英伟达Jetson Orin NX-YOLOv8s目标检测模型耗时分析
1 基础信息
测试模型:YOLOv8s
测试环境:Jetson Orin NX 16GB+Python+TensorRT
不同测试功率:25W、MAX功率
图像输入分辨率:1920×1080
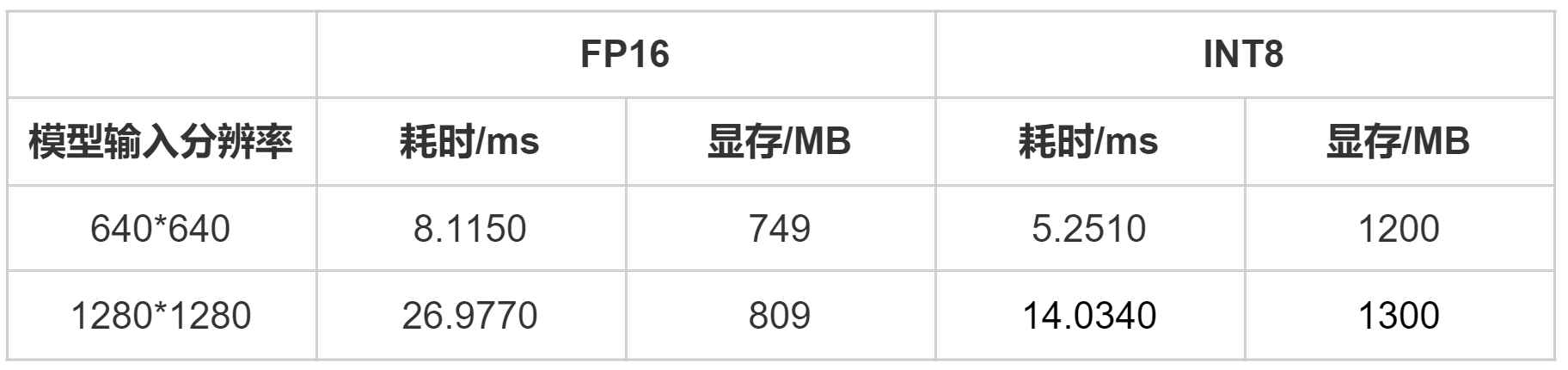
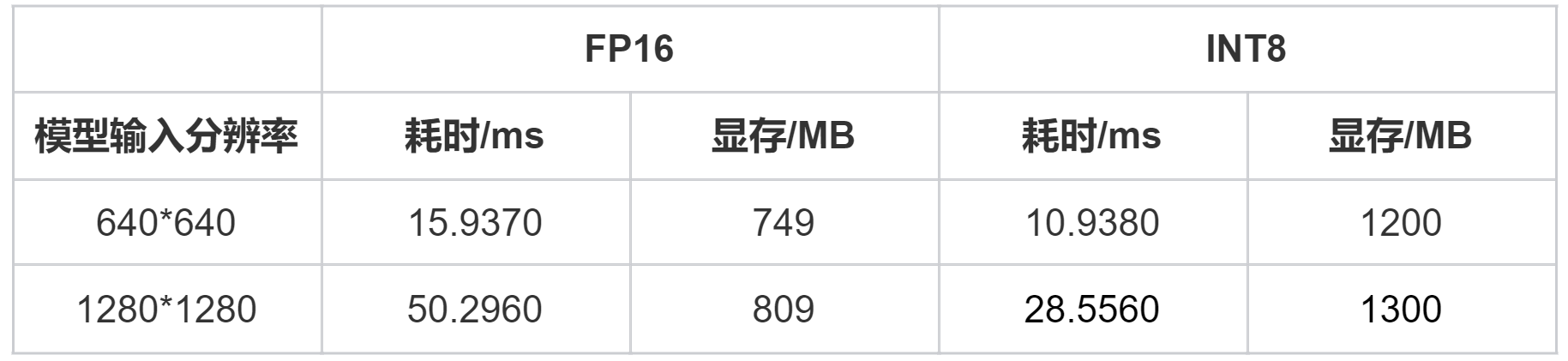
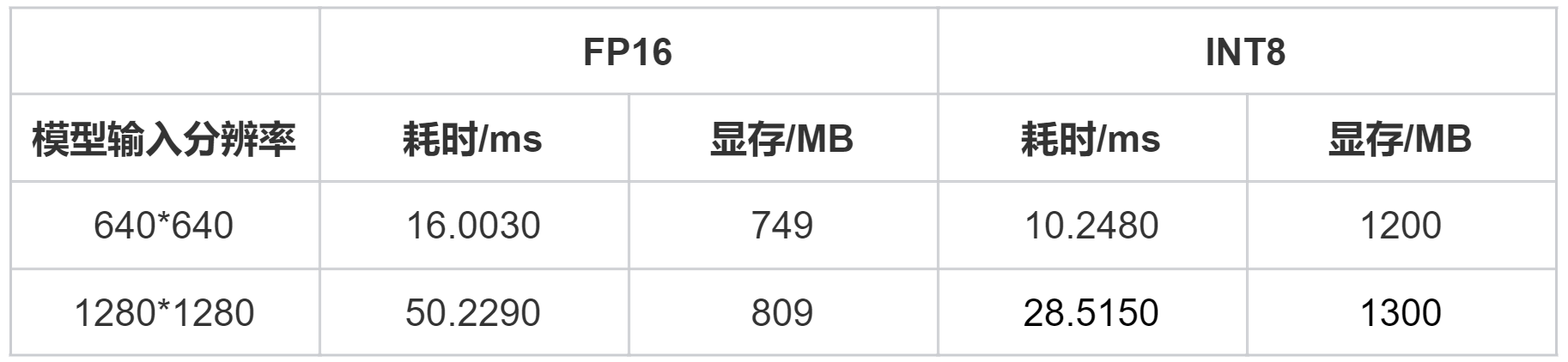
不同模型输入分辨率:640×640、1280×1280
不同模型参数类型:FP16、INT8
测试方法:热启动后,推理100次求平均。
基础库版本:jetpack=5.1.3, torch-gpu=2.1.0, torchvision=0.16.0, ultralytics=8.3.146
2 TensorRT转换命令
2.1 方式1:trtexec转换
FP16:
# 静态
trtexec --onnx=det.onnx --saveEngine=det.trt --fp16
# 动态
trtexec --onnx=det.onnx --minShapes=images:1x3x640x640 --optShapes=images:2x3x1280x1280 --maxShapes=images:4x3x3840x3840 --saveEngine=det.trt --fp16 --device=0
Int8:【需要校准集】
略
2.2 方式2:YOLO代码导出
FP16:
from ultralytics import YOLO
# trt
model = YOLO('yolov8s.pt')
# FP16
out = model.export(format="engine", imgsz=1280, dynamic=True, verbose=False, batch=1, workspace=2, half=True)
Int8:【需要校准集】
from ultralytics import YOLO
# trt
model = YOLO('yolov8s.pt')
# INT8--需要加载校准集,对应coco.yaml中的val
out = model.export(format="engine", imgsz=1280, dynamic=True, verbose=False, batch=1, workspace=2, int8=True, data="coco.yaml")
3 模型推理具体耗时与分析
# 查询目前的板子功耗模式
sudo nvpmodel -q
# 设置MAXN功率模式
sudo nvpmodel -m 0
# 设置25W功率模式
sudo nvpmodel -m 3# 开启性能模式
sudo jetson_clocks
3.1 功率:MAX
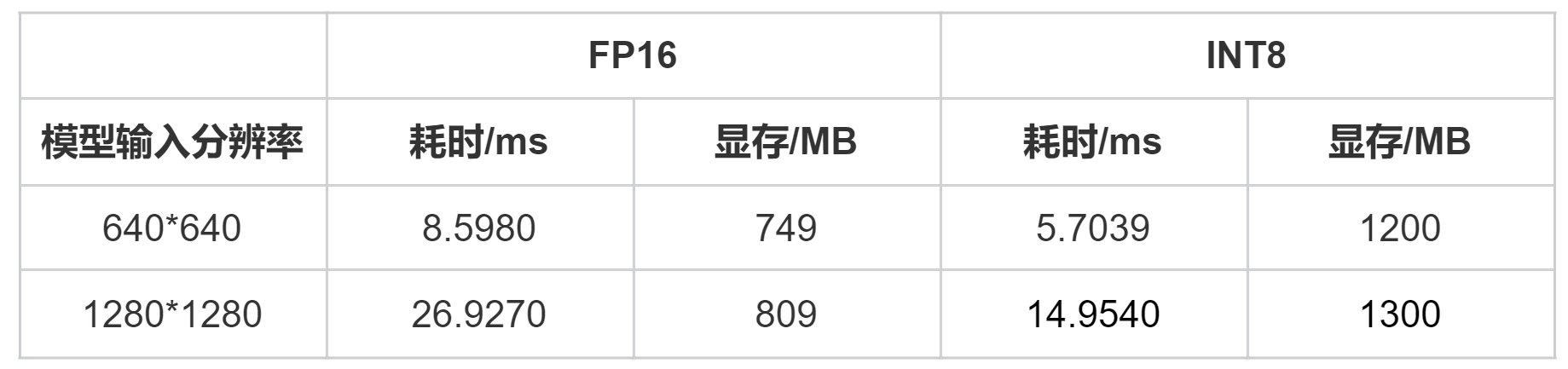
3.1.1 640*640–FP16
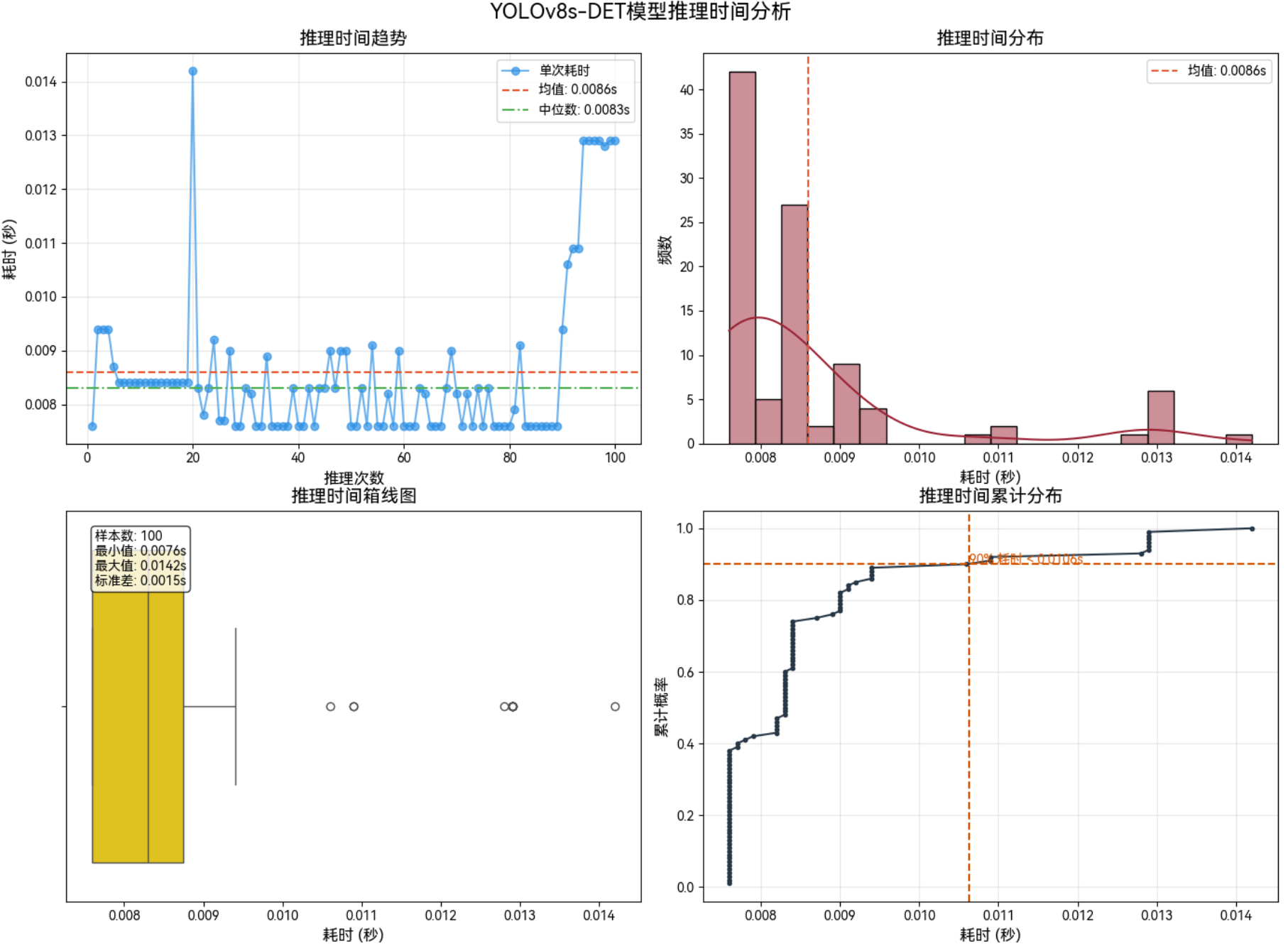
3.1.2 640*640–Int8
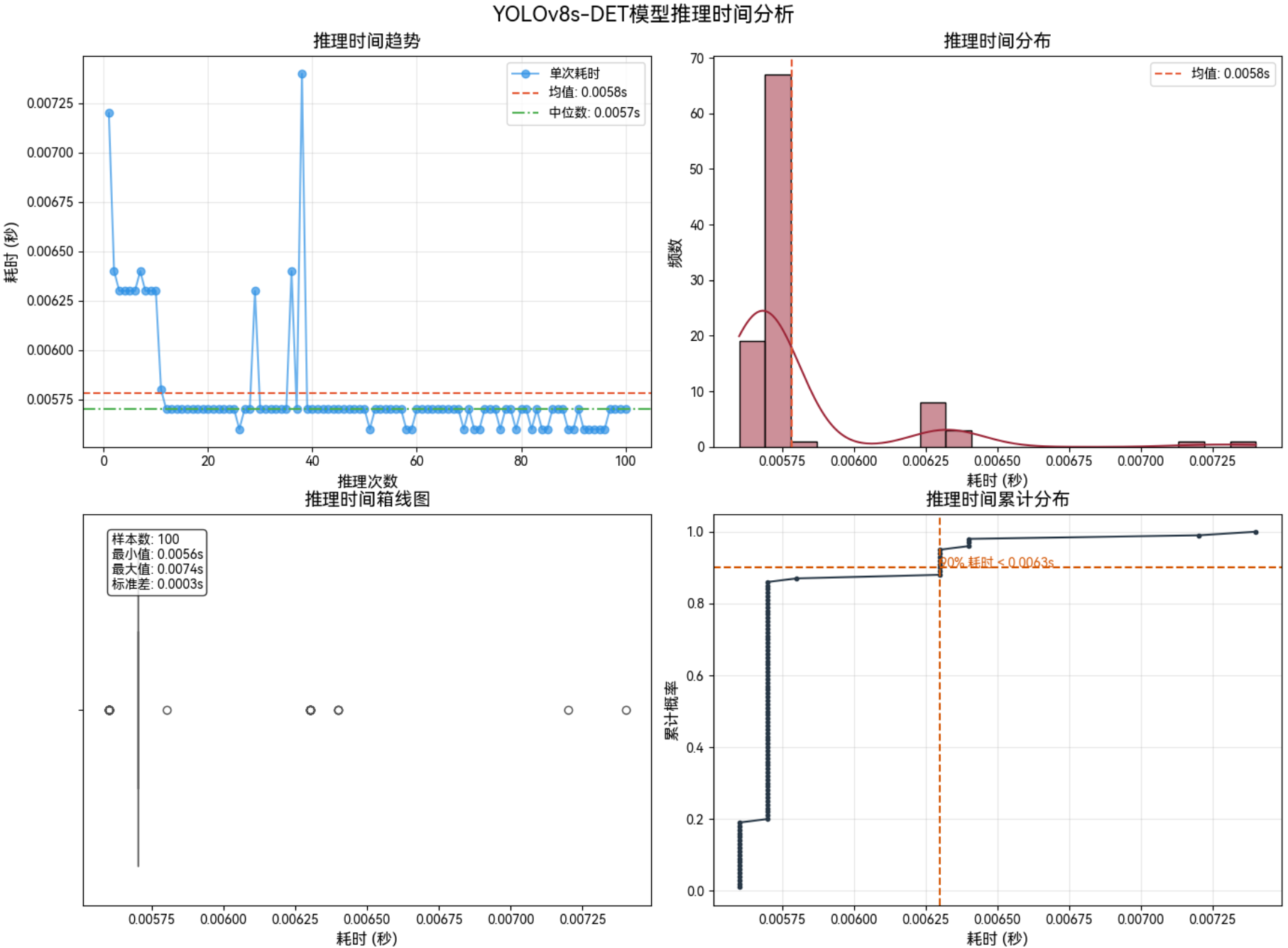
3.1.3 1280*1280–FP16
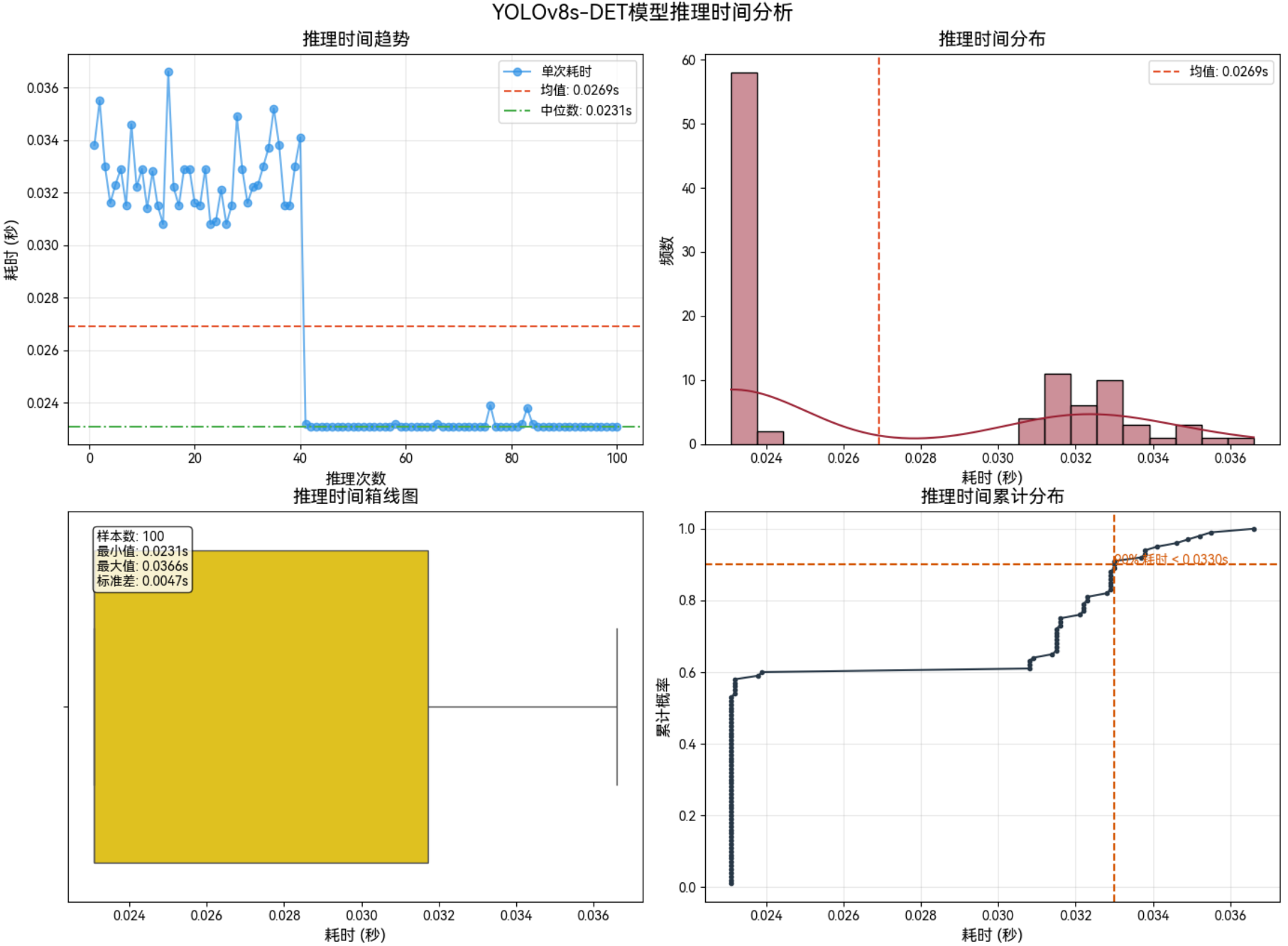
3.1.4 1280*1280–Int8
3.2 功率:MAX+性能模式
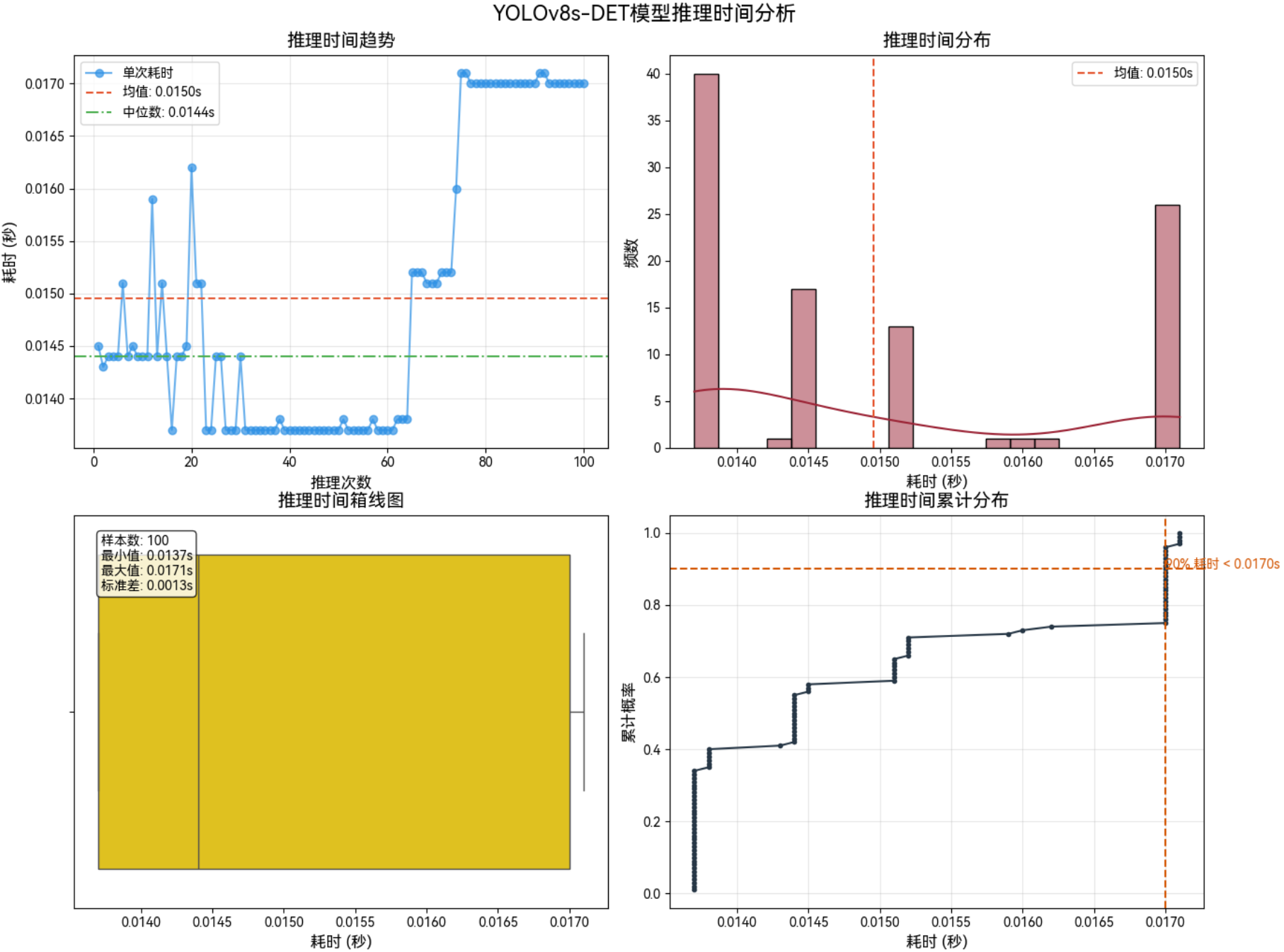
3.2.1 640*640–FP16
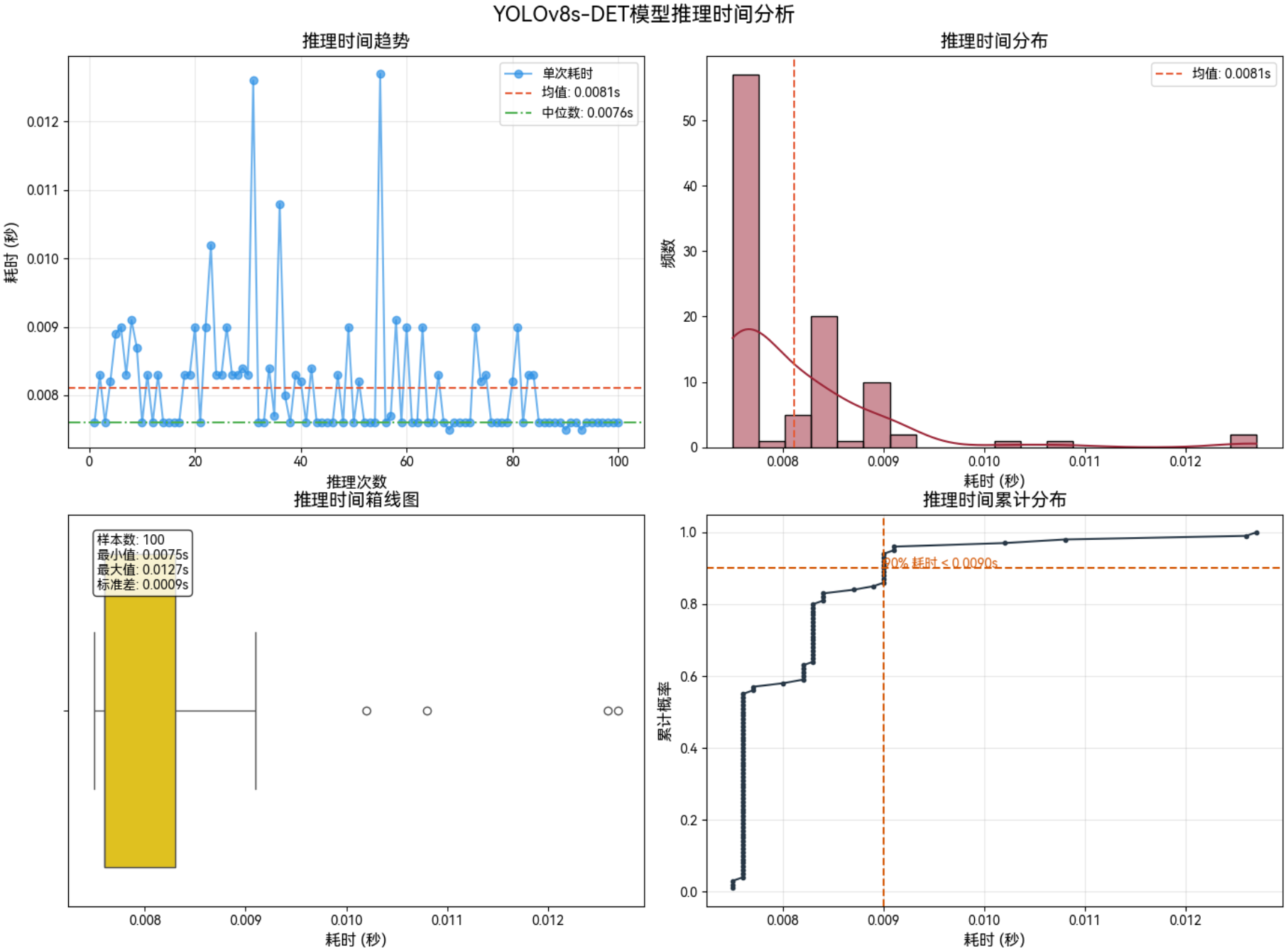
3.2.2 640*640–Int8
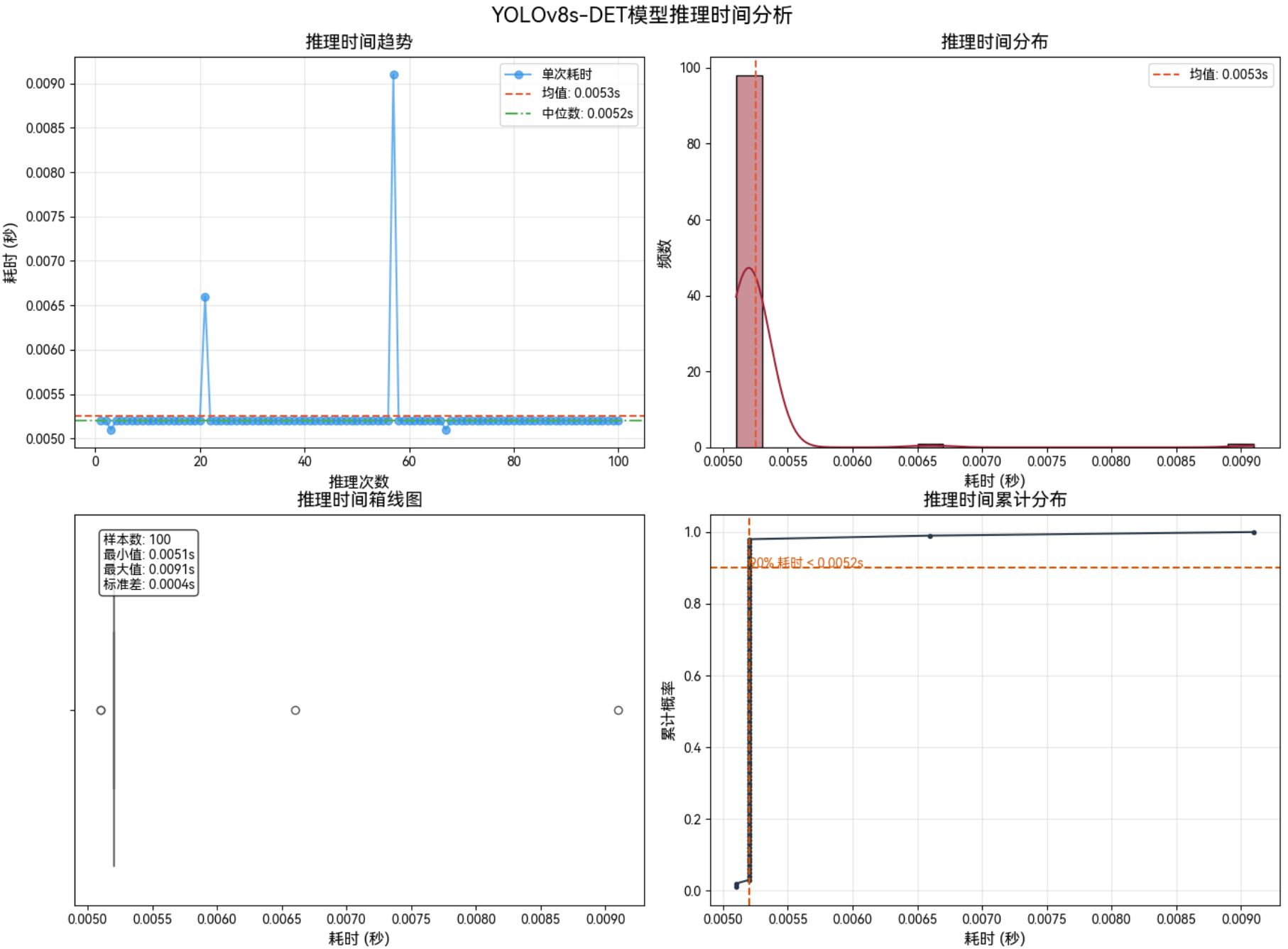
3.2.3 1280*1280–FP16
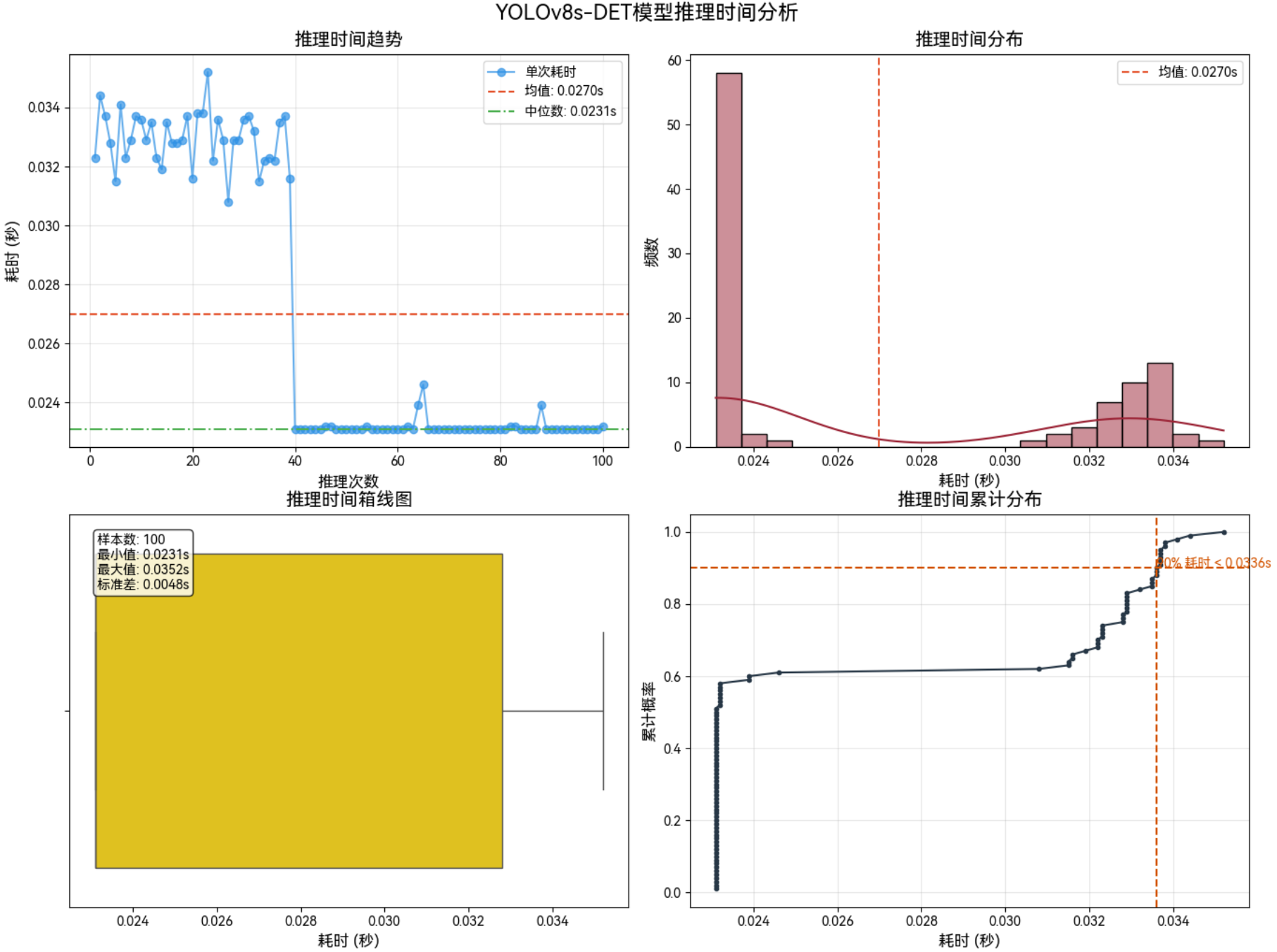
3.2.4 1280*1280–Int8
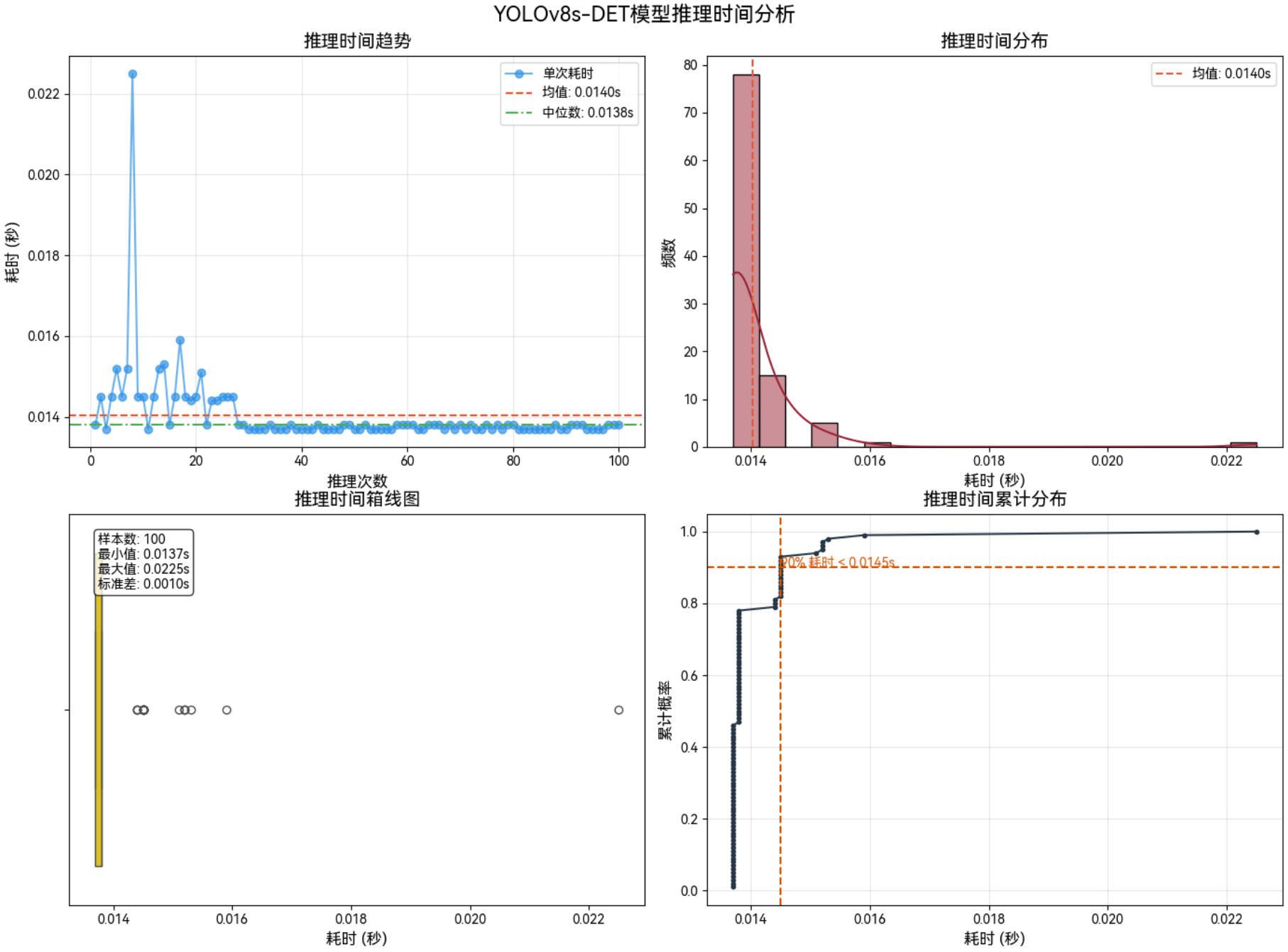
3.3 功率:25W
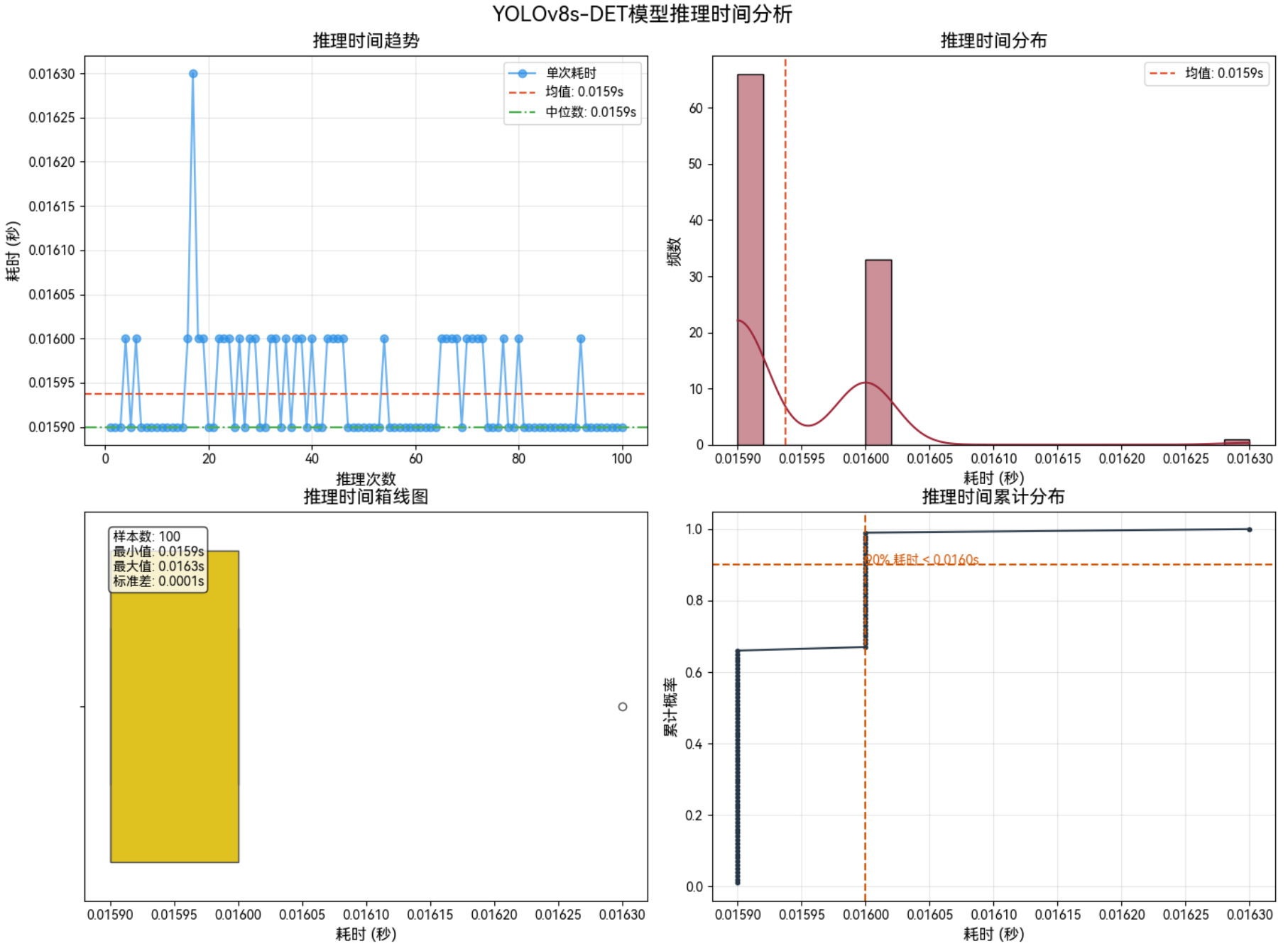
3.3.1 640*640–FP16
3.3.2 640*640–Int8
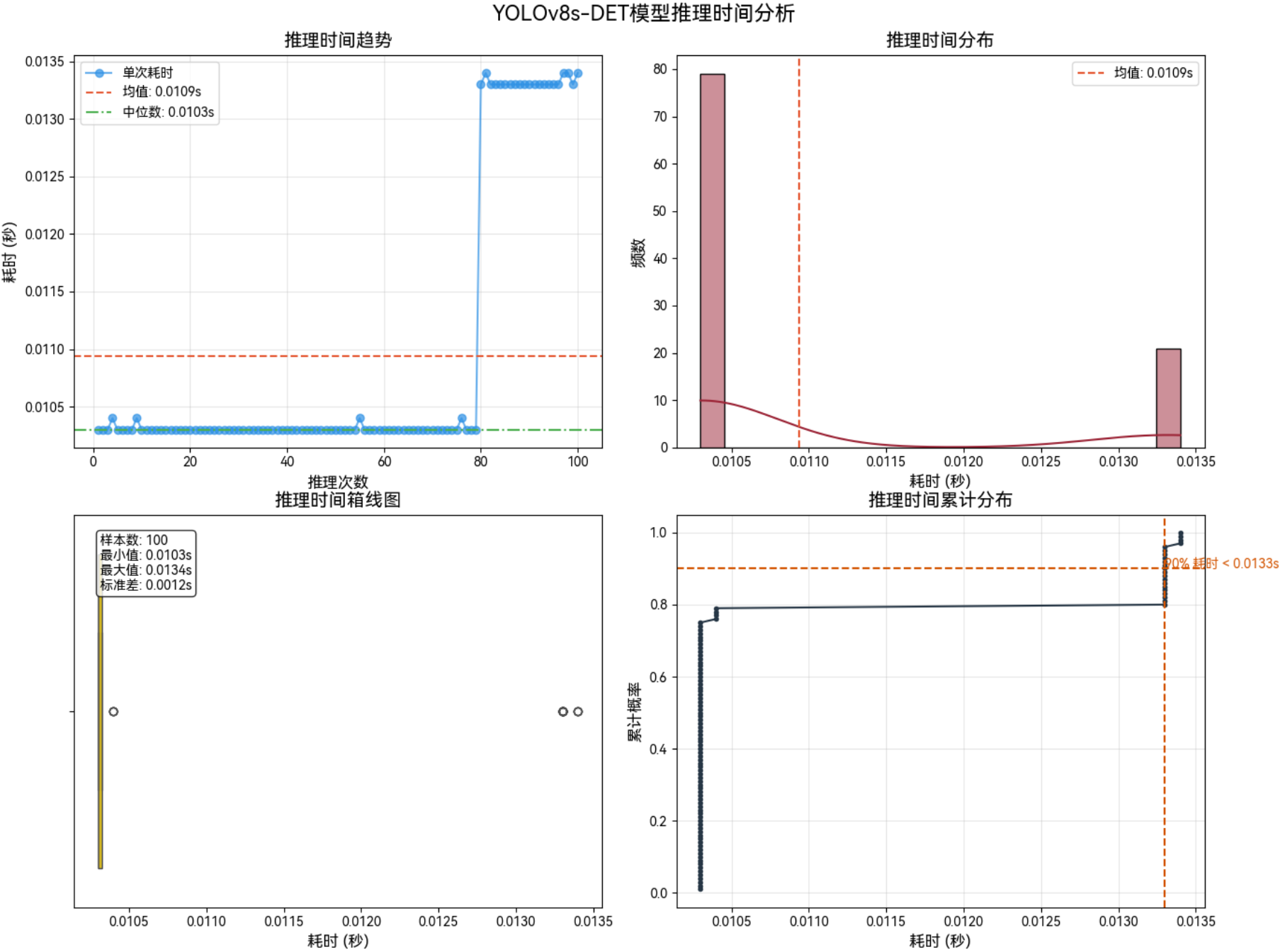
3.3.3 1280*1280–FP16
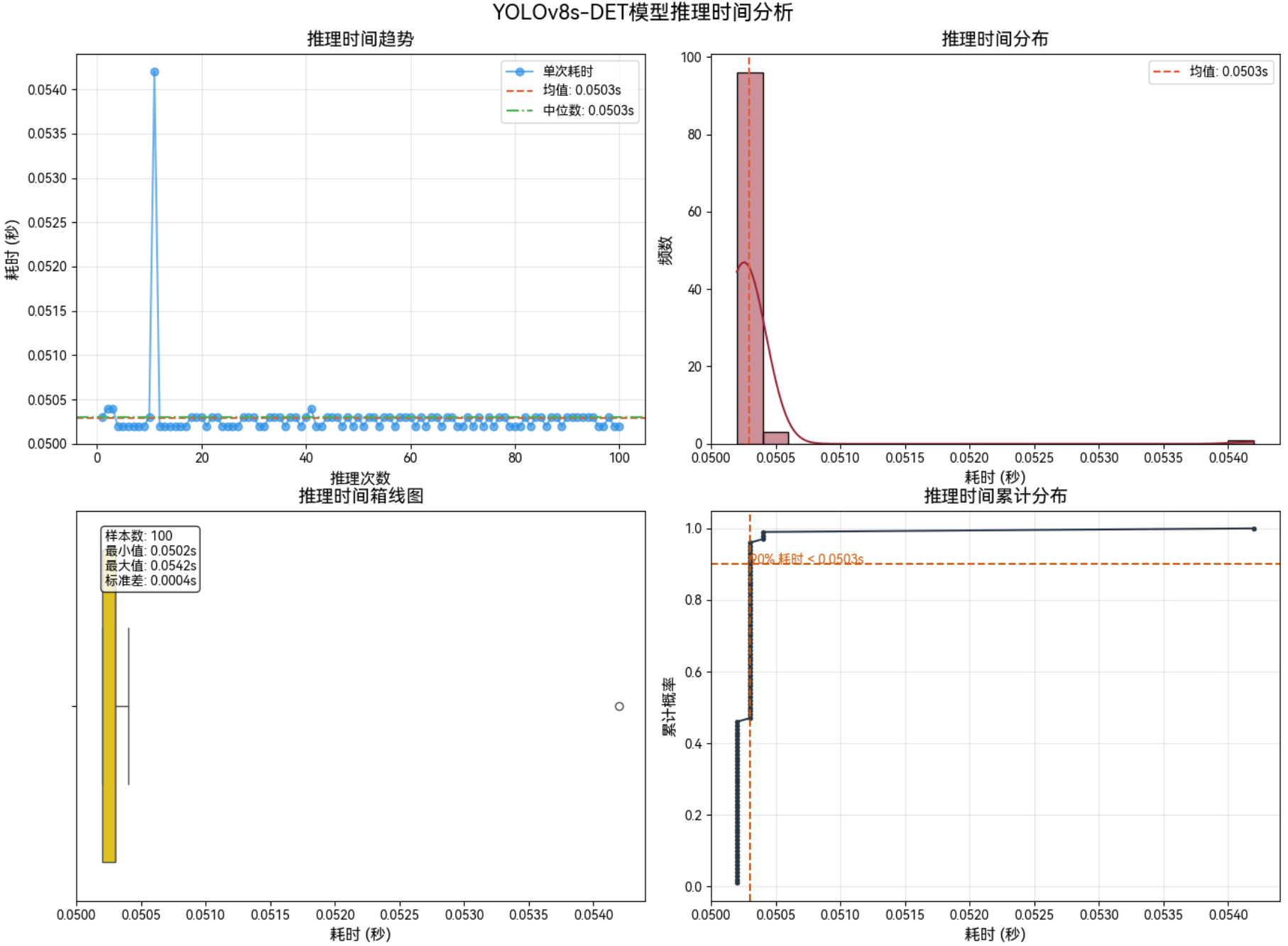
3.3.4 1280*1280–Int8
3.4 功率:25W+性能模式
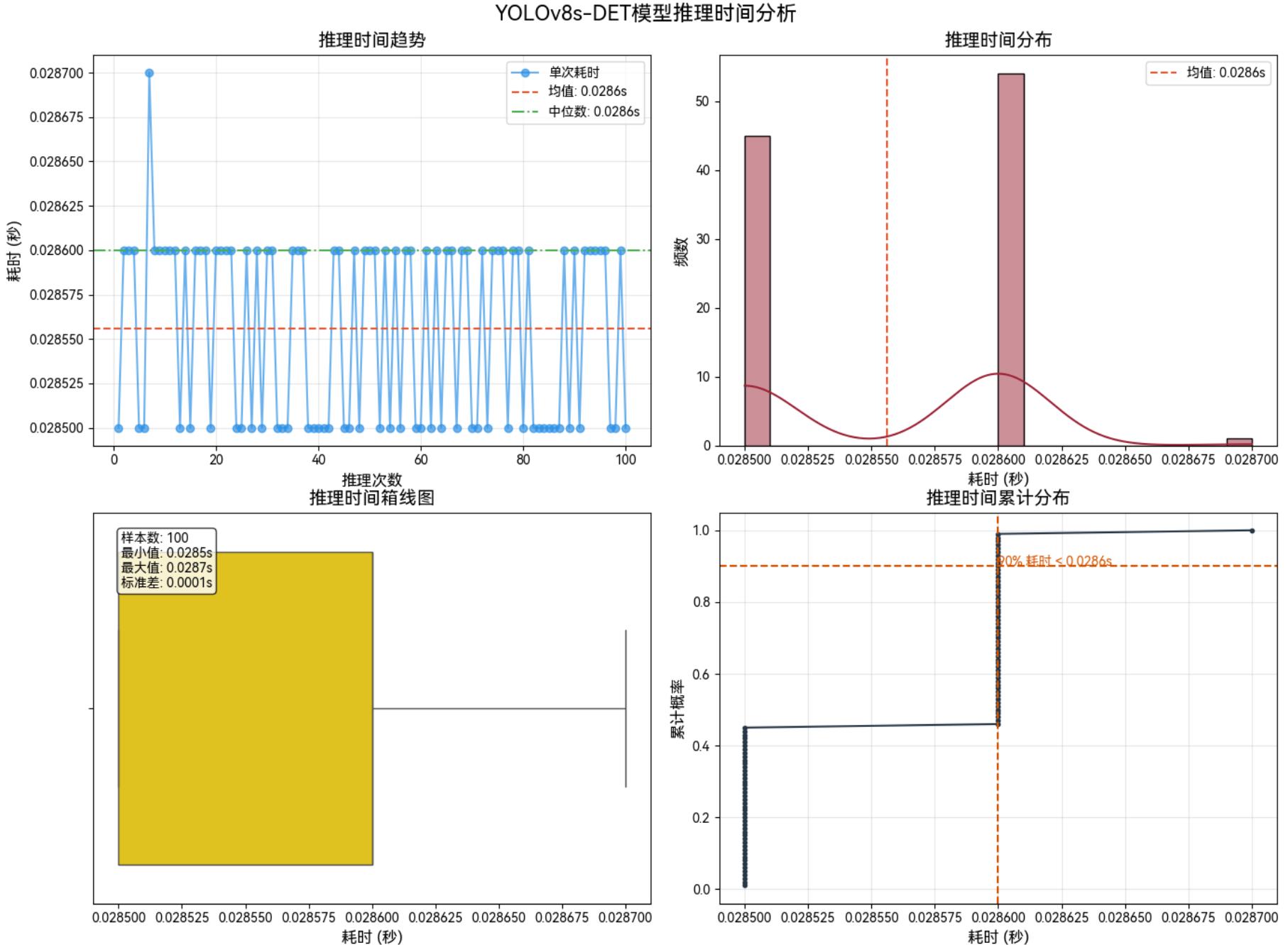
