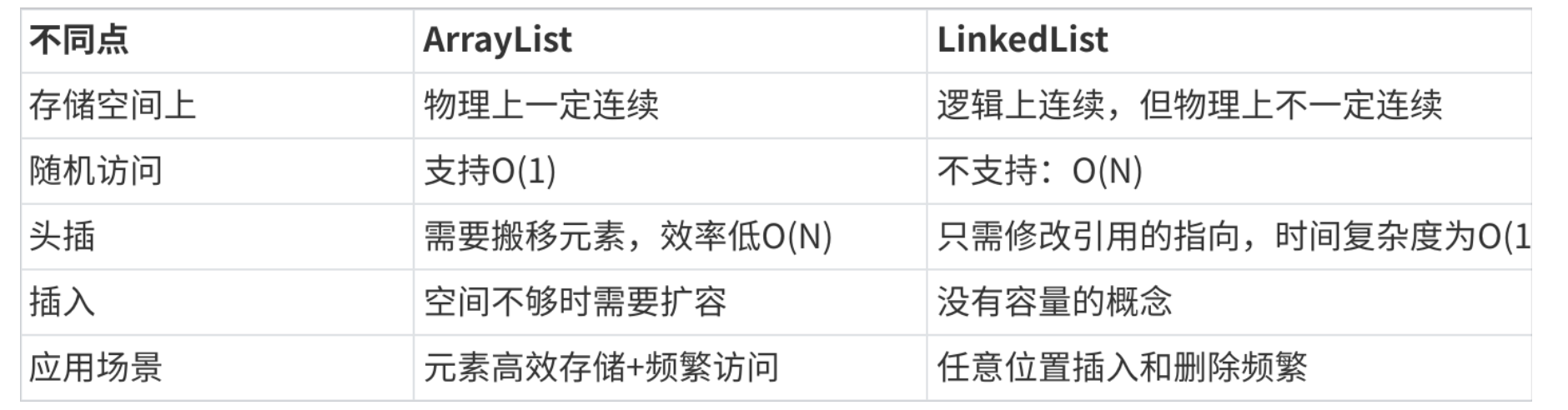
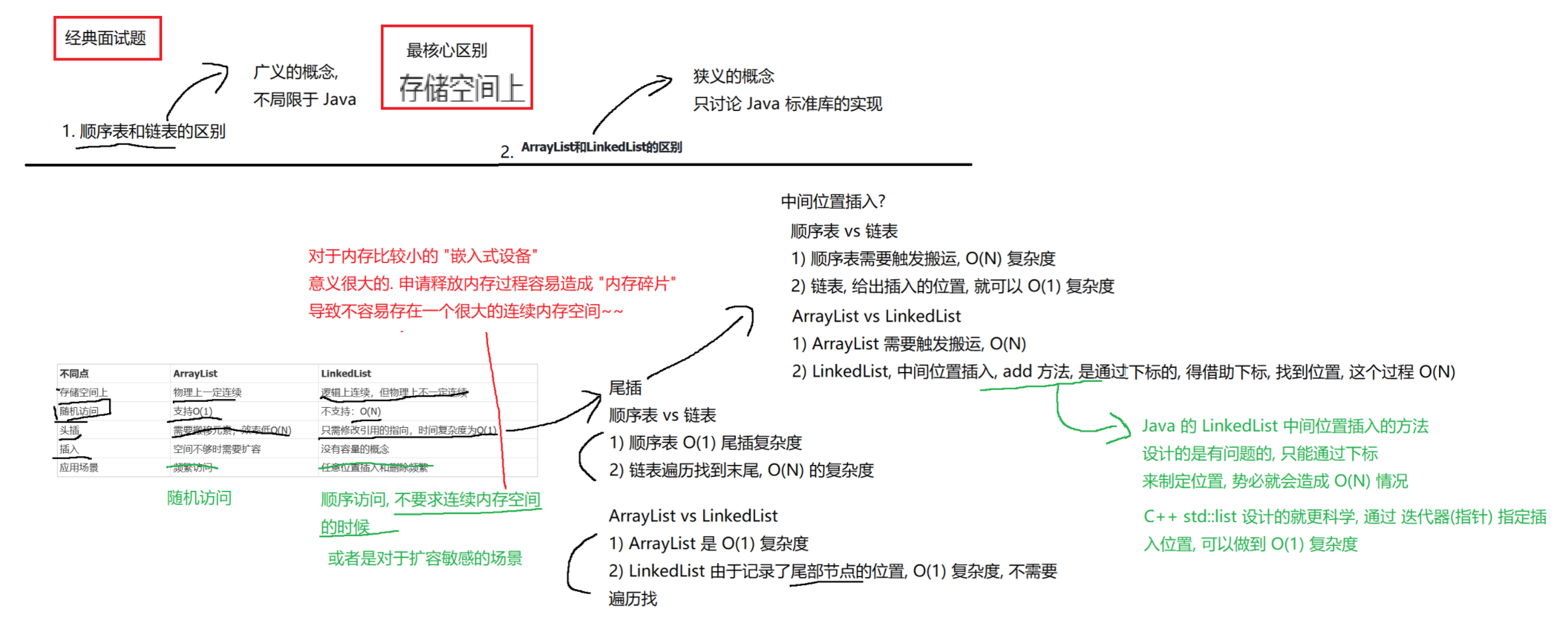
数据结构--3:LinkedList与链表
 1.链表的概念及结构 2.构造 常见操作 遍历 3.单向链表模拟实现 4.双向链表模拟实现 5.面试题
1.链表的概念及结构 2.构造 常见操作 遍历 3.单向链表模拟实现 4.双向链表模拟实现 5.面试题

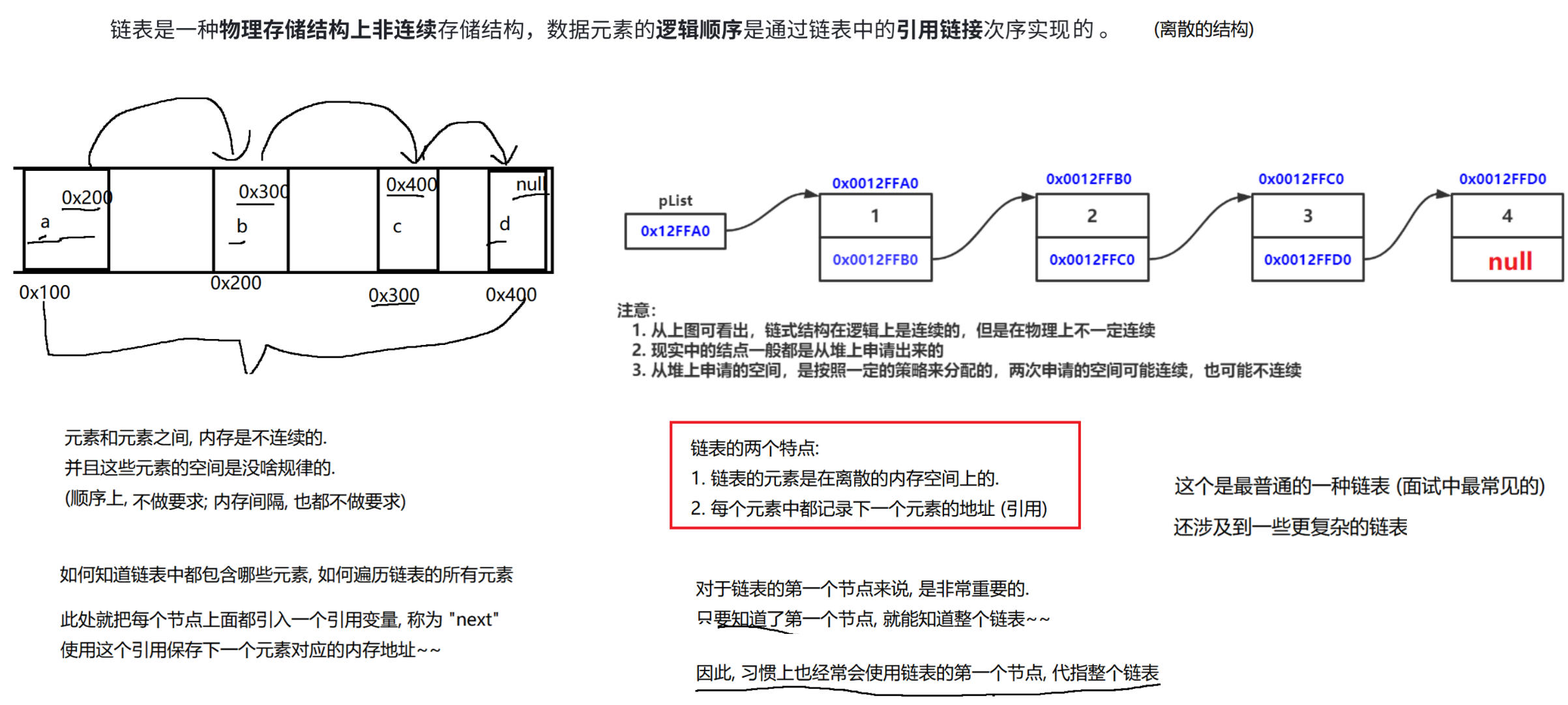
1.链表的概念及结构
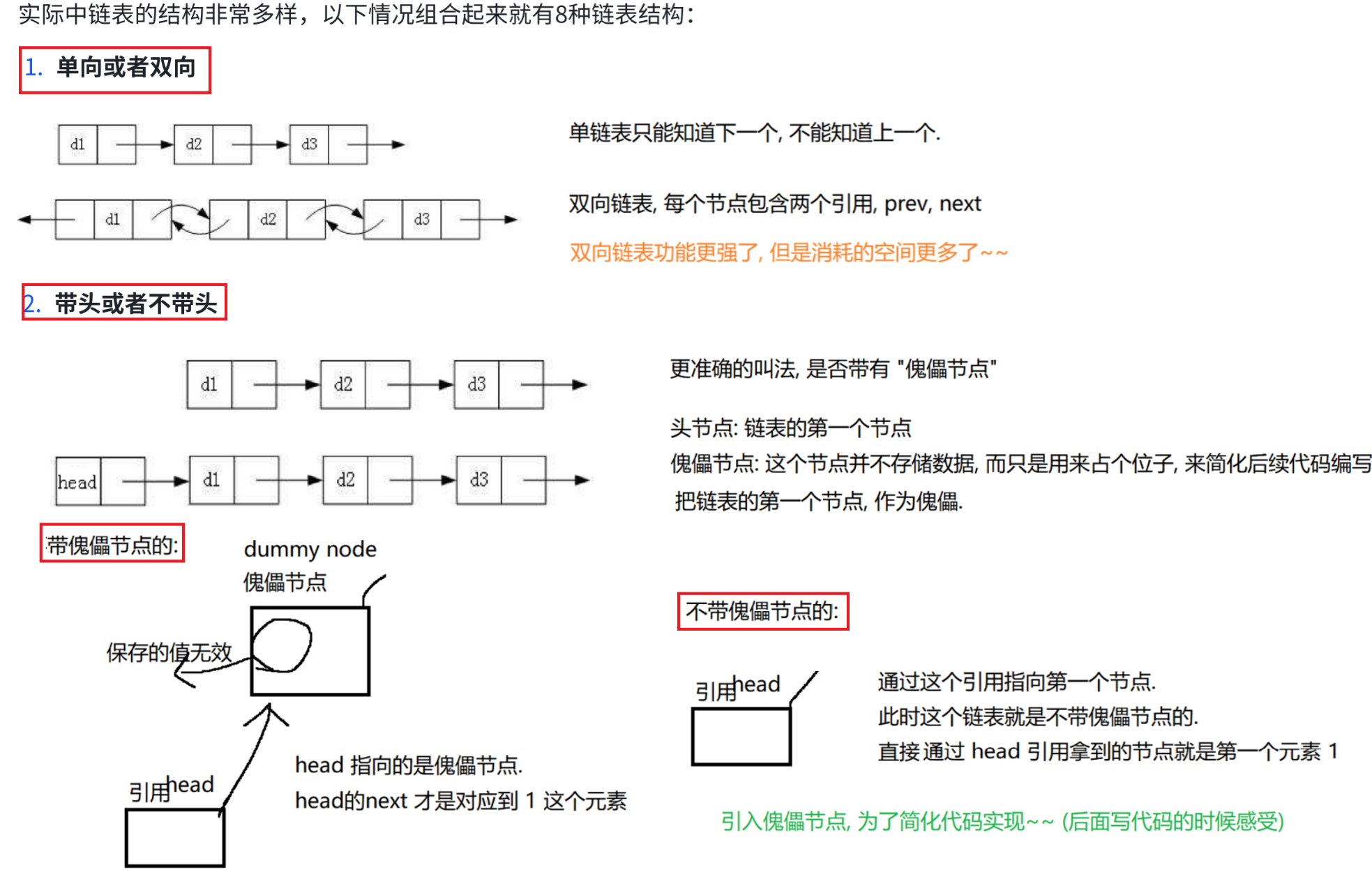
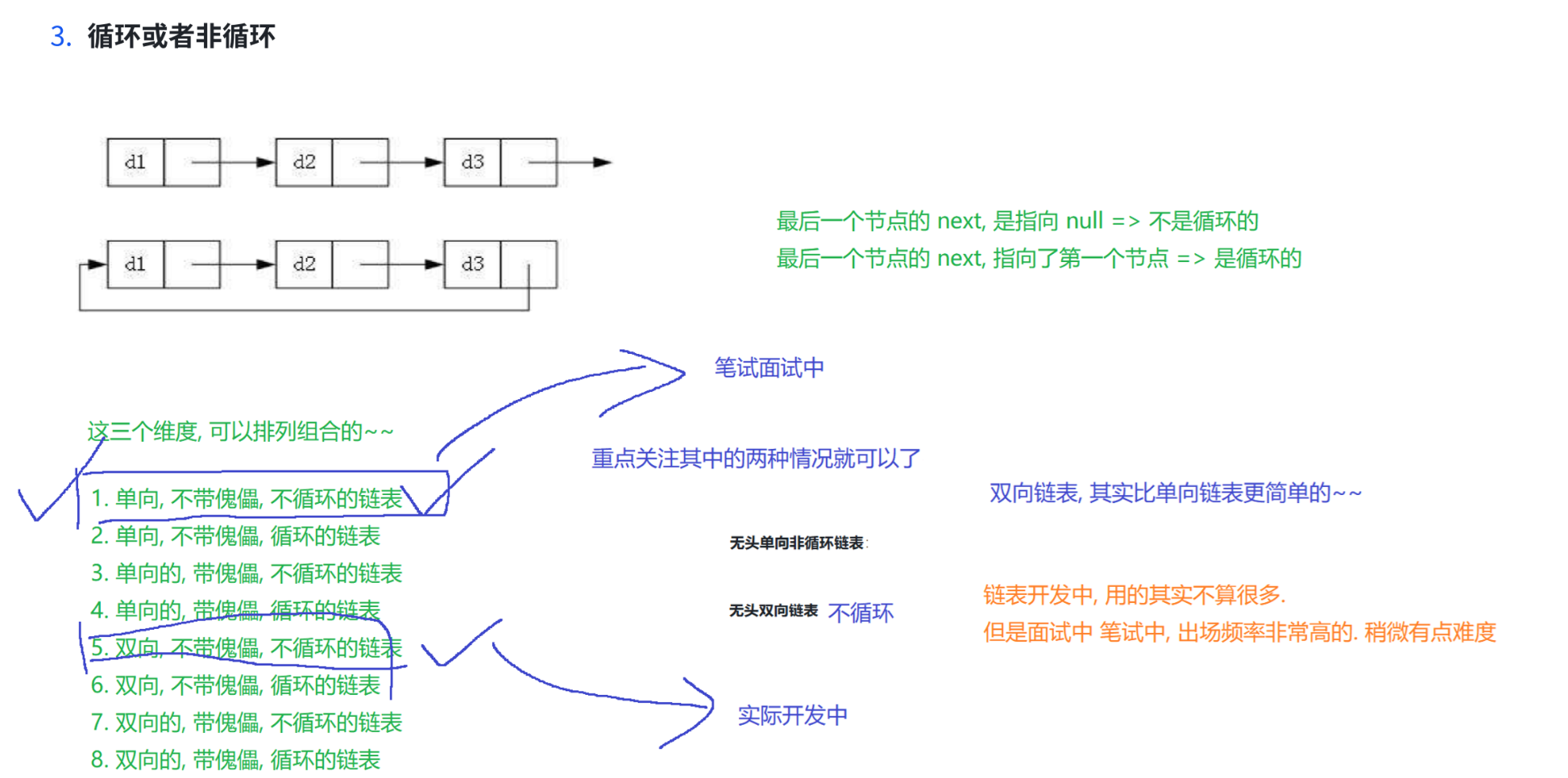
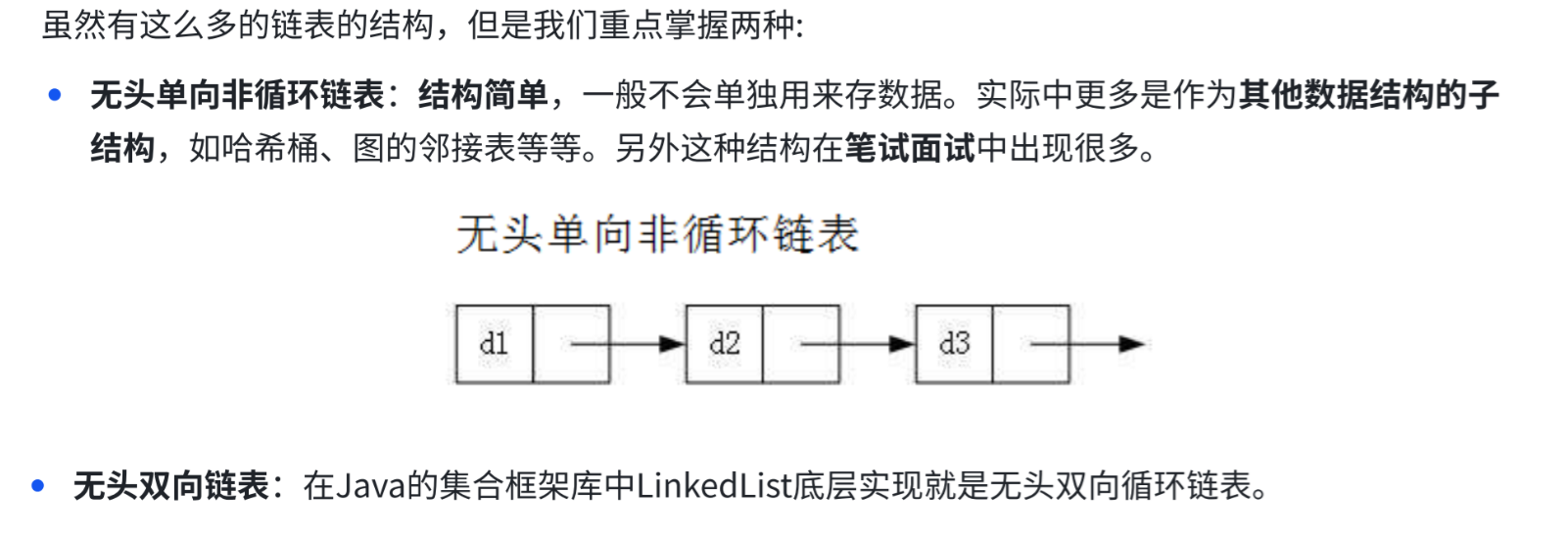

