计算机听觉分类分析:从音频信号处理到智能识别的完整技术实战

🌟 Hello,我是蒋星熠Jaxonic!
🌈 在浩瀚无垠的技术宇宙中,我是一名执着的星际旅人,用代码绘制探索的轨迹。
🚀 每一个算法都是我点燃的推进器,每一行代码都是我航行的星图。
🔭 每一次性能优化都是我的天文望远镜,每一次架构设计都是我的引力弹弓。
🎻 在数字世界的协奏曲中,我既是作曲家也是首席乐手。让我们携手,在二进制星河中谱写属于极客的壮丽诗篇!
摘要
从最初接触简单的音频波形分析,到如今能够构建复杂的深度学习模型进行实时音频分类,这个过程充满了技术突破的喜悦。
计算机听觉分类分析,本质上是让机器具备"听懂"声音的能力。它不仅仅是简单的音频识别,更是一个涉及信号处理、特征工程、机器学习和深度学习的综合性技术领域。在我的实际项目中,我曾经处理过语音识别、音乐分类、环境声音检测等多种应用场景,每一个场景都有其独特的技术挑战和解决方案。
这项技术的核心在于如何将连续的音频信号转换为计算机能够理解和处理的数字特征,然后通过智能算法实现准确的分类识别。从传统的MFCC特征提取到现代的深度学习端到端训练,技术的演进让我们能够处理越来越复杂的音频分析任务。特别是在实时性要求较高的应用中,如何平衡准确性和效率成为了关键的技术考量。
在本文中,我将结合自己的实战经验,从音频信号的基础理论出发,逐步深入到特征提取、模型训练、性能优化等各个环节,为大家呈现一个完整的计算机听觉分类分析技术体系。
1. 音频信号基础与预处理
1.1 音频信号的数字化表示
音频信号在计算机中以数字形式存储,通过采样率和量化位数来描述其质量特征。理解这些基础概念对于后续的特征提取至关重要。
import numpy as np
import librosa
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy import signal
import soundfile as sfclass AudioProcessor:"""音频信号处理器"""def __init__(self, sample_rate=22050):self.sample_rate = sample_ratedef load_audio(self, file_path, duration=None):"""加载音频文件Args:file_path: 音频文件路径duration: 加载时长(秒)Returns:audio_data: 音频数据sr: 采样率"""try:audio_data, sr = librosa.load(file_path, sr=self.sample_rate, duration=duration)return audio_data, srexcept Exception as e:print(f"音频加载失败: {e}")return None, Nonedef normalize_audio(self, audio_data):"""音频归一化处理"""# 幅度归一化到[-1, 1]范围max_val = np.max(np.abs(audio_data))if max_val > 0:normalized = audio_data / max_valelse:normalized = audio_datareturn normalizeddef apply_window(self, audio_data, window_type='hann'):"""应用窗函数减少频谱泄漏"""window = signal.get_window(window_type, len(audio_data))windowed_audio = audio_data * windowreturn windowed_audio
这段代码展示了音频信号的基础处理流程。load_audio方法使用librosa库加载音频文件,支持多种格式;normalize_audio方法进行幅度归一化,防止数值溢出;apply_window方法应用窗函数,这在频域分析中非常重要。
1.2 音频预处理管道
class AudioPreprocessor:"""音频预处理管道"""def __init__(self, sample_rate=22050, n_fft=2048, hop_length=512):self.sample_rate = sample_rateself.n_fft = n_fftself.hop_length = hop_lengthdef remove_silence(self, audio_data, threshold=0.01):"""移除静音段"""# 计算短时能量frame_length = 1024energy = np.array([np.sum(audio_data[i:i+frame_length]**2) for i in range(0, len(audio_data)-frame_length, frame_length//2)])# 找到非静音段non_silent_frames = energy > threshold * np.max(energy)# 重构音频processed_audio = []for i, is_speech in enumerate(non_silent_frames):if is_speech:start_idx = i * frame_length // 2end_idx = start_idx + frame_lengthprocessed_audio.extend(audio_data[start_idx:end_idx])return np.array(processed_audio)def apply_filters(self, audio_data):"""应用滤波器组合"""# 高通滤波器去除低频噪声sos_high = signal.butter(5, 80, btype='high', fs=self.sample_rate, output='sos')filtered_audio = signal.sosfilt(sos_high, audio_data)# 低通滤波器去除高频噪声sos_low = signal.butter(5, 8000, btype='low', fs=self.sample_rate, output='sos')filtered_audio = signal.sosfilt(sos_low, filtered_audio)return filtered_audio
预处理管道包含了静音检测和滤波处理。remove_silence方法通过短时能量计算识别并移除静音段,这对于提高分类准确性很重要;apply_filters方法应用带通滤波器,去除不必要的频率成分。
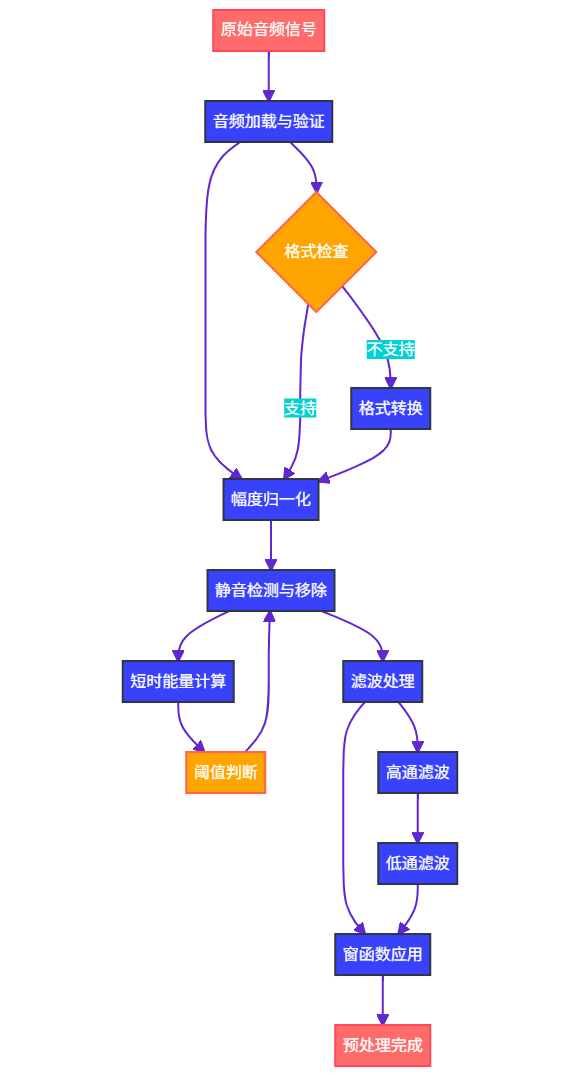
图1:音频预处理流程图 - 展示了从原始音频到预处理完成的完整流程
2. 音频特征提取技术
2.1 传统特征提取方法
传统的音频特征提取主要基于信号处理理论,包括时域特征、频域特征和倒谱特征等。
class TraditionalFeatureExtractor:"""传统音频特征提取器"""def __init__(self, sample_rate=22050, n_mfcc=13, n_fft=2048):self.sample_rate = sample_rateself.n_mfcc = n_mfccself.n_fft = n_fftdef extract_mfcc(self, audio_data):"""提取MFCC特征"""# 计算MFCC特征mfcc = librosa.feature.mfcc(y=audio_data,sr=self.sample_rate,n_mfcc=self.n_mfcc,n_fft=self.n_fft)# 计算一阶和二阶差分mfcc_delta = librosa.feature.delta(mfcc)mfcc_delta2 = librosa.feature.delta(mfcc, order=2)# 合并特征features = np.vstack([mfcc, mfcc_delta, mfcc_delta2])return featuresdef extract_spectral_features(self, audio_data):"""提取频谱特征"""# 计算频谱质心spectral_centroids = librosa.feature.spectral_centroid(y=audio_data, sr=self.sample_rate)[0]# 计算频谱带宽spectral_bandwidth = librosa.feature.spectral_bandwidth(y=audio_data, sr=self.sample_rate)[0]# 