【Block总结】ConverseNet:神经网络中的反向卷积算子
1. 论文信息
- 标题:Reverse Convolution and Its Applications to Image Restoration
- 发布平台:arXiv
- 论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2508.09824
- 代码仓库:https://github.com/cszn/converseNet
- 任务领域:图像恢复(去噪、超分辨率、去模糊)
- 核心贡献:提出了一种新的反向卷积算子(Converse2D),可逆转标准卷积操作,并构建了基于该算子的ConverseNet网络。
2. 方法详解
2.1 问题背景
卷积(Conv)和转置卷积(ConvTranspose)是深度学习中常用的两种基本操作。然而,转置卷积并不是卷积的数学逆运算,它只是通过插零和卷积实现上采样,并不能真正逆转卷积过程。
2.2 目标定义
给定一个卷积核 K\mathbf{K}K 和步长 sss,我们希望找到一个算子 F\mathcal{F}F 使得:
X=F(Y,K,s)\mathbf{X} = \mathcal{F}(\mathbf{Y}, \mathbf{K}, s)X=F(Y,K,s)
其中 Y=(X⊗K)↓s\mathbf{Y} = (\mathbf{X} \otimes \mathbf{K}) \downarrow_sY=(X⊗K)↓s 是卷积+下采样的结果。
2.3 优化问题构建
作者将反向卷积问题构建为一个带正则化的最小二乘问题:
X∗=argminX∥Y−(X⊗K)↓s∥F2+λ∥X−X0∥F2\mathbf{X}^* = \arg\min_{\mathbf{X}} \left\| \mathbf{Y} - (\mathbf{X} \otimes \mathbf{K}) \downarrow_s \right\|_F^2 + \lambda \left\| \mathbf{X} - \mathbf{X}_0 \right\|_F^2X∗=argXmin∥Y−(X⊗K)↓s∥F2+λ∥X−X0∥F2
其中 X0\mathbf{X}_0X0 是初始估计(如零或插值结果),λ\lambdaλ 是正则化参数。
2.4 闭式解与傅里叶变换
在循环边界假设下,该问题有闭式解,可通过傅里叶变换高效计算:
X∗=F−1(1λ(L−FK‾⊙s(FKL)⇓s∣FK∣2⇓s+λ))\mathbf{X}^* = \mathcal{F}^{-1} \left( \frac{1}{\lambda} \left( \mathbf{L} - \overline{\mathbf{F}_K} \odot_s \frac{ (\mathbf{F}_K \mathbf{L}) \Downarrow_s }{ |\mathbf{F}_K|^2 \Downarrow_s + \lambda } \right) \right)X∗=F−1(λ1(L−FK⊙s∣FK∣2⇓s+λ(FKL)⇓s))
其中 L=FK‾FY↑s+λFX0\mathbf{L} = \overline{\mathbf{F}_K} \mathbf{F}_{Y \uparrow_s} + \lambda \mathbf{F}_{X_0}L=FKFY↑s+λFX0,符号含义见论文。
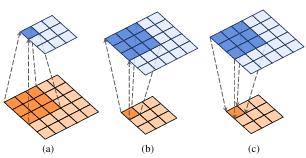
图1: 标准卷积(a)、转置卷积(b)和反向卷积©的结构差异示意图。每个子图显示了一个输入特征图(橙色)及其对应的输出特征图(蓝色)。
3. 创新点
- 提出Converse2D算子:首次将反向卷积问题形式化为可学习的神经网络模块。
- 闭式解与非迭代计算:通过傅里叶变换实现高效计算,避免迭代优化。
- 可学习的正则化参数:λ\lambdaλ 通过可学习参数自适应调整。
- 构建ConverseBlock:将Converse2D与LayerNorm、1×1卷积、GELU激活结合,形成类似Transformer的结构。
- 多任务适用性:在去噪、超分、去模糊等多个图像恢复任务中验证有效性。
4. 实验结果
4.1 高斯去噪(Set12, BSD68)
| 模型 | 参数量 | PSNR (Set12) | PSNR (BSD68) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DnCNN | - | 基准 | 基准 |
| Converse-DnCNN | 更多 | 更高 | 更高 |
4.2 超分辨率(Set5, Urban100)
| 模型 | PSNR (Set5) | PSNR (Urban100) |
|---|---|---|
| SRResNet | 基准 | 基准 |
| Converse-SRResNet | 相当 | 相当 |
4.3 去模糊(BSD100, Urban100)
| 模型 | 盲/非盲 | PSNR (BSD100) | PSNR (Urban100) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ConvNet | 盲 | 较低 | 较低 |
| ConverseNet | 盲 | 更高 | 更高 |
| Converse-USRNet | 非盲 | 最高 | 最高 |
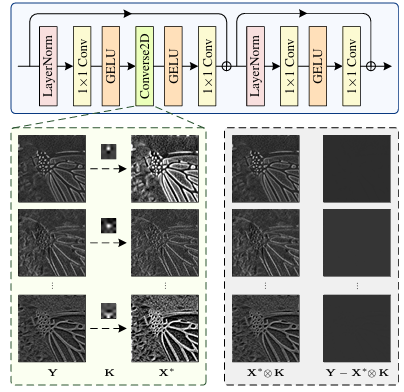
图2: 提出的反向卷积块的结构。绿色虚线框显示了一个Converse2D算子(s=1s=1s=1)的三个输入特征图(即Y\mathbf{Y}Y)、相应的核(即K)和相应的输出(即X∗\mathbf{X}^{*}X∗),而灰色虚线框显示了相应的重建结果(即X∗⊗K\mathbf{X}^{*}\otimes\mathbf{K}X∗⊗K)和误差图(即Y−X∗⊗K\mathbf{Y}-\mathbf{X}^{*}\otimes\mathbf{K}Y−X∗⊗K)。
5. 总结
- 贡献:提出了一种数学上严谨的反向卷积算子Converse2D,可逆转卷积操作,适用于多种图像恢复任务。
- 优势:非迭代、可学习、多通道支持、端到端训练。
- 局限:计算复杂度较高,依赖于傅里叶变换。
- 未来方向:扩展到生成模型、大规模视觉任务、更复杂的退化模型。
6. 完整代码实现
以下是论文中Converse2D算子及其相关模块的完整PyTorch实现:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from collections import OrderedDict"""