3.4.1 640*640–FP16
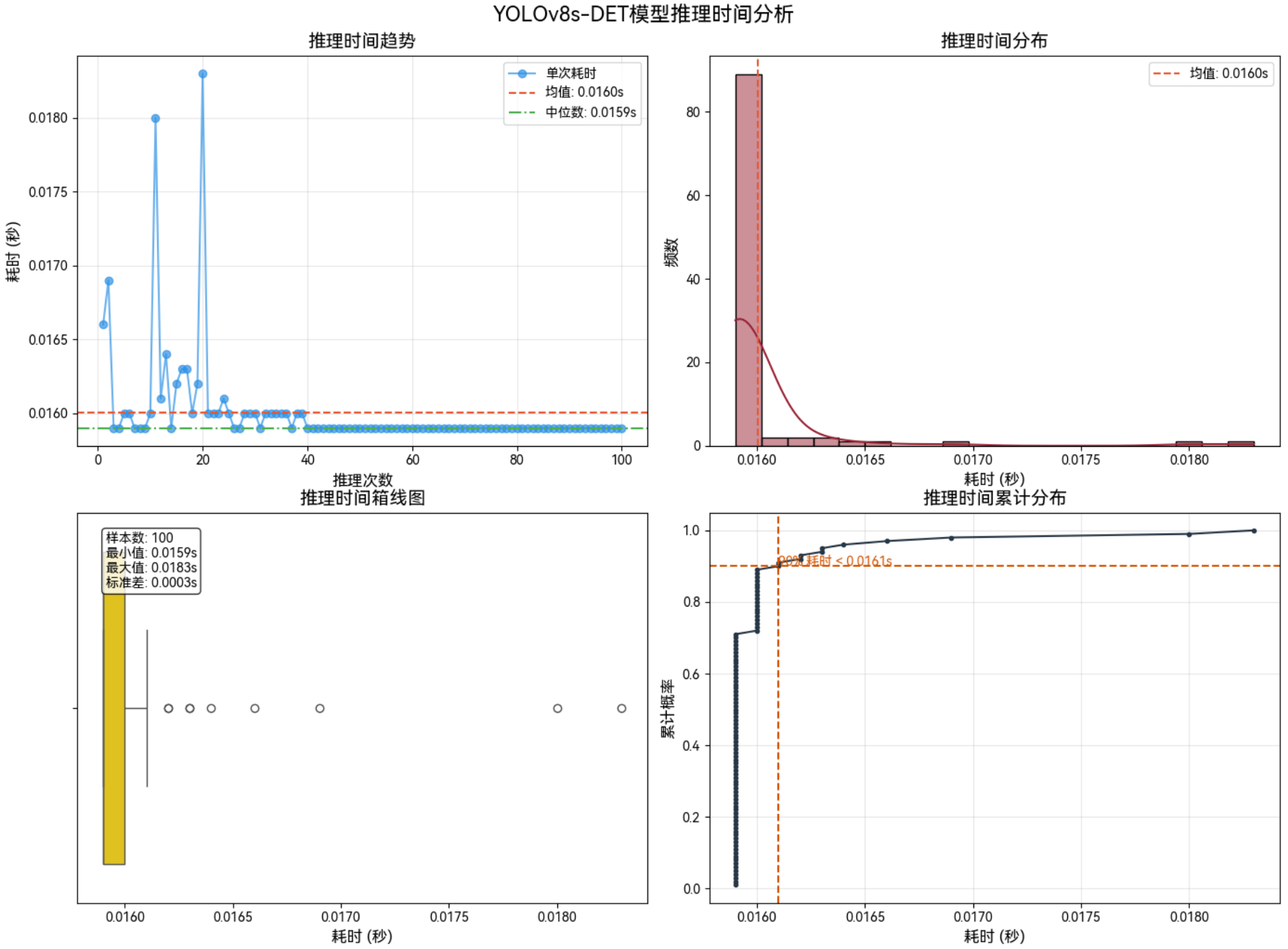
3.4.2 640*640–Int8
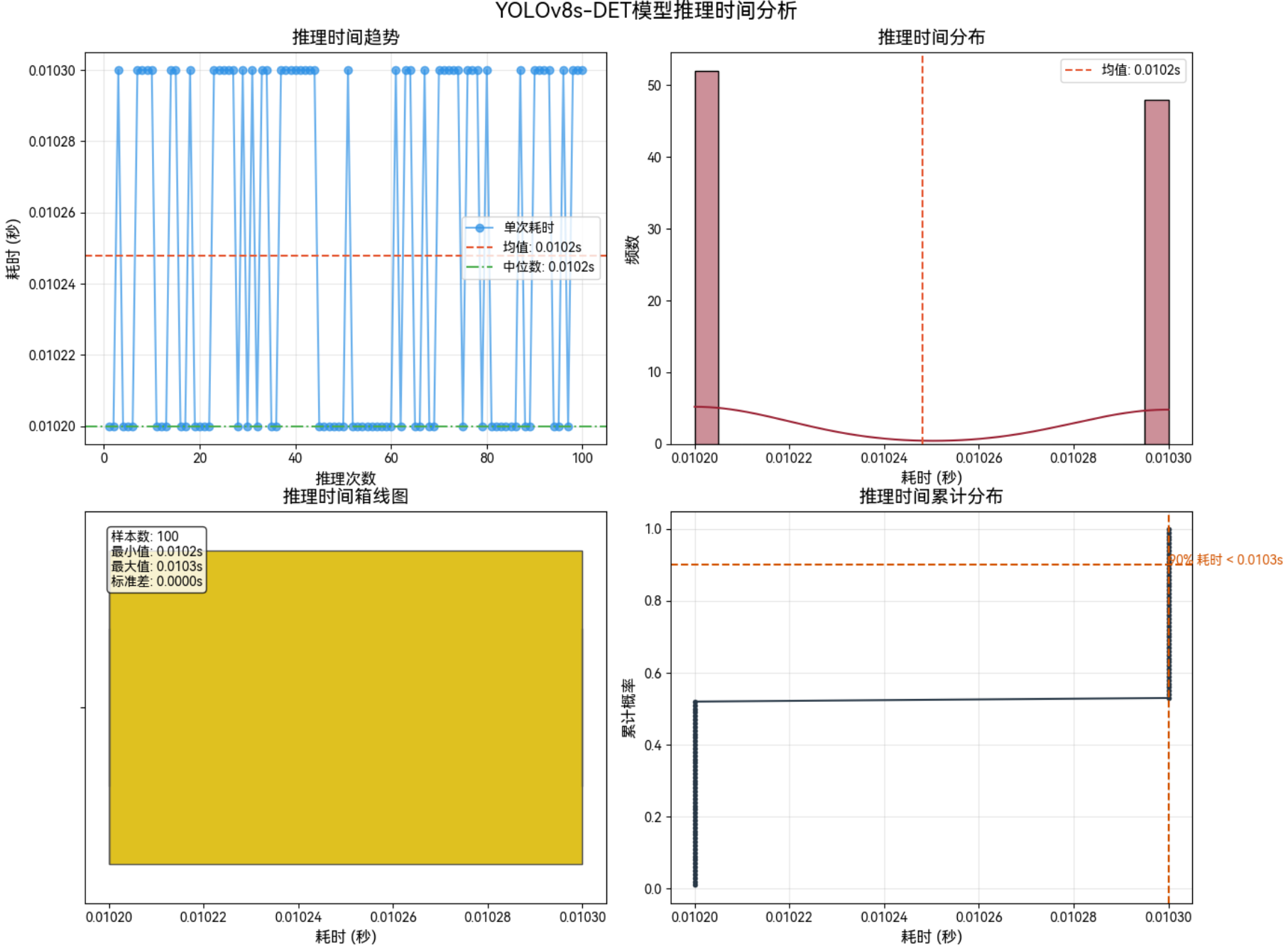
3.4.3 1280*1280–FP16
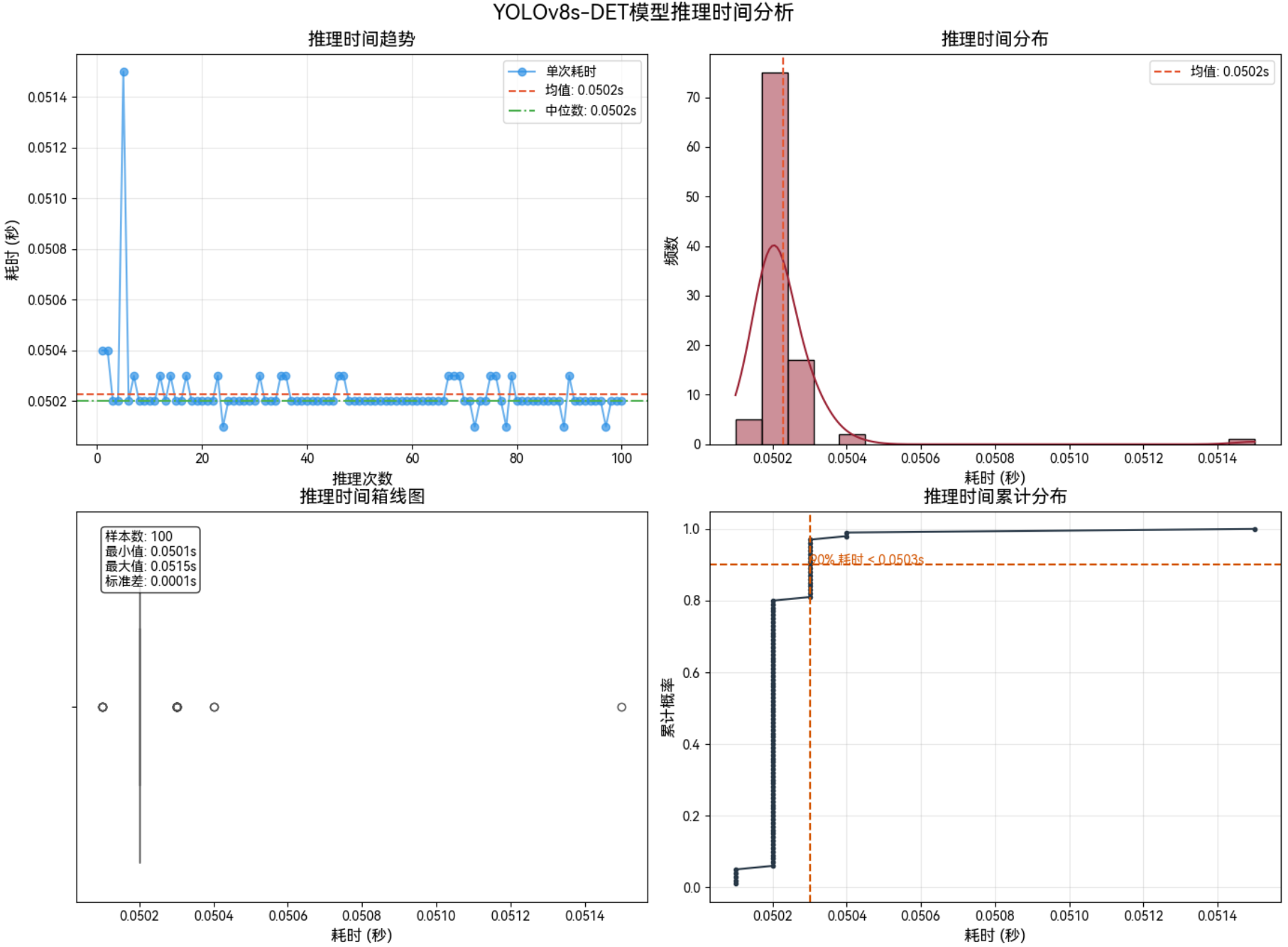
3.4.4 1280*1280–Int8
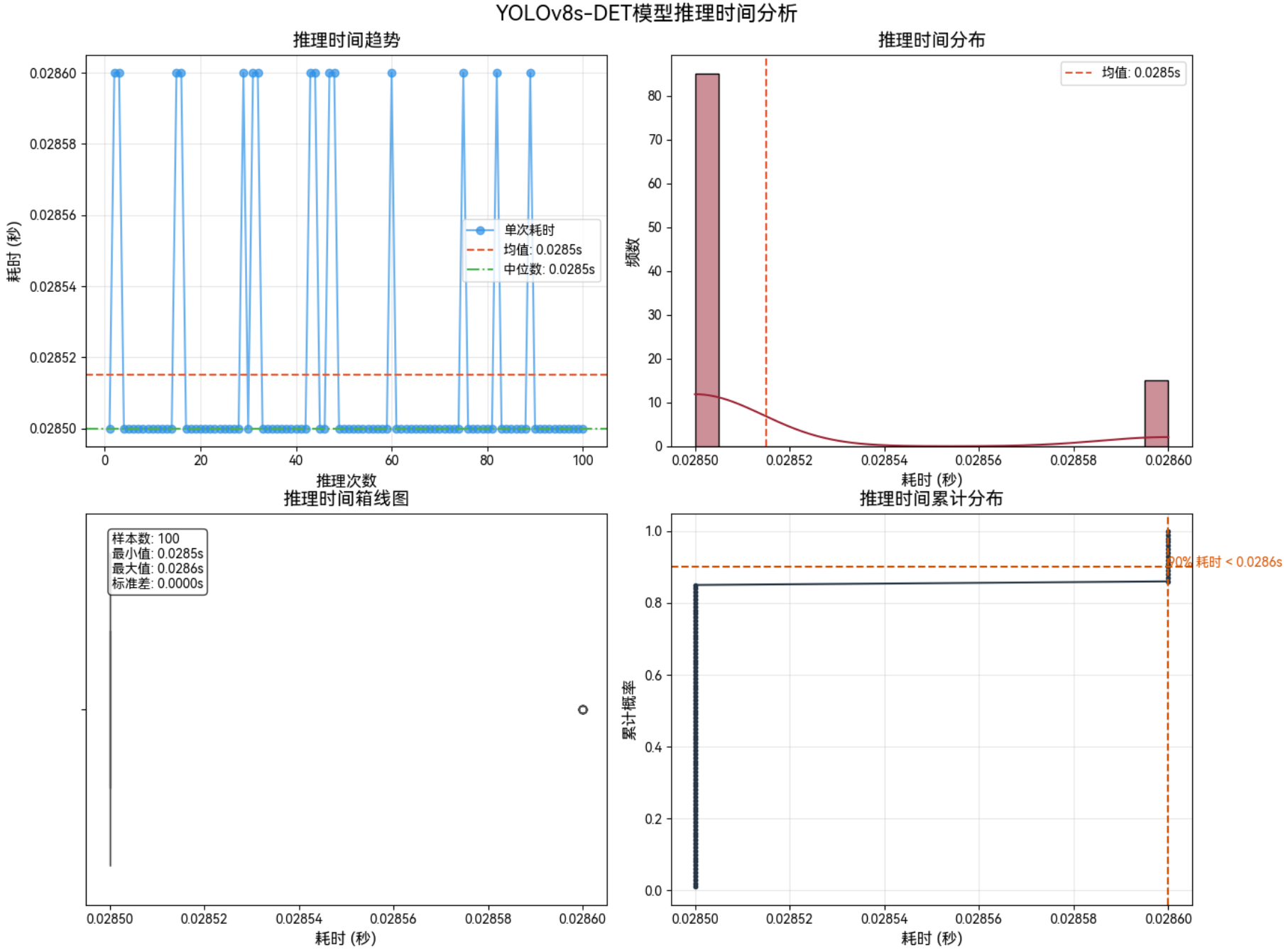
4 模型前后处理耗时分析
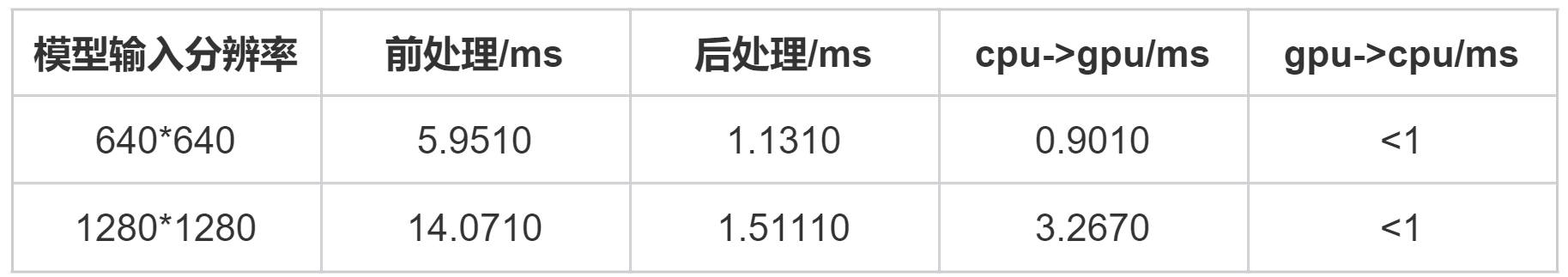
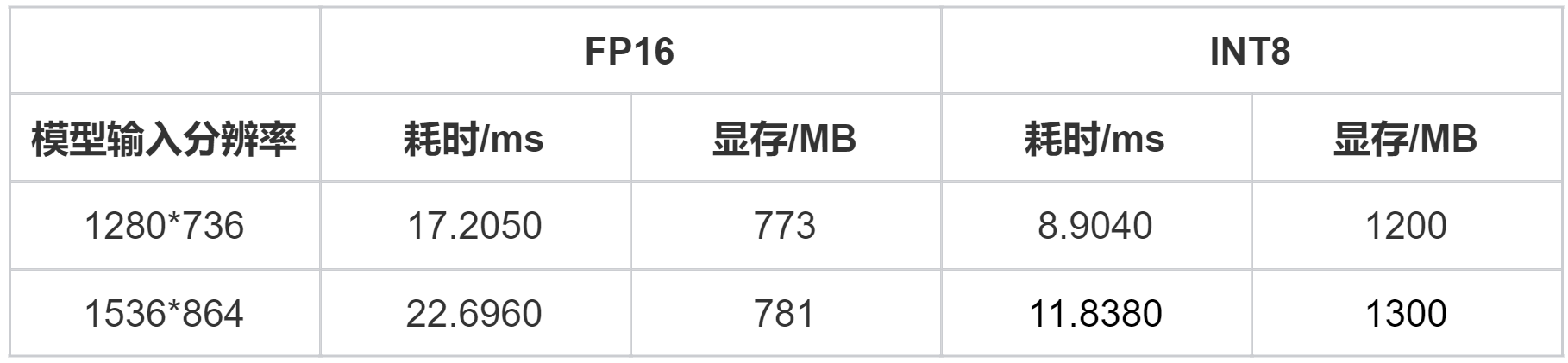
5 其它特殊分辨率
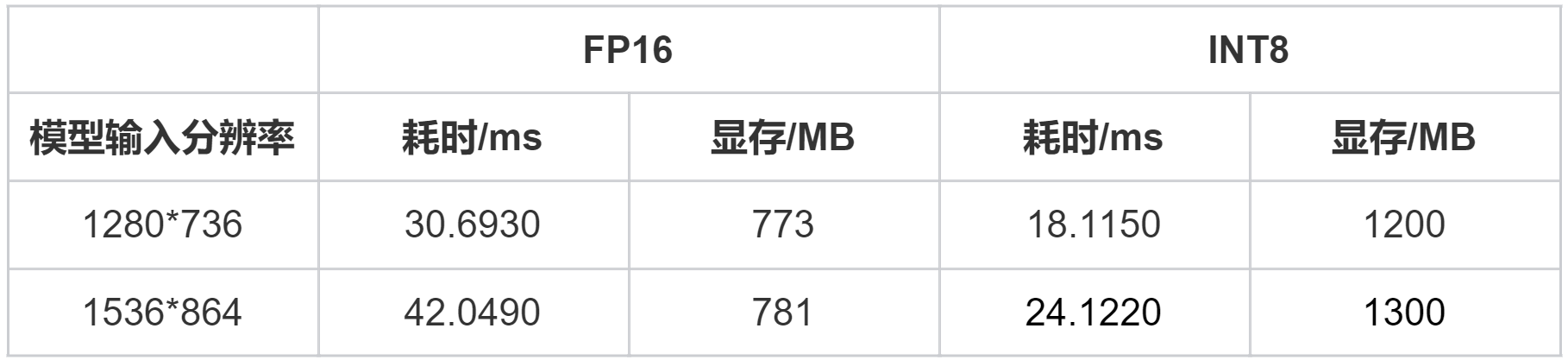
5.1 25W
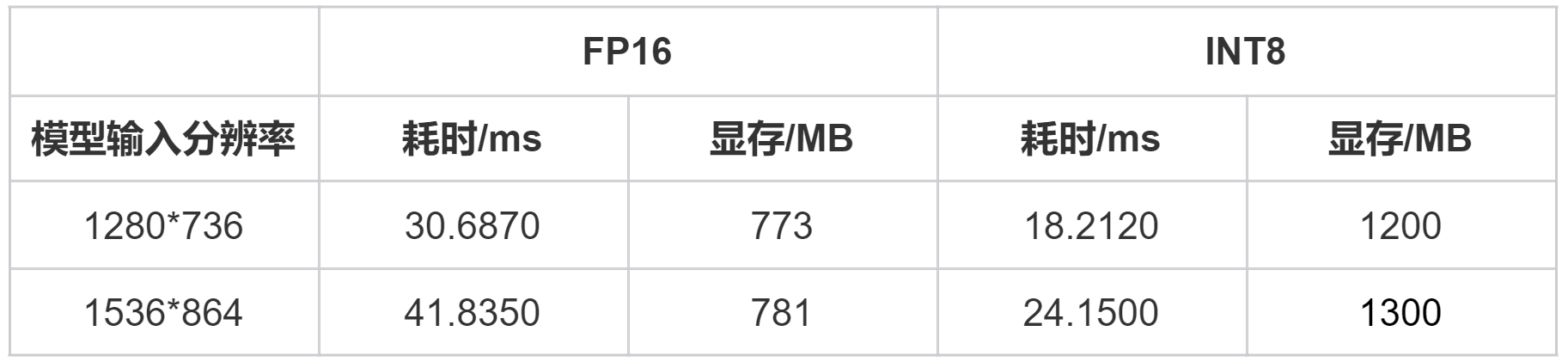
5.2 25W+性能模式
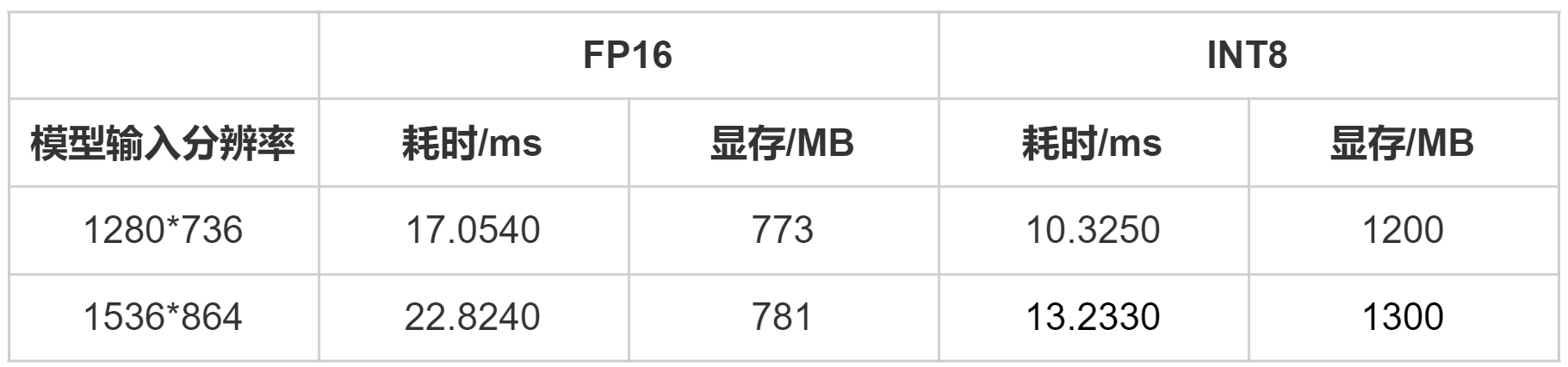
5.3 MAX
5.4 MAX+性能模式
6 运行代码
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore", category=DeprecationWarning)import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
import tensorrt as trt
from collections import OrderedDict, namedtuple
import jsonimport cv2
import timeimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
import osdef load_harmonyos_font(font_path="HarmonyOS_Sans_SC_Regular.ttf"):"""加载HarmonyOS字体"""if not os.path.exists(font_path):print(f"警告: 未找到字体文件 {font_path},将使用默认字体")return Nonetry:font = FontProperties(fname=font_path)# 测试字体是否可用plt.text(0.5, 0.5, "测试", fontproperties=font)plt.close()print("HarmonyOS字体加载成功")return fontexcept Exception as e:print(f"字体加载失败: {e},将使用默认字体")return Nonedef visualize_inference_times(time_list, title="STDC推理时间可视化分析", font_path="HarmonyOS_Sans_SC_Regular.ttf"):"""可视化推理时间列表,支持加载HarmonyOS字体参数:time_list: 包含每次推理时间的列表(单位:秒)title: 图表标题font_path: HarmonyOS字体文件路径"""# 加载字体harmony_font = load_harmonyos_font(font_path)# 计算统计指标times = np.array(time_list)mean_time = np.mean(times)median_time = np.median(times)min_time = np.min(times)max_time = np.max(times)std_time = np.std(times)num_samples = len(times)# 创建画布(2行2列布局)fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(14, 12))fig.suptitle(title, fontproperties=harmony_font, fontsize=16, y=0.99)# 设置字体的辅助函数def set_font(ax, title, xlabel, ylabel):ax.set_title(title, fontproperties=harmony_font, fontsize=14)ax.set_xlabel(xlabel, fontproperties=harmony_font, fontsize=12)ax.set_ylabel(ylabel, fontproperties=harmony_font, fontsize=12)for label in ax.get_xticklabels() + ax.get_yticklabels():label.set_fontproperties(harmony_font)# 1. 