计算频谱对比度spectral_contrast = librosa.feature.spectral_contrast(y=audio_data, sr=self.sample_rate)# 计算频谱滚降点spectral_rolloff = librosa.feature.spectral_rolloff(y=audio_data, sr=self.sample_rate)[0]return {'centroid': spectral_centroids,'bandwidth': spectral_bandwidth,'contrast': spectral_contrast,'rolloff': spectral_rolloff}def extract_rhythm_features(self, audio_data):"""提取节奏特征"""# 计算节拍跟踪tempo, beats = librosa.beat.beat_track(y=audio_data, sr=self.sample_rate)# 计算零交叉率zcr = librosa.feature.zero_crossing_rate(audio_data)[0]# 计算RMS能量rms = librosa.feature.rms(y=audio_data)[0]return {'tempo': tempo,'beats': beats,'zcr': zcr,'rms': rms}
这个特征提取器实现了三类重要的传统特征:MFCC特征是最常用的音频特征,能够很好地表示音频的频谱包络;频谱特征描述了音频的频域特性;节奏特征则捕获了音频的时域动态信息。
2.2 深度学习特征提取
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torchaudio
from torch.nn import functional as Fclass DeepFeatureExtractor(nn.Module):"""基于深度学习的特征提取器"""def __init__(self, n_mels=128, n_fft=2048, hop_length=512):super(DeepFeatureExtractor, self).__init__()self.n_mels = n_melsself.n_fft = n_fftself.hop_length = hop_length# Mel频谱图变换self.mel_transform = torchaudio.transforms.MelSpectrogram(sample_rate=22050,n_fft=n_fft,hop_length=hop_length,n_mels=n_mels)# 卷积特征提取层self.conv_layers = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel_size=3, padding=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(32),nn.ReLU(),nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2),nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=3, padding=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(64),nn.ReLU(),nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2),nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=3, padding=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(128),nn.ReLU(),nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((8, 8)))# 注意力机制self.attention = nn.MultiheadAttention(embed_dim=128, num_heads=8, batch_first=True)def forward(self, audio_tensor):"""前向传播提取深度特征"""# 转换为Mel频谱图mel_spec = self.mel_transform(audio_tensor)mel_spec = torch.log(mel_spec + 1e-8) # 对数变换# 添加通道维度if len(mel_spec.shape) == 3:mel_spec = mel_spec.unsqueeze(1)# 卷积特征提取conv_features = self.conv_layers(mel_spec)# 重塑为序列格式用于注意力机制batch_size, channels, height, width = conv_features.shapesequence_features = conv_features.view(batch_size, channels, -1)sequence_features = sequence_features.permute(0, 2, 1)# 应用注意力机制attended_features, attention_weights = self.attention(sequence_features, sequence_features, sequence_features)# 全局平均池化global_features = torch.mean(attended_features, dim=1)return global_features, attention_weights
深度学习特征提取器结合了Mel频谱图变换、卷积神经网络和注意力机制。这种端到端的方法能够自动学习最适合特定任务的特征表示,通常比手工设计的特征更加有效。

图2:特征提取时序图 - 展示了传统特征与深度特征的并行提取和融合过程
3. 分类算法与模型设计
3.1 传统机器学习分类器
传统的机器学习方法在音频分类中仍然具有重要价值,特别是在数据量较小或需要可解释性的场景中。
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier, GradientBoostingClassifier
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score, GridSearchCV
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, confusion_matrix
import joblibclass TraditionalClassifier:"""传统机器学习分类器集成"""def __init__(self):self.models = {}self.scalers = {}self.best_model = Nonedef prepare_models(self):"""准备多种分类模型"""self.models = {'random_forest': RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100,max_depth=10,random_state=42,n_jobs=-1),'gradient_boosting': GradientBoostingClassifier(n_estimators=100,learning_rate=0.1,max_depth=6,random_state=42),'svm': SVC(kernel='rbf',C=1.0,gamma='scale',probability=True,random_state=42)}# 为每个模型准备标准化器for model_name in self.models.keys():self.scalers[model_name] = StandardScaler()def train_and_evaluate(self, X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test):"""训练并评估所有模型"""results = {}for model_name, model in self.models.items():print(f"训练 {model_name} 模型...")