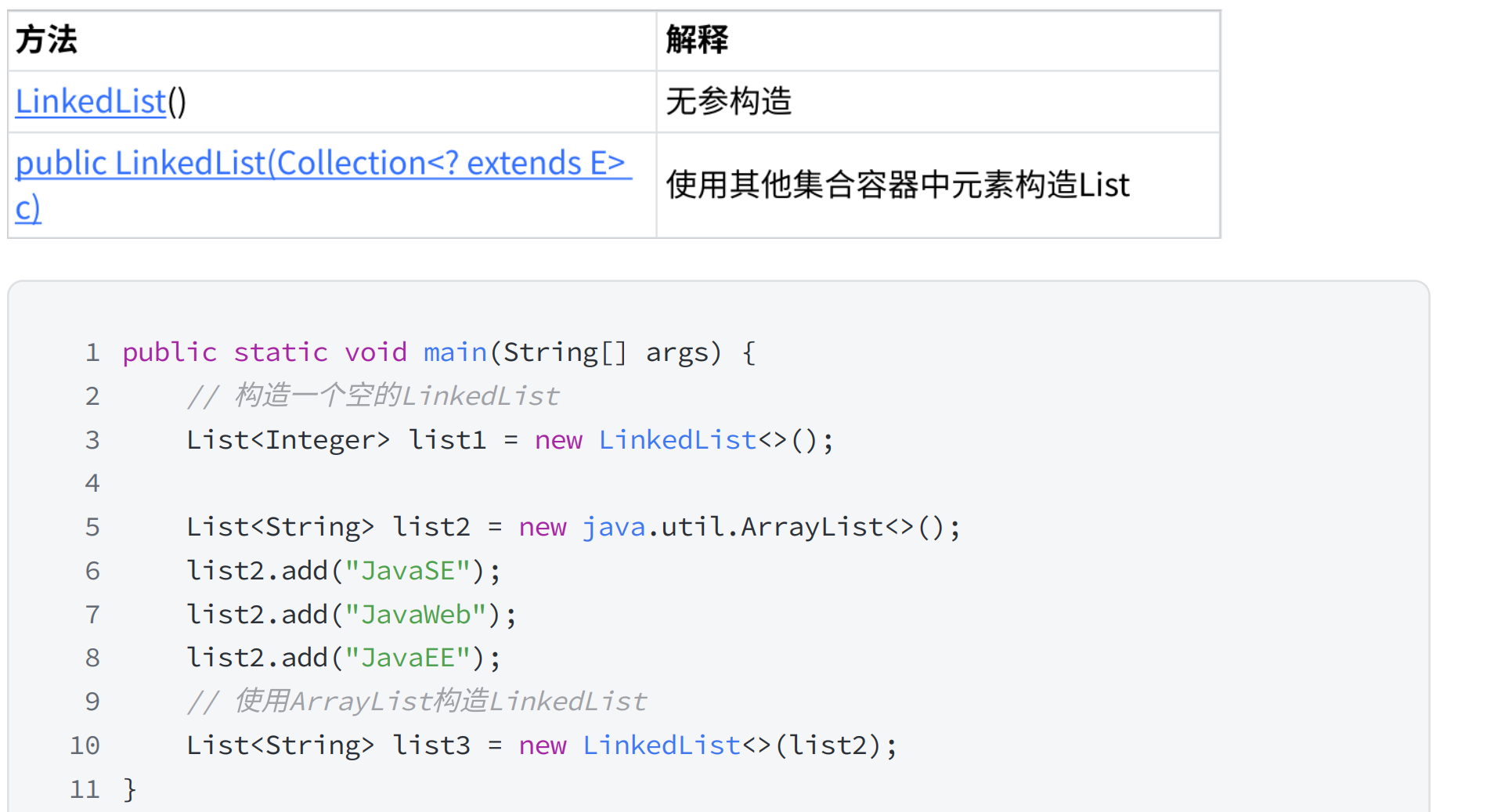
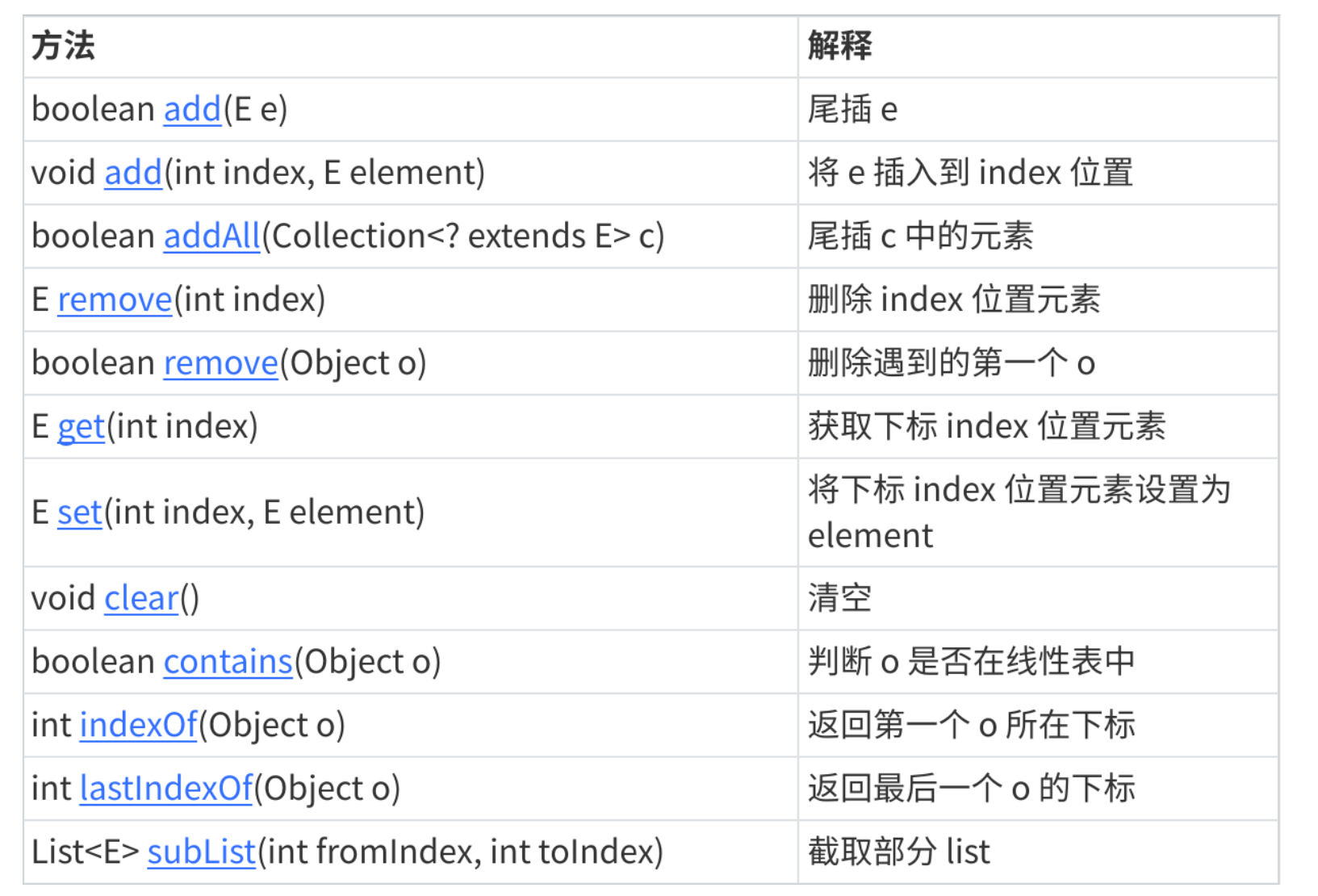
2.构造 常见操作 遍历 (与顺序表相似)



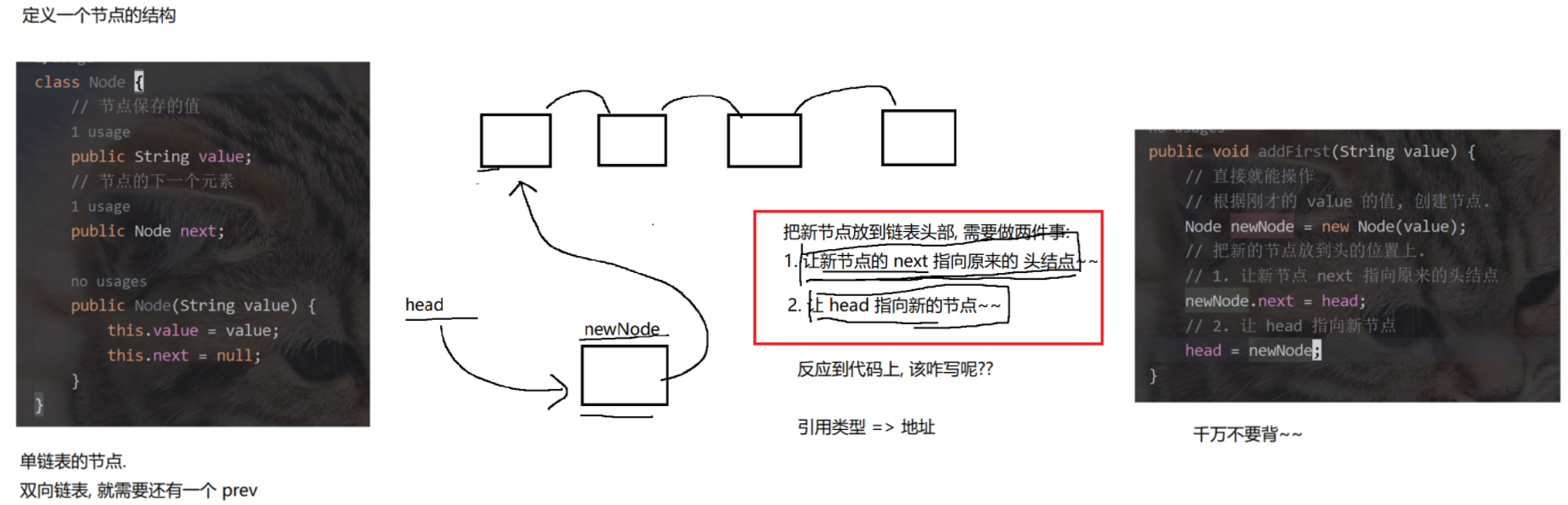
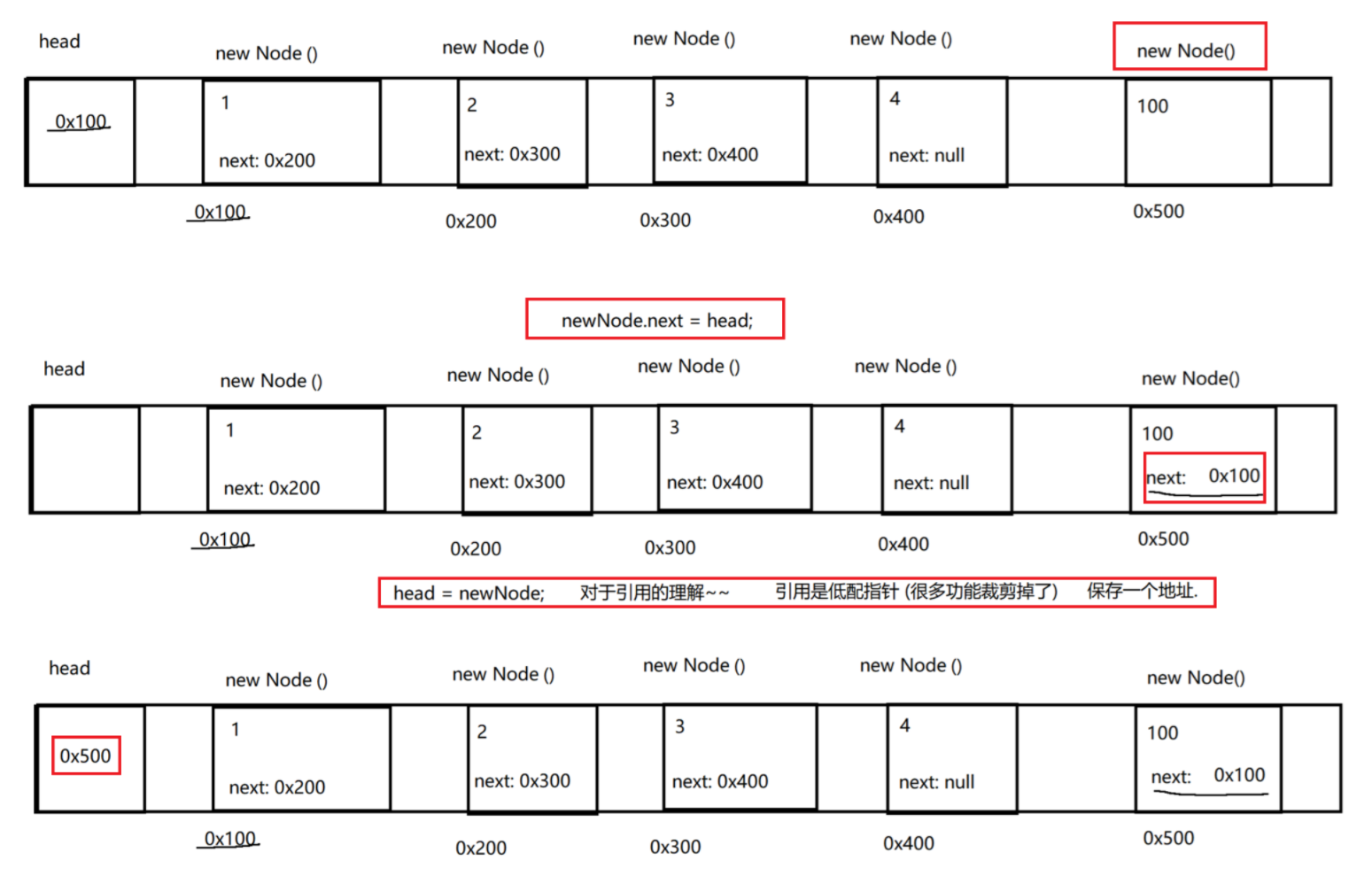
3.无傀儡、不循环、单向链表的模拟实现
代码实现
// 不写成泛型的方式. 只是保存 String 类型的数据~~
// 泛型方式, 写起来更麻烦一些. 未来面试的时候, 一般也都不要写泛型版本的.// 实现一个 单向不带傀儡 不循环的链表 表示一个链表的节点
// 对于节点这个类来说, 本身功能单一, 比较简单; 如果搞一些 get set 方法, 后续代码就会显的难看.
