Java--多线程基础知识(2)
一.多线程的中断
1.通过自定义的变量来作为标志位
import java.util.Scanner;public class Demo1 {public static boolean flg = false;public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{while (!flg){System.out.println("t1线程正在执行");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {System.out.println("t1线程被中断");}}System.out.println("t1线程停止");});t1.start();Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);scanner.next();flg = true;}
}
在代码中,我们将 flg 作为标志位,当代码运行的时候我们需要输入任意键为就可以改变 flg,以此来达到停止代码运行的作用;
注意:flg 必须作为全局变量,因为 lambda 捕获的局部变量是不能被修改的,这是为了确保代码的安全性和一致性,由于我们要对flg 进行修改,所以我们要将 flg 作为全局变量。
2.使用 Thread.interrupted() 或者
Thread.currentThread.isInterrupted()代替标志位
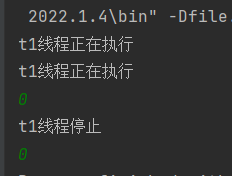
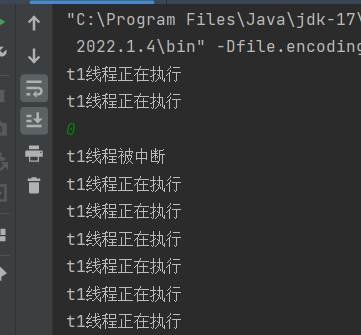
import java.util.Scanner;public class Demo2 {public static void main(String[] args) {Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{Thread cur = Thread.currentThread();while (!cur.isInterrupted()){System.out.println("t1线程正在执行");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {System.out.println("t1线程被中断");}}System.out.println("t1线程停止");});t1.start();Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);scanner.next();t1.interrupt();}
}
以上代码我们将 cur.isInterrupted 作为标志位,当我们输入任意字符之后就会调用 t1.interrupt() 方法,将标志位改为 false,但是运行后并且输入后我们发现代码仍在执行,
Java的线程中断机制有这样的设计:
当一个线程在阻塞状态(Thread.join,Thread.sleep,Thread.wait)下被中断时,中断标志位会被自动清除,也就是说当调用 Thread.interrupt() 之后,虽然 !cur.isInterrupted() 改为了 false,但是由于被清除了标志位,又变为了 true,这才导致程序仍然在运行。
也就是说 interrupt 方法做了两件事:首先将标志位设置为了 true,但是由于唤醒了 sleep ,以异常的方式返回了,清除了线程的标志位,将标志位重新设置为了 false。针对这种情况,我们需要在 catch 中做更详细的处理。
二.线程的等待与安全问题
public class Demo3 {static int result = 0;public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {result++;}});Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {result++;}});t1.start();t2.start();Thread.sleep(1000);System.out.println( result);}
}
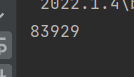
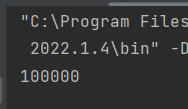
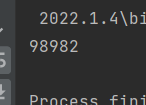
以上代码我们创建了两个线程 : 分别是 t1,t2,这两个线程同时对 result ++,正常情况下,result 的结果肯定是100000的,但在我们运行代码后:
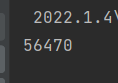
我们发现并没有到达100000,这就是多线程引发的线程安全问题,线程对 result++ 要进行三个操作:首先将 result 从主内存中读取到工作内存中,其次将 result 在工作内存中++,最后将result的值放回到主内存中,问题就出在这几步上,由于操作不是原子的,导致在 t1 从主内存中读取到 result的值并且++之后,t2也进行了从主内存中读取到了 result 的值,此时t1 和t2都需要将工作内存中的值写入到主内存当中,这样就会导致其中一个线程的值会覆盖掉另一个线程的值,这才导致了 result 的值并没有到达100000;
针对这个问题:
我们可以让某一个线程通过 Thread.sleep() 来等待另一个线程运行,但这种方法我们无法确定另一个线程运行多久,所以不推荐使用。
第二个方法是运行 join() 方法,
public class Demo3 {static int result = 0;public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {result++;}});Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {result++;}});t1.start();t1.join();t2.start();Thread.sleep(1000);System.out.println( result);}
}
在 t2 运行之前调用 t1.join() 方法,此时main线程会等待 t1 线程运行完成之后再往下走调用 t2.start,此时就解决了上述问题。
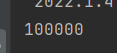
三.线程的状态
线程的状态分为六种:

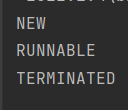
new,runnable,terminated 状态演示:
public class Demo4 {public static void main(String[] args) {Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {}});System.out.println(t1.getState());t1.start();System.out.println(t1.getState());try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}System.out.println(t1.getState());}}
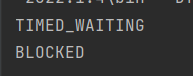
timed_waiting , blocked 状态演示:
public class Demo5{static Object object = new Object();public static void main(String[] args) {Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{synchronized( object){try {Thread.sleep(10000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}});Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{synchronized ( object){while ( true){}}});t1.start();t2.start();try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}System.out.println(t1.getState());System.out.println(t2.getState());}
}
将上述部分代码进行更改,就可以得到 waiting 状态:
Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{synchronized( object){try {object.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}});![]()
四.线程的锁
还是对上述的线程安全问题进行解决,线程安全问题其中的导火索之一便是代码的非原子性,由于一件事情要分几步来操作,这种情况容易出问题,所以就出现了锁,锁可以将几个步骤的操作绑定在一起,这样就可以变相的实现代码的原子化。
public class Demo6 {static int result = 0;static Object locker = new Object();public static void add(int a){synchronized (locker){result++;}}public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {add(result);}});Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {add(result);}});t1.start();t2.start();Thread.sleep(100);System.out.println( result);}
}
sychronized(Object object){ }
其中 sychronized 就是锁的关键字,他需要的参数是 Object 类,就像是对 object 上了锁,其他人想要进是没有办法的,除非你释放了锁,当你走完{ }的时候,此时就完成了对锁的释放。
上述代码我们对 add类里面的内容上了锁,我们还可以对线程的内容直接加锁:
public class Demo6 {static int result = 0;static Object locker = new Object();public static void add(int a){result++;}public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{synchronized(locker){for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {add(result);}}});Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{synchronized(locker){for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {add(result);}};});t1.start();t2.start();Thread.sleep(100);System.out.println( result);}
}
运行结果不变;
要注意:我们不能只对一个线程加锁,那样的话是没有意义的:
public class Demo6 {static int result = 0;static Object locker = new Object();public static void add(int a){result++;}public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{synchronized(locker){for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {add(result);}}});Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {add(result);};});t1.start();t2.start();Thread.sleep(100);System.out.println( result);}
}
这是因为如果我们只对一个线程的内容上锁了,另一个线程没有对同一个Object类上锁,两个线程还是会各自运行各自的。
最后就是:两个线程针对不同的 Object 类上锁也会有线程安全问题:
public class Demo6 {static int result = 0;static Object locker = new Object();static Object locker2 = new Object();public static void add(int a){result++;}public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{synchronized(locker){for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {add(result);}}});Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{synchronized(locker2){for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {add(result);};}});t1.start();t2.start();Thread.sleep(100);System.out.println( result);}
}