# 特征标准化scaler = self.scalers[model_name]X_train_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)X_test_scaled = scaler.transform(X_test)# 训练模型model.fit(X_train_scaled, y_train)# 交叉验证评估cv_scores = cross_val_score(model, X_train_scaled, y_train, cv=5, scoring='accuracy')# 测试集评估test_score = model.score(X_test_scaled, y_test)y_pred = model.predict(X_test_scaled)results[model_name] = {'cv_mean': cv_scores.mean(),'cv_std': cv_scores.std(),'test_accuracy': test_score,'predictions': y_pred,'model': model,'scaler': scaler}print(f"{model_name} - CV准确率: {cv_scores.mean():.4f} (±{cv_scores.std():.4f})")print(f"{model_name} - 测试准确率: {test_score:.4f}")print("-" * 50)# 选择最佳模型best_model_name = max(results.keys(), key=lambda x: results[x]['test_accuracy'])self.best_model = results[best_model_name]return resultsdef hyperparameter_tuning(self, X_train, y_train, model_name='random_forest'):"""超参数调优"""if model_name == 'random_forest':param_grid = {'n_estimators': [50, 100, 200],'max_depth': [5, 10, 15, None],'min_samples_split': [2, 5, 10],'min_samples_leaf': [1, 2, 4]}elif model_name == 'svm':param_grid = {'C': [0.1, 1, 10, 100],'gamma': ['scale', 'auto', 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1],'kernel': ['rbf', 'poly', 'sigmoid']}else:return None# 网格搜索grid_search = GridSearchCV(self.models[model_name],param_grid,cv=5,scoring='accuracy',n_jobs=-1,verbose=1)# 特征标准化scaler = self.scalers[model_name]X_train_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)# 执行搜索grid_search.fit(X_train_scaled, y_train)print(f"最佳参数: {grid_search.best_params_}")print(f"最佳交叉验证分数: {grid_search.best_score_:.4f}")return grid_search.best_estimator_
这个分类器集成了随机森林、梯度提升和支持向量机三种经典算法。train_and_evaluate方法实现了完整的训练评估流程,包括特征标准化、交叉验证和测试集评估;hyperparameter_tuning方法提供了自动化的超参数优化功能。
3.2 深度学习分类网络
class AudioClassificationNet(nn.Module):"""音频分类深度神经网络"""def __init__(self, num_classes, input_dim=128, dropout_rate=0.3):super(AudioClassificationNet, self).__init__()self.num_classes = num_classes# 特征提取器self.feature_extractor = DeepFeatureExtractor()# 分类头self.classifier = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(input_dim, 256),nn.BatchNorm1d(256),nn.ReLU(),nn.Dropout(dropout_rate),nn.Linear(256, 128),nn.BatchNorm1d(128),nn.ReLU(),nn.Dropout(dropout_rate),nn.Linear(128, 64),nn.BatchNorm1d(64),nn.ReLU(),nn.Dropout(dropout_rate),nn.Linear(64, num_classes))# 初始化权重self._initialize_weights()def _initialize_weights(self):"""权重初始化"""for m in self.modules():if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight)if m.bias is not None:nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm1d):nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)def forward(self, x):"""前向传播"""# 提取深度特征features, attention_weights = self.feature_extractor(x)# 分类预测logits = self.classifier(features)return logits, attention_weightsclass AudioTrainer:"""音频分类模型训练器"""def __init__(self, model, device='cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'):self.model = model.to(device)self.device = deviceself.criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()self.optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=0.001, weight_decay=0.01)self.scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingLR(self.optimizer, T_max=100)def train_epoch(self, dataloader):"""训练一个epoch"""self.model.train()total_loss = 0correct = 0total = 0for batch_idx, (data, target) in enumerate(dataloader):data, target = data.to(self.device), target.to(self.device)# 前向传播self.optimizer.zero_grad()output, _ = self.model(data)loss = self.criterion(output, target)# 反向传播loss.backward()torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(self.model.parameters(), max_norm=1.0)self.optimizer.step()# 统计total_loss += loss.item()_, predicted = output.max(1)total += target.size(0)correct += predicted.eq(target).sum().item()if batch_idx % 10 == 0:print(f'Batch {batch_idx}, Loss: {loss.item():.4f}, 'f'Acc: {100.*correct/total:.2f}%')return total_loss / len(dataloader), 100. * correct / totaldef validate(self, dataloader):"""验证模型"""self.model.eval()total_loss = 0correct = 0total = 0with torch.no_grad():for data, target in dataloader:data, target = data.to(self.device), target.to(self.device)output, _ = self.model(data)loss = self.criterion(output, target)total_loss += loss.item()_, predicted = output.max(1)total += target.size(0)correct += predicted.eq(target).sum().item()return total_loss / len(dataloader), 100. * correct / total
