ros2-tf树查看
首先先介绍一个在ubuntu20中能够使用的阿克曼转向的模型系统,car_demo,我们使用foxy,noetic,galactic三种都进行了测试,以下是最终的可用仿真环境。
git clone https://github.com/chan-yuu/car_demo.git -b foxy
编译即可
colcon build
同时也提供了其他ros版本的仿真环境,今天的主要目的是认识ros2的tf系统。
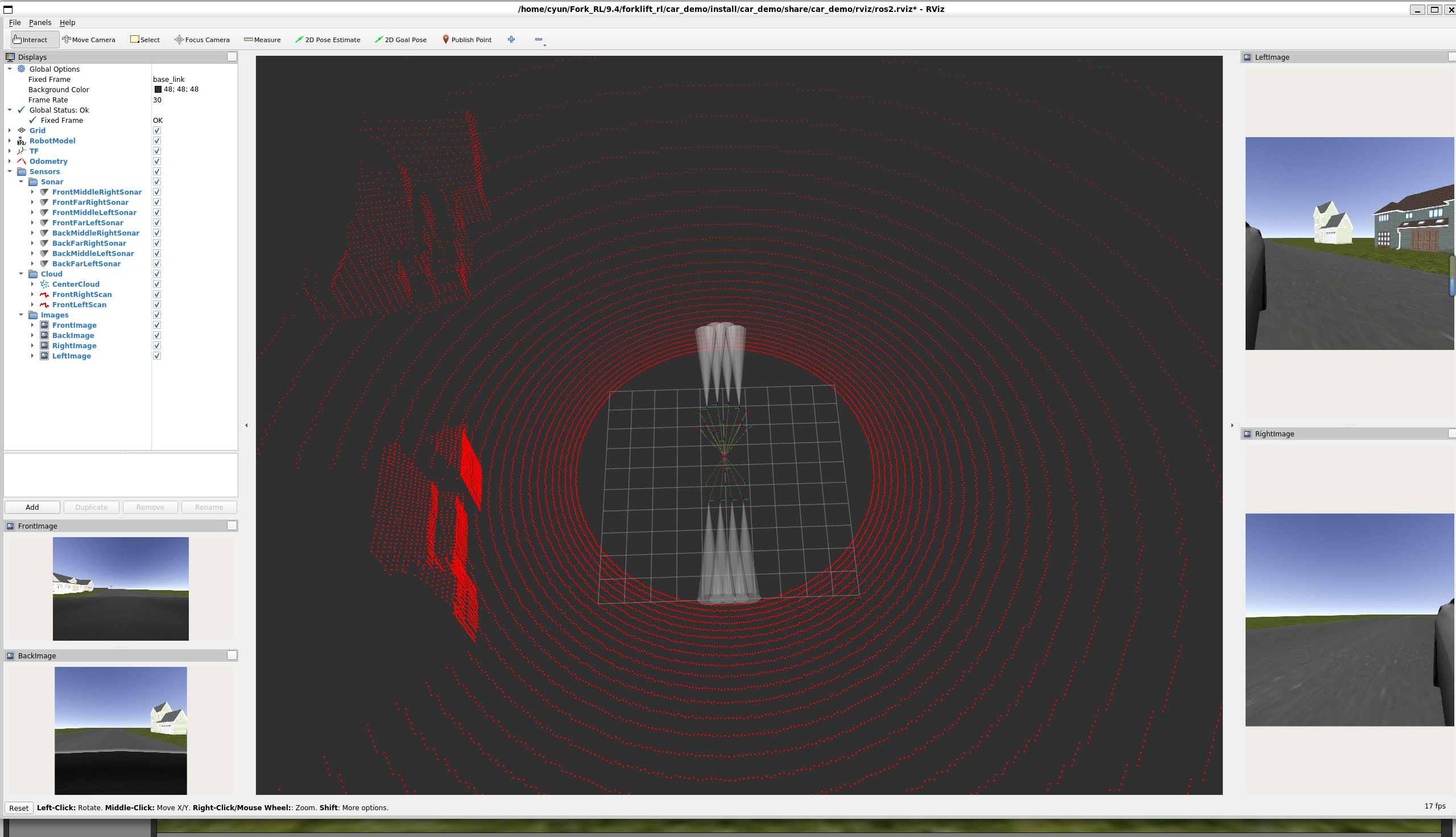
启动仿真环境
ros2 launch car_demo demo.launch.py
!!![debug]这个仿真环境比较占用资源,并且摩擦并没有调的很好,车辆会在静止时依然滑动都是常有的事。
由于ros2中rqt工具无法直接查看tf树,我们需要额外安装其他的工具实现可视化。
查看TF树结构
工具直接安装:
sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-tf2-tools
ros2 run tf2_tools view_frames.py
生成了cv和pdf文件直接查看:
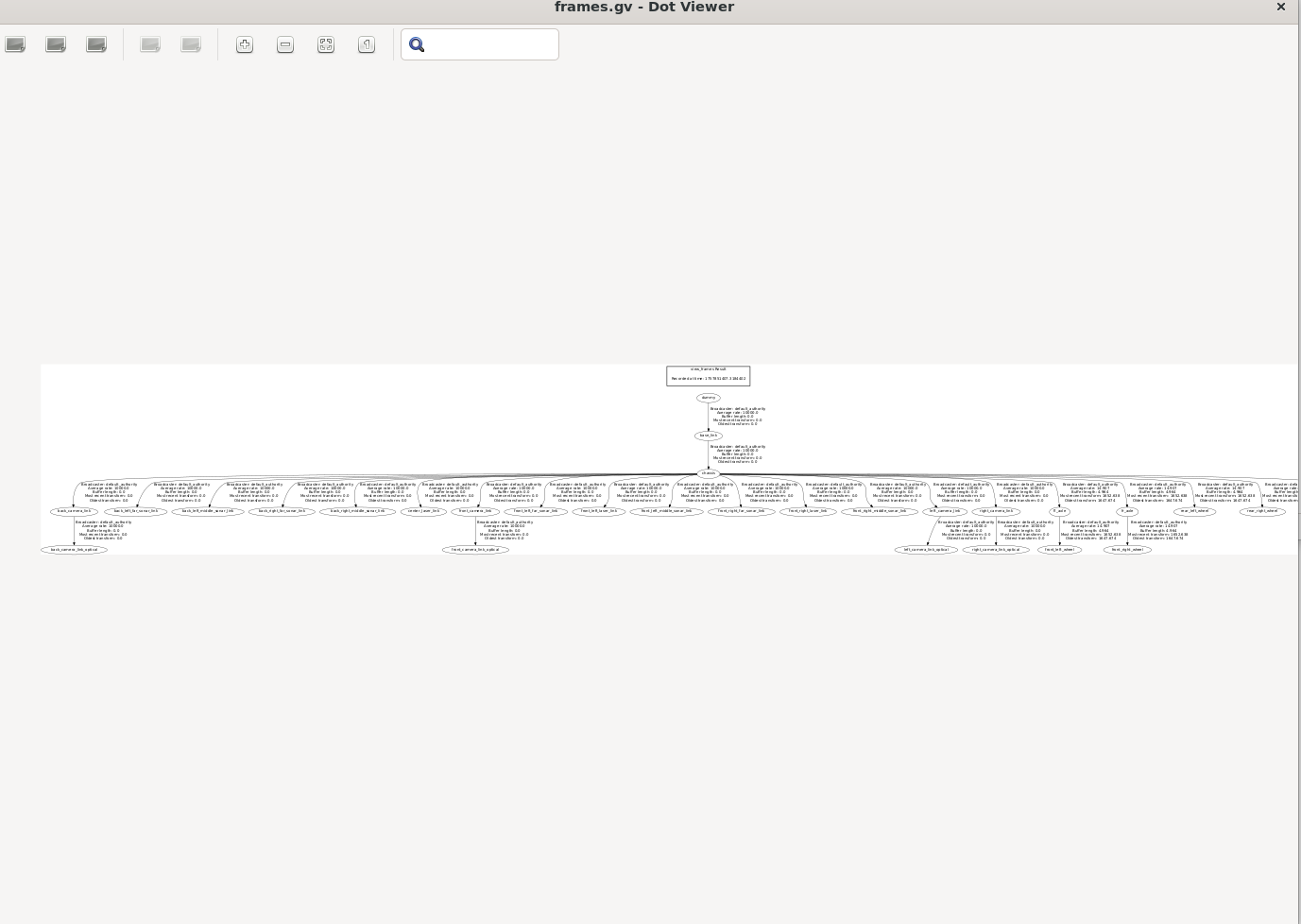
实时监控TF
更加推荐这种实时监控的方式,是rqt的独立的工具,没有进行集成,安装方式为:
sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-rqt-tf-tree
ros2 run rqt_tf_tree rqt_tf_tree
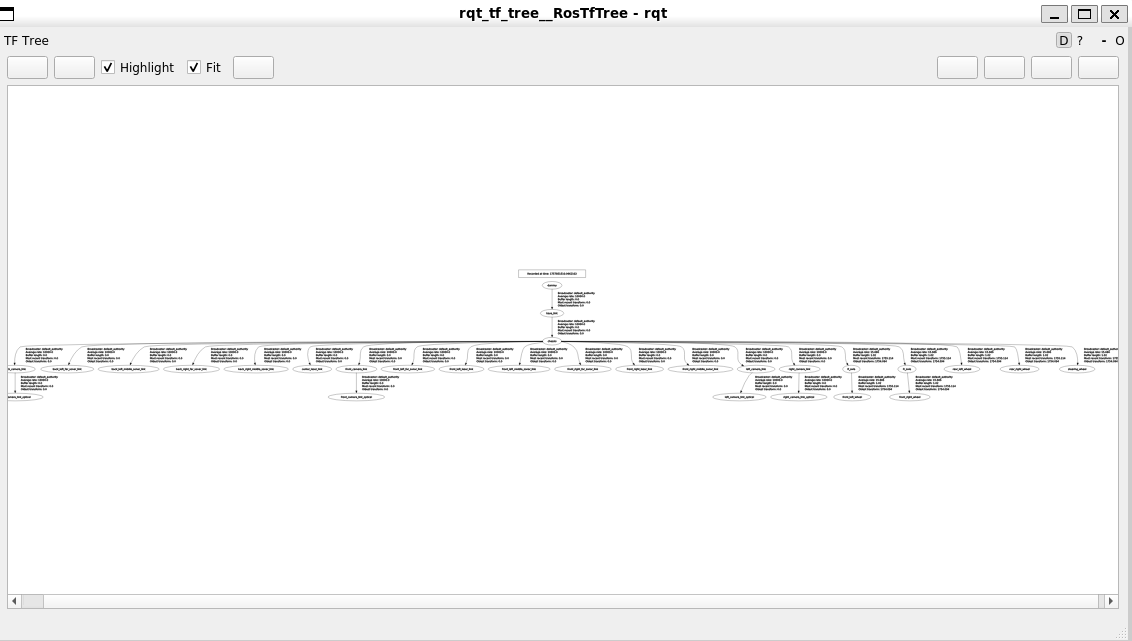
查看特定变换
最后是通过tf2_ros 的tf2_echo 来直接打印坐标关系。借这个打印我们也来分析一下两个坐标的tf关系是怎么计算出来的。
ros2 run tf2_ros tf2_echo <源坐标系> <目标坐标系>
例如:ros2 run tf2_ros tf2_echo dummy base_link
cyun@cyun:~/Fork_RL/9.4/forklift_rl/car_demo$ ros2 run tf2_ros tf2_echo dummy base_link
[INFO] [1757851831.521967212] [tf2_echo]: Waiting for transform dummy -> base_link: Invalid frame ID "dummy" passed to canTransform argument target_frame - frame does not exist
At time 0.0
- Translation: [0.000, 0.000, 0.000]
- Rotation: in Quaternion [0.000, 0.000, 0.000, 1.000]