# --------------------------------------------
# LayerNorm for Vision Normalization
# --------------------------------------------
"""class LayerNorm(nn.Module):'''LayerNorm that supports two data formats: channels_last (default) or channels_first.The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs. channels_last corresponds to inputs withshape (batch_size, height, width, channels) while channels_first corresponds to inputswith shape (batch_size, channels, height, width).'''def __init__(self, normalized_shape, eps=1e-6, data_format="channels_last"):super().__init__()self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(normalized_shape))self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(normalized_shape))self.eps = epsself.data_format = data_formatif self.data_format not in ["channels_last", "channels_first"]:raise NotImplementedErrorself.normalized_shape = (normalized_shape,)def forward(self, x):if self.data_format == "channels_last":return F.layer_norm(x, self.normalized_shape, self.weight, self.bias, self.eps)elif self.data_format == "channels_first":u = x.mean(1, keepdim=True)s = (x - u).pow(2).mean(1, keepdim=True)x = (x - u) / torch.sqrt(s + self.eps)x = self.weight[:, None, None] * x + self.bias[:, None, None]return xdef sequential(*args):"""Advanced nn.Sequential.Args:nn.Sequential, nn.ModuleReturns:nn.Sequential"""if len(args) == 1:if isinstance(args[0], OrderedDict):raise NotImplementedError('sequential does not support OrderedDict input.')return args[0] # No sequential is needed.modules = []for module in args:if isinstance(module, nn.Sequential):for submodule in module.children():modules.append(submodule)elif isinstance(module, nn.Module):modules.append(module)return nn.Sequential(*modules)"""
# --------------------------------------------
# implementation of Converse2d operator ^_^
# --------------------------------------------
"""class Converse2D(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, scale=1, padding=2, padding_mode='circular', eps=1e-5):super(Converse2D, self).__init__()"""Converse2D Operator for Image Restoration Tasks.Args:x (Tensor): Input tensor of shape (N, in_channels, H, W), whereN is the batch size, H and W are spatial dimensions.in_channels (int): Number of channels in the input tensor.out_channels (int): Number of channels produced by the operation.kernel_size (int): Size of the kernel.scale (int): Upsampling factor. For example, `scale=2` doubles the resolution.padding (int): Padding size. Recommended value is `kernel_size - 1`.padding_mode (str, optional): Padding method. One of {'reflect', 'replicate', 'circular', 'constant'}.Default is `circular`.eps (float, optional): Small value added to denominators for numerical stability.Default is a small value like 1e-5.Returns:Tensor: Output tensor of shape (N, out_channels, H * scale, W * scale), where spatial dimensionsare upsampled by the given scale factor."""self.in_channels = in_channelsself.out_channels = out_channelsself.kernel_size = kernel_sizeself.scale = scaleself.padding = paddingself.padding_mode = padding_modeself.eps = eps# ensure depthwiseassert self.out_channels == self.in_channelsself.