推理时间趋势图(折线图)ax1 = axes[0, 0]ax1.plot(range(1, num_samples+1), times, marker='o', color='#2E91E5', alpha=0.7, label='单次耗时')ax1.axhline(mean_time, color='#E55934', linestyle='--', label=f'均值: {mean_time:.4f}s')ax1.axhline(median_time, color='#4CAF50', linestyle='-.', label=f'中位数: {median_time:.4f}s')set_font(ax1, '推理时间趋势', '推理次数', '耗时 (秒)')ax1.legend(prop=harmony_font)ax1.grid(alpha=0.3)# 2. 推理时间分布直方图ax2 = axes[0, 1]sns.histplot(times, kde=True, ax=ax2, color='#9B2335', bins=min(20, num_samples//2))ax2.axvline(mean_time, color='#E55934', linestyle='--', label=f'均值: {mean_time:.4f}s')set_font(ax2, '推理时间分布', '耗时 (秒)', '频数')ax2.legend(prop=harmony_font)# 3. 箱线图(展示分布特征)ax3 = axes[1, 0]sns.boxplot(x=times, ax=ax3, color='#FFD700')set_font(ax3, '推理时间箱线图', '耗时 (秒)', '')# 添加统计信息文本stats_text = (f'样本数: {num_samples}\n'f'最小值: {min_time:.4f}s\n'f'最大值: {max_time:.4f}s\n'f'标准差: {std_time:.4f}s')ax3.text(0.05, 0.95, stats_text, transform=ax3.transAxes, verticalalignment='top', bbox=dict(boxstyle='round', facecolor='white', alpha=0.8),fontproperties=harmony_font)# 4. 累计分布函数(CDF)ax4 = axes[1, 1]sorted_times = np.sort(times)cdf = np.arange(1, len(sorted_times)+1) / len(sorted_times)ax4.plot(sorted_times, cdf, color='#273746', marker='.')set_font(ax4, '推理时间累计分布', '耗时 (秒)', '累计概率')# 标注90%的推理耗时p90 = np.percentile(times, 90)ax4.axvline(p90, color='#D35400', linestyle='--')ax4.axhline(0.9, color='#D35400', linestyle='--')ax4.text(p90, 0.9, f'90% 耗时 < {p90:.4f}s', color='#D35400',fontproperties=harmony_font)ax4.grid(alpha=0.3)plt.tight_layout()plt.show()# Binding 命名元组
Binding = namedtuple("Binding", ("name", "dtype", "shape", "data", "ptr"))# TensorRT -> PyTorch dtype 映射
trt_to_torch_dtype_dict = {trt.DataType.BOOL: torch.bool,trt.DataType.INT8: torch.int8,trt.DataType.INT32: torch.int32,trt.DataType.HALF: torch.float16,trt.DataType.FLOAT: torch.float32,
}# NumPy -> PyTorch dtype 映射
np_to_torch_dtype = {np.bool_: torch.bool,np.uint8: torch.uint8,np.int8: torch.int8,np.int16: torch.int16,np.int32: torch.int32,np.int64: torch.int64,np.float16: torch.float16,np.float32: torch.float32,np.float64: torch.float64