At time 0.0
- Translation: [0.000, 0.000, 0.000]
- Rotation: in Quaternion [0.000, 0.000, 0.000, 1.000]
At time 0.0
- Translation: [0.000, 0.000, 0.000]
- Rotation: in Quaternion [0.000, 0.000, 0.000, 1.000]
ros2 run tf2_ros tf2_echo map base_link
旋转平移矩阵的转移关系分析:
在 ROS 2 中,tf2_echo输出的平移和旋转参数描述了源坐标系到目标坐标系的变换关系。这些参数在机器人系统中用于坐标转换、运动规划、传感器数据融合等关键任务。下面从数学角度详细说明其含义和用法:
假设存在两个坐标系:
源坐标系:A(如base_link)
目标坐标系:B(如odom)
tf2_echo A B输出的是从 A 到 B 的变换,即:如何将一个点在 A 中的坐标转换到 B 中。
变换公式的核心是齐次变换矩阵(4×4 矩阵),它同时包含平移和旋转信息:
plaintext
| R₁₁ R₁₂ R₁₃ tₓ |
| R₂₁ R₂₂ R₂₃ tᵧ |
| R₃₁ R₃₂ R₃₃ t_z |
| 0 0 0 1 |
其中:
R 是 3×3 旋转矩阵(由四元数转换而来)
tₓ, tᵧ, t_z 是平移向量(Translation输出值)
2. 平移向量(Translation)的使用
输出的[tₓ, tᵧ, t_z]表示:
目标坐标系 B 的原点在源坐标系 A 中的坐标(注意看,这里就是直接用源坐标系给出的目标坐标系的原点位置)。
若一个点P在 A 中的坐标为P_A = [x, y, z, 1](齐次坐标),经过平移后在 B 中的坐标计算为:
plaintext
P_B(平移) = P_A - [tₓ, tᵧ, t_z, 0]
(注:齐次坐标的最后一位为 1 时表示点,平移时加平移向量;为 0 时表示向量,平移不影响)
3. 旋转(Rotation)的表示与使用
ROS 2 中旋转默认用四元数[x, y, z, w]表示,其对应数学定义为:
plaintext
四元数 q = w + x·i + y·j + z·k
其中w是实部,x,y,z是虚部,满足x² + y² + z² + w² = 1。
3.1 四元数到旋转矩阵的转换
四元数需要先转换为旋转矩阵R才能用于坐标计算,转换公式为:
plaintext
R = [
[1-2y²-2z², 2xy-2zw, 2xz+2yw ],
[2xy+2zw, 1-2x²-2z², 2yz-2xw ],
[2xz-2yw, 2yz+2xw, 1-2x²-2y² ]
]
3.2 旋转的应用
若点P_A在 A 中经过旋转后到 B 中的坐标为P_B(旋转),则:
plaintext
P_B(旋转) = R × P_A
(× 表示矩阵乘法,P_A为 3×1 列向量)
