SME-Econometrics
数据的来源

Experimental data and non-experimental data
实验数据(experimental data)
非实验数据(non-experimental / observational data)
1. 数据获取方式
-
实验数据:研究者可以主动操控自变量(比如设置不同的处理组/对照组),然后观察因变量的反应。
- 例子:在实验室里控制肥料用量,比较作物产量差异。
-
非实验数据:研究者不能操控自变量,只能记录现实中自然发生的数据。
- 例子:统计不同收入家庭的消费水平,但无法人为随机分配“收入高低”。
2. 可重复性
-
实验数据:可以在相同条件下反复试验,保证结果的可验证性。
-
非实验数据:条件不可控,通常不可重复,只能依赖统计方法去控制偏差。
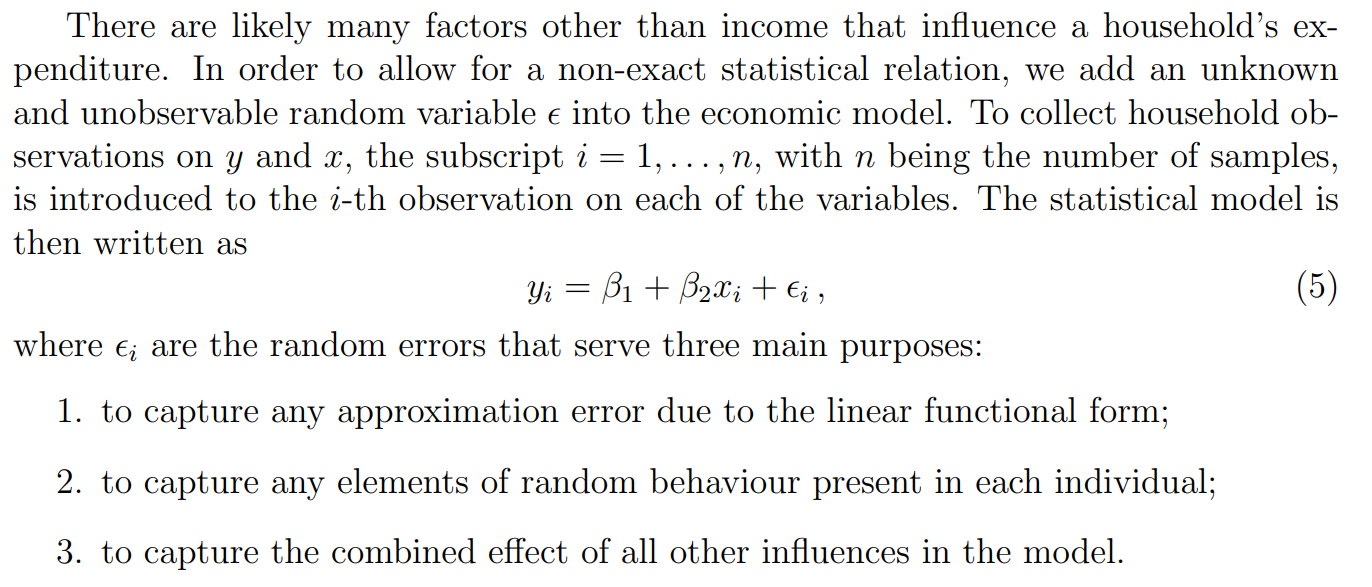
Regression 来源(种子)
-
the offspring of larger than average size parents tended to be smaller than their parents
- 翻译:比平均值更大的父母的后代,往往比父母小一些。
-
the offspring of smaller than average size parents tended to be larger than their parents
- 翻译:比平均值更小的父母的后代,往往比父母大一些。
Population Regression 术语