class Node{public String value; // 节点保存的值public Node next; // 节点的下一个元素public Node(String value){this.value = value;this.next = null;}
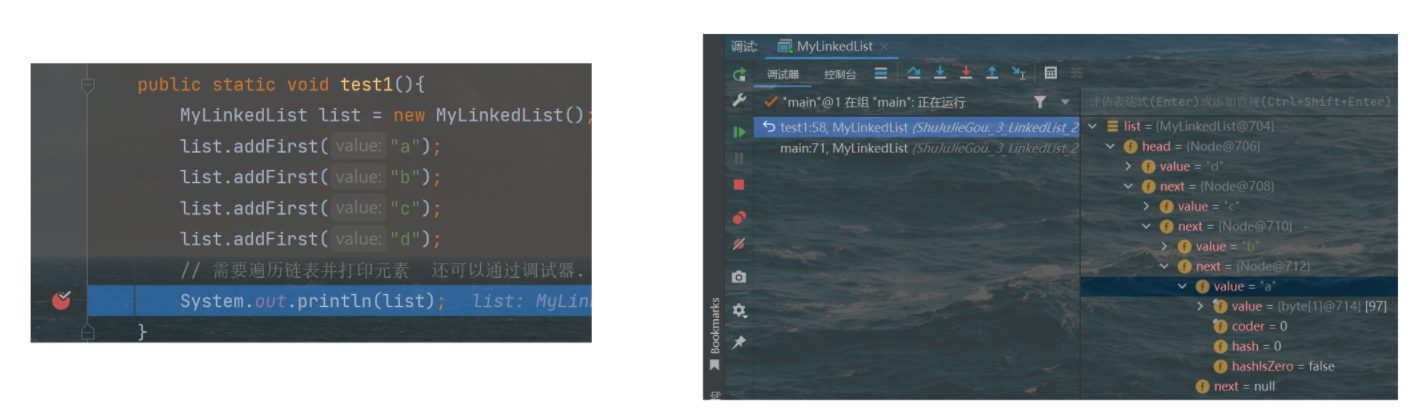
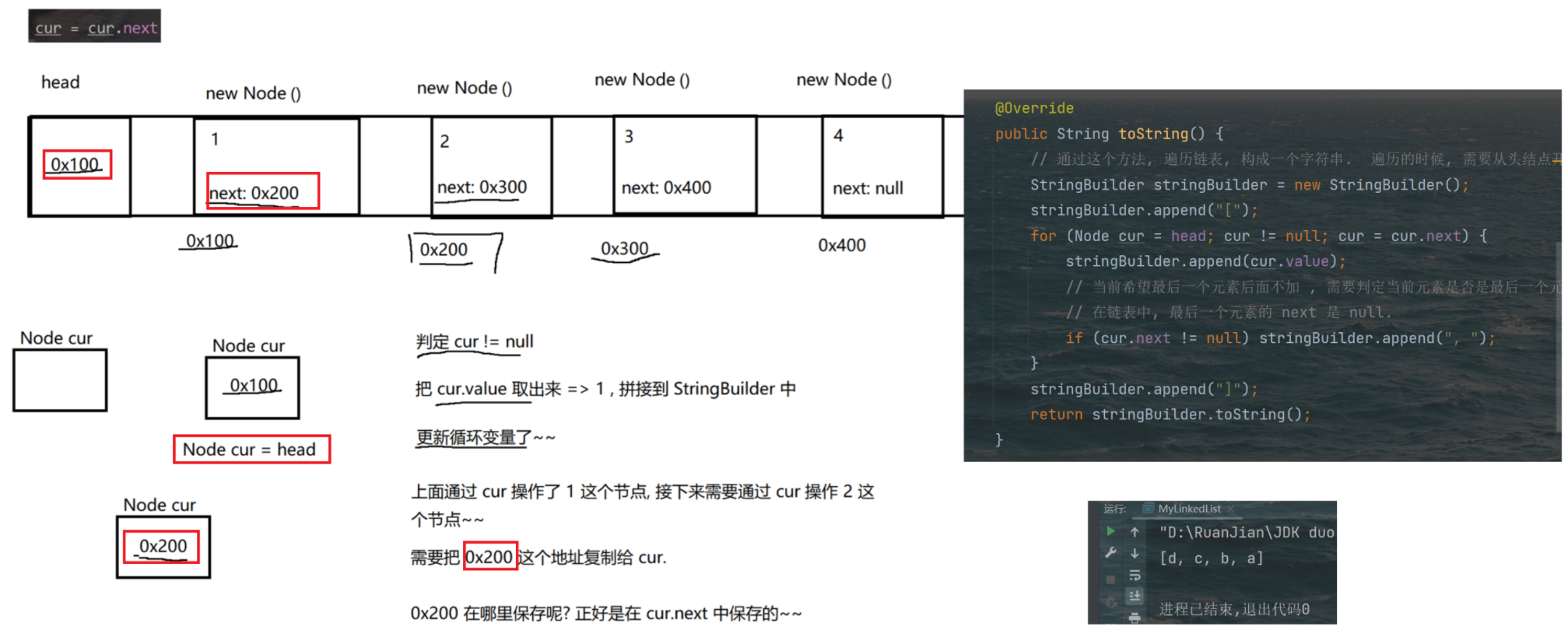
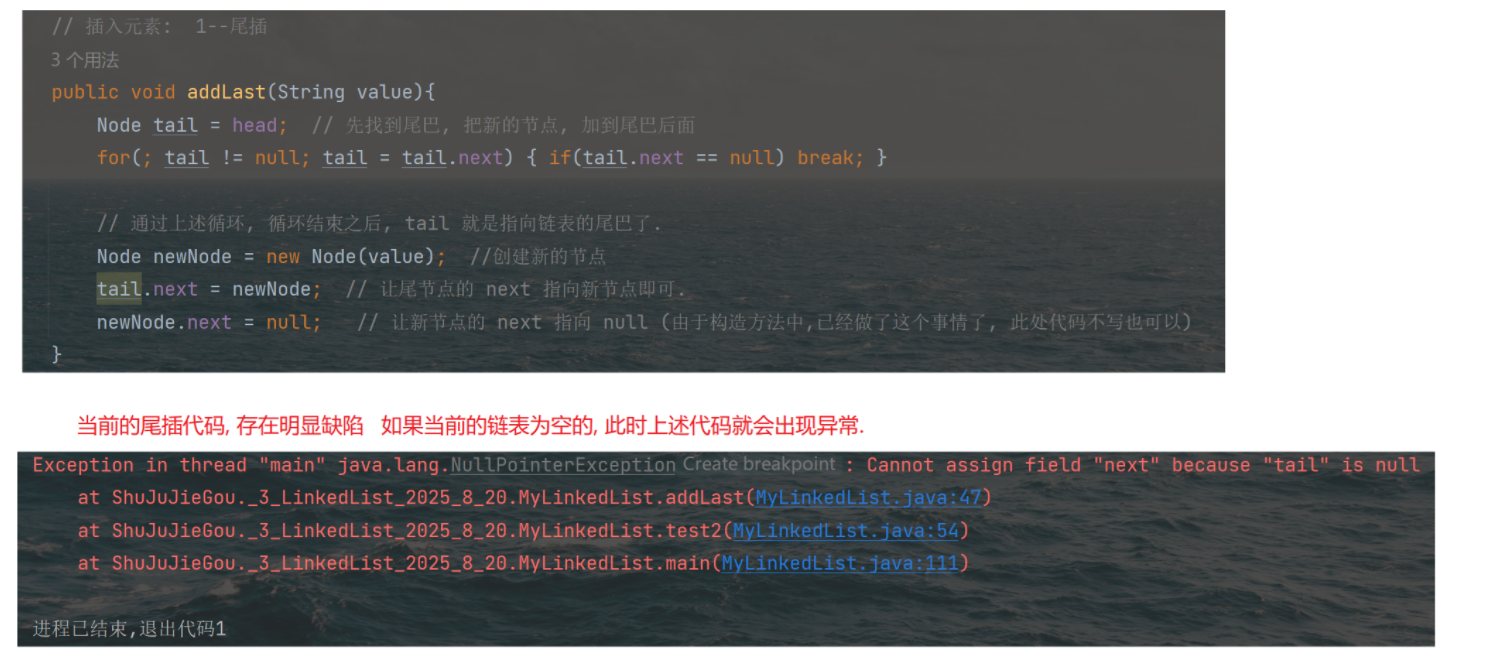
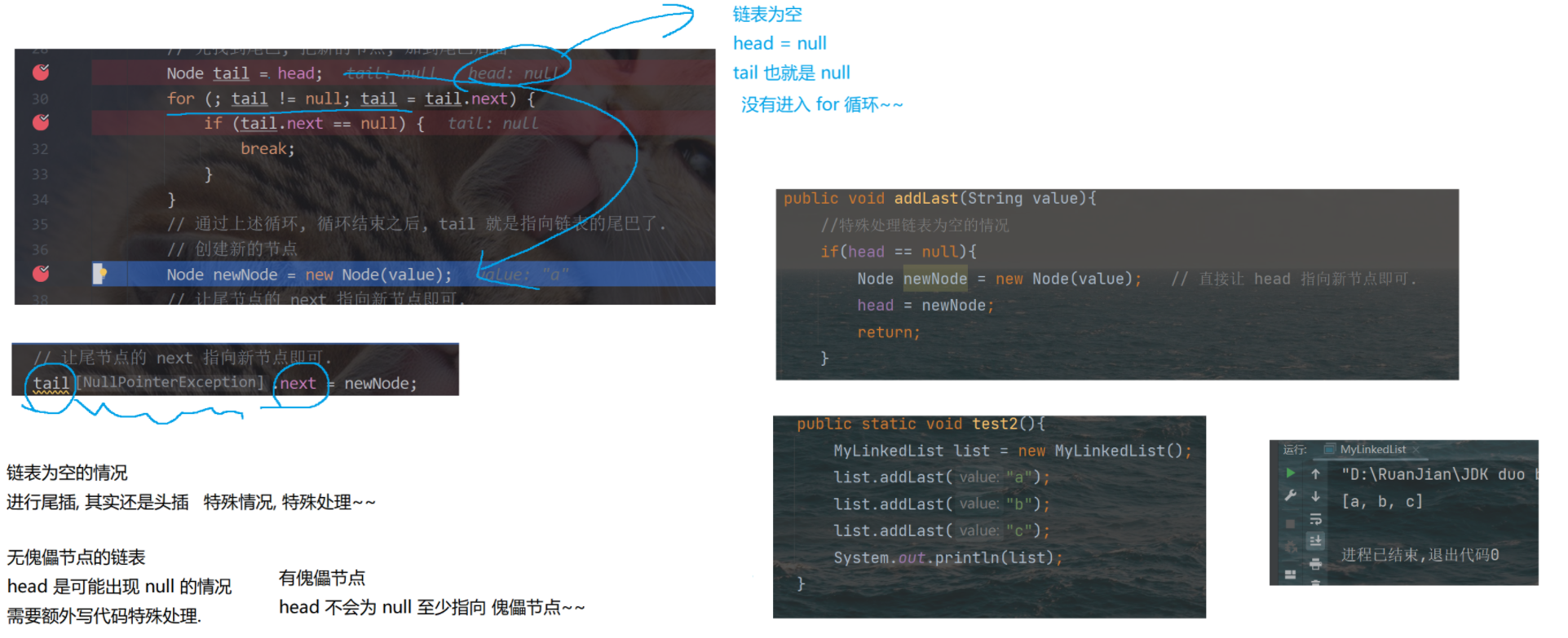
}public class MyLinkedList {// 把链表的头结点表示出来, 此时整个链表就能够获取到了. 此处不包含傀儡节点, head == null 的时候表示空的链表.private Node head = null;// 不像顺序表, 需要使用 size 之类的表示 "有效元素" 区间.// 链表不需要. 如果搞一个 size 记录个数, 也是可以的. 不记录, 通过其他方式获取也行.// 能不能再这里加一个 size, 插入元素, size++, 删除元素 size-- , 完全可以的 实际开发中涉及到链表实现, 大多都是这么做的.// 但是面试中给的链表, 一般都是不通过 size 记录的, 要求你写一个方法计算 size.// 插入元素: 1--尾插public void addLast(String value){//特殊处理链表为空的情况if(head == null){Node newNode = new Node(value); // 直接让 head 指向新节点即可.head = newNode;return;}Node tail = head; // 先找到尾巴, 把新的节点, 加到尾巴后面for(; tail != null; tail = tail.next) { if(tail.next == null) break; }// 通过上述循环, 循环结束之后, tail 就是指向链表的尾巴了.Node newNode = new Node(value); //创建新的节点tail.next = newNode; // 让尾节点的 next 指向新节点即可.newNode.next = null; // 让新节点的 next 指向 null (由于构造方法中,已经做了这个事情了, 此处代码不写也可以)}public static void test2(){MyLinkedList list = new MyLinkedList();list.addLast("a");list.addLast("b");list.addLast("c");System.out.println(list);}// 插入元素: 2-头插public void addFirst(String value) {// 直接就能操作 根据刚才的 value 的值, 创建节点,把新的节点放到头的位置上.Node newNode = new Node(value);newNode.next = head; // 1、让新节点 next 指向原来的头结点head = newNode; // 2、让 head 指向新节点}@Overridepublic String toString() {// 通过这个方法, 遍历链表, 构成一个字符串. 遍历的时候, 需要从头结点开始, 进行一个一个元素的打印StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();stringBuilder.append("[");for (Node cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {stringBuilder.append(cur.value);// 当前希望最后一个元素后面不加 , 需要判定当前元素是否是最后一个元素.// 在链表中, 最后一个元素的 next 是 null.if (cur.next != null) stringBuilder.append(", ");}stringBuilder.append("]");return stringBuilder.toString();}public static void test1(){MyLinkedList list = new MyLinkedList();list.addFirst("a");list.addFirst("b");list.addFirst("c");list.addFirst("d");// 需要遍历链表并打印元素 还可以通过调试器.System.out.println(list);}//插入元素: 3-指定位置插入public void add(int index, String value){// 1. 先判断 index 是否合法 index == size 的时候, 表示尾插, 也是合法情况, 不需要抛出异常.if(index < 0 || index > size()) throw new RuntimeException("下标超出范围");// 2. 针对头插的特殊处理.if (index == 0) { addFirst(value); return; }// 3. 根据当前 value 值, 创建新的节点.Node newNode = new Node(value);// 4. 找到 index 要插入的位置的前一个节点 由于当前的链表是 "单向链表" 每个节点, 只能找到 next.// 插入新节点, 需要修改前一个节点的 next 值. 前一个节点的下标, 应该就是 index - 1Node prev = head;for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) { prev = prev.next; }// 5. 通过上述循环, 就让 prev 指向 index - 1 的位置.newNode.next = prev.next;prev.next = newNode;}// 虽然没有现成的 size, 我们可以自己写一个. 遍历一下链表就可以了.// 这样的过程, 时间复杂度是 O(N)public int size() {int size = 0;for (Node cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next) size++;return size;}private static void test3(){MyLinkedList list = new MyLinkedList();list.add(0,"a");list.add(1,"b");list.add(2,"c");list.add(3,"d");list.add(0,"x");System.out.println(list);}// 判定某个元素是否在链表中包含public boolean contains(String value) {for (Node cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {// 注意! 此处的 value 是 String. String 的比较, 应该使用 equals 方法.if (cur.value.equals(value)) return true;}// 整个循环都结束了, 才 return false.return false;}//返回查找元素的下标public int indexOf(String value) {int index = 0;for (Node cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {if (cur.value.equals(value)) return index;index++;}// 通过上述循环, 不能找到值相同的元素, 没触发上述的 return, 就只能返回 -1 表示没找到了.return -1;}private static void test4() {MyLinkedList list = new MyLinkedList();list.add(0, "a");list.add(1, "b");list.add(2, "c");list.add(3, "d");System.out.println(list.contains("d"));System.out.println(list.contains("x"));System.out.println(list.indexOf("d"));System.out.println(list.indexOf("x"));}// 删除链表中的元素--按照下标删除public void remove(int index) {// 这个代码中, 如果链表为空, size 就是 0 了.if (index < 0 || index >= size()) throw new RuntimeException("下标超出范围");// 1. 