4. 完整坐标变换公式
结合平移和旋转,从源坐标系 A 到目标坐标系 B 的完整变换为:
plaintext
P_B = R × P_A + t
用齐次矩阵表示则更简洁:
plaintext
[P_B] [R t] [P_A]
[ 1 ] = [0 1] [ 1 ]
5. 坐标系迁移的实际意义
例如tf2_echo base_link odom输出:
平移[0.1, 0.2, 0.3]:表示odom原点在base_link前方 0.1m、右侧 0.2m、上方 0.3m 处
四元数[0,0,sin0.5θ,cos0.5θ](绕 z 轴旋转 θ 角):表示odom相对base_link绕 z 轴旋转了 θ 角
当机器人移动时,这个变换会实时更新,通过上述公式可以:
将传感器数据(如激光雷达在base_link下的坐标)转换到世界坐标系(odom)中
反之,将世界坐标系中的目标点转换到机器人本地坐标系,用于路径规划
总结
Translation是目标坐标系原点在源坐标系中的位置
Quaternion通过转换为旋转矩阵描述两坐标系的姿态关系
完整变换公式:目标坐标 = 旋转矩阵 × 源坐标 + 平移向量
以下是一个用transformations实现的例子(ros2下)
import rclpy
from rclpy.node import Node
from tf2_ros import TransformBroad
caster
from geometry_msgs.msg import TransformStamped
import transformations
import mathclass GpsOdomTFPublisher(Node):def __init__(self):super().__init__('gps_odom_tf_publisher')# 创建TF广播器self.tf_broadcaster = TransformBroadcaster(self)# 设置定时器,定期发布TF变换self.timer = self.create_timer(0.1, self.broadcast_transform)# 定义odom在gps坐标系中的初始位姿self.odom_origin_in_gps = (580000.0, 4360000.0, 0.0) # x, y, zself.odom_yaw_in_gps = math.radians(90) # 90度转换为弧度self.get_logger().info('GPS-Odom TF发布器已启动')# 待转换的GPS点和航向self.gps_point = (580001.0, 4360001.0, 0.0) # GPS坐标self.gps_heading = math.radians(50) # GPS航向角(50度,弧度)# 执行转换self.convert_gps_to_odom()def