深度学习网络结合了特征提取和分类两个部分。网络使用了批归一化、Dropout等正则化技术防止过拟合;训练器实现了完整的训练循环,包括梯度裁剪、学习率调度等优化技巧。
| 算法类型 | 优势 | 劣势 | 适用场景 | 训练时间 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 随机森林 | 抗过拟合、可解释性强 | 对噪声敏感 | 小数据集、特征工程 | 短 |
| 支持向量机 | 泛化能力强、理论基础扎实 | 参数调优复杂 | 中等数据集、非线性分类 | 中等 |
| 梯度提升 | 预测精度高、处理缺失值 | 容易过拟合 | 结构化数据、竞赛 | 中等 |
| 深度学习 | 端到端学习、特征自动提取 | 需要大量数据、计算资源 | 大数据集、复杂模式 | 长 |
图3:分类算法性能占比饼图 - 展示了不同算法在音频分类任务中的相对性能
4. 模型评估与优化
4.1 评估指标体系
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.metrics import (accuracy_score, precision_score, recall_score, f1_score,roc_auc_score, confusion_matrix, classification_report
)
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltclass ModelEvaluator:"""模型评估器"""def __init__(self):self.metrics_history = []def comprehensive_evaluation(self, y_true, y_pred, y_prob=None, class_names=None):"""综合评估模型性能"""# 基础指标计算accuracy = accuracy_score(y_true, y_pred)precision = precision_score(y_true, y_pred, average='weighted')recall = recall_score(y_true, y_pred, average='weighted')f1 = f1_score(y_true, y_pred, average='weighted')metrics = {'accuracy': accuracy,'precision': precision,'recall': recall,'f1_score': f1}# 如果提供了概率预测,计算AUCif y_prob is not None:try:auc = roc_auc_score(y_true, y_prob, multi_class='ovr')metrics['auc'] = aucexcept ValueError:metrics['auc'] = None# 混淆矩阵cm = confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred)# 分类报告report = classification_report(y_true, y_pred, target_names=class_names,output_dict=True)# 保存评估历史self.metrics_history.append(metrics)return metrics, cm, reportdef plot_confusion_matrix(self, cm, class_names, title='Confusion Matrix'):"""绘制混淆矩阵热力图"""plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))sns.heatmap(cm, annot=True, fmt='d', cmap='Blues',xticklabels=class_names,yticklabels=class_names)plt.title(title)plt.xlabel('Predicted Label')plt.ylabel('True Label')plt.tight_layout()plt.show()def plot_metrics_trend(self):"""绘制指标变化趋势"""if not self.metrics_history:print("没有评估历史数据")returnmetrics_df = pd.DataFrame(self.metrics_history)plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))for metric in ['accuracy', 'precision', 'recall', 'f1_score']:if metric in metrics_df.columns:plt.plot(metrics_df.index, metrics_df[metric], marker='o', label=metric.capitalize())plt.xlabel('Evaluation Round')plt.ylabel('Score')plt.title('Model Performance Metrics Trend')plt.legend()plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)plt.tight_layout()plt.show()def calculate_class_balance_metrics(self, y_true):"""计算类别平衡性指标"""from collections import Counterclass_counts = Counter(y_true)total_samples = len(y_true)# 计算类别分布class_distribution = {cls: count/total_samples for cls, count in class_counts.items()}# 计算不平衡比率max_count = max(class_counts.values())min_count = min(class_counts.values())imbalance_ratio = max_count / min_countreturn {'class_counts': class_counts,'class_distribution': class_distribution,'imbalance_ratio': imbalance_ratio}
评估器提供了全面的性能评估功能。comprehensive_evaluation方法计算多种评估指标;plot_confusion_matrix方法可视化分类结果;calculate_class_balance_metrics方法分析数据集的类别平衡性。
4.2 模型优化策略