}class UnifiedTRTModel(nn.Module):def __init__(self,weights="yolo11n.engine",device=torch.device("cuda:0"),fp16=False,input_names=['images'],output_names=None,fixed_output_shapes=None):"""统一的 TensorRT 模型封装器,支持 YOLO、xfeat 等多种模型。参数:weights (str): TensorRT engine 文件路径。device (torch.device): 推理设备,默认为 cuda:0。fp16 (bool): 是否启用半精度推理。input_names (list): 输入张量名称列表。output_names (list): 输出张量名称列表(可选,自动读取)。fixed_output_shapes (dict): 固定输出 shape,如 {'output': (1000, 2)}。"""super().__init__()self.np_to_torch_dtype = np_to_torch_dtypeself.trt_to_torch_dtype = trt_to_torch_dtype_dictself.input_names = input_namesself.output_names = output_namesself.fixed_output_shapes = fixed_output_shapes or {}self.fp16 = fp16self.device = device if device.type != "cpu" else torch.device("cpu")self.stream = torch.cuda.Stream(device=device) if torch.cuda.is_available() else None# 获取权重文件路径w = str(weights[0] if isinstance(weights, list) else weights)logger = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.INFO)trt.init_libnvinfer_plugins(logger, namespace='')print(f"Loading {w} for TensorRT inference...")with open(w, "rb") as f, trt.Runtime(logger) as runtime:try:meta_len = int.from_bytes(f.read(4), byteorder="little")metadata = json.loads(f.read(meta_len).decode("utf-8"))except UnicodeDecodeError:f.seek(0)metadata = Nonemodel = runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(f.read())context = model.create_execution_context()is_trt10 = not hasattr(model, "num_bindings")# 自动获取输出名称 & 解析绑定信息(合并版本)bindings = OrderedDict()binding_addrs = OrderedDict()dynamic = Falsefp16 = Falseoutput_names = []for i in (range(model.num_io_tensors) if is_trt10 else range(model.num_bindings)):if is_trt10:name = model.get_tensor_name(i)dtype = trt.nptype(model.get_tensor_dtype(name))if model.get_tensor_mode(name) == trt.TensorIOMode.INPUT:if -1 in tuple(context.get_tensor_shape(name)):dynamic = Truecontext.set_input_shape(name, tuple(model.get_tensor_profile_shape(name, 0)[1]))if dtype == np.float16:fp16 = Trueelif