Example

Population Regression 函数
定义
For simplicity, we assume that it is reasonable to model the relationship as a linear function, which is also known as the population regression function: y=E(y∣x)=β1+β2xy = E(y|x) = β_1 + β_2xy=E(y∣x)=β1+β2x where β1β_1β1 and β2β_2β2 are unknown parameters.
More specifically, β1β_1β1 denotes the intercept parameter (i.e., the level of household expenditure on food when the income x is zero), while β2β_2β2 represents the slope parameter.
性质
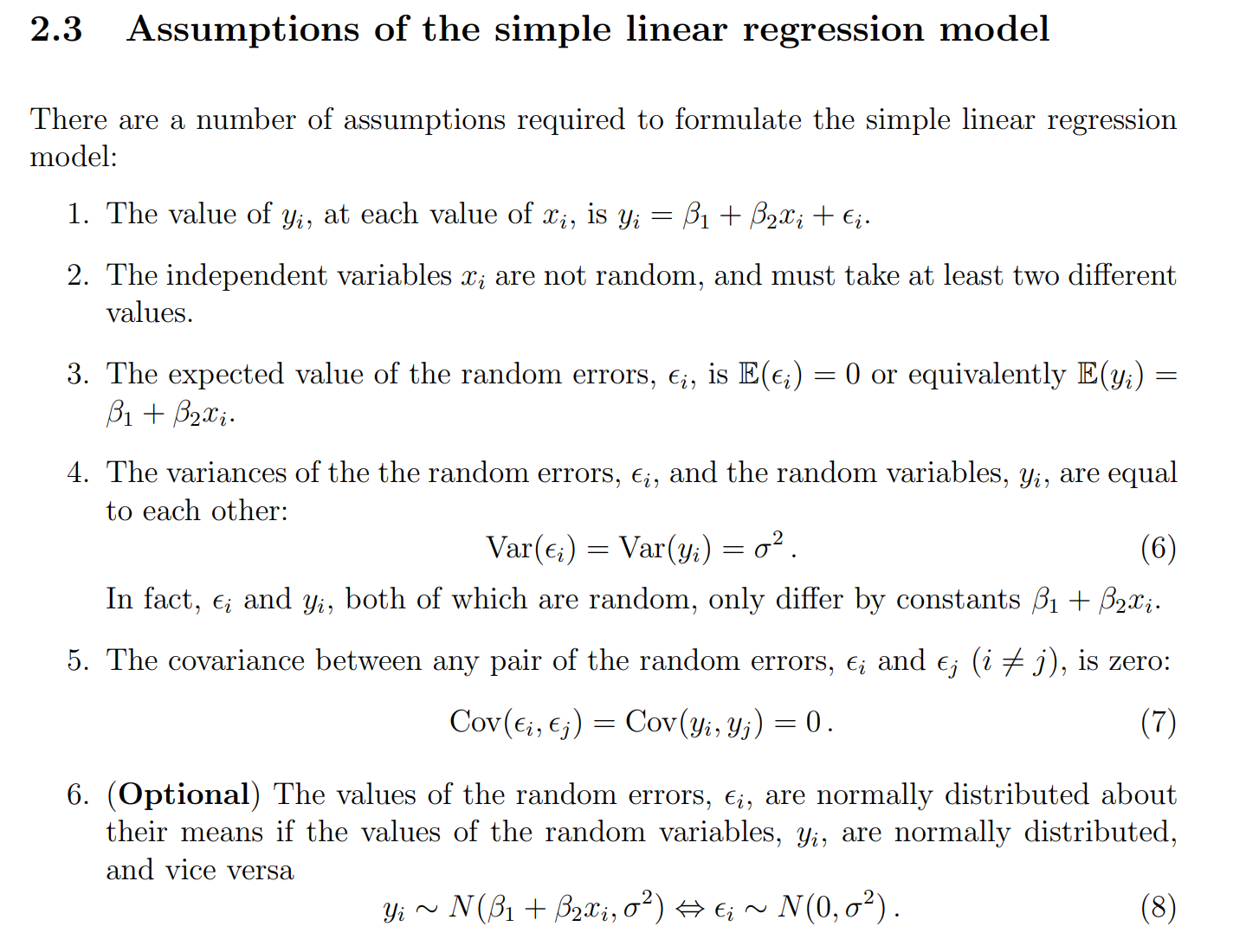
性质5:
涉及到 “独立 (independence)” 和 “不相关 (uncorrelated)” 的关系:
1. 独立 ⇒ 不相关
-
如果两个随机变量 X,Y独立,那么一定有:
Cov(X,Y)=0\text{Cov}(X,Y) = 0Cov(X,Y)=0
-
原因是:
Cov(X,Y)=E[(X−E[X])(Y−E[Y])]\text{Cov}(X,Y) = E[(X - E[X])(Y - E[Y])]Cov(X,Y)=E[(X−E[X])(Y−E[Y])]
独立时 E[XY]=E[X]E[Y]E[XY]=E[X]E[Y]E[XY]=E[X]E[Y],所以协方差为 0。
2. 不相关 ⇏ 独立
-
协方差为零只说明 线性关系不存在,但并不意味着两者没有其他更复杂的依赖。
-
比如:
-
设 X∼U(−1,1)X \sim U(-1,1)X∼U(−1,1),取Y=X2Y = X^2Y=X2。
-
显然 XXX和 YYY不独立(因为知道 X 的值就能推断 Y 的范围)。
-
但是计算协方差:Cov(X,Y)=0\text{Cov}(X,Y) = 0Cov(X,Y)=0。
-
-
说明它们可能有 非线性关系,但线性相关性为零。