特殊处理 index 为 0 的情况.if (index == 0) {head = head.next;return;}// 2. 找到被删除元素的前一个节点位置.Node prev = head;for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) { prev = prev.next; }// 3. 循环结束, prev 就指向待删除元素的前一个位置了.Node toRemove = prev.next;// 4. 进行删除操作prev.next = toRemove.next;}private static void test5() {MyLinkedList list = new MyLinkedList();list.add(0, "a");list.add(1, "b");list.add(2, "c");list.add(3, "d");list.remove(1);System.out.println(list);}// 删除链表中的元素--按照值来删除public void remove(String value) {if (head == null) return; // 链表为空, 直接返回.// 1. 要删除的元素是 headif (head.value.equals(value)) {head = head.next;return;}// 2. 根据 value 值, 找到待删除元素的前一个位置.Node prev = head;for (; prev != null; prev = prev.next) {if (prev.next != null && prev.next.value.equals(value)) break;}// 3. 通过上述循环, prev 就指向了待删除元素的前一个位置.// 注意, 上述循环的结束可能有两种情况 value 的值找到匹配的了 或 链表遍历完了, 也没找到.if (prev == null) return; // 没找到, 直接返回.// 4. 真正进行删除操作.Node toRemove = prev.next;prev.next = toRemove.next;}private static void test6() {MyLinkedList list = new MyLinkedList();list.add(0, "a");list.add(1, "b");list.add(2, "c");list.add(3, "d");list.remove("b");System.out.println(list);}// 清空链表的所有元素public void clear() {// 直接修改 head, head 原来指向的所有 Node 对象都没有引用指向了. 都会被释放掉.head = null;}public static void main(String[] args) {//test1(); test2(); test3(); test4(); test5();test6();}
}
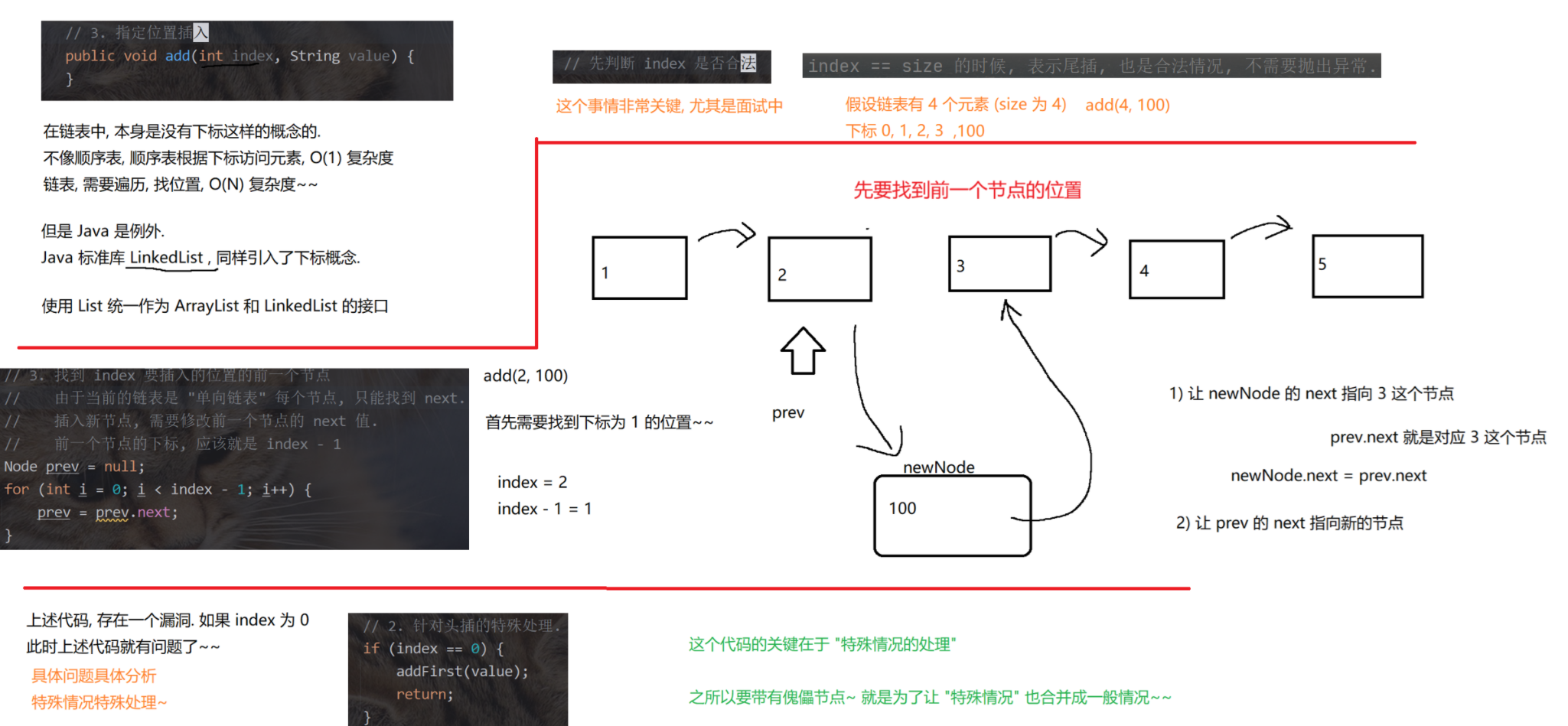
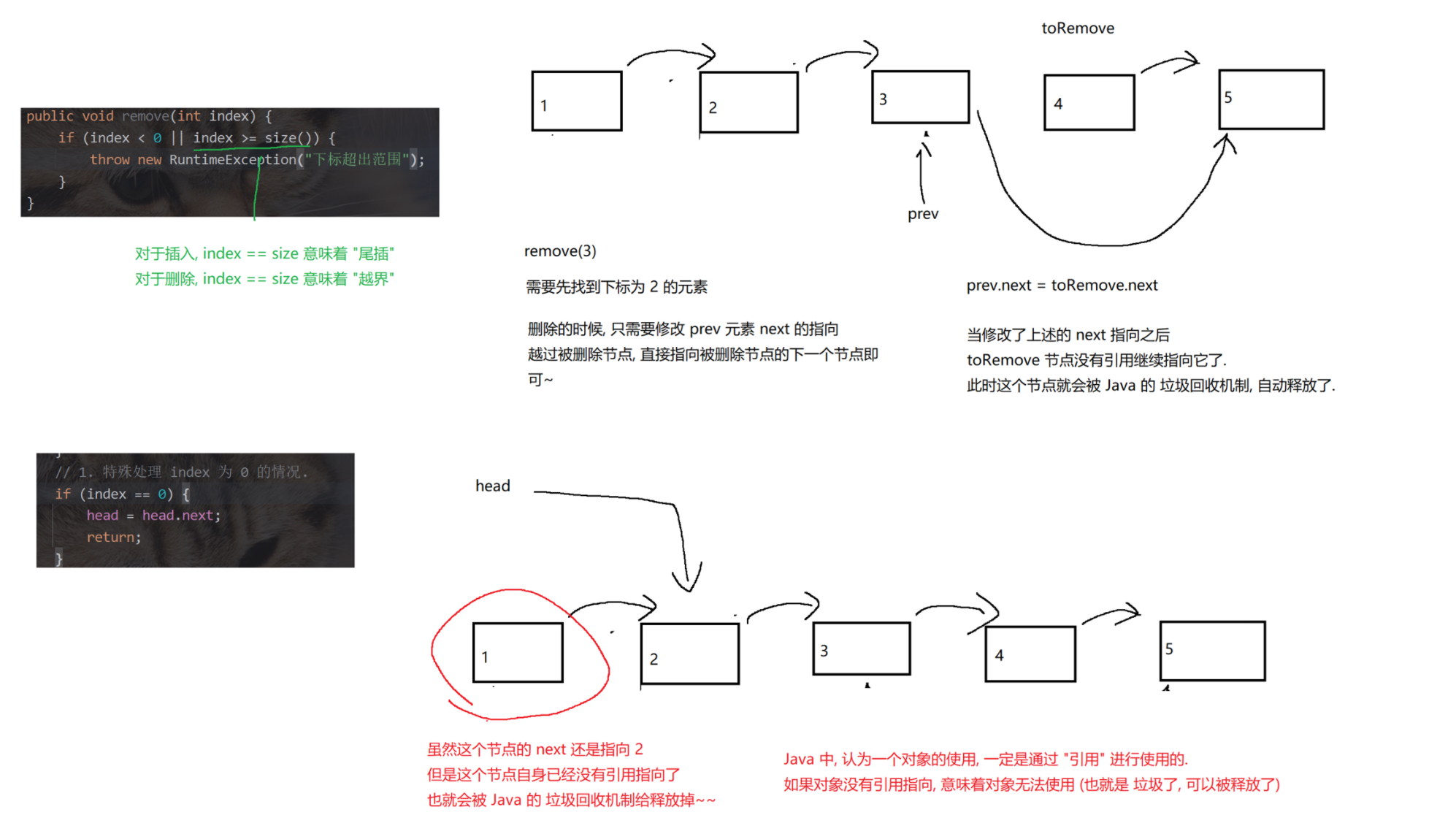
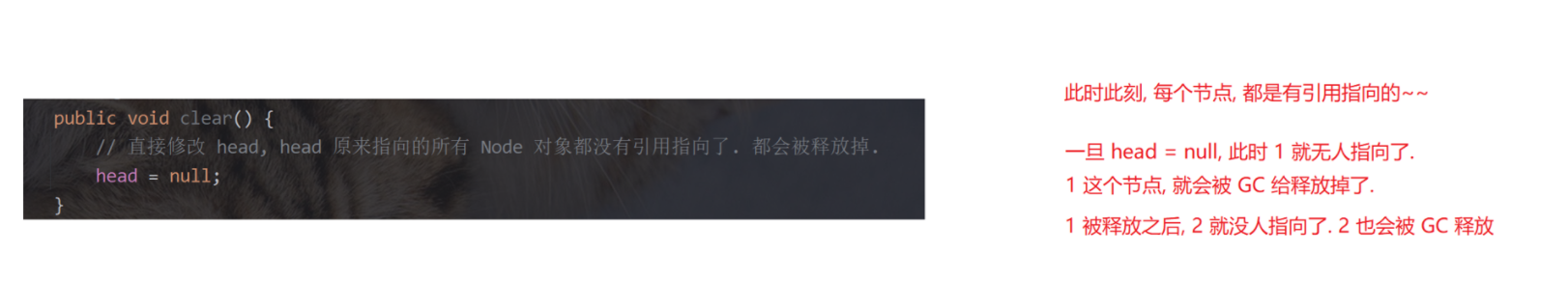
4.无傀儡、不循环、双向链表的模拟实现
代码实现
// 用这个类表示双向链表的节点.
// D => Double 此处实现双向链表.
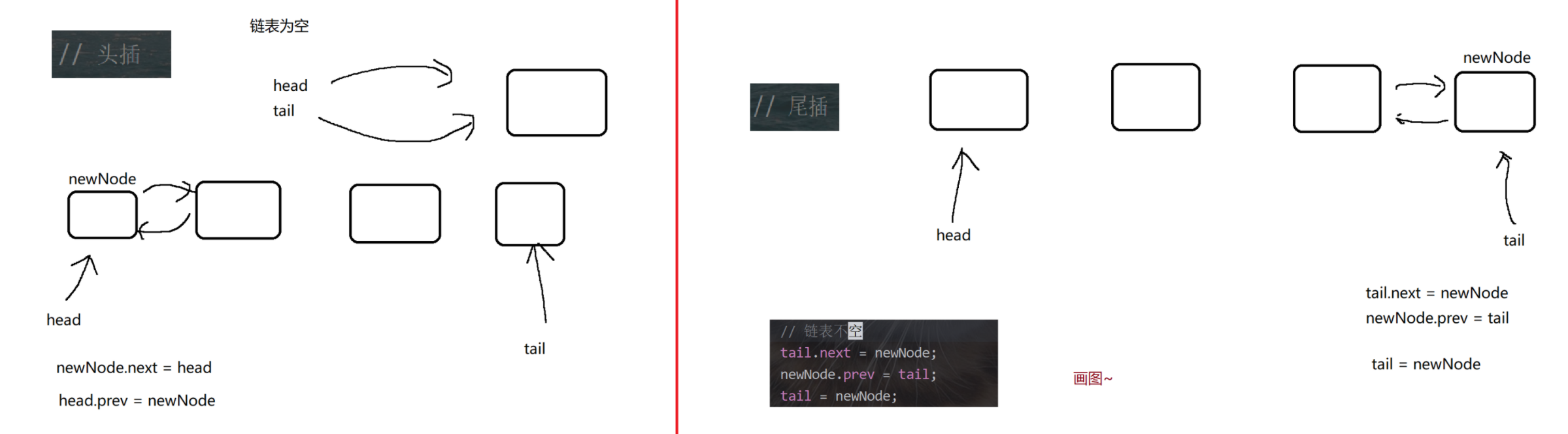
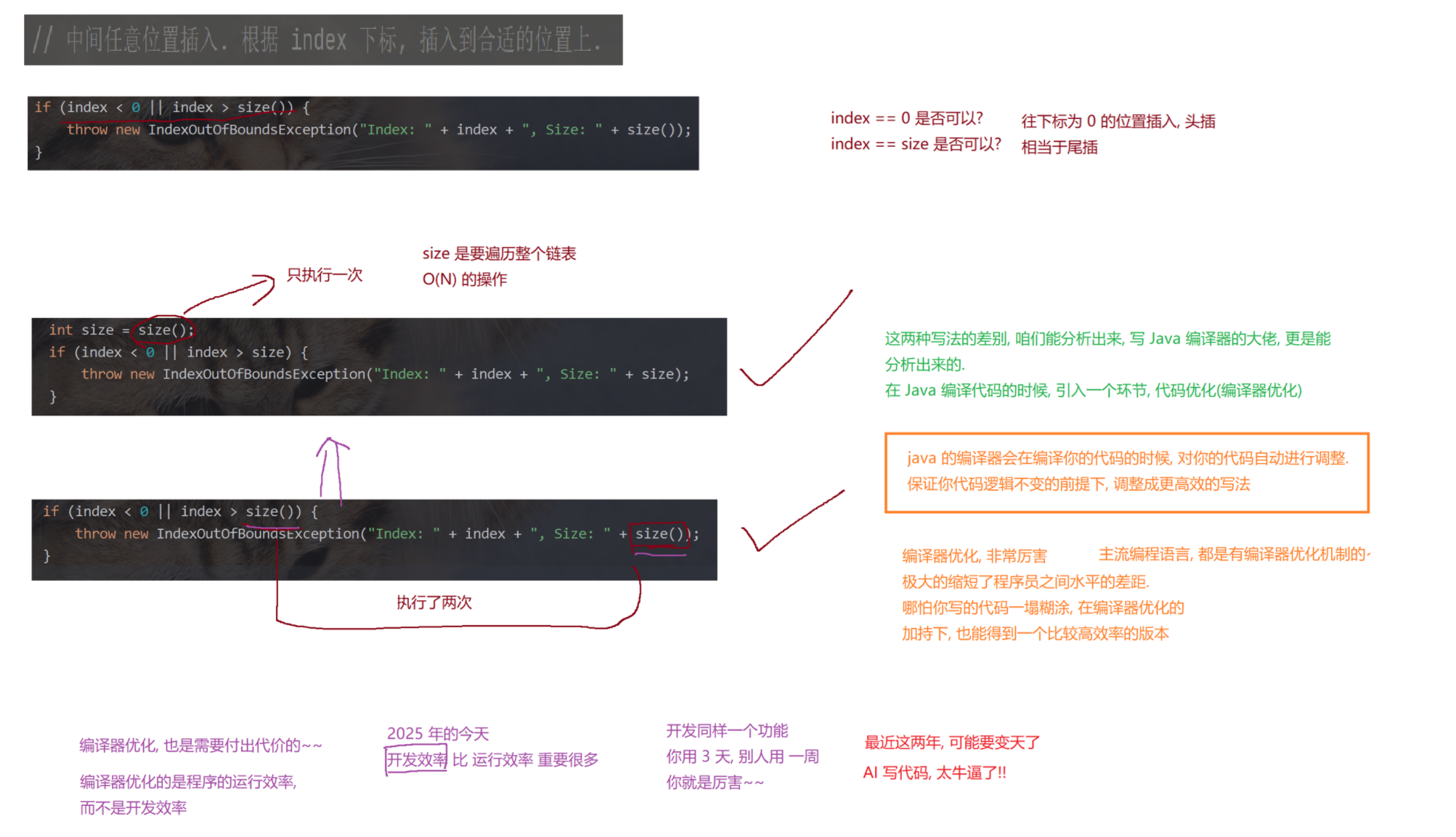
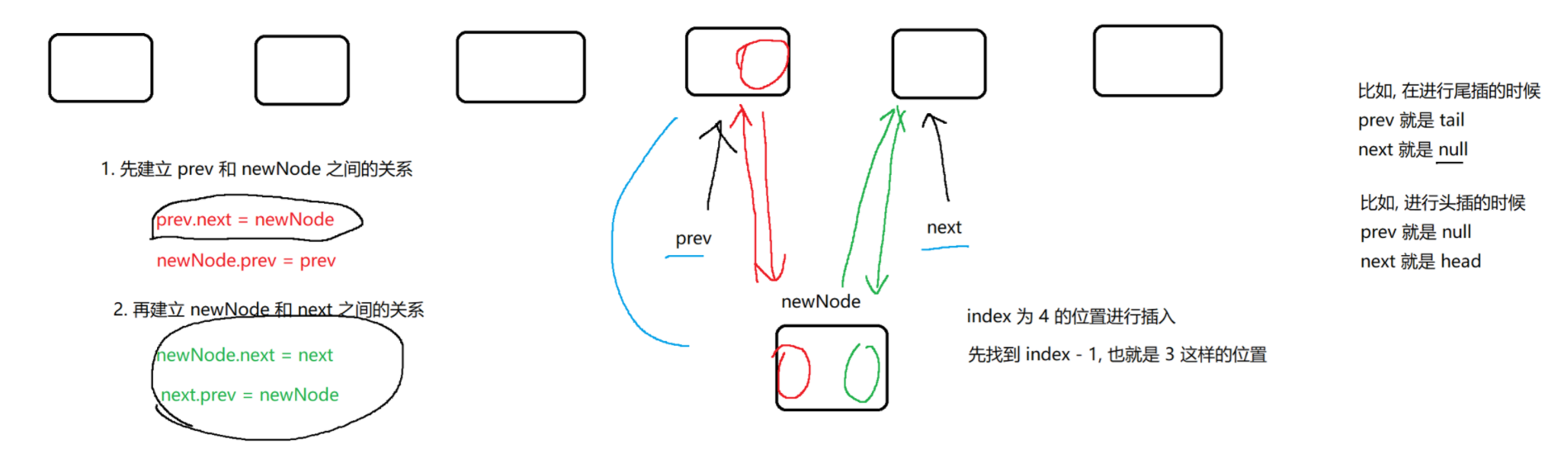
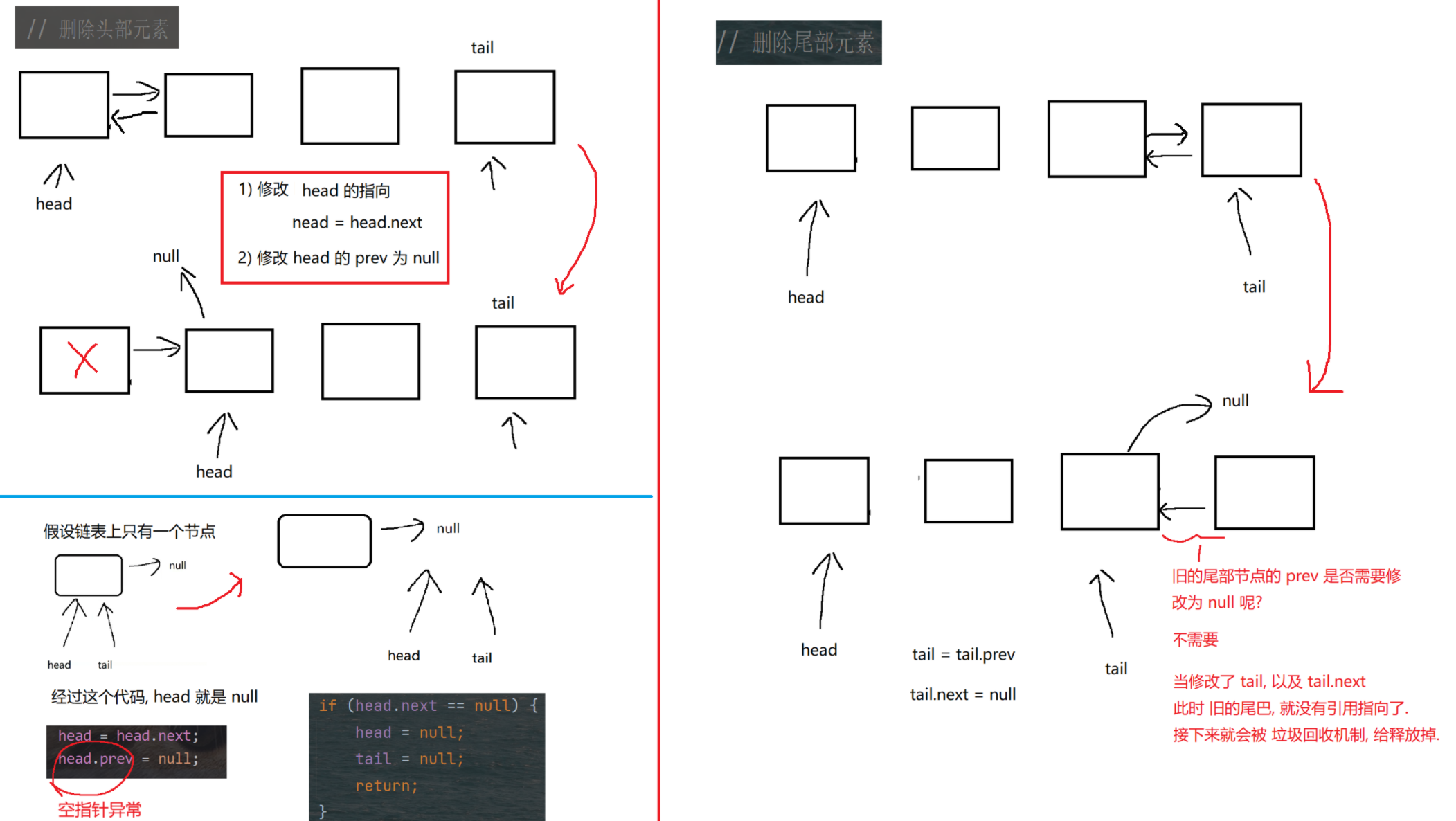
public class MyDLinkedList {// 如果不加 static, Node 就会依赖 MyDLinkedList 的 thisstatic class Node {public String val;public Node prev = null;public Node next = null;public Node(String val) {this.val = val;}}// 表示整个链表. 此处不引入傀儡节点. 使用 null 表示空的链表.private Node head = null;// 为了方便后续实现尾插操作.private Node tail = null;@Overridepublic String toString() {StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();stringBuilder.append("[");for (Node cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {stringBuilder.append(cur.val);if (cur.next != null) {stringBuilder.append(", ");}}stringBuilder.append("]");return stringBuilder.toString();}// 实现链表的一些核心操作.// 头插public void addFirst(String val) {Node newNode = new Node(val);if (head == null) {// 链表为空head = newNode;tail = newNode;} else {// 链表不空// 1. 让新节点和原来的头结点, 建立好关联关系.newNode.next = head;head.prev = newNode;// 2. 让 head 指向新节点head = newNode;}}private static void test1() {MyDLinkedList list = new MyDLinkedList();list.addFirst("a");list.addFirst("b");list.addFirst("c");list.addFirst("d");System.out.println(list);}// 尾插public void addLast(String val) {Node newNode = new Node(val);if (head == null) {// 链表为空head = newNode;tail = newNode;} else {// 链表不空tail.next = newNode;newNode.prev = tail;tail = newNode;}}private static void test2() {MyDLinkedList list = new MyDLinkedList();list.addLast("a");list.addLast("b");list.addLast("c");list.addLast("d");System.out.println(list);}// 中间任意位置插入. 