C++11 atomic
这里写目录标题
- atomic_flag
- test_and_set()
- std::atomic_flag::clear()
- 根据这两个函数设计一个简单的自旋锁
- atomic
- std::stomic 构造函数
- std::atomic::operator=() 函数
- 基本 std::atomic 类型操作
- is_lock_free()
- store()和load()
- exchange()
- compare_exchange_weak()
- compare_exchange_strong()
atomic_flag
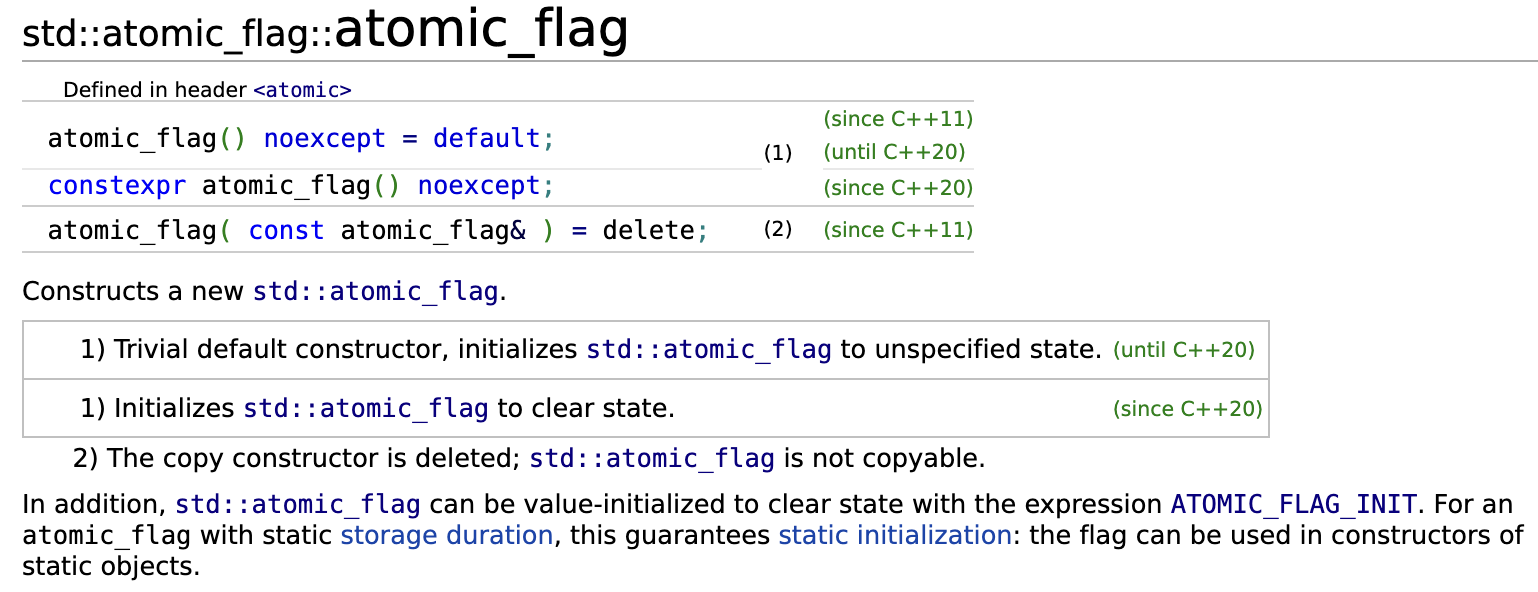
可以看出,atomic_flag 只有默认构造函数,在C++20之前,声明时需要显示初始化,C++20之后,就不需要显示初始化了,自动初始化。
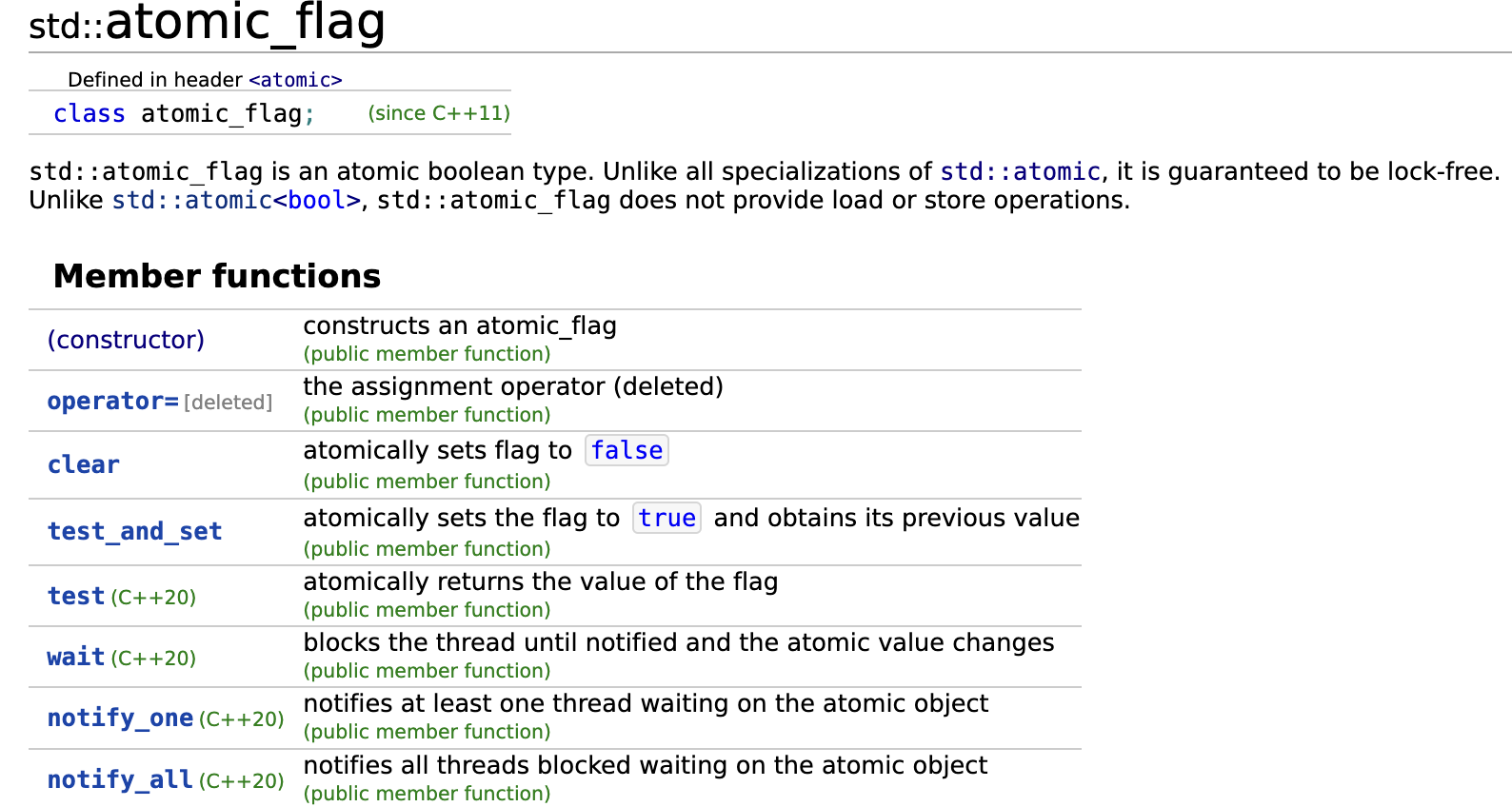
test_and_set()
设置这个对象的标志位
编译
g++ text.cpp -o text -std=c++11
#include<iostream>
#include<atomic>
#include<thread>std::atomic<bool> ready(false);std::atomic_flag winner=ATOMIC_FLAG_INIT;void func(int id) {while (!ready) {std::this_thread::yield(); //表示该线程可以让出时间片}for (int i = 0;i<1000000;i++) {}if (!winner.test_and_set()) {std::cout<<"thread #"<<id<<"won"<<std::endl;}
}int main() {std::vector<std::thread> threads;for (int i = 0;i<10;i++) {threads.push_back(std::thread(func,i));}ready = true;for (auto & th:threads) {th.join();}return 0;}
xutianyang.10@ZBMac-KYTH7H97M4 atomic % ./text
thread #7won