broadcast_transform(self):# 创建变换消息t = TransformStamped()# 设置时间戳和坐标系t.header.stamp = self.get_clock().now().to_msg()t.header.frame_id = 'gps' # 父坐标系t.child_frame_id = 'odom' # 子坐标系# 设置平移参数 (odom原点在gps中的坐标)t.transform.translation.x = self.odom_origin_in_gps[0]t.transform.translation.y = self.odom_origin_in_gps[1]t.transform.translation.z = self.odom_origin_in_gps[2]# 将90度旋转转换为四元数,使用transformations库quat = transformations.quaternion_from_euler(0, 0, self.odom_yaw_in_gps)t.transform.rotation.x = quat[0]t.transform.rotation.y = quat[1]t.transform.rotation.z = quat[2]t.transform.rotation.w = quat[3]# 发布变换self.tf_broadcaster.sendTransform(t)def convert_gps_to_odom(self):"""将GPS坐标和航向转换到odom坐标系"""# 1. 坐标点转换# 1.1 平移:减去odom原点在GPS中的坐标translated_x = self.gps_point[0] - self.odom_origin_in_gps[0]translated_y = self.gps_point[1] - self.odom_origin_in_gps[1]translated_z = self.gps_point[2] - self.odom_origin_in_gps[2]# 1.2 旋转:应用逆变换(-90度)将GPS点转换到odomtheta = -self.odom_yaw_in_gps # 逆旋转角cos_theta = math.cos(theta)sin_theta = math.sin(theta)odom_x = translated_x * cos_theta + translated_y * sin_thetaodom_y = -translated_x * sin_theta + translated_y * cos_thetaodom_z = translated_z# 2. 