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1, self.in_channels, self.kernel_size, self.kernel_size))self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, self.in_channels, 1, 1))self.weight.data = nn.functional.softmax(self.weight.data.view(1, self.in_channels, -1), dim=-1).view(1,self.in_channels,self.kernel_size,self.kernel_size)def forward(self, x):if self.padding > 0:x = nn.functional.pad(x, pad=[self.padding, self.padding, self.padding, self.padding],mode=self.padding_mode, value=0)self.biaseps = torch.sigmoid(self.bias - 9.0) + self.eps_, _, h, w = x.shapeSTy = self.upsample(x, scale=self.scale)if self.scale != 1:x = nn.functional.interpolate(x, scale_factor=self.scale, mode='nearest')# x = nn.functional.interpolate(x, scale_factor=self.scale, mode='bilinear',align_corners=False)# x = torch.zeros_like(x)FB = self.p2o(self.weight, (h * self.scale, w * self.scale))FBC = torch.conj(FB)F2B = torch.pow(torch.abs(FB), 2)FBFy = FBC * torch.fft.fftn(STy, dim=(-2, -1))FR = FBFy + torch.fft.fftn(self.biaseps * x, dim=(-2, -1))x1 = FB.mul(FR)FBR = torch.mean(self.splits(x1, self.scale), dim=-1, keepdim=False)invW = torch.mean(self.splits(F2B, self.scale), dim=-1, keepdim=False)invWBR = FBR.div(invW + self.biaseps)FCBinvWBR = FBC * invWBR.repeat(1, 1, self.scale, self.scale)FX = (FR - FCBinvWBR) / self.biasepsout = torch.real(torch.fft.ifftn(FX, dim=(-2, -1)))if self.padding > 0:out = out[..., self.padding * self.scale:-self.padding * self.scale,self.padding * self.scale:-self.padding * self.scale]return outdef splits(self, a, scale):'''Split tensor `a` into `scale x scale` distinct blocks.Args:a: Tensor of shape (..., W, H)scale: Split factorReturns:b: Tensor of shape (..., W/scale, H/scale, scale^2)'''*leading_dims, W, H = a.size()W_s, H_s = W // scale, H // scale# Reshape to separate the scale factorsb = a.view(*leading_dims, scale, W_s, scale, H_s)# Generate the permutation orderpermute_order = list(range(len(leading_dims))) + [len(leading_dims) + 1, len(leading_dims) + 3,len(leading_dims), len(leading_dims) + 2]b = b.permute(*permute_order).contiguous()# Combine the scale dimensionsb = b.view(*leading_dims, W_s, H_s, scale * scale)return bdef p2o(self, psf, shape):'''Convert point-spread function to optical transfer function.otf = p2o(psf) computes the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) of thepoint-spread function (PSF) array and creates the optical transferfunction (OTF) array that is not influenced by the PSF off-centering.Args:psf: NxCxhxwshape: [H, W]Returns:otf: NxCxHxWx2'''otf = torch.zeros(psf.shape[:-2] + shape).type_as(psf)otf[..., :psf.shape[-2], :psf.shape[-1]].copy_(psf)otf = torch.roll(otf, (-int(psf.shape[-2] / 2), -int(psf.shape[-1] / 2)), dims=(-2, -1))otf = torch.fft.fftn(otf, dim=(-2, -1))return otfdef upsample(self, x, scale=3):'''s-fold upsamplerUpsampling the spatial size by filling the new entries with zerosx: tensor image, NxCxWxH'''st = 0z = torch.zeros((x.shape[0], x.shape[1], x.shape[2] * scale, x.shape[3] * scale)).type_as(x)z[..., st::scale, st::scale].copy_(x)return z"""