class ModelOptimizer:"""模型优化器"""def __init__(self):self.optimization_history = []def feature_selection(self, X, y, method='mutual_info', k=50):"""特征选择优化"""from sklearn.feature_selection import (SelectKBest, mutual_info_classif, f_classif, chi2)if method == 'mutual_info':selector = SelectKBest(mutual_info_classif, k=k)elif method == 'f_test':selector = SelectKBest(f_classif, k=k)elif method == 'chi2':selector = SelectKBest(chi2, k=k)else:raise ValueError(f"不支持的特征选择方法: {method}")X_selected = selector.fit_transform(X, y)selected_features = selector.get_support(indices=True)print(f"原始特征数: {X.shape[1]}")print(f"选择特征数: {X_selected.shape[1]}")print(f"特征选择方法: {method}")return X_selected, selected_features, selectordef ensemble_optimization(self, models_dict, X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test):"""集成学习优化"""from sklearn.ensemble import VotingClassifierfrom sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score# 创建投票分类器voting_clf = VotingClassifier(estimators=list(models_dict.items()),voting='soft' # 使用概率投票)# 训练集成模型voting_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)# 评估性能train_score = voting_clf.score(X_train, y_train)test_score = voting_clf.score(X_test, y_test)cv_scores = cross_val_score(voting_clf, X_train, y_train, cv=5)print(f"集成模型训练准确率: {train_score:.4f}")print(f"集成模型测试准确率: {test_score:.4f}")print(f"集成模型交叉验证准确率: {cv_scores.mean():.4f} (±{cv_scores.std():.4f})")return voting_clf, {'train_accuracy': train_score,'test_accuracy': test_score,'cv_mean': cv_scores.mean(),'cv_std': cv_scores.std()}def data_augmentation_audio(self, audio_data, augmentation_factor=2):"""音频数据增强"""augmented_data = []for _ in range(augmentation_factor):# 时间拉伸stretch_rate = np.random.uniform(0.8, 1.2)stretched = librosa.effects.time_stretch(audio_data, rate=stretch_rate)# 音调变换pitch_shift = np.random.randint(-2, 3)pitched = librosa.effects.pitch_shift(stretched, sr=22050, n_steps=pitch_shift)# 添加噪声noise_factor = np.random.uniform(0.001, 0.01)noise = np.random.normal(0, noise_factor, len(pitched))noisy = pitched + noise# 幅度缩放scale_factor = np.random.uniform(0.7, 1.3)scaled = noisy * scale_factoraugmented_data.append(scaled)return augmented_datadef hyperparameter_optimization_bayesian(self, model_class, X_train, y_train, param_space, n_calls=50):"""贝叶斯超参数优化"""from skopt import gp_minimizefrom skopt.space import Real, Integer, Categoricalfrom sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_scoredef objective(params):# 构建参数字典param_dict = {}for i, (param_name, _) in enumerate(param_space.items()):param_dict[param_name] = params[i]# 创建模型model = model_class(**param_dict)# 交叉验证评估scores = cross_val_score(model, X_train, y_train, cv=3, scoring='accuracy')# 返回负数(因为gp_minimize是最小化)return -scores.mean()# 定义搜索空间dimensions = list(param_space.values())# 执行贝叶斯优化result = gp_minimize(objective, dimensions, n_calls=n_calls, random_state=42)# 构建最优参数best_params = {}for i, (param_name, _) in enumerate(param_space.items()):best_params[param_name] = result.x[i]print(f"最优参数: {best_params}")print(f"最优交叉验证分数: {-result.fun:.4f}")return best_params, result
优化器提供了多种模型优化策略:特征选择减少维度诅咒;集成学习提高预测稳定性;数据增强扩充训练样本;贝叶斯优化自动寻找最优超参数。

图4:模型优化策略效果象限图 - 展示了不同优化策略的成本效益分析
5. 实时音频分类系统
5.1 实时处理架构
import threading
import queue
import time
from collections import deque
import pyaudioclass RealTimeAudioClassifier:"""实时音频分类系统"""def __init__(self, model, feature_extractor, sample_rate=22050, chunk_size=1024, buffer_duration=2.0):self.model = modelself.feature_extractor = feature_extractorself.sample_rate = sample_rateself.chunk_size = chunk_sizeself.buffer_duration = buffer_durationself.buffer_size = int(sample_rate * buffer_duration)# 音频缓冲区self.audio_buffer = deque(maxlen=self.buffer_size)self.audio_queue = queue.Queue()self.result_queue = queue.Queue()# 控制标志self.is_recording = Falseself.is_processing = False# 性能监控self.processing_times = deque(maxlen=100)self.classification_history = deque(maxlen=50)def start_audio_stream(self):"""启动音频流"""self.audio = pyaudio.PyAudio()self.stream = self.audio.open(format=pyaudio.paFloat32,channels=1,rate=self.sample_rate,input=True,frames_per_buffer=self.chunk_size,stream_callback=self._audio_callback)self.is_recording = Trueself.stream.start_stream()print("音频流已启动")def _audio_callback(self, in_data, frame_count, time_info, status):"""音频回调函数"""if self.is_recording:# 转换音频数据audio_data = np.frombuffer(in_data, dtype=np.float32)# 添加到缓冲区self.audio_buffer.extend(audio_data)# 如果缓冲区满了,触发处理if len(self.audio_buffer) >= self.buffer_size:audio_segment = np.array(list(self.audio_buffer))self.audio_queue.put(audio_segment.copy())return (None, pyaudio.paContinue)def start_processing_thread(self):"""启动处理线程"""self.is_processing = Trueself.processing_thread = threading.Thread(target=self._processing_loop,daemon=True)self.processing_thread.start()print("处理线程已启动")def _processing_loop(self):"""处理循环"""while self.is_processing:try:# 获取音频数据audio_data = self.audio_queue.get(timeout=1.0)# 记录处理开始时间start_time = time.time()# 特征提取features = self.feature_extractor.extract_features(audio_data)# 模型预测prediction = self.model.predict(features.reshape(1, -1))probability = self.model.predict_proba(features.reshape(1, -1))# 记录处理时间processing_time = time.time() - start_timeself.processing_times.append(processing_time)# 保存结果result = {'prediction': prediction[0],'probability': probability[0],'processing_time': processing_time,'timestamp': time.time()}self.result_queue.put(result)self.classification_history.append(result)except queue.Empty:continueexcept Exception as e:print(f"处理错误: {e}")def get_latest_result(self):"""获取最新分类结果"""try:return self.result_queue.get_nowait()except queue.Empty:return Nonedef get_performance_stats(self):"""获取性能统计"""if not self.processing_times:return Noneavg_processing_time = np.mean(self.processing_times)max_processing_time = np.max(self.processing_times)min_processing_time = np.min(self.processing_times)# 计算实时性能指标real_time_factor = self.buffer_duration / avg_processing_timereturn {'avg_processing_time': avg_processing_time,'max_processing_time': max_processing_time,'min_processing_time': min_processing_time,'real_time_factor': real_time_factor,'buffer_utilization': len(self.audio_buffer) / self.buffer_size}def stop(self):"""停止系统"""self.is_recording = Falseself.is_processing = Falseif hasattr(self, 'stream'):self.stream.stop_stream()self.stream.close()if hasattr(self, 'audio'):self.audio.terminate()print("实时分类系统已停止")
实时分类系统采用了多线程架构,音频采集和处理分离,确保系统的实时性能。start_audio_stream方法启动音频流采集;_processing_loop方法在独立线程中进行特征提取和分类预测;get_performance_stats方法监控系统性能。
5.2 性能优化与监控
class PerformanceOptimizer:"""性能优化器"""def __init__(self):self.optimization_strategies = {}def optimize_feature_extraction(self, feature_extractor):"""优化特征提取性能"""# 使用缓存减少重复计算from functools import lru_cache# 预计算常用参数feature_extractor.precompute_filters()# 批量处理优化def batch_extract_features(audio_segments):"""批量特征提取"""features_list = []for audio in audio_segments:features = feature_extractor.extract_features(audio)features_list.append(features)return np.array(features_list)return batch_extract_featuresdef model_quantization(self, model):"""模型量化优化"""if hasattr(model, 'state_dict'): # PyTorch模型import torch# 动态量化quantized_model = torch.quantization.quantize_dynamic(model, {torch.nn.Linear}, dtype=torch.qint8)return quantized_modelelse:# sklearn模型优化return modeldef memory_optimization(self, classifier):"""内存优化"""# 清理不必要的中间结果import gc# 定期垃圾回收def periodic_cleanup():gc.collect()# 设置定时清理import threadingcleanup_timer = threading.Timer(30.0, periodic_cleanup)cleanup_timer.daemon = Truecleanup_timer.start()return cleanup_timerclass SystemMonitor:"""系统监控器"""def __init__(self):self.metrics = {'cpu_usage': deque(maxlen=100),'memory_usage': deque(maxlen=100),'processing_latency': deque(maxlen=100),'classification_accuracy': deque(maxlen=100)}def collect_system_metrics(self):"""收集系统指标"""import psutil# CPU使用率cpu_percent = psutil.cpu_percent(interval=1)self.metrics['cpu_usage'].append(cpu_percent)# 内存使用率memory = psutil.virtual_memory()self.metrics['memory_usage'].append(memory.percent)return {'cpu_usage': cpu_percent,'memory_usage': memory.percent,'available_memory': memory.available / (1024**3) # GB}def generate_performance_report(self):"""生成性能报告"""report = {}for metric_name, values in self.metrics.items():if values:report[metric_name] = {'mean': np.mean(values),'std': np.std(values),'min': np.min(values),'max': np.max(values),'current': values[-1] if values else 0}return report
