C++类(上)默认构造和运算符重载
目录
- 一. 类的默认成员函数
- 1. 构造函数
- 2. 析构函数
- 3. 拷贝构造函数
- 4. 拷贝赋值运算符
- 二. 运算符重载
- 返回引用 (&)
- 返回值(非引用)
- 特殊运算符的重载
- 输入输出重载
- 三. 日期类完整代码
- Date.h
- Date .cpp
- 总结
一. 类的默认成员函数
1. 构造函数
构造函数在创建对象时自动调用,用于初始化对象的成员变量。
- 构造函数的特点:
函数名与类名相同。
没有返回值。
在实例化对象自动调用构造函数。
可以重载。
如果没有显示定义构造函数,编译器会自动生成一个无参的默认构造函数。如果显示定义了编译器不在自动生成。
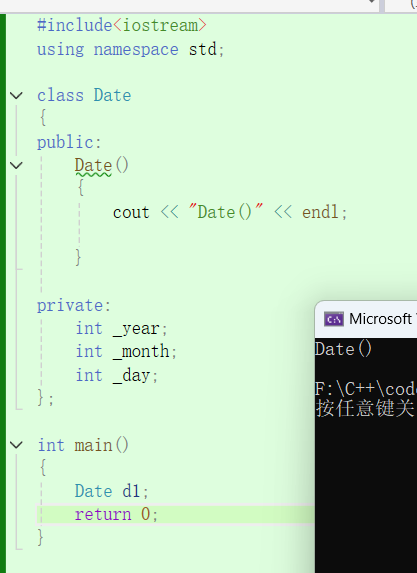
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
public:Date(){cout << "Date()" << endl;}
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};int main()
{Date d1;return 0;
}
- 全缺省函数和无参构造函数只能存在一个,虽然构成函数重载,但是在调用时会存在歧义。缺省函数应当在函数声明处写上缺省值。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 2000, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void print(){cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day <<endl;}
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};int main()
{Date d1(2025,9,1);d1.print();return 0;
}
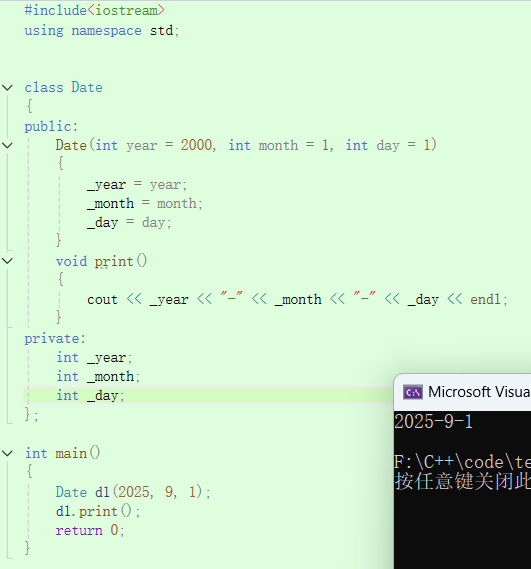
- 对于自定义类型成员函数要调用默认构造函数初始化,没有则会报错。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class Stack
{
public://进行初始化Stack(){_a = nullptr;_top = 0;_capacity = 0;}
private:int* _a;int _top;int _capacity;
};class MyQueue
{
private://会调用构造函数进行初始化,如果没有则报错Stack _pushst;Stack _popst;
};int main()
{MyQueue mq;return 0;
}
2. 析构函数
析构函数在对象生命周期结束时自动调用,用于释放资源。
在类名前面加上
~,就是析构函数,例:~Date。
一个类只能有一个析构函数。
一个局域的多个对象,析构的调用顺序是后定义的先析构。
3. 拷贝构造函数
拷贝构造函数用于一个已存在的对象进行初始化一个新的对象。
拷贝同类型的对象来初始化就是拷贝构造。
拷贝构造函数第一个参数必须是当前类类型对象的引用。
调用拷贝构造之前要传值传参,传值传参是一种拷贝,又形成一个新的拷贝构造,就形成了无穷递归了。
如果没有显示调用拷贝构造函数,编译器会自动生成拷贝构造函数,自动生成的拷贝构造函数会完成浅拷贝/值拷贝。在需要申请空间时就需要显示写拷贝构造函数。
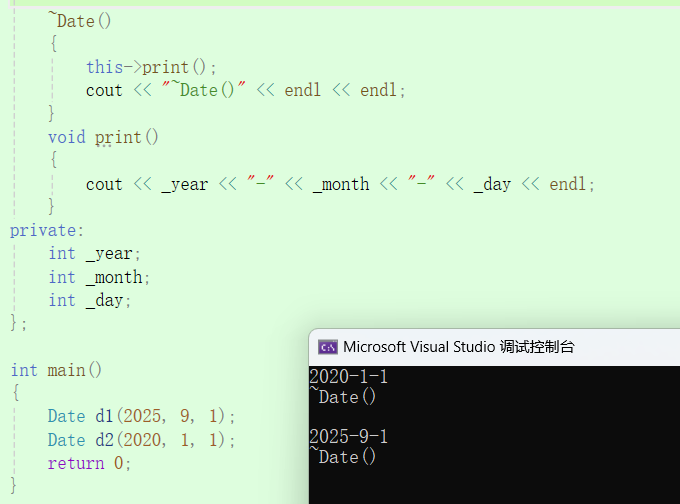
class Date
{
public://全缺省构造函数Date(int year = 2000, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}//拷贝构造Date(const Date& d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}//析构函数~Date(){this->print();cout << "~Date()" << endl << endl;}void print(){cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;}
