数字图像处理-图像编码
1 实验题目
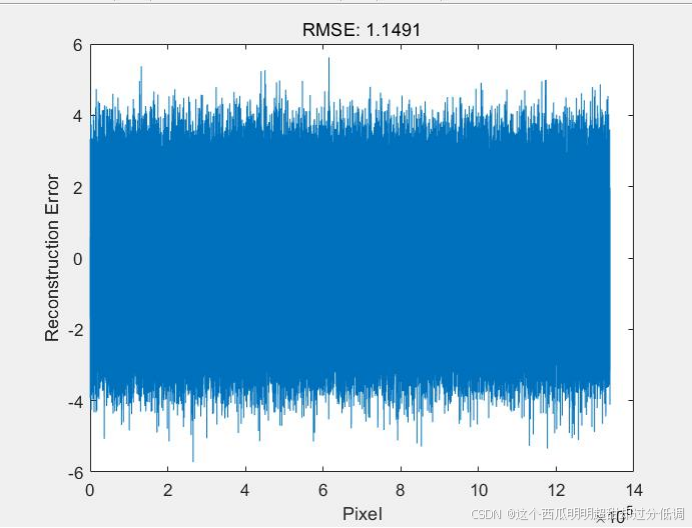
对图像用离散余弦变换进行块编码和解码,并分析块大小的对于细节的影响影响, 给出 RMSE 重建误差曲线。
2 程序源代码
clc;
close all;
clear all;
% 读取图像
img = imread('photo.jpg');
% 将图像转换为灰度图像
gray_img = rgb2gray(img);
% 将图像分成 8x8 的块
blocks = im2col(gray_img, [8 8], 'distinct');
% 对每个块进行 DCT 变换
dct_blocks = dct2(blocks);
% 对 DCT 系数进行量化
quantized_blocks = round(dct_blocks / 4);%定义量化步长为 4
% 对量化后的 DCT 系数进行反量化
dct_blocks = quantized_blocks * 4;
% 对每个块进行 IDCT 变换
idct_blocks = idct2(dct_blocks);
% 将块重新组合成图像
reconstructed_img = col2im(idct_blocks, [8 8], size(gray_img), 'distinct');
% 计算重建误差
error = double(gray_img) - reconstructed_img;
% 计算均方根误差(RMSE)
rmse = sqrt(mean(error(:).^2));
figure;
subplot(121),imshow(quantized_blocks),title('块编码');
subplot(122),imshow(reconstructed_img),title('块解码');
% 绘制重建误差曲线
figure;
plot(error(:));
xlabel('Pixel');
ylabel('Reconstruction Error');
title(['RMSE: ', num2str(rmse)]);3 运行结果

块大小对细节的影响,较小的块大小可以更好地保留图像细节,因为小块更能够 适应图像中的细微变化。然而,较小的块大小也会增加编码和解码的计算量,并且可 能导致一些块边界的伪影。较大的块大小可以减少计算量,但可能会导致细节的丢失。