性能优化器提供了多层次的优化策略:特征提取优化通过缓存和批处理提高效率;模型量化减少内存占用和计算复杂度;系统监控器实时跟踪资源使用情况。
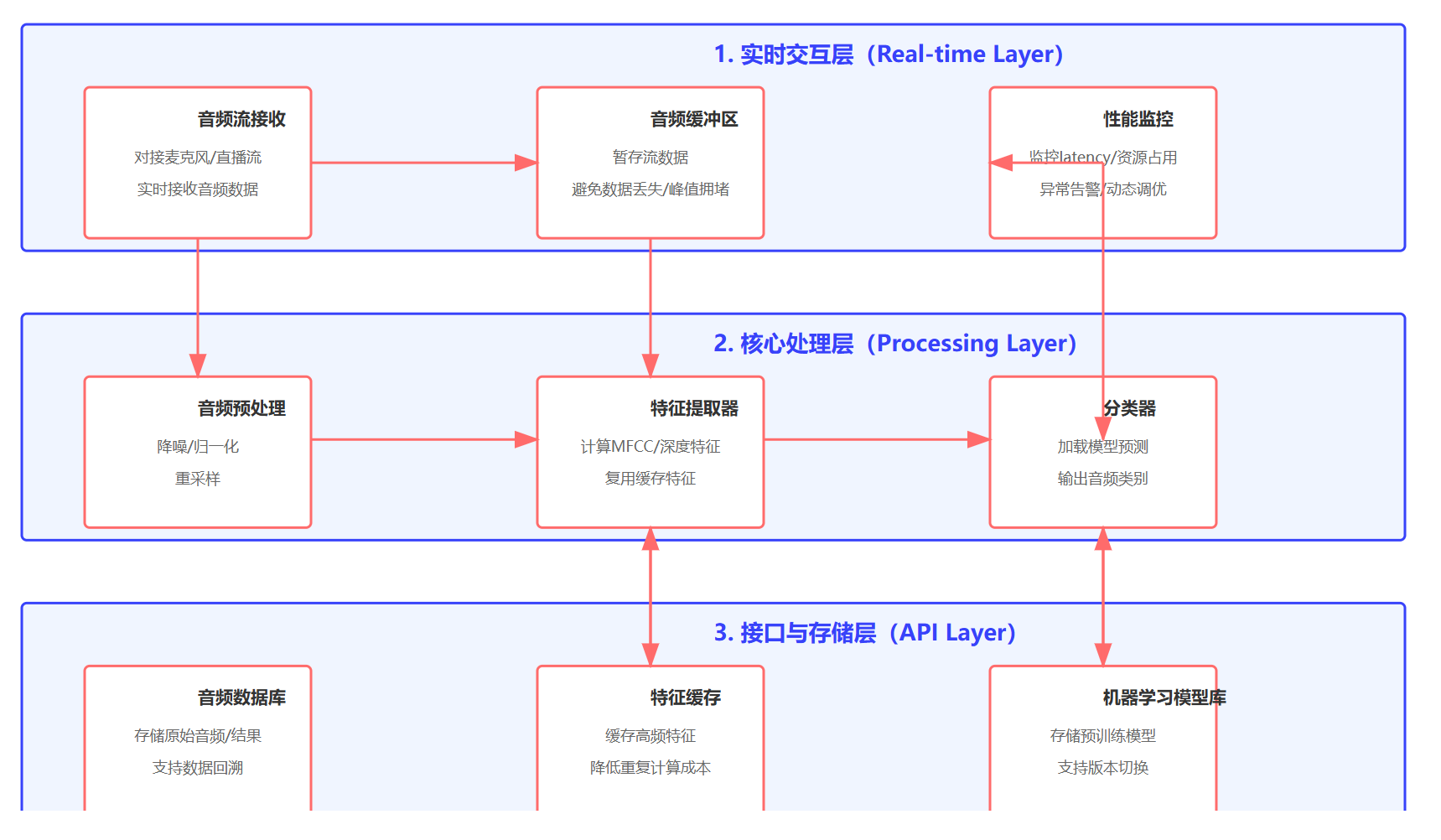
图5:实时音频分类系统架构图 - 展示了系统的分层架构和组件交互关系
6. 应用案例与实战项目
6.1 语音情感识别项目
class EmotionRecognitionSystem:"""语音情感识别系统"""def __init__(self):self.emotions = ['angry', 'happy', 'sad', 'neutral', 'fear', 'disgust', 'surprise']self.feature_extractor = Noneself.model = Nonedef prepare_emotion_features(self, audio_data, sr=22050):"""提取情感相关特征"""features = {}# 基础声学特征features['mfcc'] = librosa.feature.mfcc(y=audio_data, sr=sr, n_mfcc=13).mean(axis=1)# 韵律特征features['pitch'] = librosa.yin(audio_data, fmin=50, fmax=300)features['pitch_mean'] = np.nanmean(features['pitch'])features['pitch_std'] = np.nanstd(features['pitch'])# 能量特征features['energy'] = librosa.feature.rms(y=audio_data)[0]features['energy_mean'] = np.mean(features['energy'])features['energy_std'] = np.std(features['energy'])# 频谱特征features['spectral_centroid'] = np.mean(librosa.feature.spectral_centroid(y=audio_data, sr=sr))features['spectral_bandwidth'] = np.mean(librosa.feature.spectral_bandwidth(y=audio_data, sr=sr))features['spectral_rolloff'] = np.mean(librosa.feature.spectral_rolloff(y=audio_data, sr=sr))# 零交叉率features['zcr'] = np.mean(librosa.feature.zero_crossing_rate(audio_data))# 合并所有特征feature_vector = np.concatenate([features['mfcc'],[features['pitch_mean'], features['pitch_std']],[features['energy_mean'], features['energy_std']],[features['spectral_centroid'], features['spectral_bandwidth']],[features['spectral_rolloff'], features['zcr']]])return feature_vectordef train_emotion_model(self, X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test):"""训练情感识别模型"""from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifierfrom sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder, StandardScaler# 标签编码self.label_encoder = LabelEncoder()y_train_encoded = self.label_encoder.fit_transform(y_train)y_test_encoded = self.label_encoder.transform(y_test)# 特征标准化self.scaler = StandardScaler()X_train_scaled = self.scaler.fit_transform(X_train)X_test_scaled = self.scaler.transform(X_test)# 训练模型self.model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=200,max_depth=15,min_samples_split=5,random_state=42)self.model.fit(X_train_scaled, y_train_encoded)# 评估模型train_accuracy = self.model.score(X_train_scaled, y_train_encoded)test_accuracy = self.model.score(X_test_scaled, y_test_encoded)print(f"训练准确率: {train_accuracy:.4f}")print(f"测试准确率: {test_accuracy:.4f}")# 特征重要性分析feature_importance = self.model.feature_importances_return train_accuracy, test_accuracy, feature_importancedef predict_emotion(self, audio_data, sr=22050):"""预测音频情感"""if self.model is None:raise ValueError("模型未训练")# 提取特征features = self.prepare_emotion_features(audio_data, sr)features_scaled = self.scaler.transform(features.reshape(1, -1))# 预测prediction = self.model.predict(features_scaled)[0]probabilities = self.model.predict_proba(features_scaled)[0]# 解码标签emotion = self.label_encoder.inverse_transform([prediction])[0]# 构建结果result = {'emotion': emotion,'confidence': np.max(probabilities),'probabilities': dict(zip(self.label_encoder.classes_, probabilities))}return result
情感识别系统专门针对语音情感分析任务设计。prepare_emotion_features方法提取了与情感表达相关的多维特征,包括韵律、能量、频谱等;predict_emotion方法提供了完整的情感预测功能,返回情感类别和置信度。
6.2 音乐流派分类项目