# --------------------------------------------
# implementation of Converse Block
# --------------------------------------------
"""class ConverseBlock(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, scale=1, padding=2, padding_mode='replicate',eps=1e-5):super(ConverseBlock, self).__init__()"""ConverseBlock: A Convolutional Block for Image Restoration using Converse2D Operations.This block consists of two main sub-blocks, each incorporating normalization, pointwise convolution,non-linearity, and (optionally) a custom reverse convolution (`Converse2D`) for learnable upsampling.It also includes residual connections to preserve information and improve gradient flow.Args:in_channels (int): Number of channels in the input tensor.out_channels (int): Number of channels to be produced by the block.kernel_size (int, optional): Kernel size used in the `Converse2D` operation. Default: 3.scale (int, optional): Upsampling scale factor. Default: 1 (no upsampling).padding (int, optional): Padding size for `Converse2D`. Default: 2.padding_mode (str, optional): Padding mode to use in `Converse2D`. One of {'reflect', 'replicate', 'circular', 'constant'}. Default: 'circular'.eps (float, optional): A small epsilon value for numerical stability in normalization layers. Default: 1e-6.Forward:x (Tensor): Input tensor of shape (N, in_channels, H, W)Returns:Tensor: Output tensor of shape (N, out_channels, H * scale, W * scale)"""self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(LayerNorm(in_channels, eps=1e-5, data_format="channels_first"),nn.Conv2d(in_channels, 2 * out_channels, 1, 1, 0),nn.GELU(),Converse2D(2 * out_channels, 2 * out_channels, kernel_size, scale=scale,padding=padding, padding_mode=padding_mode, eps=eps),nn.GELU(),nn.Conv2d(2 * out_channels, out_channels, 1, 1, 0))self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(LayerNorm(in_channels, eps=1e-5, data_format="channels_first"),nn.Conv2d(out_channels, 2 * out_channels, 1, 1, 0),nn.GELU(),nn.Conv2d(2 * out_channels, out_channels, 1, 1, 0))def forward(self, x):x = self.conv1(x) + xx = self.conv2(x) + xreturn xclass ConverseBlockAlphaVariant(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, scale=1, padding=2, padding_mode='replicate',eps=1e-5):super(ConverseBlockAlphaVariant, self).