xutianyang.10@ZBMac-KYTH7H97M4 atomic % ./text
thread #9won
xutianyang.10@ZBMac-KYTH7H97M4 atomic % ./text
thread #2won
xutianyang.10@ZBMac-KYTH7H97M4 atomic % ./text
thread #1won
xutianyang.10@ZBMac-KYTH7H97M4 atomic % ./text
thread #9won
通过结果可以看出,只有一个线程运行成功了,可以知道winner.test_and_set()操作是原子的。
bool test_and_set (memory_order sync = memory_order_seq_cst) volatile noexcept;
bool test_and_set (memory_order sync = memory_order_seq_cst) noexcept;
返回winner之前有没有设置过,如果设置过了返回true,没设置过返回false;
std::atomic_flag::clear()
清除这个对象的标志位,设置标志位为false
void clear (memory_order sync = memory_order_seq_cst) volatile noexcept;
void clear (memory_order sync = memory_order_seq_cst) noexcept;
这个demo可以看出来,通过test_and_set()可以严格控制顺序
编译
g++ text.cpp -o text -std=c++11
#include<thread>
#include<iostream>
#include<atomic>
#include<vector>
std::atomic_flag lock_stream = ATOMIC_FLAG_INIT;
std::stringstream ss;void func(int id) {//只有第一次设置的lock_stream 才返回false;while (lock_stream.test_and_set()) {}ss<<"thread: "<<id<<std::endl;lock_stream.clear(); //清除这个标记位