航向角转换# 航向角 = GPS航向角 - odom相对gps的旋转角(90度)odom_heading = self.gps_heading - self.odom_yaw_in_gps# 归一化到[-π, π]odom_heading = (odom_heading + math.pi) % (2 * math.pi) - math.pi# 打印结果self.get_logger().info(f"GPS坐标: {self.gps_point}")self.get_logger().info(f"GPS航向角: {math.degrees(self.gps_heading):.1f}°")self.get_logger().info(f"Odom坐标: ({odom_x:.2f}, {odom_y:.2f}, {odom_z:.2f})")self.get_logger().info(f"Odom航向角: {math.degrees(odom_heading):.1f}°")# 验证旋转计算(90度逆旋转的特殊情况)verify_x = translated_yverify_y = -translated_xself.get_logger().info(f"旋转验证: ({verify_x:.2f}, {verify_y:.2f})")self.get_logger().info(f"航向验证: {math.degrees(self.gps_heading - math.pi/2):.1f}°")def main(args=None):rclpy.init(args=args)node = GpsOdomTFPublisher()rclpy.spin(node)node.destroy_node()rclpy.shutdown()if __name__ == '__main__':main()
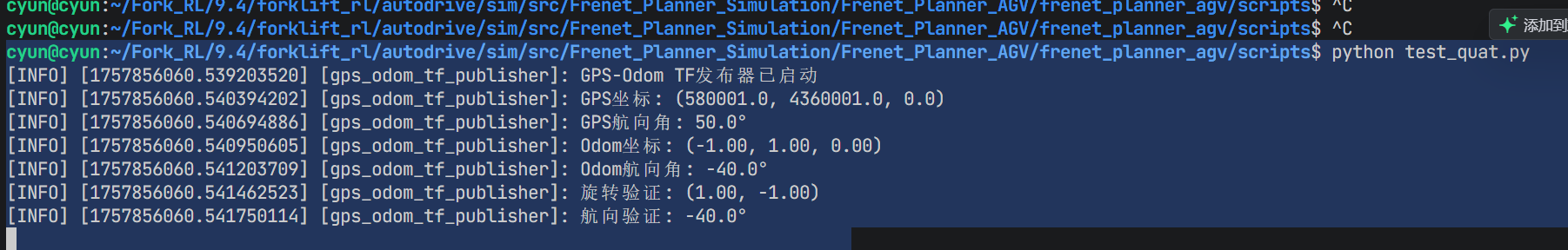
cyun@cyun:~/Fork_RL/9.4/forklift_rl/autodrive/sim/src/Frenet_Planner_Simulation/Frenet_Planner_AGV/frenet_planner_agv/scripts$ python test_quat.py
[INFO] [1757896880.219417976] [gps_odom_tf_publisher]: GPS-Odom TF发布器已启动
[INFO] [1757896880.220089600] [gps_odom_tf_publisher]: GPS坐标: (580001.0, 4360001.0, 0.0)
[INFO] [1757896880.220395713] [gps_odom_tf_publisher]: GPS航向角: 50.0°
[INFO] [1757896880.220799054] [gps_odom_tf_publisher]: Odom坐标: (-1.00, 1.00, 0.00)
[INFO] [1757896880.221059341] [gps_odom_tf_publisher]: Odom航向角: -40.0°