根据 index 下标, 插入到合适的位置上.public void add(int index, String val) {if (index < 0 || index > size()) {throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: " + index + ", Size: " + size());}// 如果 index 为 0, 说明是头插.if (index == 0) {addFirst(val);return;}// 如果 index 为 size(), 说明是尾插if (index == size()) {addLast(val);return;}// 处理中间的一般情况.// 根据 index 下标, 找到待插入位置的前一个位置. 前一个元素的下标 index - 1.Node prev = head;for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) { prev = prev.next; }// 经过上述循环, prev 已经指向待插入节点的前一个位置了.// 把后一个节点的位置也记录出来.Node next = prev.next;// 新节点的插入, 就是要放到 prev 和 next 之间.Node newNode = new Node(val);// a) 建立 prev 和 newNode 的关联关系.prev.next = newNode;newNode.prev = prev;// b) 建立 newNode 和 next 之间的关联关系.newNode.next = next;next.prev = newNode;}// 获取链表长度.public int size() {int size = 0;for (Node cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {size++;}return size;}private static void test3() {MyDLinkedList list = new MyDLinkedList();list.add(0, "a");list.add(1, "b");list.add(2, "c");list.add(3, "d");list.add(3, "x");// 预期结果: [a, b, c, x, d]System.out.println(list);}// 判定元素是否存在.public boolean contains(String val) {// 遍历链表, 看 val 是否存在, 存在返回 true, 不存在返回 false.for (Node cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {if (cur.val.equals(val)) return true;}return false;}// 查找元素, 返回该元素的下标. 如果没找到, 返回 -1.public int indexOf(String val) {int index = 0;for (Node cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {if (cur.val.equals(val)) return index;index++;}return -1;}private static void test4() {MyDLinkedList list = new MyDLinkedList();list.add(0, "a");list.add(1, "b");list.add(2, "c");list.add(3, "d");System.out.println(list.contains("a"));System.out.println(list.contains("x"));System.out.println(list.indexOf("c"));System.out.println(list.indexOf("x"));}// 删除头部元素public void removeFirst() {if (head == null) return; // 空链表不需要删除.// 针对只有一个节点的情况特殊处理.if (head.next == null) {head = null;tail = null;return;}head = head.next;head.prev = null;}private static void test5() {MyDLinkedList list = new MyDLinkedList();list.add(0, "a");list.add(1, "b");list.add(2, "c");list.add(3, "d");list.removeFirst();System.out.println(list);list.removeFirst();System.out.println(list);list.removeFirst();System.out.println(list);list.removeFirst();System.out.println(list);}// 删除尾部元素public void removeLast() {if (head == null) return; // 空链表不需要删除.if (head.next == null) {// 只有一个节点, 特殊处理.head = null;tail = null;return;}tail = tail.prev;tail.next = null;}private static void test6() {MyDLinkedList list = new MyDLinkedList();list.add(0, "a");list.add(1, "b");list.add(2, "c");list.add(3, "d");list.removeLast();System.out.println(list);list.removeLast();System.out.println(list);list.removeLast();System.out.println(list);list.removeLast();System.out.println(list);}// 指定位置删除public void remove(int index) {if (index < 0 || index >= size())throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: " + index + ", Size: " + size());if (index == 0) {removeFirst(); // 头删return;}if (index == size() - 1) {removeLast(); // 尾删return;}// 一般情况. 找到待删除节点的前一个位置. index - 1 的位置.Node prev = head;for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) { prev = prev.next; }// 循环结束, prev 指向待删除元素的前一个位置了.// toRemove 就是要删除的元素了.Node toRemove = prev.next;// 指向待删除元素的下一个位置.Node next = toRemove.next;prev.next = next;next.prev = prev;}public static void test7() {MyDLinkedList list = new MyDLinkedList();list.add(0, "a");list.add(1, "b");list.add(2, "c");list.add(3, "d");list.remove(3);System.out.println(list);list.remove(1);System.out.println(list);list.remove(0);System.out.println(list);}// 指定值删除public void remove(String val) {if (head == null) {return ;}// 判定头删/尾删特殊情况if (head.val.equals(val)) {removeFirst();return;}if (tail.val.equals(val)) {removeLast();return;}// 一般情况. 