}int main() {std::vector<std::thread> threads;for (int i = 0;i<10;i++) {threads.push_back(std::thread(func,i));}for (auto &th:threads) {th.join();}std::cout<<ss.str()<<std::endl;return 0;
}xutianyang.10@ZBMac-KYTH7H97M4 atomic % ./text2
thread: 0
thread: 1
thread: 2
thread: 3
thread: 4
thread: 5
thread: 6
thread: 7
thread: 8
thread: 9根据这两个函数设计一个简单的自旋锁
std::atomic_flag lock = ATOMIC_FLAG_INIT;
void f(int n) {while (lock.test_and_set(std::memory_order_acquire)) {} //第一次设置会返回false,第二次访问会返回true//临界区std::cout<<"Output from thread: "<<n<<std::endl;lock.clear(std::memory_order_release);
}int main() {std::vector<std::thread> threads;for (int i = 0;i<10;i++) {threads.emplace_back(f, i);}for (auto &th:threads) {th.join();}// std::cout<<ss.str()<<std::endl;return 0;
}xutianyang.10@ZBMac-KYTH7H97M4 atomic % ./text2
Output from thread: 0
Output from thread: 1
Output from thread: 3
Output from thread: 4
Output from thread: 6
Output from thread: 2
Output from thread: 5
Output from thread: 7
Output from thread: 8
Output from thread: 9atomic
std::atomic 是模板类.