model.get_tensor_mode(name) == trt.TensorIOMode.OUTPUT:output_names.append(name)shape = tuple(context.get_tensor_shape(name))else:name = model.get_binding_name(i)dtype = trt.nptype(model.get_binding_dtype(i))if model.binding_is_input(i):if -1 in tuple(model.get_binding_shape(i)):dynamic = Truecontext.set_binding_shape(i, tuple(model.get_profile_shape(0, i)[1]))if dtype == np.float16:fp16 = Trueelif model.get_tensor_mode(name) == trt.TensorIOMode.OUTPUT:output_names.append(name)shape = tuple(context.get_binding_shape(i))# 注意:替换xfeat shape(0, 2)-->(1000, 2)if name in self.fixed_output_shapes:shape = self.fixed_output_shapes[name]# 创建 buffer 并记录地址im = torch.from_numpy(np.empty(shape, dtype=dtype)).to(self.device)bindings[name] = Binding(name, dtype, shape, im, int(im.data_ptr()))binding_addrs[name] = int(im.data_ptr())# 去重输出名称(防止重复)self.output_names = list(dict.fromkeys(output_names))# 注册变量self.model = modelself.context = contextself.bindings = bindingsself.binding_addrs = binding_addrsself.dynamic = dynamicself.is_trt10 = is_trt10def forward(self, *inputs):"""推理函数,支持多输入和手动设置输出 shape。参数:*inputs: 输入张量列表(顺序需与 input_names 一致)返回:tuple: 输出张量列表"""assert len(inputs) == len(self.input_names), \f"Expected {len(self.input_names)} inputs but got {len(inputs)}"contiguous_inputs = [x.contiguous().to(self.device) for x in inputs]for i, input_name in enumerate(self.input_names):im = contiguous_inputs[i]if self.fp16 and im.dtype != torch.float16:im = im.half()if self.dynamic and im.shape != self.bindings[input_name].shape:if self.is_trt10:self.context.set_input_shape(input_name, im.shape)self.bindings[input_name] = self.bindings[input_name]._replace(shape=im.shape)# 确保双输入尺寸对应后再修改输出尺寸if i == len(self.input_names) - 1:for name in self.output_names:# 注意:替换xfeat shape(0, 2)-->(1000, 2)if name in self.fixed_output_shapes:shape = self.fixed_output_shapes[name]self.bindings[name].data.resize_(shape)else:self.bindings[name].data.resize_(tuple(self.context.get_tensor_shape(name)))else:idx = self.model.get_binding_index(input_name)self.context.set_binding_shape(idx, im.shape)self.bindings[input_name] = self.bindings[input_name]._replace(shape=im.shape)# 