__init__()"""ConverseBlockAlphaVariant: Only difference is the addition of alpha parameters to the convolution blocks."""self.alpha1 = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros((1, out_channels, 1, 1)), requires_grad=True)self.alpha2 = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros((1, out_channels, 1, 1)), requires_grad=True)self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(LayerNorm(in_channels, eps=1e-5, data_format="channels_first"),nn.Conv2d(in_channels, 2 * out_channels, 1, 1, 0),nn.GELU(),Converse2D(2 * out_channels, 2 * out_channels, kernel_size, scale=scale,padding=padding, padding_mode=padding_mode, eps=eps),nn.GELU(),nn.Conv2d(2 * out_channels, out_channels, 1, 1, 0))self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(LayerNorm(in_channels, eps=1e-5, data_format="channels_first"),nn.Conv2d(out_channels, 2 * out_channels, 1, 1, 0),nn.GELU(),nn.Conv2d(2 * out_channels, out_channels, 1, 1, 0))def forward(self, x):x = self.alpha1 * self.conv1(x) + xx = self.alpha2 * self.conv2(x) + xreturn xclass ResidualBlock(nn.Module):"""Residual block---Conv-ReLU-Conv-+-|________________|"""def __init__(self, num_features=64):super(ResidualBlock, self).__init__()self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(num_features, num_features, 3, 1, 1, bias=True)self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(num_features, num_features, 3, 1, 1, bias=True)def forward(self, x):out = F.relu(self.conv1(x), inplace=True)out = self.conv2(out)return x + outif __name__ == "__main__":# 定义输入张量大小(Batch、Channel、Height、Wight)B, C, H, W = 16, 64, 40, 40input_tensor = torch.randn(B, C, H, W) # 随机生成输入张量dim = C# 创建 Converse2D 实例block = Converse2D(in_channels=64, out_channels=64,kernel_size=3,scale=2)device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")sablock = block.to(device)print(sablock)input_tensor = input_tensor.to(device)# 执行前向传播output = sablock(input_tensor)# 打印输入和输出的形状print(f"Input: {input_tensor.shape}")print(f"Output: {output.shape}")block = ConverseBlock(in_channels=64, out_channels=64,kernel_size=3,scale=1)device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")sablock = block.to(device)print(sablock)input_tensor = input_tensor.to(device)# 执行前向传播output = sablock(input_tensor)# 打印输入和输出的形状print(f"Input: {input_tensor.shape}")print(f"Output: {output.shape}")block = ConverseBlockAlphaVariant(in_channels=64, out_channels=64,kernel_size=3,scale=1)device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")sablock = block.to(device)print(sablock)input_tensor = input_tensor.to(device)# 执行前向传播output = sablock(input_tensor)# 打印输入和输出的形状print(f"Input: {input_tensor.shape}")print(f"Output: {output.shape}")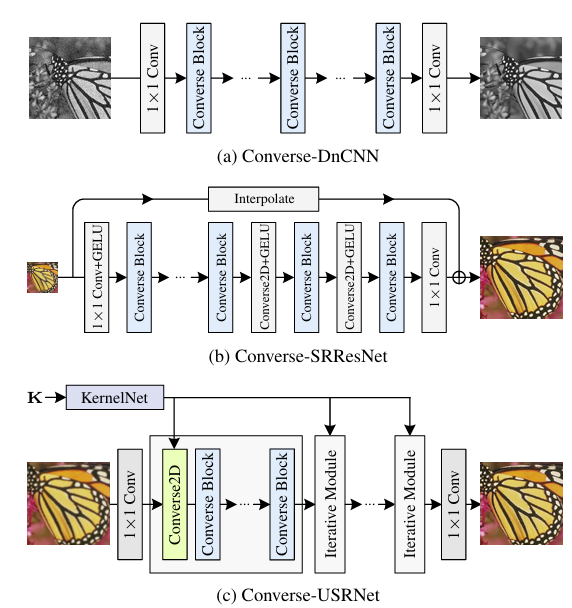
图3: 提出的基于Converse的网络架构,用于去噪(a)、超分辨率(b)和去模糊©。
7. 代码讲解
7.1 Converse2D 核心类
- 初始化:定义卷积核、尺度、填充等参数,使用Softmax初始化核权重。
forward:实现反向卷积的闭式解计算流程,包括:- 上采样输入
- 傅里叶变换计算
- 分块处理与逆变换
- 裁剪输出
splits:将张量分块为 s×ss \times ss×s 块,用于频域处理。p2o:将点扩散函数(PSF)转换为光学传递函数(OTF),用于傅里叶域计算。upsample:通过插零实现上采样。
7.2 ConverseBlock 模块
- 包含两个子模块,每个子模块包含:
- LayerNorm
- 1×1卷积扩展通道
- GELU激活
- Converse2D操作(可选上采样)
- 1×1卷积压缩通道
- 使用残差连接增强梯度流动和信息保留。
8. 结语
ConverseNet 提出了一种新颖且数学上严谨的反向卷积算子,为深度神经网络中的逆问题求解提供了新思路。其模块化设计使其易于集成到现有架构中,并在多个图像恢复任务中表现出色。代码实现充分利用了傅里叶变换的高效性,适合进一步研究与扩展。
如果需要进一步扩展或应用于其他任务(如生成模型或视频处理),可参考其设计思想与代码结构进行适配。