遍历链表, 找到待删除元素的位置.Node toRemove = head;for (; toRemove != null; toRemove = toRemove.next) {if (toRemove.val.equals(val)) {break;}}// 通过上述循环, 此时 toRemove 就指向了待删除元素.if (toRemove == null) return; // 要删除的值在链表中不存在的.// 真正进行删除.Node prev = toRemove.prev;Node next = toRemove.next;// 重新构建 prev 和 next 之间的关联关系.prev.next = next;next.prev = prev;}private static void test8() {MyDLinkedList list = new MyDLinkedList();list.add(0, "a");list.add(1, "b");list.add(2, "c");list.add(3, "d");list.remove("b");System.out.println(list);}public void clear() {// 清空链表head = null;tail = null;}// 未来的课程会学习一些 "单元测试框架" (JUnit 等)// 只需要给单元测试方法上加上特定注解, 即可执行到.public static void main(String[] args) {// test1();// test2();// test3();// test4();// test5();// test6();// test7();test8();}
}
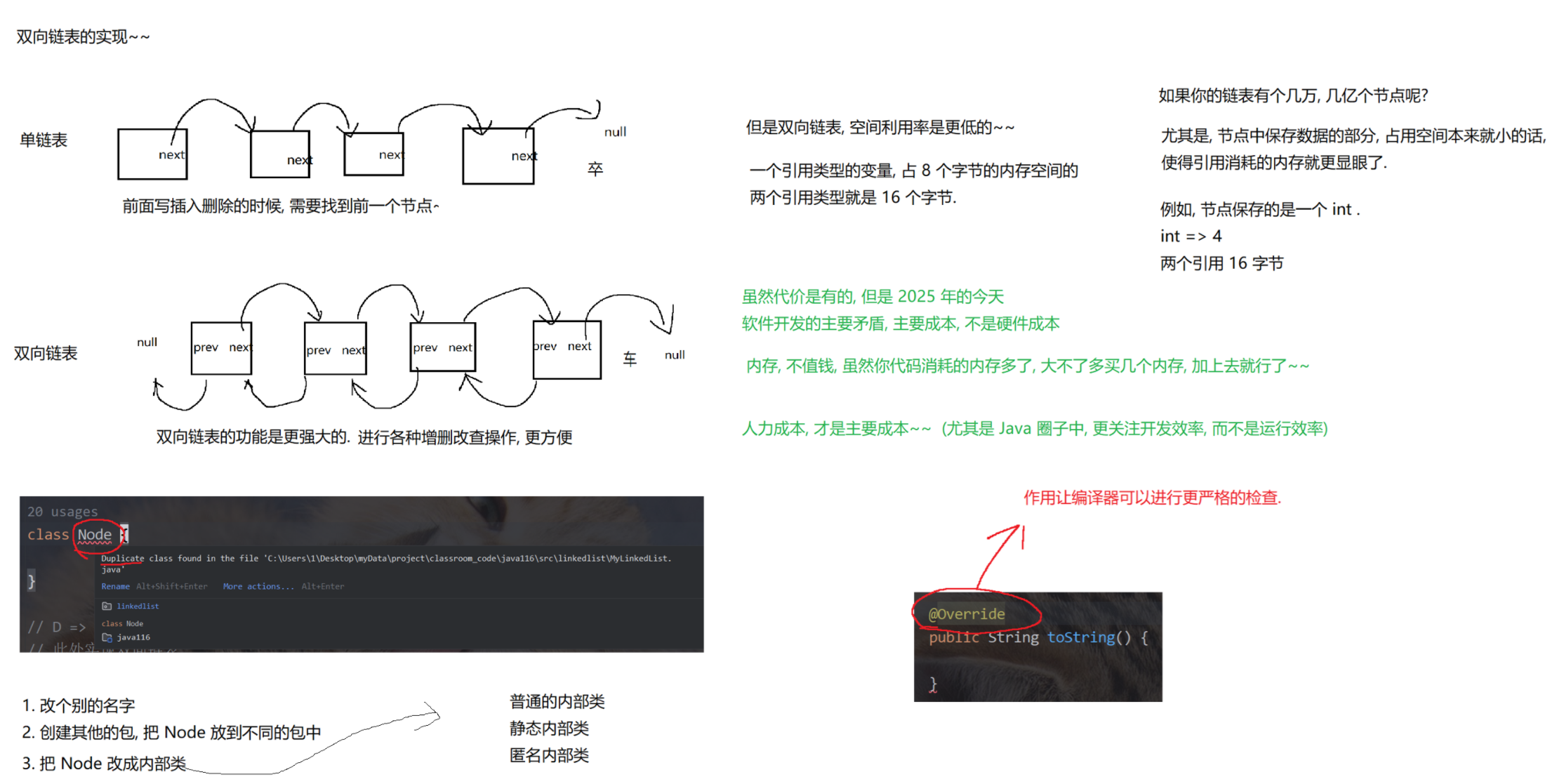
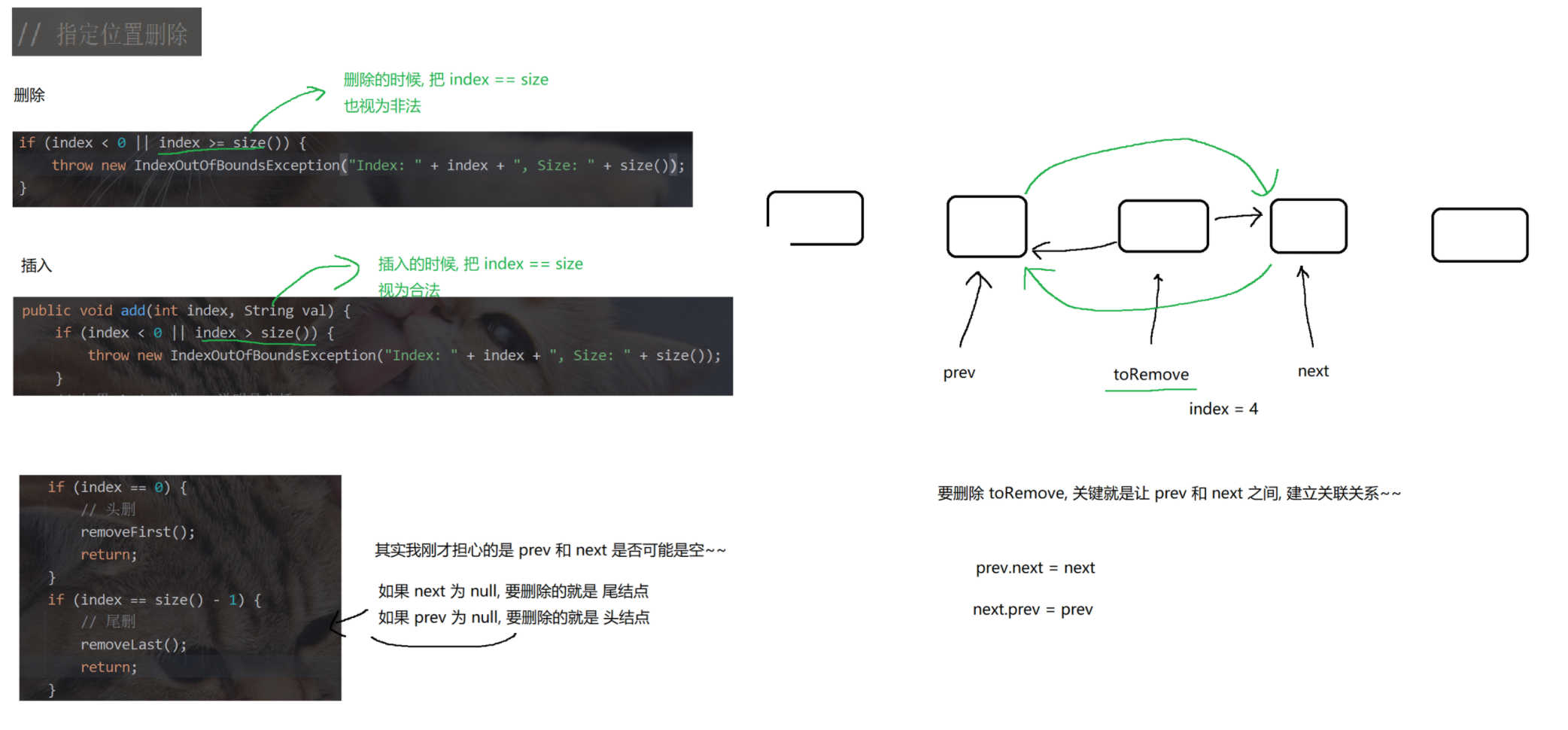
5.面试题(重点)
class ListNode {int val;ListNode next;ListNode() {}ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
}


(1)删除链表中等于给定值val的所有节点
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/description/
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {// 1. 判定链表是否是空的.if (head == null) {return null;}// 2. 遍历链表, 找到每一个值为 val 的节点. 从 head 之后的元素开始遍历.ListNode prev = head;ListNode cur = head.next;while (cur != null) {if (cur.val == val) {// 触发删除操作, 把 cur 给删掉.prev.next = cur.next;// 删除 cur 位置的节点之后, 需要移动 cur 指向下一个位置.cur = prev.next;} else {// 没有触发删除.// 移动 prev 和 cur 的指向prev = cur;cur = cur.next;}}// 3. 最后判定头结点的删除情况if (head.val == val) {head = head.next;}return head;}
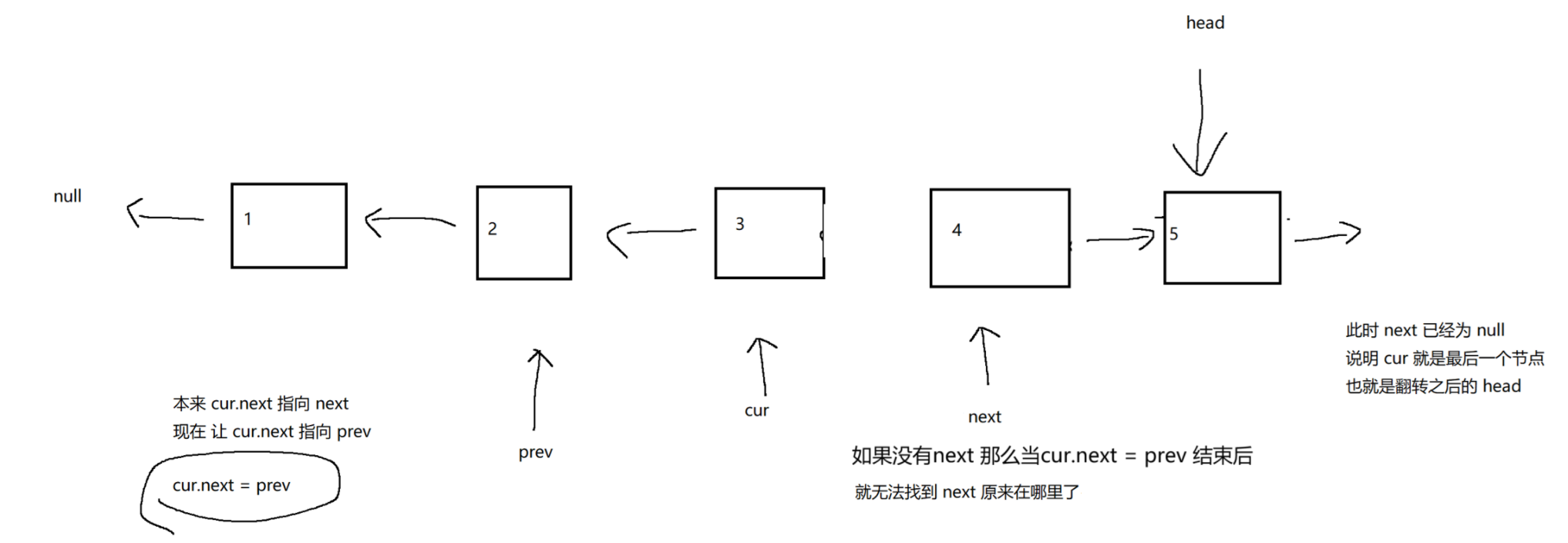
(2)反转⼀个单链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/description/
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {// 1. 判定链表为空if (head == null) return null;// 2. 如果链表只有一个节点, 不需要翻转的.if (head.next == null) return head;// 3. 处理一般情况.ListNode newHead = null;ListNode prev = null;ListNode cur = head;ListNode next = cur.next;while (cur != null) {// 每次循环, 都需要先把 next 的位置记录下来, 再进行后续修改.next = cur.next;// 如果 next 已经是 null, 说明 cur 就是最后一个节点. 让这个节点作为新的头节点.if (next == null) newHead = cur;// 进行翻转操作.cur.next = prev;// 更新 prev 和 cur 的指向.prev = cur;cur = next;}return newHead;}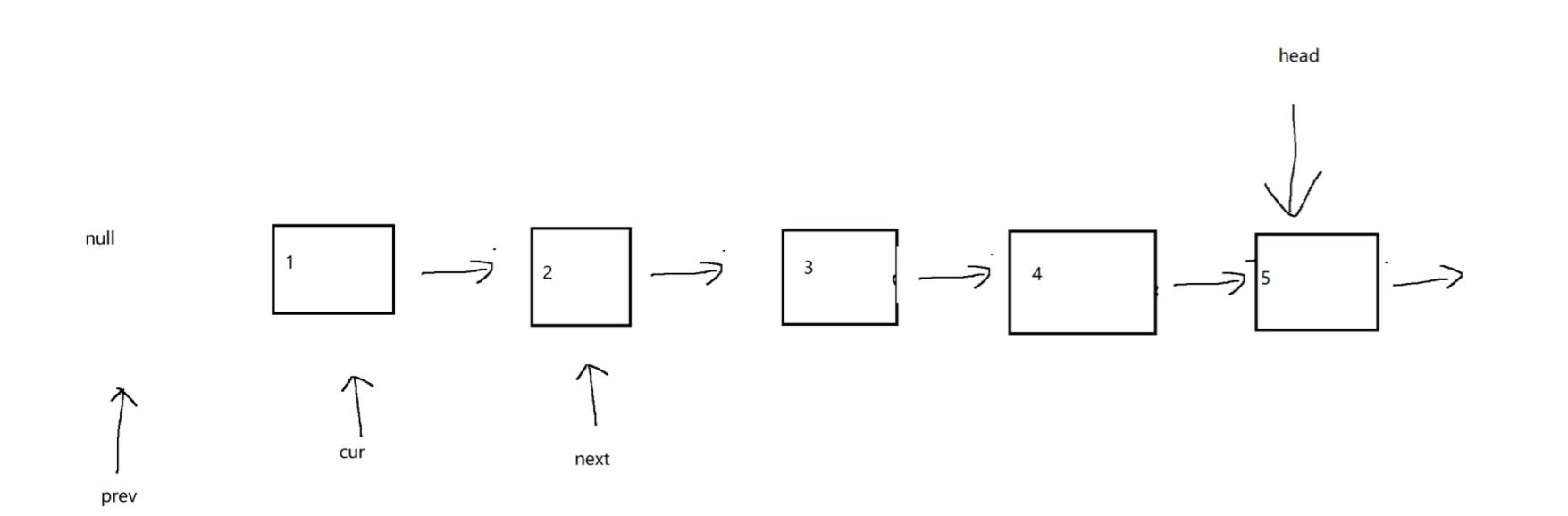
(3)给定⼀个带有头结点head的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第⼆个中间结点。
https://leetcode.cn/problems/middle-of-the-linked-list/description/
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {// 1. 判定链表为空if (head == null) return null;// 2. 求链表的长度.int size = size(head);// 3. 求出 size/2 的位置.int mid = size / 2;// 4. 从 head 出发, 走 mid 步就可以了.ListNode cur = head;for (int i = 0; i < mid; i++) {cur = cur.next;}return cur;}// 虽然没有现成的 size, 我们可以自己写一个. 遍历一下链表就可以了. 这样的过程, 时间复杂度是 O(N)public int size(ListNode head) {int size = 0;for (ListNode cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next) size++;return size;}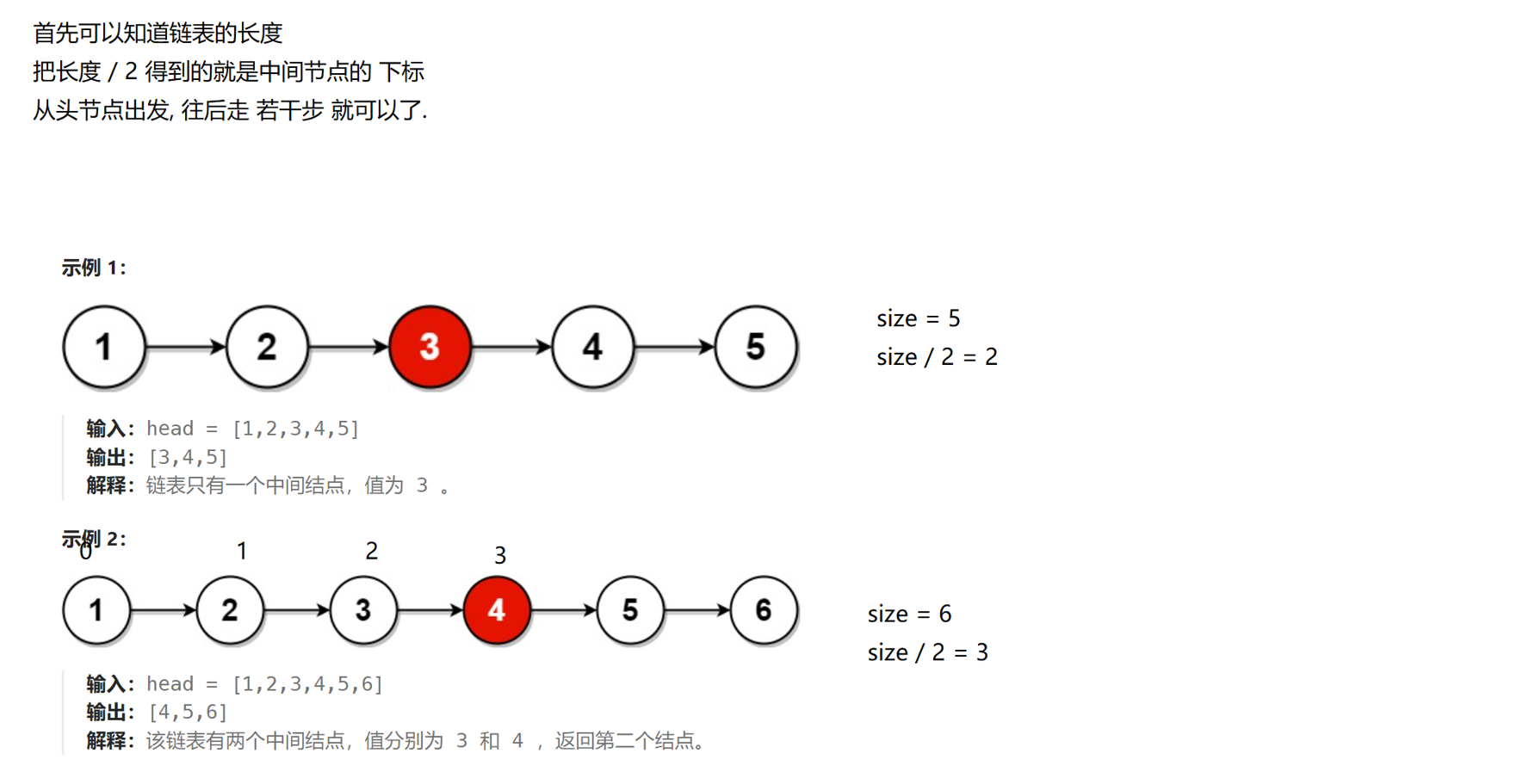
(4)输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。
https://leetcode.cn/problems/kth-node-from-end-of-list-lcci/description/
public int kthToLast(ListNode head, int k) {// 1. 判定链表为空, 判定 k 有效.if (head == null) return 0;// 此处正常来说是要返回非法的值. 要么返回 null 要么是抛出异常.// 但是这两个做法在 OJ 中是不行的. 要返回int 实在没有别的非法值了, 就返回 0.// 2. 计算整个链表的长度.int size = size(head);if (k <= 0 || k > size(head)) return 0;// 注意条件的边界, 要不要写 == , 需要代入数字判定.// k == 0 不行, 约定 k 必须从 1 开始 (题目的例子中给定隐式条件)// k == size 认为是可以的. 刚才数了一下, 长度为 5 的链表, 头节点元素, 倒数第 5 个.// 3. 根据 k 和长度计算出要走的步数 (size - k)int step = size - k;// 4. 从 head 出发, 走 size - k 步, 就行了.ListNode cur = head;for (int i = 0; i < step; i++) {cur = cur.next;}return cur.val;}public int size(ListNode head) {int size = 0;for (ListNode cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next) size++;return size;}