template <class T> struct atomic;
原子类对象的主要特点就是从不同的线程访问不会导致数据竞争(data race)。因此从不同线程访问某个原子对象是良性(well-defined)行为,而通常对于非原子类型而言,并发访问某个对象会导致未定义(undifined)行为。
C++11标准中基本的std::atomic模版如下:
template < class T > struct atomic {bool is_lock_free() const volatile;bool is_lock_free() const;void store(T, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst) volatile;void store(T, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst);T load(memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst) const volatile;T load(memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst) const;operator T() const volatile;operator T() const;T exchange(T, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst) volatile;T exchange(T, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst);bool compare_exchange_weak(T &, T, memory_order, memory_order) volatile;bool compare_exchange_weak(T &, T, memory_order, memory_order);bool compare_exchange_strong(T &, T, memory_order, memory_order) volatile;bool compare_exchange_strong(T &, T, memory_order, memory_order);bool compare_exchange_weak(T &, T, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst) volatile;bool compare_exchange_weak(T &, T, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst);bool compare_exchange_strong(T &, T, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst) volatile;bool compare_exchange_strong(T &, T, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst);atomic() = default;constexpr atomic(T);atomic(const atomic &) = delete;atomic & operator=(const atomic &) = delete;atomic & operator=(const atomic &) volatile = delete;T operator=(T) volatile;T operator=(T);
};
针对整形(integral)的特化版本:其中 integal 代表了如下类型char, signed char, unsigned char, short, unsigned short, int, unsigned int, long, unsigned long, long long, unsigned long long, char16_t, char32_t, wchar_t:
template <> struct atomic<integral> {bool is_lock_free() const volatile;bool is_lock_free() const;void store(integral, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst) volatile;void store(integral, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst);integral load(memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst) const volatile;integral load(memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst) const;operator integral() const volatile;operator integral() const;integral exchange(integral, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst) volatile;integral exchange(integral, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst);bool compare_exchange_weak(integral&, integral, memory_order, memory_order) volatile;bool compare_exchange_weak(integral&, integral, memory_order, memory_order);bool compare_exchange_strong(integral&, integral, memory_order, memory_order) volatile;bool compare_exchange_strong(integral&, integral, memory_order, memory_order);bool compare_exchange_weak(integral&, integral, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst) volatile;bool compare_exchange_weak(integral&, integral, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst);bool compare_exchange_strong(integral&, integral, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst) volatile;bool compare_exchange_strong(integral&, integral, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst);integral fetch_add(integral, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst) volatile;integral fetch_add(integral, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst);integral fetch_sub(integral, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst) volatile;integral fetch_sub(integral, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst);integral fetch_and(integral, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst) volatile;integral fetch_and(integral, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst);integral fetch_or(integral, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst) volatile;integral fetch_or(integral, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst);integral fetch_xor(integral, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst) volatile;integral fetch_xor(integral, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst);atomic() = default;constexpr atomic(integral);atomic(const atomic&) = delete;atomic& operator=(const atomic&) = delete;atomic& operator=(const atomic&) volatile = delete;integral operator=(integral) volatile;integral operator=(integral);integral operator++(int) volatile;integral operator++(int);integral operator--(int) volatile;integral operator--(int);integral operator++() volatile;integral operator++();integral operator--() volatile;integral operator--();integral operator+=(integral) volatile;integral operator+=(integral);integral operator-=(integral) volatile;integral operator-=(integral);integral operator&=(integral) volatile;integral operator&=(integral);integral operator|=(integral) volatile;integral operator|=(integral);integral operator^=(integral) volatile;integral operator^=(integral);