确保双输入尺寸对应后再修改输出尺寸if i == len(self.input_names) - 1:for name in self.output_names:idx_out = self.model.get_binding_index(name)# 注意:替换xfeat shape(0, 2)-->(1000, 2)if name in self.fixed_output_shapes:shape = self.fixed_output_shapes[name]self.bindings[name].data.resize_(shape)else:self.bindings[name].data.resize_(tuple(self.context.get_binding_shape(idx_out)))self.binding_addrs[input_name] = int(im.data_ptr())outputs = []for output_name in self.output_names:output = self.bindings[output_name].dataself.binding_addrs[output_name] = int(output.data_ptr())outputs.append(output)if self.stream:self.context.execute_async_v2(list(self.binding_addrs.values()), self.stream.cuda_stream)self.stream.synchronize()else:self.context.execute_v2(list(self.binding_addrs.values()))return tuple(outputs) if len(outputs) > 1 else outputs[0]def from_numpy(self, x):"""将 numpy 数组转换为 PyTorch 张量。参数:x (np.ndarray): 要转换的数组。返回:(torch.Tensor): 转换后的张量"""return torch.tensor(x).to(self.device) if isinstance(x, np.ndarray) else x# 前处理,包括:resize, pad, HWC to CHW,BGR to RGB,归一化,增加维度CHW -> BCHW
def preprocess(img, model_height, model_width):"""Pre-processes the input image.Args:img (Numpy.ndarray): image about to be processed.Returns:img_process (Numpy.ndarray): image preprocessed for inference.ratio (tuple): width, height ratios in letterbox.pad_w (float): width padding in letterbox.pad_h (float): height padding in letterbox."""# Resize and pad input image using letterbox() (Borrowed from Ultralytics)shape = img.shape[:2] # original image shapenew_shape = (model_height, model_width)r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])ratio = r, rnew_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))pad_w, pad_h = (new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0]) / 2, (new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1]) / 2 # wh paddingif shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resizeimg = cv2.resize(img, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)top, bottom = int(round(pad_h - 0.1)), int(round(pad_h + 0.1))left, right = int(round(pad_w - 0.1)), int(round(pad_w + 0.1))img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=(114, 114, 114)) # 填充# Transforms: HWC to CHW -> BGR to RGB -> div(255) -> contiguous -> add axis(optional)img = np.ascontiguousarray(np.einsum('HWC->CHW', img)[::-1], dtype=np.single) / 255.0img_process = img[None] if len(img.shape) == 3 else imgreturn img_process, ratio, (pad_w, pad_h)# 后处理,包括:阈值过滤与NMS
def postprocess(preds, im0, ratio, pad_w, pad_h, conf_threshold, iou_threshold):"""Post-process the prediction.Args:preds (Numpy.ndarray): predictions come from ort.session.run().im0 (Numpy.ndarray): [h, w, c] original input image.ratio (tuple): width, height ratios in letterbox.pad_w (float): width padding in letterbox.pad_h (float): height padding in letterbox.conf_threshold (float): conf threshold.iou_threshold (float): iou threshold.Returns:boxes (List): list of bounding boxes."""x = preds # outputs: predictions (1, 84, 8400)x = x.cpu().numpy()# Transpose the first output: (Batch_size, xywh_conf_cls, Num_anchors) -> (Batch_size, Num_anchors, xywh_conf_cls)x = np.einsum('bcn->bnc', x) # (1, 8400, 84)# Predictions filtering by conf-thresholdx = x[np.amax(x[..., 4:], axis=-1) > conf_threshold]# Create a new matrix which merge these(box, score, cls) into one# For more details about `numpy.c_()`: https://numpy.org/doc/1.26/reference/generated/numpy.c_.htmlx = np.c_[x[..., :4], np.amax(x[..., 4:], axis=-1), np.argmax(x[..., 4:], axis=-1)]# NMS filtering# 经过NMS后的值, np.array([[x, y, w, h, conf, cls], ...]), shape=(-1, 4 + 1 + 1)x = x[cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(x[:, :4], x[:, 4], conf_threshold, iou_threshold)]# 重新缩放边界框,为画图做准备if len(x) > 0:# Bounding boxes format change: cxcywh -> xyxyx[..., [0, 1]] -= x[..., [2, 3]] / 2x[..., [2, 3]] += x[..., [0, 1]]# Rescales bounding boxes from model shape(model_height, model_width) to the shape of original imagex[..., :4] -= [pad_w, pad_h, pad_w, pad_h]x[..., :4] /= min(ratio)# Bounding boxes boundary clampx[..., [0, 2]] = x[:, [0, 