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};int main()
{Date d1(2025, 9 ,1);//已存在的对象进行初始化一个新的对象Date d2(d1);return 0;
}
- 对于自定义类型,传值传参需要调用拷贝构造函数。

- 深拷贝与浅拷贝
浅拷贝:直接复制成员变量的值(包括指针地址)。
示例:Date 类无需深拷贝
因为 Date 类中没有指针成员,所以默认的浅拷贝是安全的。
深拷贝:为指针成员重新分配内存并复制内容。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class Stack
{
public:Stack(int n = 4){_a =(int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int));_size = 0;_capacity = n;}//深拷贝Stack(const Stack& s){//开辟新的空间_a = (int*)malloc(s._size * sizeof(int));_size = s._size;_capacity = s._capacity;//拷贝值memcpy(_a, s._a, sizeof(int) * _size);}void push(int x){if (_size == _capacity){int* tmp = (int*)malloc(2 * _capacity * sizeof(int));memcpy(tmp, _a, sizeof(int) * _size);free(_a);_a = tmp;_capacity *= 2;}_a[_size++] = x;}~Stack(){free(_a);_a = nullptr;_size = 0;_capacity = 0;}
private:int* _a;int _size;int _capacity;
};int main()
{Stack st1;st1.push(1);st1.push(2);st1.push(3);//深拷贝Stack st2(st1);return 0;
}
4. 拷贝赋值运算符
将一个已存在对象的值赋给另一个已存在的对象。
可以进行连续赋值。
在没有显示实现时也会自动生成。
默认拷贝赋值运算符行为跟默认拷贝构造函数类似。
对内置类型完成浅拷贝,对于自定义类型需要显示调用。
class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 2000, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}Date(const Date& d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}//拷贝赋值运算符Date& operator=(const Date& d){if (this != &d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}return *this;}
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};int main()
{Date d1(2025, 9, 1);Date d2(d1);Date d3(2024, 7, 21);//用于两个已存在对象之间的赋值操作d1 = d3;return 0;
}
二. 运算符重载
运算符重载是一种允许用户自定义类型(类或结构体)重新定义或赋予 C++ 内置运算符新含义的机制。其核心目的是增强代码的直观性和可表达性 ,让自定义类型的对象能像内置类型(如 int, double)一样,使用自然的运算符语法进行操作。
- 运算符重载是具有特殊名字的函数,名字是由
operator加上运算符共同构成的。和函数一样也具有返回值类型和参数列表以及函数体。 - 对于大多数运算符,传入的参数不应被函数修改。使用
const &避免不必要的拷贝,效率高。
示例:bool operator==(const Date& d) const
返回引用 (&)
