用Postman实现自动化接口测试和默认规范
主要功能
软件入口
- workplaces:工作区
- collections:集合
- environment:环境
- request:接口请求的最小单位
Request
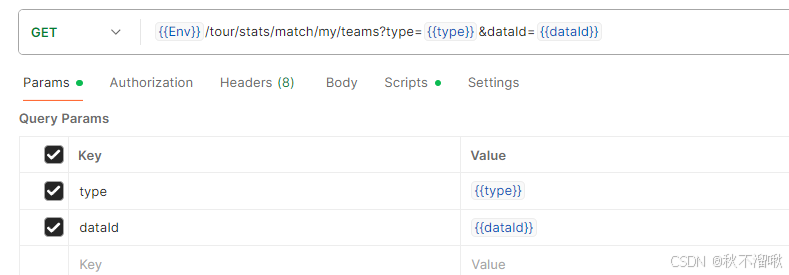
- 地址栏:输入URL
- Params:参数列表,一般get请求用到
- Authorization:鉴权,collections和request中都有,控制范围不一样
- header:请求头
- Body:请求体
- 发送Json数据: Raw->json
- 发送Form表单: x-www-form-urlencoded
- 发送文件:form-data
- Script:脚本
- Setting:配置
- Cookies:缓存
Run Collection
Iterations 可以控制发送请求的数量
生成测试报告时,可以打开runner->persist responses for a session,查看生成报告的响应内容
内置对象
介绍
Postman 在执行请求时自动注入的全局对象,无需手动定义
主要内置对象
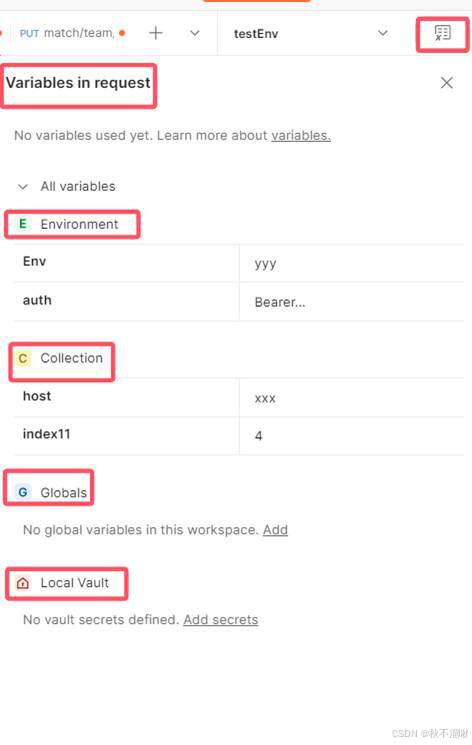
- pm.globals 全局变量
- pm.environment 环境变量
- pm.collectionVariables 集合变量(pm9.0+)
- pm.variables 临时变量/局部变量
- Pm.response 处理响应数据,仅限tests脚本
- Pm.interationdata 访问集合运行时的外部数据(如csv)
- Pm.visualizar 在 Visualize 选项卡中渲染可视化HTML/图表
- Pm.info 请求元数据
- Pm.sendRequest 发送异步请求
- Pm.requests 直接控制底层请求引擎(如超时、代理等)
Pm.response的简单断言
- pm.response.to.have.status(code)
验证状态码(如 200、404)。
- pm.response.to.have.header(key)
验证响应头是否存在。
- pm.response.to.be.json
验证响应体是否为 JSON。
- pm.response.to.include.json(key)
验证 JSON 响应中是否包含指定字段。
Pm.collectionVariables的数据管理
这里以集合变量为例,其他变量类似
pm.collectionVariables.get("key")
pm.collectionVariables.set("key", "value")内置变量对象的作用域优先级
Globals<environmet<collectionVariables<variables
示例
// 从存储中获取 JSON 字符串并解析为对象const testCases = JSON.parse(pm.variables.get("testCases"));- pm.variables.get("testCases")
获取名为 "testCases" 的变量值(可能是之前通过 pm.variables.set() 存储的)。 - JSON.parse()
将字符串(如 '[{"dataId":1,"expectedCode":0}]')解析为 JavaScript 对象。 - const testCases
声明一个常量,存储解析后的对象,防止后续代码意外修改它。
变量存储
内置动态变量
https://postman.xiniushu.com/docs/writing-scripts/script-references/variables-list
原创文章,请勿转载:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33562122/article/details/151761769
脚本
postman使用的是nodeJs,原生支持是JavaScript,不支持其他语言
JavaScript基础
数据类型
Number:64位浮点数,取值范围±2^53 - 1,大数要用bigInt,在数字末位加n,或直接转成字符串类型存储。
String:双引号包裹,取值范围:无固定上限,受内存限制。
Boolean: 取值范围:true/false
Null:空对象指针,取值范围:null
Undefined:未初始化,取值范围:undefined
Symbol:唯一且不可变的值,对象属性键
BigInt(ES2020):表示任意精度的整数
Set:唯一值集合,去重
Map:键值对集合,键可为任意类型
JavaScript声明变量
声明变量:使用 var、let 或 const 声明变量
| 特性 | var | let | const |
| 作用域 | 函数作用域 | 块级作用域 | 块级作用域 |
| 变量提升 | 是(undefined) | 是(未初始化) | 是(未初始化) |
| 可重复声明 | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| 可重新赋值 | 是 | 是 | 否 |
| 适用场景 | 旧代码兼容 | 循环、临时变量 | 常量、固定值 |
Script执行顺序
Collections pre-requests -> requests pre-requests -> collections post-response ->requests post-response
常用的 JavaScript 内置方法
Postman 的测试脚本(Pre-request Script/Tests)基于 JavaScript,支持以下核心方法:
1. JSON 处理
- JSON.stringify(obj)
- 将对象转为 JSON 字符串
用途:数据存储、Api请求、调试):
基本语法
Json.stringify(value, replacer?, space?)