2]].clip(0, im0.shape[1])x[..., [1, 3]] = x[:, [1, 3]].clip(0, im0.shape[0])return x[..., :6] # boxeselse:return np.array([])if __name__ == "__main__":# 示例用法:YOLOv8 目标检测model = UnifiedTRTModel(weights='det_fp16.engine',# weights='det_int8.engine',device=torch.device("cuda:0"),input_names=['images'],output_names=['output0'])# warmup# one_tensor = torch.zeros(1, 3, 640, 640, dtype=torch.float32).to('cuda:0')# one_tensor = torch.zeros(1, 3, 1280, 1280, dtype=torch.float32).to('cuda:0')# one_tensor = torch.zeros(1, 3, 736, 1280, dtype=torch.float32).to('cuda:0')one_tensor = torch.zeros(1, 3, 864, 1536, dtype=torch.float32).to('cuda:0')for _ in range(10):out = model(one_tensor)print('热启动结束,推理开始!')pre_times = []cpu_gpu_times =[]infer_times = []post_times =[]# 测试求平均推理耗时n = 100for _ in range(n):img0 = cv2.imread('test.jpg')t1 = time.time()# img, ratio, (pad_w, pad_h) = preprocess(img0, 640, 640)# img, ratio, (pad_w, pad_h) = preprocess(img0, 1280, 1280)# img, ratio, (pad_w, pad_h) = preprocess(img0, 736, 1280)img, ratio, (pad_w, pad_h) = preprocess(img0, 864, 1536)t2 = time.time()img_tensor = torch.from_numpy(img).to('cuda:0')t3 = time.time()out = model(img_tensor)t4 = time.time()out = postprocess(out, img0, ratio, pad_w, pad_h, 0.25, 0.45)t5 = time.time()for (*box, conf, cls_) in out:cv2.rectangle(img0, (int(box[0]), int(box[1])), (int(box[2]), int(box[3])),(0, 0, 255), 2, cv2.LINE_AA)pre_times.append(round(t2 - t1, 4))cpu_gpu_times.append(round(t3 - t2, 4))infer_times.append(round(t4 - t3, 4))post_times.append(round(t5 - t4, 4))print('cpu->gpu耗时为:{:.4f}ms'.format((t3 - t2) * 1000))print('总耗时为:{:.4f}ms, 预处理耗时为:{:.4f}ms,推理耗时为:{:.4f}ms,后处理耗时为:{:.4f}ms'.format((t5 - t1) * 1000, (t2 - t1) * 1000, (t4 - t3) * 1000, (t5 - t4) * 1000))print('预处理平均耗时:{:.4f}ms, cpu->gpu平均耗时:{:.4f}ms, 推理平均耗时:{:.4f}ms, 后处理平均耗时:{:.4f}ms'.format(sum(pre_times)*1000 / n, sum(cpu_gpu_times)*1000 / n, sum(infer_times)*1000 / n, sum(post_times)*1000 / n))cv2.imwrite('res.jpg', img0)visualize_inference_times(infer_times, title="YOLOv8s-DET模型推理时间分析", font_path='../HarmonyOS_Sans_SC_Regular.ttf')
