count=Count('id')) \.order_by('region')labels = [item['day'].strftime('%Y-%m-%d') for item in data]counts = [item['count'] for item in data]total_likes = [item['total_likes'] for item in data]else:labels, counts, total_likes, province_data = [], [], [], []post_with_most_likes = WeiboPost.objects.aggregate(Max('likeNum'))post_with_most_reposts = WeiboPost.objects.aggregate(Max('reposts_count'))post_with_most_comments = WeiboPost.objects.aggregate(Max('commentsLen'))context = {'types': types,'labels': labels,'counts': counts,'total_likes': total_likes,'selected_type': selected_type,'post_with_most_likes': post_with_most_likes['likeNum__max'],'post_with_most_reposts': post_with_most_reposts['reposts_count__max'],'post_with_most_comments': post_with_most_comments['commentsLen__max'],'province_data': list(province_data),}return render(request, 'wbwzfx.html', context)def wbplfx(request):# 获取所有文章并按创建时间降序排序articles = Article.objects.all().order_by('-created_at')# 对每篇文章进行情绪分析,并分类情绪for article in articles:s = SnowNLP(article.content)# 获取情绪倾向分数sentiment_score = s.sentiments# 根据情绪分数对情绪进行分类if sentiment_score > 0.6:article.sentiment_category = "积极"elif sentiment_score < 0.4:article.sentiment_category = "消极"else:article.sentiment_category = "中性"# 设置分页,每页20条记录paginator = Paginator(articles, 20)# 从请求中获取页码号page_number = request.GET.get('page')page_obj = paginator.get_page(page_number)return render(request, 'wbplfx.html', {'page_obj': page_obj})def yhfxxt(request):uid = request.GET.get('uid')if not uid:# 如果没有提供 uid,渲染 HTML 页面而不是调用 APIreturn render(request, 'yhfxxt.html')# 调用修改后的 yonghu 函数,获取数据user_data = yonghu(uid)if user_data:# 将数据传递到模板context = {'name': user_data[0],'fans': user_data[1],'location': user_data[2],'ip_location': user_data[3],'birthday': user_data[4],'labels': user_data[5],'last_post_date': user_data[6],'average_interval': user_data[7],'next_expected_post': user_data[8],'recent_posts': user_data[9],}return render(request, 'yhfxxt.html', context)else:# 在出错或未找到用户数据的情况下,可以添加适当的处理return JsonResponse({'error': 'User data could not be retrieved.'}, status=500)def yqssfx(request):# 检查是否有GET请求并获取`str`参数query_str = request.GET.get('str', '')if query_str: # 如果有输入print("正在调用yqssfx函数、yuqin函数,接收到:")print(query_str)data = yuqin(query_str)print("已完成!调用yuqin函数")if data:return render(request, 'yqssfx.html', {'data': data})else:return render(request, 'yqssfx.html', {'error': '无法获取数据'})else:# 如果没有输入或者str为空,只渲染空模板或带有提示的模板return render(request, 'yqssfx.html', {'error': '请输入查询字符串'})def post_type_statistics(request):data = WeiboPost.objects.values('type').annotate(total=Count('type')).order_by('type')return JsonResponse(list(data), safe=False)def index(request):top_posts = WeiboPost.objects.order_by('-likeNum')[:10]hot_searches = hs() # 调用获取热搜的函数authors = Article.objects.values_list('authorGender', flat=True)male_count = sum(1 for gender in authors if gender == 'm')female_count = sum(1 for gender in authors if gender == 'f')total_count = len(authors)male_ratio = (male_count / total_count) * 100female_ratio = (female_count / total_count) * 100context = {'male_ratio': male_ratio,'female_ratio': female_ratio}most_common_region = Article.objects.values('region').annotate(count=Count('region')).order_by('-count').first()# 将男女比例数据转换为 JSON 格式传递给前端context_json = json.dumps(context)total_entries = Article.objects.count()max_content_len = WeiboPost.objects.aggregate(max_content_len=Max('contentLen'))['max_content_len']province_data = WeiboPost.objects.values('region').annotate(count=Count('id')).order_by('region')return render(request, 'index.html', {'top_posts': top_posts, 'hot_searches': hot_searches,'context_json': context_json,'most_common_region': most_common_region,'total_entries':total_entries,'max_content_len':max_content_len,'province_data': list(province_data)})🍅✌感兴趣的可以先收藏起来,点赞关注不迷路,想学习更多项目可以查看主页,大家在毕设选题,项目编程以及论文编写等相关问题都可以给我留言咨询,希望可以帮助同学们顺利毕业!🍅✌
5、源码获取方式
🍅由于篇幅限制,获取完整文章或源码、代做项目的,拉到文章底部即可看到个人联系方式。🍅
点赞、收藏、关注,不迷路,下方查看👇🏻获取联系方式👇🏻