(5)将两个有序链表合并为⼀个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/description/
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {// 1. 判定链表为空if (list1 == null) return list2; if (list2 == null) return list1;// 2. 准备两个引用指向两个链表.ListNode cur1 = list1;ListNode cur2 = list2;// 3. 准备一个新的链表, 用于存放合并后的结果. 同时也保存链表的尾巴. 后续都是尾插. 记录尾巴, 比较方便进行尾插的.// 此处如果使用 "带有傀儡节点" 的方式来实现尾插, 后续会更简单. 一个节点 既是头结点 也是尾结点ListNode newHead = new ListNode(0);ListNode newTail = newHead;// 4. 进入循环, 开始合并.while (cur1 != null && cur2 != null) {// 判定这两个引用较小的值.if (cur1.val < cur2.val) {// cur1 比较小, 插入到 newTail 之后. 结果链表不为空链表. 尾插.newTail.next = cur1;// 插入完毕之后, 让 newTail 指向新的尾巴.newTail = cur1;// 更新 cur1 指向下一个节点.cur1 = cur1.next;} else {// cur2 比较小, 插入到 newTail 之后.newTail.next = cur2;// 插入完毕之后, 让 newTail 指向新的尾巴. 因为newTail需要一直保持自己是尾结点newTail = cur2;// 更新 cur2 指向下一个节点.cur2 = cur2.next;}}// 5. 上述循环完毕, 意味着 cur1 或者 cur2 有一个已经遍历完了. 只需要把剩余的节点, 挂到新链表末尾即可.if (cur1 != null) newTail.next = cur1; // cur1 还有剩余, 挂到 newTail 之后.if (cur2 != null) newTail.next = cur2; // cur2 还有剩余, 挂到 newTail 之后.// 6. 返回合并后的链表. newHead 指向的是傀儡节点. 真正的头结点是 newHead.nextreturn newHead.next;}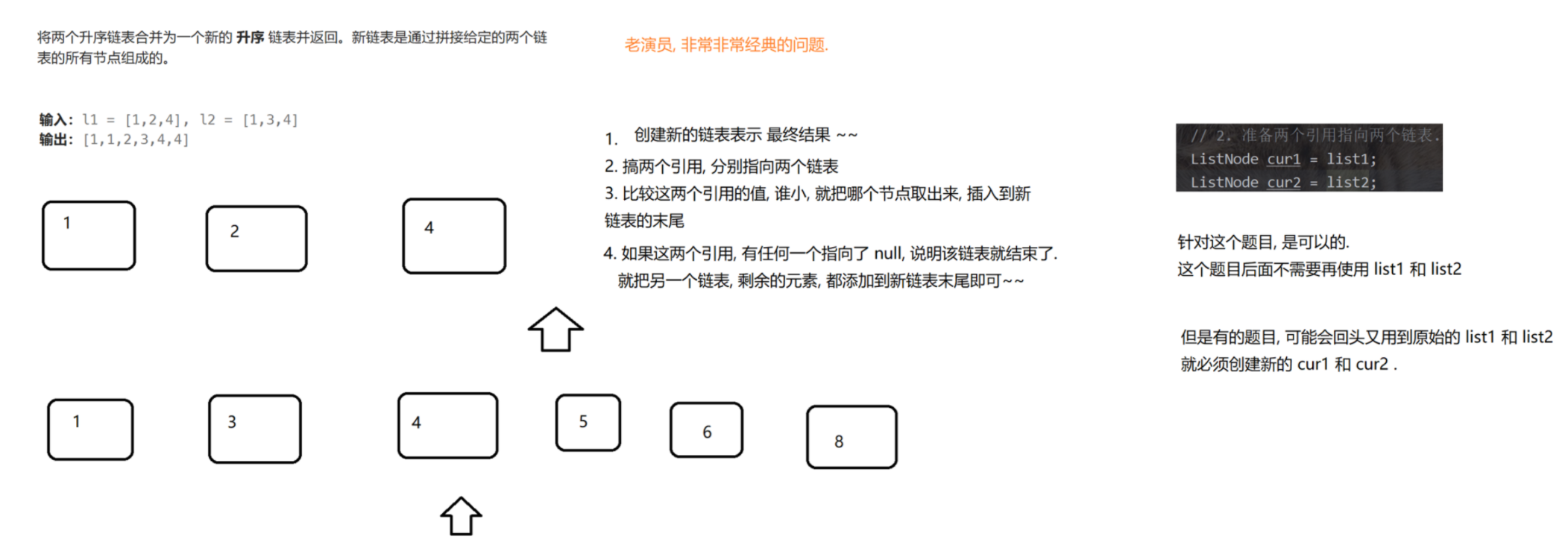
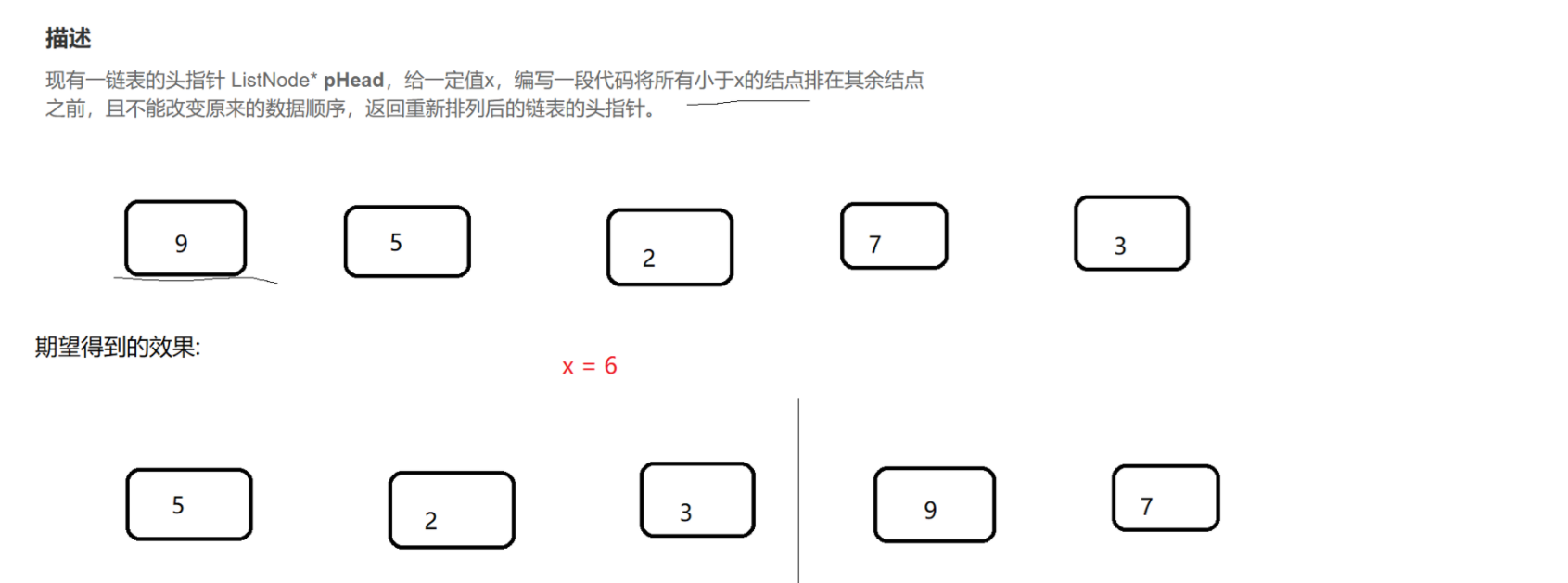
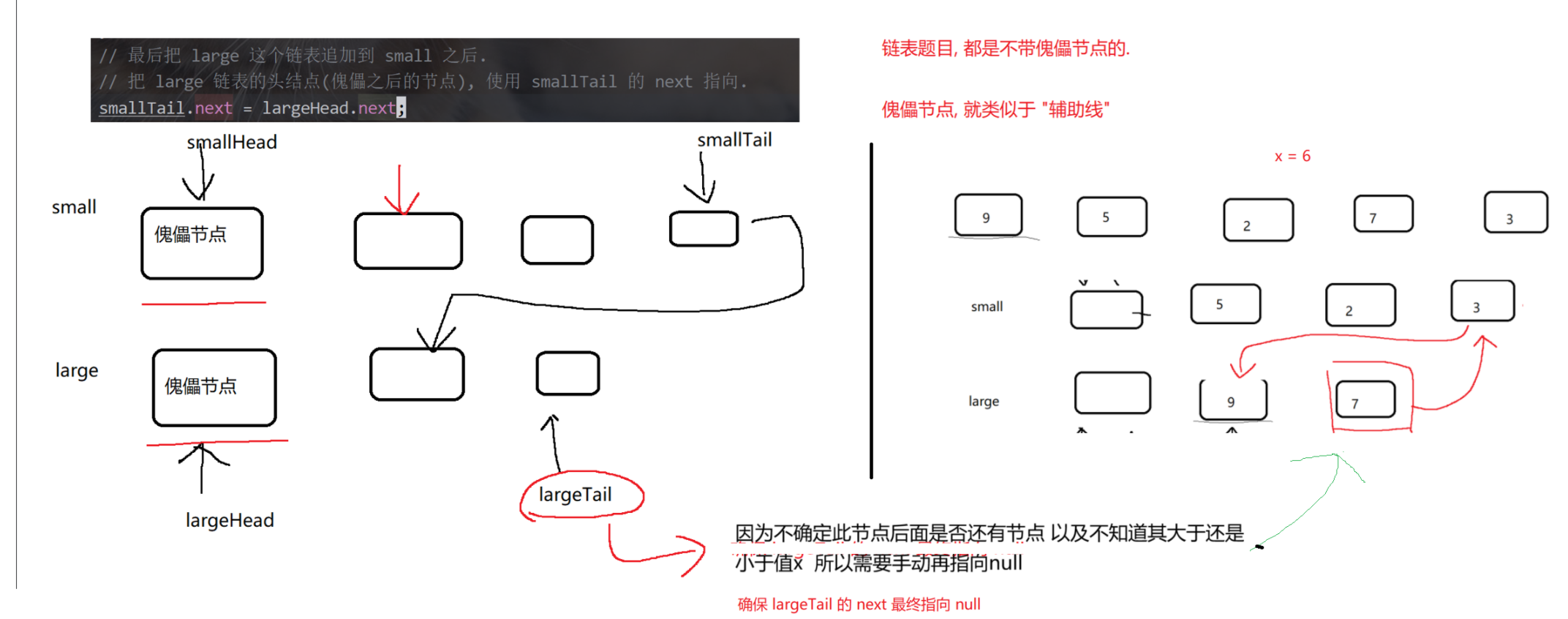
(6)编写代码,以给定值x为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于x的结点排在⼤于或等于x的结点之前。
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/0e27e0b064de4eacac178676ef9c9d70?tpId=8&&tqId=11004&rp=2&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/cracking-the-coding-interview/question-ranking
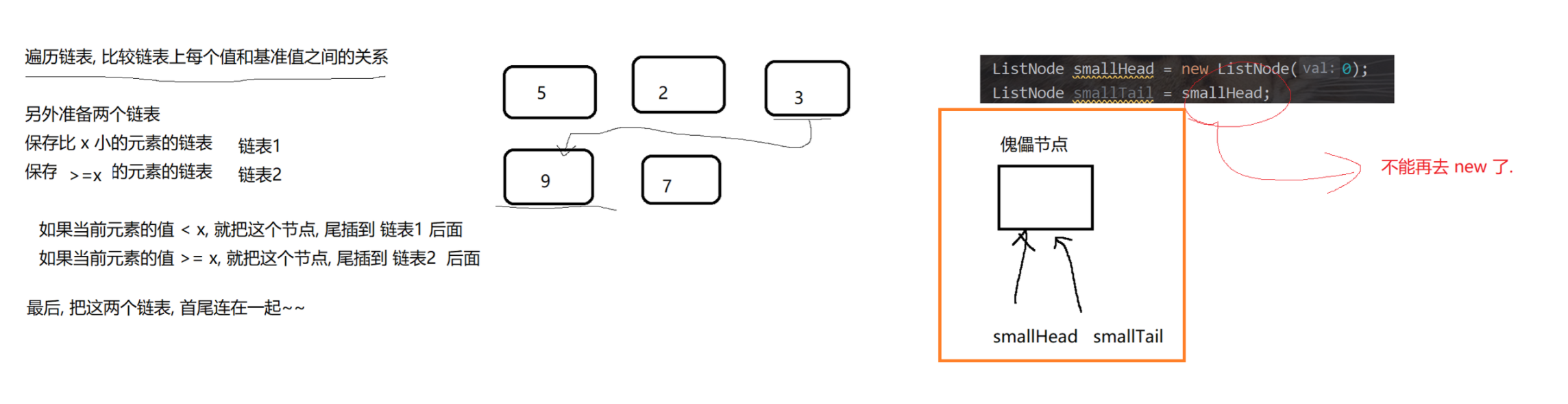
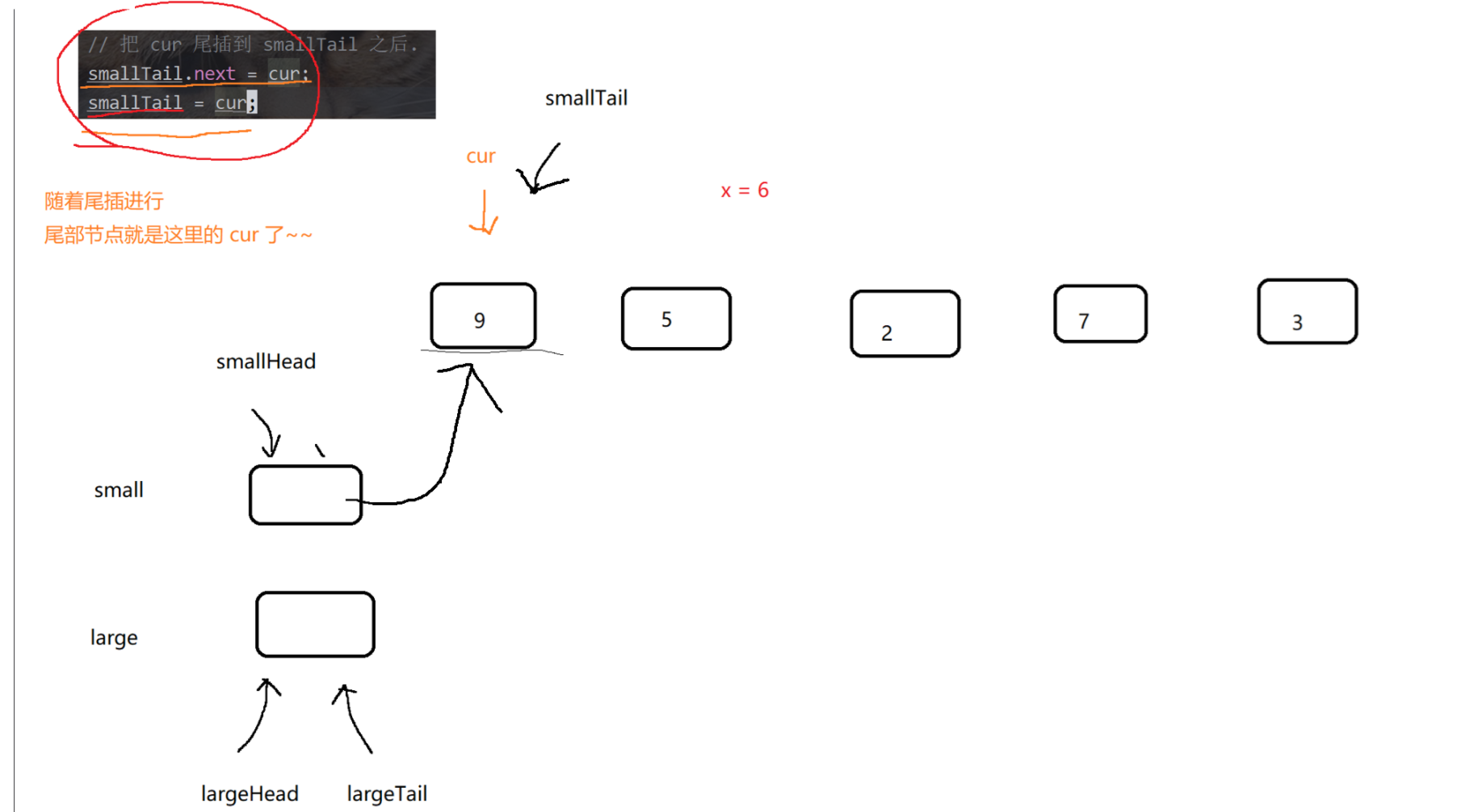
public ListNode partition(ListNode pHead, int x) {if (pHead == null) return null;if (pHead.next == null) return pHead; // 链表只有一个节点, 得到的结果还是本身.// 针对一般情况, 先创建两个链表.// 由于接下来都是尾插, 为了方便, 直接创建 tail 指向尾部节点, 并且创建傀儡节点, 简化逻辑.ListNode smallHead = new ListNode(0);ListNode smallTail = smallHead;ListNode largeHead = new ListNode(0);ListNode largeTail = largeHead;// 遍历链表for (ListNode cur = pHead; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {if (cur.val < x) {// 把 cur 尾插到 smallTail 之后.smallTail.next = cur;smallTail = cur;} else {// 把 cur 尾插到 largeTail 之后.largeTail.next = cur;largeTail = cur;}}// 最后把 large 这个链表追加到 small 之后.// 把 large 链表的头结点(傀儡之后的节点), 使用 smallTail 的 next 指向.smallTail.next = largeHead.next;// 稳妥起见, 把 largeTail 的 next 指向 null. 避免出现 由于 largeTail next 不为空导致的链表出错.largeTail.next = null;return smallHead.next;}
(7)链表的回文结构
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/d281619e4b3e4a60a2cc66ea32855bfa?tpId=49&&tqId=29370&rp=1&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/2016test/question-ranking
// 空间复杂度 O(N) 的版本.public boolean chkPalindrome2(ListNode A) {if (A == null) return true; // 空链表, 视为回文if (A.next == null) return true; // 只有一个节点, 也视为回文// 1. 把链表复制一份ListNode newHead = new ListNode(0);ListNode newTail = newHead;for (ListNode cur = A; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {ListNode newNode = new ListNode(cur.val);newTail.next = newNode;newTail = newNode;}newHead = newHead.next;// 傀儡节点不再使用了.// 2. 把复制的链表逆置ListNode prev = null;ListNode cur = newHead;while (cur != null) {ListNode next = cur.next;if (next == null) newHead = cur;// 关键操作cur.next = prev;prev = cur;cur = next;}// 3. 比较两个链表是否相同ListNode cur1 = A;ListNode cur2 = newHead;while (cur1 != null && cur2 != null) {if (cur1.val != cur2.val) return false; // 出现不相等的情况, 一定不是回文.cur1 = cur1.next;cur2 = cur2.next;}if (cur1 == null && cur2 == null) return true; // 两个链表同时遍历完, 长度相同, 就是回文return false; // 两个链表长度不同, 不是回文.