class MusicGenreClassifier:"""音乐流派分类器"""def __init__(self):self.genres = ['rock', 'pop', 'jazz', 'classical', 'electronic', 'hip-hop']self.segment_duration = 30 # 30秒片段def extract_music_features(self, audio_data, sr=22050):"""提取音乐特征"""features = {}# 节奏特征tempo, beats = librosa.beat.beat_track(y=audio_data, sr=sr)features['tempo'] = tempofeatures['beat_strength'] = np.mean(librosa.onset.onset_strength(y=audio_data, sr=sr))# 和声特征chroma = librosa.feature.chroma_stft(y=audio_data, sr=sr)features['chroma_mean'] = np.mean(chroma, axis=1)features['chroma_std'] = np.std(chroma, axis=1)# 音色特征mfcc = librosa.feature.mfcc(y=audio_data, sr=sr, n_mfcc=20)features['mfcc_mean'] = np.mean(mfcc, axis=1)features['mfcc_std'] = np.std(mfcc, axis=1)# 频谱特征spectral_contrast = librosa.feature.spectral_contrast(y=audio_data, sr=sr)features['spectral_contrast'] = np.mean(spectral_contrast, axis=1)# 音调特征tonnetz = librosa.feature.tonnetz(y=audio_data, sr=sr)features['tonnetz_mean'] = np.mean(tonnetz, axis=1)# 合并特征向量feature_vector = np.concatenate([[features['tempo'], features['beat_strength']],features['chroma_mean'],features['chroma_std'],features['mfcc_mean'],features['mfcc_std'],features['spectral_contrast'],features['tonnetz_mean']])return feature_vectordef segment_audio(self, audio_data, sr=22050):"""将音频分割为固定长度片段"""segment_samples = self.segment_duration * srsegments = []for i in range(0, len(audio_data), segment_samples):segment = audio_data[i:i + segment_samples]if len(segment) == segment_samples:segments.append(segment)return segmentsdef train_genre_classifier(self, audio_files, labels):"""训练流派分类器"""from sklearn.svm import SVCfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScalerfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split# 提取所有特征all_features = []all_labels = []for audio_file, label in zip(audio_files, labels):# 加载音频audio_data, sr = librosa.load(audio_file, sr=22050)# 分割音频segments = self.segment_audio(audio_data, sr)# 提取每个片段的特征for segment in segments:features = self.extract_music_features(segment, sr)all_features.append(features)all_labels.append(label)# 转换为numpy数组X = np.array(all_features)y = np.array(all_labels)# 划分训练测试集X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42, stratify=y)# 特征标准化self.scaler = StandardScaler()X_train_scaled = self.scaler.fit_transform(X_train)X_test_scaled = self.scaler.transform(X_test)# 训练SVM分类器self.model = SVC(kernel='rbf',C=10,gamma='scale',probability=True,random_state=42)self.model.fit(X_train_scaled, y_train)# 评估性能train_accuracy = self.model.score(X_train_scaled, y_train)test_accuracy = self.model.score(X_test_scaled, y_test)return train_accuracy, test_accuracy, X_test_scaled, y_test
音乐流派分类器专注于音乐的结构化特征提取。extract_music_features方法提取了节奏、和声、音色等音乐特有的特征;segment_audio方法将长音频分割为标准片段,提高训练效率。
“在音频分析的世界里,每一个波形都承载着丰富的信息,每一次频谱变换都揭示着声音的本质。机器学习让我们能够从这些数字化的声波中提取出人类情感、音乐风格、甚至是说话者的身份特征。”
结语
在我的实际项目经验中,我发现成功的音频分类系统往往需要在多个维度上进行精心设计:首先是数据预处理的质量,这直接影响后续所有环节的效果;其次是特征工程的深度,传统特征与深度学习特征的有机结合往往能带来意想不到的性能提升;再次是模型选择的合理性,不同的应用场景需要不同的算法策略;最后是系统优化的全面性,实时性能、准确性和资源消耗之间的平衡是工程实践中的核心挑战。
特别值得一提的是,随着深度学习技术的快速发展,端到端的学习范式正在改变传统的音频处理流程。但这并不意味着传统方法的完全淘汰,相反,将传统信号处理的领域知识与现代机器学习技术相结合,往往能够构建出更加鲁棒和高效的系统。
在未来的技术发展中,我认为几个方向特别值得关注:一是多模态融合技术,将音频与视觉、文本等其他模态信息结合,构建更加智能的感知系统;二是边缘计算优化,让复杂的音频分析算法能够在资源受限的设备上高效运行;三是自监督学习方法,减少对标注数据的依赖,提高模型的泛化能力;四是可解释性研究,让AI系统的决策过程更加透明和可信。
作为一名技术实践者,我始终相信技术的价值在于解决实际问题。计算机听觉分类分析技术已经在语音识别、音乐推荐、医疗诊断、安防监控等众多领域展现出巨大的应用潜力。每一次技术突破都可能催生新的应用场景,每一个算法优化都可能带来用户体验的显著提升。
■ 我是蒋星熠Jaxonic!如果这篇文章在你的技术成长路上留下了印记
■ 👁 【关注】与我一起探索技术的无限可能,见证每一次突破
■ 👍 【点赞】为优质技术内容点亮明灯,传递知识的力量
■ 🔖 【收藏】将精华内容珍藏,随时回顾技术要点
■ 💬 【评论】分享你的独特见解,让思维碰撞出智慧火花
■ 🗳 【投票】用你的选择为技术社区贡献一份力量
■ 技术路漫漫,让我们携手前行,在代码的世界里摘取属于程序员的那片星辰大海!
参考链接
- Librosa: Audio Analysis Library for Python
- PyTorch Audio Processing Tutorial
- Scikit-learn Machine Learning Library
- Speech and Audio Processing Research Papers
- Real-time Audio Processing Best Practices
关键词标签
#音频分类 #机器学习 #深度学习 #特征提取 #实时处理