value:要转换的 JavaScript 对象或值。
replacer(可选):过滤或修改属性的函数或数组。
space(可选):缩进空格数(用于美化输出)。
const data = { name: "Alice", age: 25 };
pm.environment.set("userData", JSON.stringify(data));- JSON.parse(str)
- 将 JSON 字符串转为对象(如解析响应体):
const response = pm.response.json(); // 直接解析(Postman 封装方法)
// 或手动解析
const jsonStr = pm.response.text();
const parsedData = JSON.parse(jsonStr);2. 断言测试
- pm.test(description, callback)
pm.test("Status code is 200", () => {
pm.response.to.have.status(200);
});- pm.expect(value).to.method()
- 链式断言(支持 equal、include、exist 等):
- 链式断言(支持 equal、include、exist 等):
pm.expect(pm.response.json()).to.have.property("token");pm.expect(res.code).to.be.a('number');pm.expect(res.code,`current code is ${res.code},is not ${code}`).to.eql(code);pm.expect(res.msg).to.eql('success')3. 环境变量操作
- pm.environment.get(key) / pm.environment.set(key, value)
- 读写环境变量:
pm.environment.set("token", "abc123");
const token = pm.environment.get("token");4. 日期与时间
- Date 对象
- 生成时间戳或格式化日期:
const now = new Date();
console.log(now.toISOString()); // 输出 ISO 格式时间5. 字符串与数组操作
- 字符串方法:includes()、split()、join() 等。
const str = "hello,world";
console.log(str.split(",")); // ["hello", "world"]- 数组方法:push()、pop()、map()、filter() 等。
const arr = [1, 2, 3];
const doubled = arr.map(x => x * 2); // [2, 4, 6]6. 数学运算
- Math 对象:生成随机数、四舍五入等。
const randomNum = Math.floor(Math.random() * 100); // 0-99 随机整数7. 异步请求(Postman 特有)
- pm.sendRequest(url, callback)
发送自定义请求并处理响应:
javascript
pm.sendRequest("https://api.example.com/data", (err, res) => {if (err) console.error(err);else console.log(res.json());
});8.正则表达式
Match()
示例:获取请求中的dataId的number类型值
const url = pm.request.url.toString()const dataId = parseInt(url.match(/dataId=(\d+)/)[1]);9.字符串插值
动态变量
pm.variables.replaceIn('{{$timestamp}}')字符串插值(用反引号)
`current msg is ${res.msg},is not ${msg}`原创文章,请勿转载:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33562122/article/details/151761769
10.其他
查找对象中的列表
const testCases = JSON.parse(pm.variables.get("testCases"));// 找到当前dataId对应的预期结果const testCase = testCases.find(item => item.dataId === dataId);if(!testCase){throw new Error('No test case defined for dataId= ${dataId}');}获取对象的数据类型
对象.type
接口测试协作规范
1. 组建团队workplaces,提高效率和协作性(建议)
2. 按接口的模块分类collections,提高可维护性。亦可按维护人员构建接口集。
3. 按按测试环境和开发环境配置配置environments
4. 除调试外,地址和参数应做好request的参数化
5. 变量按照最小原则存储,避免冲突
6. header一般来说只需要content-type和authorition,其他不是必须的,保持最小原则
7. 鉴权使用authorition管理,放置到collection->Authrizaton中。
i. Auth Type =Oauth 2.0
ii. Add auth data to =request data
iii. Token = Token值
8. params不要直接写地址栏上,写在params中
9. 按照测试用例把测试用例插入到Script中 ,下面是模版
const testCases = [{name:"B1-正向测试",type:"contest",dataId:"735759304270827526",code:0,msg:"success"},{name:"B2-错误的type",type:"contest1",dataId:"735759304270827526",code:3,msg:"invalid params"},{name:"B3-空的type",type:"",dataId:"735759304270827526",code:3,msg:"params error"},{name:"B4-错误的dataId",type:"contest",dataId:"735759304270827529",code:3,msg:"invalid params"},{name:"B5-空的dataId",type:"contest",dataId:undefined,code:3,msg:"params error"}
]
pm.variables.set("testCases",JSON.stringify(testCases));const index = pm.collectionVariables.get("currentIndex") % (testCases.length) || 0;
pm.variables.set("dataId",testCases[index].dataId);
pm.variables.set("type",testCases[index].type);
10. 集合公共方法
// Pre-requests
// 游标初始化
if (pm.collectionVariables.get("currentIndex")===undefined){pm.collectionVariables.set("currentIndex", -1);
}
// request测试,打开下面代码,关闭Collection代码,控制游标下移
pm.collectionVariables.set("currentIndex", pm.collectionVariables.get("currentIndex") + 1);// collection测试,打开下面代码,关闭request代码,控制游标下移
// pm.collectionVariables.set("currentIndex", pm.info.iteration);// Post-response
const testCases = JSON.parse(pm.variables.get("testCases"));
const index = pm.collectionVariables.get("currentIndex") % (testCases.length) || 0;
const code =testCases[index].code;
const msg = testCases[index].msg;pm.test("response body code and msg", function () {pm.response.to.have.status(200);const res = pm.response.json();console.info(testCases[index].name);console.info(res);pm.expect(res.code,`current code is ${res.code},is not ${code}`).to.eql(code);if(msg){pm.expect(res.msg,`current msg is ${res.msg},is not ${msg}`).to.eql(msg);}});11. 断言错误输出应具体清晰
12. 变量使用小驼峰命名法