用于修改左操作数的运算符,期望其返回值可作为左值。
主要包括:
- 赋值运算符
=,+=,-=,*=,/= - 前置
++和--
返回引用避免了返回时的拷贝开销,并且支持链式操作。
返回值(非引用)
用于不修改操作数、而是生成新结果的运算符。
主要包括:
- 算术运算符:
+,-,*,/ - 关系运算符:
==,!=,<,> - 后缀
++和--(必须返回值,因为需要返回旧状态)。
特殊运算符的重载
自增(++)和自减(–)
区分前后值: 通过一个形参int来区分。
- 前置应进行自增/自减操作,然后返回对象自身的引用。
自增:Date& operator++();自减:Date& operator--(); - 后置应首先创建当前对象状态的一个临时对象,然后对自身进行自增/自减操作,最后返回哪个临时对象。
自增:Date operator++(int);自减:Date operator--(int);
输入输出重载
输出流 ostream和输入流istream 是C++标准库中定义的类,分别用于处理输出和输入操作。头文件<iostream>是标准输入输出系统的基础。
- 为什么不推荐在类内重载
语法问题:操作数的顺序
输入输出运算符的重载需要特定的参数顺序
<<的左操作数必须是ostream&
>>的左操作数必须是istream&
错误的示范:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{public:Date(int year = 2000, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}// 错误的重载方式(成员函数)// 此时左操作数是当前对象,右操作数是ostream// 使用方式会变成:Date << cout,不符合习惯ostream& operator<<(ostream& out) {out << _year << "/" << _month << "/"<<_day;return os;}
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};int main() {Date d(2025, 9, 1);d << cout; //奇怪的调用方式:对象 << 流// 我们想要的是:cout << 对象return 0;
}
因为成员函数的局限性,成员函数的第一个隐式参数是this指针,这意味着左操作数必须是类的对象,但是这样违背了cout << d 的自然语法
正确的做法:在类外定义(但是会有访问权限问题)
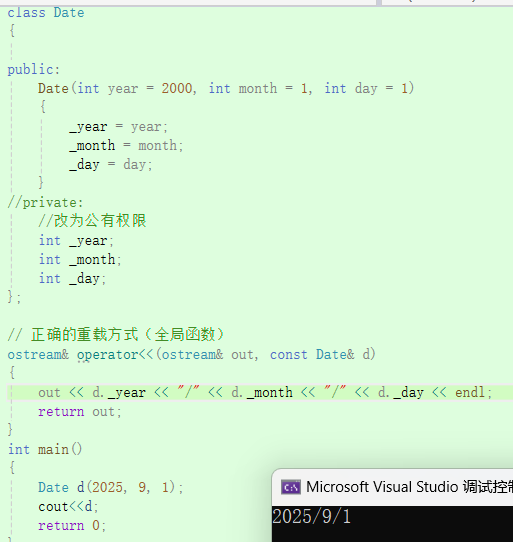
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 2000, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};
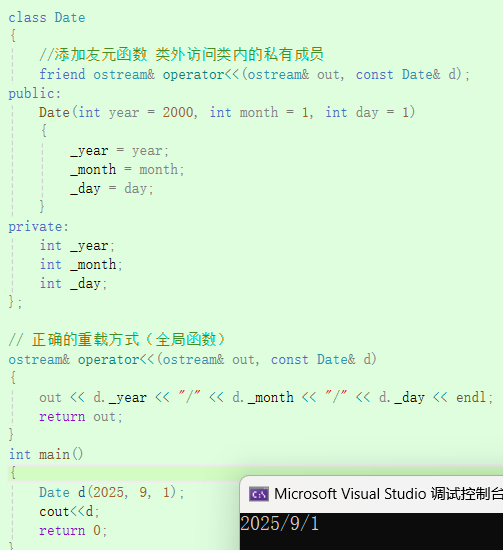
// 正确的重载方式(全局函数)
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d)
{out << d._year << "/" << d._month << "/" << d._day;return out;
}int main() {Date d(2025, 9, 1);cout << d;return 0;
}
解决方案:
-
把访问的成员变量从私有改为公有。
-
使用友元函数。
友元函数: 不是类的成员函数,但可以访问类的所有成员(包括私有成员)
声明位置: 在类内部声明,使用 friend 关键字
定义位置: 在类外部定义,不需要 类名:: 限定
友元函数的特点:
不是成员函数: 没有 this 指针
突破封装: 可以访问类的私有和保护成员
单向关系: A 是 B 的友元 ≠ B 是 A 的友元
输入与输出也是使用相同的方法将 ostream 改成 istream
示例:
istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);
以下运算符不能被重载
-
作用域运算符
::
它的功能是在编译期确定一个成员所属的命名空间或者类。这个操作必须在编译时完全确定。 -
成员访问运算符
.