};
针对指针的特化版本:
template <class T> struct atomic<T*> {bool is_lock_free() const volatile;bool is_lock_free() const;void store(T*, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst) volatile;void store(T*, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst);T* load(memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst) const volatile;T* load(memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst) const;operator T*() const volatile;operator T*() const;T* exchange(T*, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst) volatile;T* exchange(T*, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst);bool compare_exchange_weak(T*&, T*, memory_order, memory_order) volatile;bool compare_exchange_weak(T*&, T*, memory_order, memory_order);bool compare_exchange_strong(T*&, T*, memory_order, memory_order) volatile;bool compare_exchange_strong(T*&, T*, memory_order, memory_order);bool compare_exchange_weak(T*&, T*, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst) volatile;bool compare_exchange_weak(T*&, T*, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst);bool compare_exchange_strong(T*&, T*, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst) volatile;bool compare_exchange_strong(T*&, T*, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst);T* fetch_add(ptrdiff_t, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst) volatile;T* fetch_add(ptrdiff_t, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst);T* fetch_sub(ptrdiff_t, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst) volatile;T* fetch_sub(ptrdiff_t, memory_order = memory_order_seq_cst);atomic() = default;constexpr atomic(T*);atomic(const atomic&) = delete;atomic& operator=(const atomic&) = delete;atomic& operator=(const atomic&) volatile = delete;T* operator=(T*) volatile;T* operator=(T*);T* operator++(int) volatile;T* operator++(int);T* operator--(int) volatile;T* operator--(int);T* operator++() volatile;T* operator++();T* operator--() volatile;T* operator--();T* operator+=(ptrdiff_t) volatile;T* operator+=(ptrdiff_t);T* operator-=(ptrdiff_t) volatile;T* operator-=(ptrdiff_t);
};
std::stomic 构造函数

- 默认构造函数,由默认构造函数创建的 std::atomic 对象处于未初始化(uninitialized)状态,对处于未初始化(uninitialized)状态 std::atomic象可以由 atomic_init 函数进行初始化。
- 初始化构造函数,由类型 T初始化一个 std::atomic对象,初始化操作不是原子的
- 拷贝构造函数被禁用。
看一个例子,谁先数完数,谁赢
#include <atomic>
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <vector>std::atomic<bool> ready(false);
std::atomic_flag winner = ATOMIC_FLAG_INIT;void func(int id) {while (!ready) {std::this_thread::yield();}for (int i = 0;i<1000000;i++){}if (!winner.test_and_set()) {std::cout<<"thread #"<<id<<"won"<<std::endl;}
}int main() {std::vector<std::thread> threads;std::cout<<"spawning 10 threads that count to 1 million..\n";for (int i = 1;i<=10;i++) threads.emplace_back(func, i);ready = true;for (auto& th:threads) {th.join();}return 0;
}xutianyang.10@ZBMac-KYTH7H97M4 atomic % g++ -o text3 text3.cpp -std=c++11
xutianyang.10@ZBMac-KYTH7H97M4 atomic % ./text3
spawning 10 threads that count to 1 million..
thread #7won
xutianyang.10@ZBMac-KYTH7H97M4 atomic % ./text3
spawning 10 threads that count to 1 million..
thread #9won
xutianyang.10@ZBMac-KYTH7H97M4 atomic % ./text3
spawning 10 threads that count to 1 million..
thread #10won
xutianyang.10@ZBMac-KYTH7H97M4 atomic % ./text3
spawning 10 threads that count to 1 million..
thread #9won
xutianyang.10@ZBMac-KYTH7H97M4 atomic %
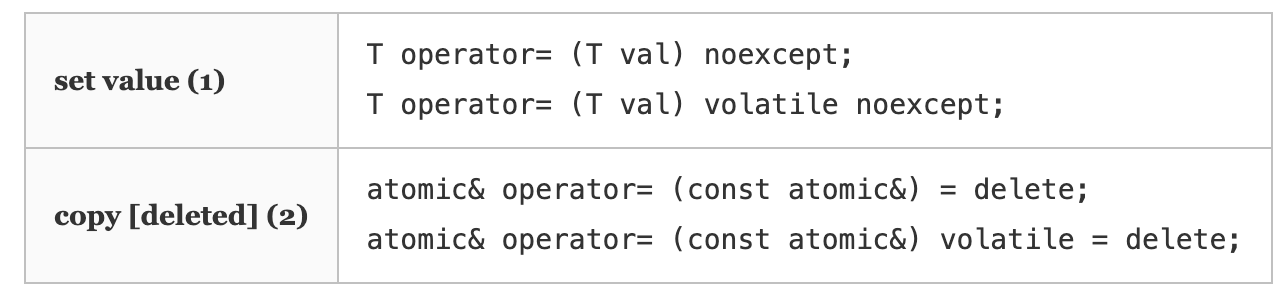
std::atomic::operator=() 函数
普通的赋值拷贝操作已经被禁用。但是一个类型为T的变量可以赋值给相应的原子类型变量(相当于隐式转换),该操作是原子的,内存顺序(Memory Order)默认为顺序一致性(std::memory_order_seq_cst),如果需要指定其他的内存序,需要使用std::atomic::store()。
#include <atomic>
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <vector>std::atomic<int> foo(0);void print_foo() {while (foo == 0) {std::this_thread::yield();}std::cout<<"foo:"<<foo<<std::endl;
}void set_foo(int i) {foo = i; // 调用 std::atomic::operator=().