[INFO] [1757896880.221254674] [gps_odom_tf_publisher]: 旋转验证: (1.00, -1.00)
[INFO] [1757896880.221423286] [gps_odom_tf_publisher]: 航向验证: -40.0°
此时的tf关系为:
ros2 run tf2_ros tf2_echo gps odom
cyun@cyun:~/Fork_RL/9.4/forklift_rl/autodrive/sim/src/Frenet_Planner_Simulation/Frenet_Planner_AGV/frenet_planner_agv/scripts$ ros2 run tf2_ros tf2_echo gps odom
[INFO] [1757896939.554518347] [tf2_echo]: Waiting for transform gps -> odom: Invalid frame ID "gps" passed to canTransform argument target_frame - frame does not exist
At time 1757896940.409354626
- Translation: [580000.000, 4360000.000, 0.000]
- Rotation: in Quaternion [0.707, 0.000, 0.000, 0.707]
At time 1757896941.409428650
- Translation: [580000.000, 4360000.000, 0.000]
- Rotation: in Quaternion [0.707, 0.000, 0.000, 0.707]
At time 1757896942.409346144
- Translation: [580000.000, 4360000.000, 0.000]
- Rotation: in Quaternion [0.707, 0.000, 0.000, 0.707]
At time 1757896943.409368130
- Translation: [580000.000, 4360000.000, 0.000]
- Rotation: in Quaternion [0.707, 0.000, 0.000, 0.707]
At time 1757896944.409341732
- Translation: [580000.000, 4360000.000, 0.000]
- Rotation: in Quaternion [0.707, 0.000, 0.000, 0.707]
从这里的结果修正一下之前说的四元数的旋转关系,我们只需要知道绕着z轴旋转需要以下内容:
(sin0.5θ,0,0,cos0.5θ)
以上就是对于tf关系的解析的整个过程,理解旋转平移关系是关键。