}// 空间复杂度 O(1) 的版本.public boolean chkPalindrome(ListNode A) {if (A == null) return true;if (A.next == null) return true;// 1. 找到链表中间节点.int size = size(A);int step = size / 2;ListNode B = A;for (int i = 0; i < step; i++) { B = B.next; } // 此时 B 指向的就是中间节点了.// 2. 针对 B 这个链表进行逆置.ListNode prev = null;ListNode cur = B;while (cur != null) {ListNode next = cur.next;if (next == null) B = cur; // cur 就是新的头节点cur.next = prev;prev = cur;cur = next;}// 3. 比较 A 和 B 两个链表是否相同.ListNode cur1 = A;ListNode cur2 = B;while (cur1 != null && cur2 != null) {if (cur1.val != cur2.val) return false;cur1 = cur1.next;cur2 = cur2.next;}// 不去考虑长度问题了. 如果节点是偶数个, 此时 A 的长度就是会比 B 多一个.return true;}public int size(ListNode head) {int size = 0;for (ListNode cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {size++;}return size;}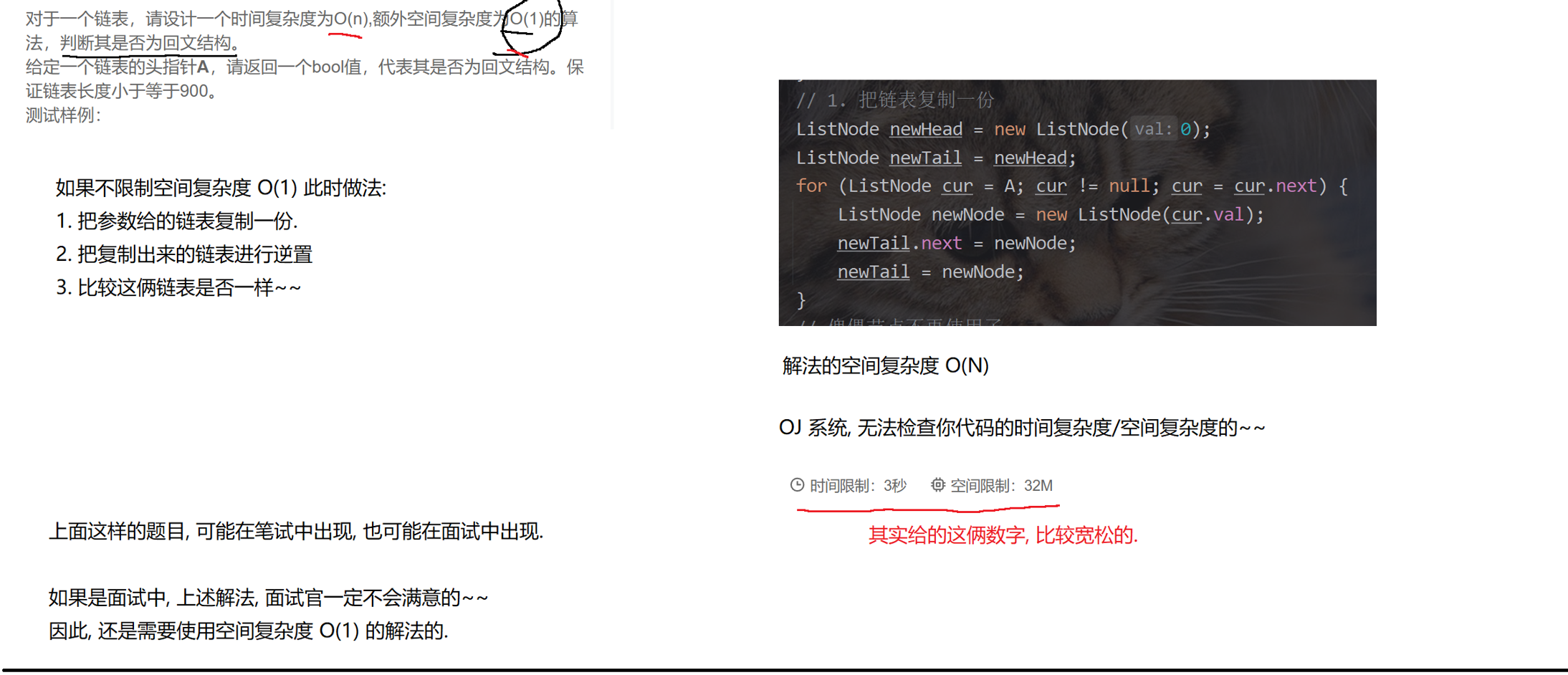
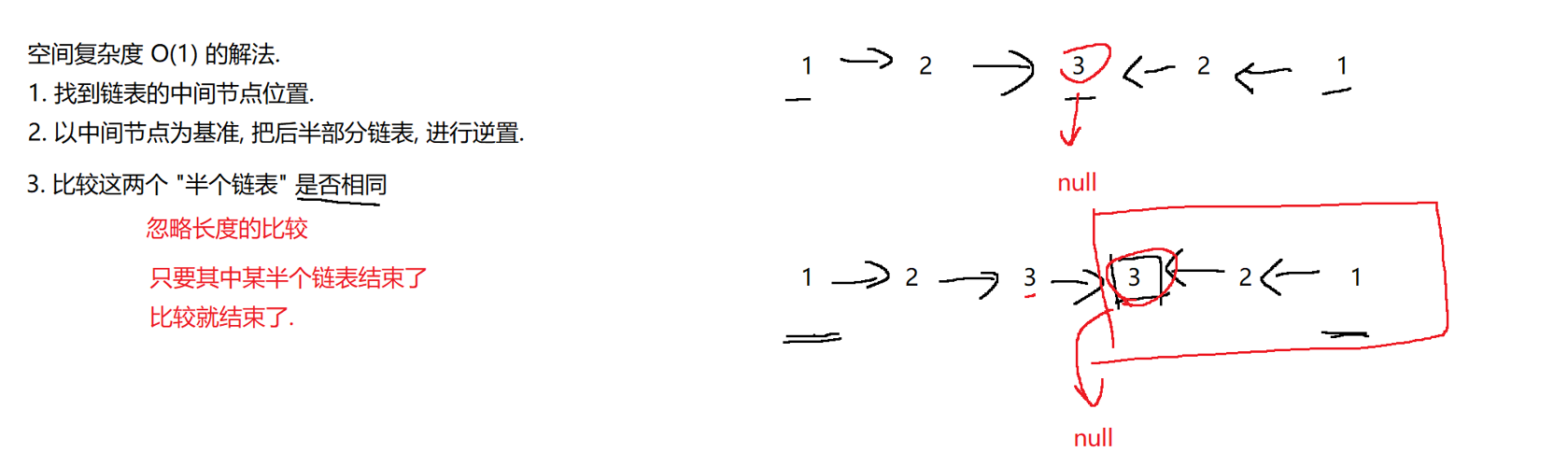
(8)输入两个链表,找出它们的第⼀个公共结点。
https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/description/
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {// 判定空的情况先放一放, 先往后写, 再回头看是否需要判空// 1. 求两个链表的长度.int sizeA = size(headA);int sizeB = size(headB);// 2. 让长的链表的引用先往后走 长度差值 步.ListNode curA = headA;ListNode curB = headB;if (sizeA > sizeB) {// A 链表先走, sizeA - sizeB 步.for (int i = 0; i < sizeA - sizeB; i++) {curA = curA.next;}} else {// B 链表先走, sizeB - sizeA 步.for (int i = 0; i < sizeB - sizeA; i++) {curB = curB.next;}}// 3. 再让两个引用同时出发, 往后各自走一步, 看什么时候两个引用指向同一个节点 (相遇), 此时的这个节点就是交点.while (curA != null && curB != null) {if (curA == curB) return curA; // 两个引用相遇了. 此时得到的这个节点就是链表的交点.curA = curA.next;curB = curB.next;}// 4. 如果遍历结束, 两个引用也没有相遇, 说明链表不相交.return null;}public int size(ListNode head) {int size = 0;for (ListNode cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {size++;}return size;}
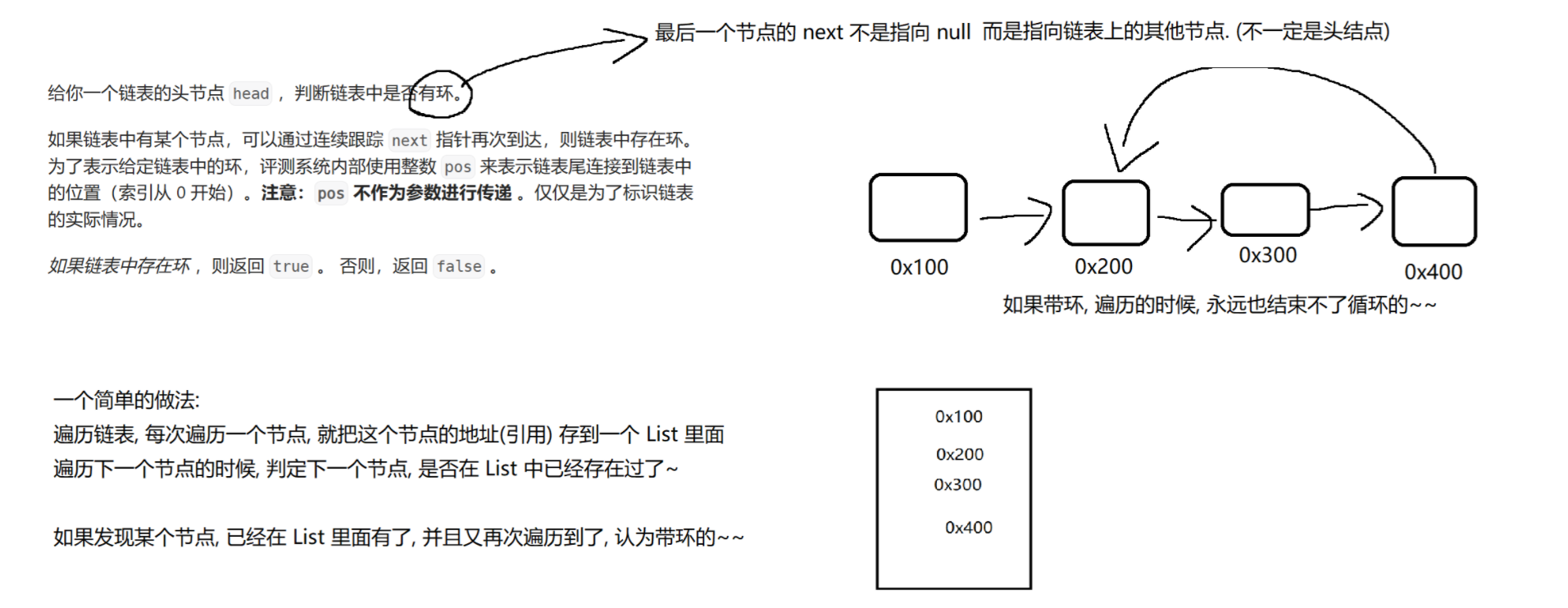
(9)给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle/description/
//空间复杂度 O(N) 时间复杂度 O(N^2)public boolean hasCycle2(ListNode head) {// 朴素的做法: 使用 List 记录遍历过程中的每个节点.// 每次取到一个节点, 都先判定是否已经在 List 中出现过。 如果出现过, 就是带环的.if (head == null) return false;List<ListNode> list = new ArrayList<>();for (ListNode cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {if (list.contains(cur)) return true; // 带环了.else list.add(cur);}return false;}//空间复杂度 O(1) 时间复杂度 O(N)public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {// 使用双引用, 一个快引用, 一个慢引用. 初始情况下, 两个引用都指向 head.// 让快引用一次走两步, 慢引用一次走一步. 判定是否会重合. 如果重合就是带环了.if (head == null) return false;ListNode slow = head;ListNode fast = head;while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;if (fast == slow) return true;}// 没有出发上述 return true, 反而是触发了 fast 为 null 或者 fast.next 为 null.// 此时链表无环的.return false;}
![]()

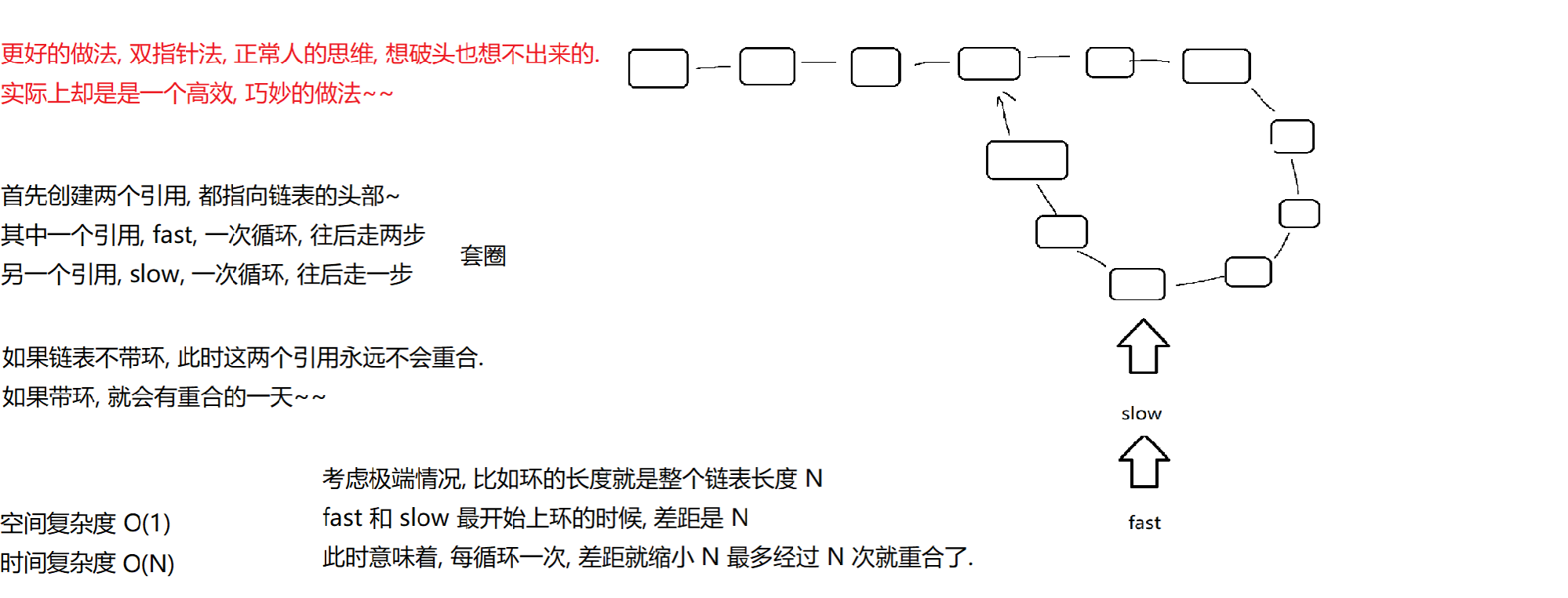

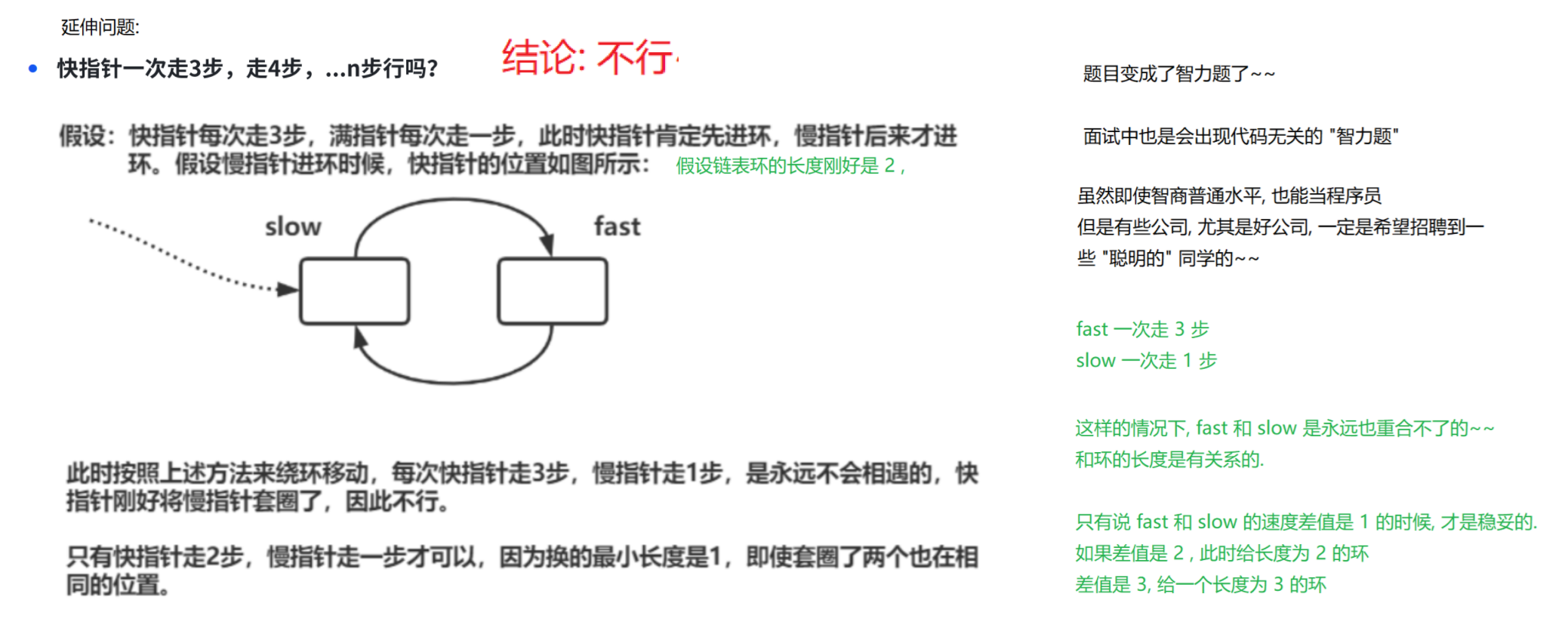
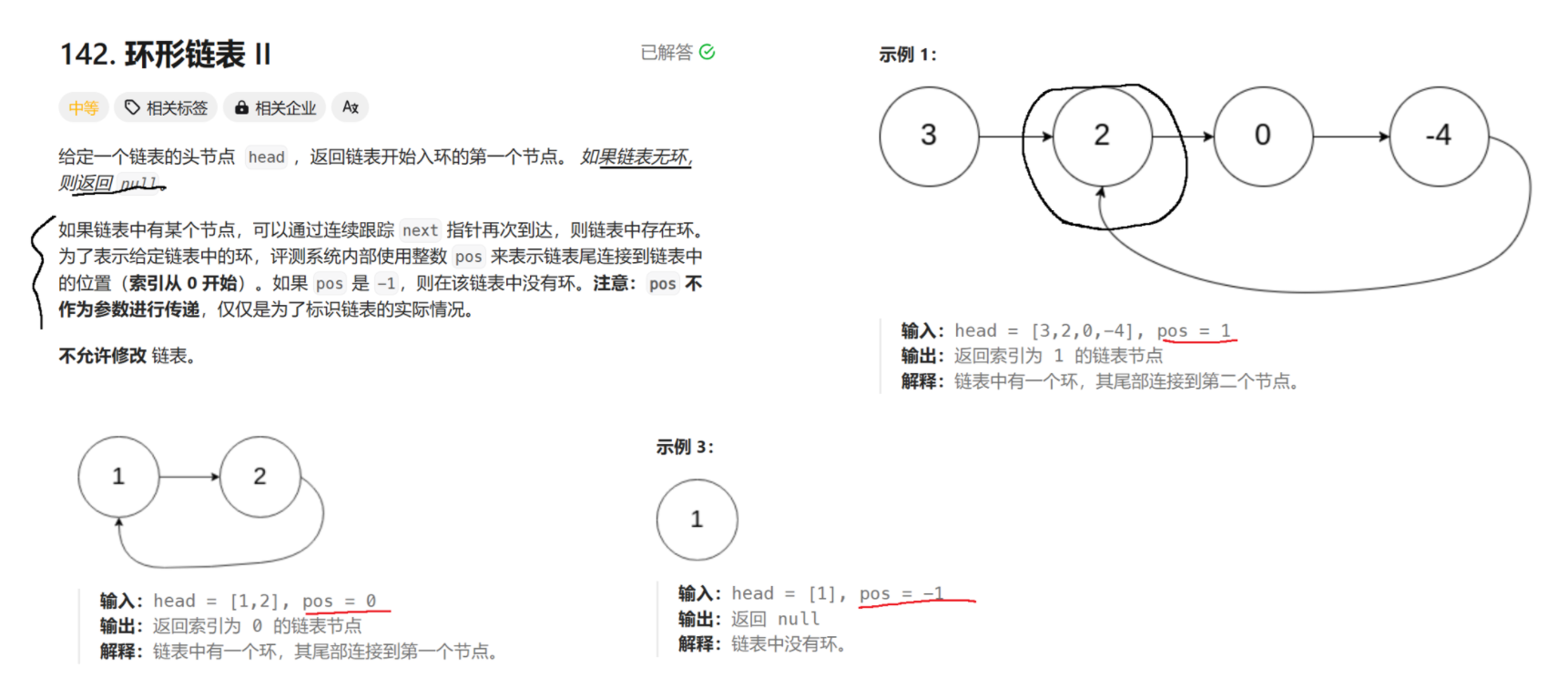
(10)给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第⼀个节点。如果链表无环,则返回NULL
https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/description/
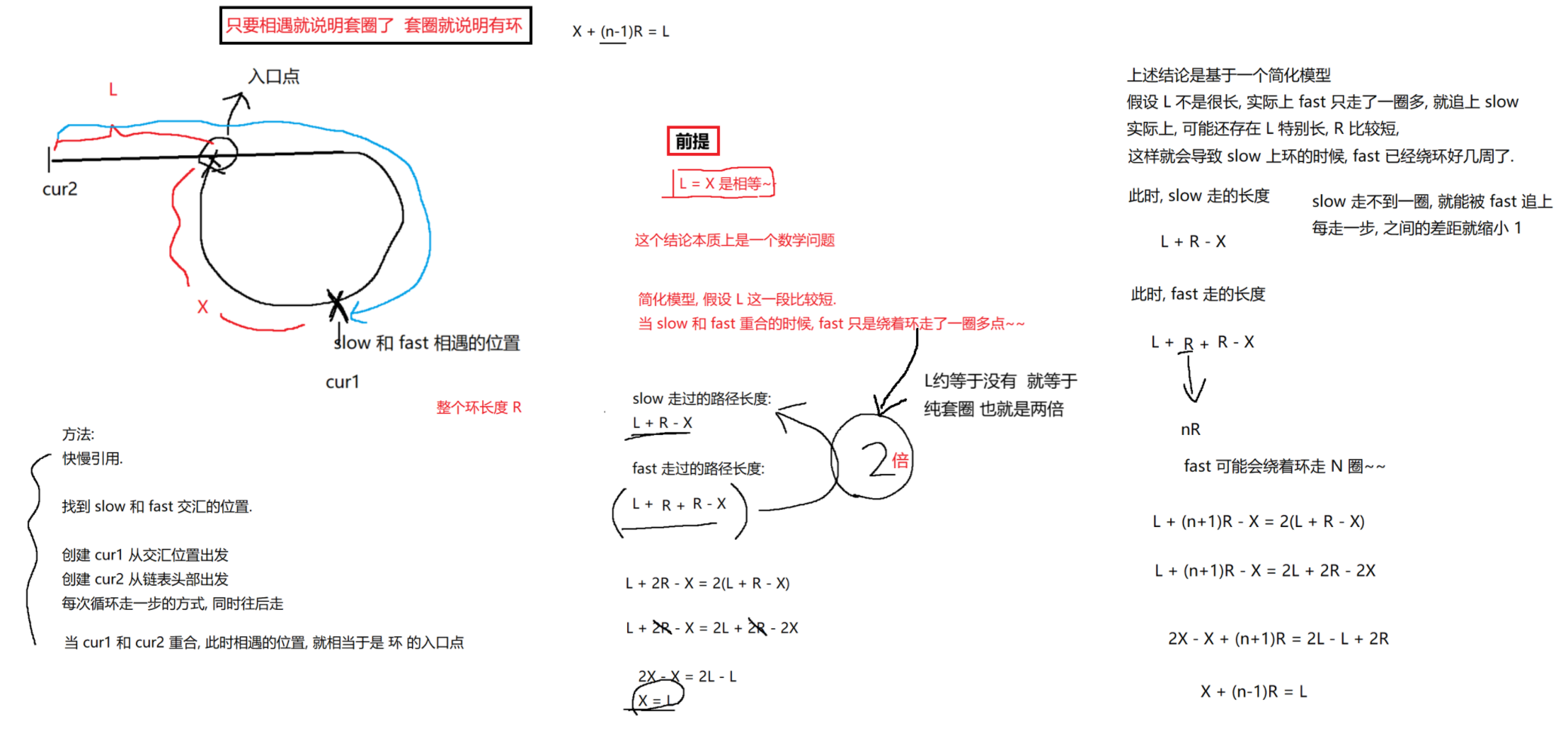
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {if (head == null) return null;// 1. 使用快慢指针, 找到相遇位置. 如果不相遇, 说明无环.ListNode slow = head;ListNode fast = head;while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;if (fast == slow) break;}// 循环结束, 需要判定, 是因为 fast 和 slow 重合, 结束循环的, 还是因为 fast 为 null 结束循环的.if (fast == null || fast.next == null) return null; // 无环的情况, fast 已经到末尾了.// 2. 设置一个 cur1 , 从 head 出发, 设置 cur2 从交汇位置出发. 两个引用同时往前走.// 两个引用重合的位置, 就是环的入口点.ListNode cur1 = head;ListNode cur2 = slow;// 这里的循环一定不会死循环的. 通过数学公式已经证明了, cur1 和 cur2 是必定会相遇.// 而且相遇的位置就是环的入口.while (cur1 != cur2) {cur1 = cur1.next;cur2 = cur2.next;}// 循环结束, 说明 cur1 和 cur2 相遇了.return cur1;}