}int main() {std::vector<std::thread> threads;std::thread first(print_foo);std::thread second(set_foo, 10);first.join();second.join();return 0;
}xutianyang.10@ZBMac-KYTH7H97M4 atomic % g++ -o text3 text3.cpp -std=c++11
xutianyang.10@ZBMac-KYTH7H97M4 atomic % ./text3
foo:10基本 std::atomic 类型操作
is_lock_free()
用来检查该原子变量是不是无锁的,因为有些类型可能不支持。
bool is_lock_free() const volatile noexcept;
bool is_lock_free() const noexcept;
std::atomic<int> atomicInt;
std::atomic<bool> atomicBool;
std::atomic<long long> atomicLongLong;std::cout << "atomic<int> is lock-free: " << atomicInt.is_lock_free() << std::endl;
std::cout << "atomic<bool> is lock-free: " << atomicBool.is_lock_free() << std::endl;
std::cout << "atomic<long long> is lock-free: " << atomicLongLong.is_lock_free() << std::endl;xutianyang.10@ZBMac-KYTH7H97M4 atomic % g++ -o text3 text3.cpp -std=c++11
xutianyang.10@ZBMac-KYTH7H97M4 atomic % ./text3
foo:10
atomic<int> is lock-free: 1
atomic<bool> is lock-free: 1
atomic<long long> is lock-free: 1store()和load()
修改被封装的值,std::atomic::store 函数将类型为 T 的参数 val 复制给原子对象所封装的值。T 是 std::atomic 类模板参数。另外参数 sync 指定内存序(Memory Order),可能的取值如下:
void store (T val, memory_order sync = memory_order_seq_cst) volatile noexcept;
void store (T val, memory_order sync = memory_order_seq_cst) noexcept;
加载被封装的值
T load (memory_order sync = memory_order_seq_cst) const volatile noexcept;
T load (memory_order sync = memory_order_seq_cst) const noexcept;
#include <atomic>
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <vector>std::atomic<int> foo(0);void print_foo() {int x;do {x = foo.load(std::memory_order_relaxed); //加载foo值}while (x==0);std::cout<<"foo:"<<foo<<std::endl;
}void set_foo(int i) {foo.store(i, std::memory_order_relaxed); //设置foo值为i
}int main() {std::vector<std::thread> threads;std::thread first(print_foo);std::thread second(set_foo, 10);first.join();second.join();return 0;
}
exchange()
读取并且修改被封装的值为val,并且返回旧值。整个过程是原子的。
T exchange (T val, memory_order sync = memory_order_seq_cst) volatile noexcept;
T exchange (T val, memory_order sync = memory_order_seq_cst) noexcept;
#include<iostream>
#include<atomic>
#include<thread>std::atomic<bool> ready(false);std::atomic<bool> winner;void func(int id) {while (!ready) {std::this_thread::yield(); //表示该线程可以让出时间片}for (int i = 0;i<1000000;i++) {}if (!winner.exchange(true)) {std::cout<<"thread #"<<id<<"won"<<std::endl;}
}int main() {std::vector<std::thread> threads;for (int i = 0;i<10;i++) {threads.push_back(std::thread(func,i));}ready = true;for (auto & th:threads) {th.join();}return 0;}
compare_exchange_weak()
expected期盼的值,val要修改的值。
比较被封装的值(weak)与expected值,是否相等。
如果旧值与expected相等,用val替换原子对象的值。
如果旧值与expected不相等,则将旧值赋值给expected。
- 该函数通常会读取原子对象封装的值,如果比较为 true(即原子对象的值等于 expected),则替换原子对象的旧值,但整个操作是原子的,在某个线程读取和修改该原子对象时,另外的线程不能对读取和修改该原子对象。

头插方式取得的链表
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <vector>struct Node {int data;Node* next;
};std::atomic<Node*> head_list(nullptr);void append(int val) {Node* new_node = new Node{val, head_list};//这个插入方式是线程安全的,是头插的方式while (!head_list.compare_exchange_weak(new_node->next, new_node)) {}}int main() {std::vector<std::thread> threads;for (int i = 0;i<10;i++) {threads.emplace_back(append, i);}for (auto &th:threads) {th.join();}Node* head = head_list.load();while (head) {std::cout<<head->data<<std::endl;head = head->next;}return 0;
}compare_exchange_strong()
这个跟compare_exchange_weak()的使用方法没有区别,但是weak可能会出现伪失败的情况,就是expected和旧值一样,也返回false。但是这种情况不影响原子性,失败了就失败了呗,再循环一次。所以weak适合循环条件。
strong则不会出现这种伪失败的条件。