用于直接访问对象的成员。它的行为必须是直接且高效的。如果允许重载,这会使得代码的行为极难理解,并严重阻碍编译器优化。 -
成员指针访问运算符
.*
这个运算符用于通过成员指针来访问特定对象的成员。它们与类的内存布局和指针算术密切相关,是相对底层且特殊的操作。允许重载会让本已复杂的成员指针语法变得更加晦涩难懂,并且可能引入更多风险。 -
条件运算符
?:
这是语言中唯一一个接受三个操作数的运算符。它的行为是语言标准强制规定的。允许重载它可能会破坏短路求值的特性,从而影响程序的控制流和效率。通常可以用函数调用或 if-else 语句来替代实现类似功能,因此没有重载的必要性。 -
sizeof
用于在编译时计算一个类型或对象的大小(以字节为单位)。这是一个纯粹的编译期操作,其结果由编译器根据类型系统和平台决定,不允许有任何运行时或自定义的行为。
三. 日期类完整代码
Date.h
class Date
{
public://输出流重载friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);//输入流重载friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);//打印日期void print() const;//全缺省构造函数Date(int year = 1998, int month = 1, int day = 1);//返回一个月的天数int GetMonthDay(int year, int month){assert(month > 0 && month < 13);static int arr[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };if (month == 2 && (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 || year % 400 == 0)){return 29;}return arr[month];}//判断是否有非法输入bool CheckDate();//重载==运算符bool operator ==(const Date& d) const;//重载!=运算符bool operator!=(const Date& d) const;//重载>运算符bool operator >(const Date& d) const;//重载>=运算符bool operator >=(const Date& d) const;//重载<运算符bool operator <(const Date& d) const;//重载<=运算符bool operator <=(const Date& d) const;//+天数Date operator +(int day) const;//+=天数Date& operator +=(int day);//-天数Date operator -(int day) const;//-=天数Date& operator -=(int day);//d1 - d2int operator -(const Date& d) const;//++d1 前置Date& operator ++();//d1++ 后置Date operator ++(int);//--d1 前置Date& operator --();//d1-- 后置Date operator --(int);private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};
//输出流重载
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);
//输入流重载
istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);
Date .cpp
#include"Date.h"//判断是否有非法输入
bool Date::CheckDate()
{if (_month < 1 || _month > 12 || _day < 1 || _day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){return false;}else{return true;}
}//构造函数
Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
{_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;if (!CheckDate()){cout << "日期非法: ";print();exit(1);}}//打印日期
void Date::print() const
{cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;
}//重载==运算符
bool Date::operator ==(const Date& d) const
{return (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day == d._day);
}//重载!=运算符
bool Date::operator!=(const Date& d) const
{return !(*this == d);
}//重载>运算符
bool Date::operator >(const Date& d) const
{return !(*this <= d);
}
//重载>=运算符
bool Date::operator >=(const Date& d) const
{return !(*this < d);
}
//重载<运算符
bool Date::operator <(const Date& d) const
{if (_year < d._year){return true;}else if (_year == d._year){if (_month < d._month){return true;}else if (_month == d._month){return _day < d._day;}}return false;
}//重载<=运算符
bool Date::operator <=(const Date& d) const
{return *this < d || *this == d;
}//+=天数
Date& Date::operator +=(int day)
{if (day < 0){return *this -= (-day);}_day += day;while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);_month++;if (_month == 13){_month = 1;_year++;}}return *this;
}//+天数
Date Date::operator +(int day) const
{Date tmp = *this;tmp += day;return tmp;
}//-=天数
Date& Date::operator -=(int day)
{if (day < 0){return *this += (-day);}_day -= day;while (_day <= 0){--_month;if (_month == 0){ _month = 12;--_year; }_day+=GetMonthDay(_year, _month);}return *this;
}//-天数
Date Date::operator -(int day) const
{Date tmp = *this;tmp -= day;return tmp;
}//d1 - d2
int Date::operator -(const Date& d) const
{int flag = 1;Date max = *this;Date min = d;if (*this < d){max = d;min = *this;flag = -1;}int day = 0;while (min != max){//前置++减少拷贝++min;++day;}return day * flag;
}//++d1
Date& Date::operator ++()
{return *this += 1;
}
//d1++
Date Date::operator ++(int)
{Date tmp = *this;++*this;return tmp;
}//--d1 前置
Date& Date::operator --()
{return *this -= 1;
}
//d1-- 后置
Date Date::operator --(int)
{Date tmp = *this;--*this;return tmp;
}//输出流重载
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d)
{out << d._year << "-" << d._month << "-" << d._day;return out;
}
//输入流重载
istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d)
{while (1){cout << "请输入日期:";in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;if (!d.CheckDate()){cout << "日期非法,请重新输入:" << endl;d.print();cout << "请重新输入!!!" << endl;}else{break;}}return in;
}
总结
本章到这里就结束了。相信大家对类这一块有了更深入的理解了。C++通过默认构造函数管理着对象的整个生命周期,确保了资源的自动与正确管理。运算符重载则在此基础上,赋予了自定义对象与内置类型一样的直观操作。本篇文章到这里就结束了,感谢大家的阅读,你们的点赞收藏加关注就是博主最大的动力。
C++世界的大门——基础知识总结
力扣(LeetCode) ——101. 对称二叉树(C语言)
排序(Sort)方法详解(冒泡、插入、希尔、选择、堆、快速、归并
