@Value注解的底层原理(一)
一.概述
@Value注解是如何工作的,大致分为以下几个步骤:
1.获取Value值
2.解析${}
3.解析#{SEL表达式}(对于这种情况本文没有演示)
4.类型转换
二.测试
package com.example.springdemo.demos.a14;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.DependencyDescriptor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import java.lang.reflect.Field;/*** @author zhou* @version 1.0* @description TODO* @date 2025/8/31 20:58*/
@Configuration
public class TestValue {public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException {AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TestValue.class);ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver resolver = new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver();resolver.setBeanFactory(context.getDefaultListableBeanFactory());Field home = Bean1.class.getDeclaredField("home");extracted(context, resolver, home);Field age = Bean1.class.getDeclaredField("age");extracted2(context,resolver,age);}private static void extracted(AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context, ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver resolver, Field field) {DependencyDescriptor descriptor = new DependencyDescriptor(field,true);//获取@Value的内容String value = resolver.getSuggestedValue(descriptor).toString();System.out.println(value);//解析${}value = context.getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(value);System.out.println(value);}private static void extracted2(AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context, ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver resolver, Field field) {DependencyDescriptor descriptor = new DependencyDescriptor(field,true);//获取@Value的内容String value = resolver.getSuggestedValue(descriptor).toString();System.out.println(value);//解析${}value = context.getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(value);System.out.println(value);//类型转换Object age = context.getBeanFactory().getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(value, descriptor.getDependencyType());System.out.println(age.getClass());}public class Bean1{@Value("${JAVA_HOME}")private String home;@Value("18")private int age;}}
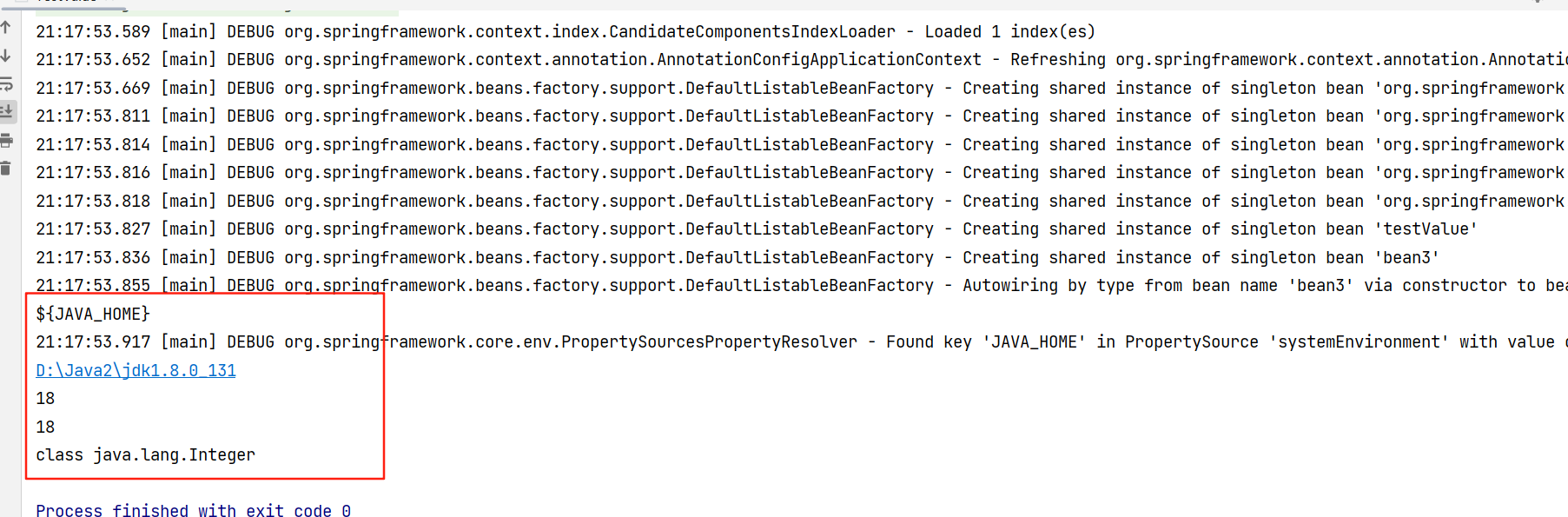
文中抽取了两个方法对@Value注解作测试
1.解析带有${}的属性
@Value("${JAVA_HOME}")
private String home;测试方法一里面详细介绍了步骤,首先需要拿到DependencyDescriptor对象,然后通过ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver对象到@Value里面的值。原始的值是${JAVA_HOME},随后通过context.getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders方法解析里面的值。
2.类型不一致转换
@Value("18")
private int age;
@Value里面的值类型是String与int类型不一致,前面获取值的步骤是一致的,不同的地方在于最后一步,利用下面的类型转换器把String类型转换为Integer类型,后面自动拆箱为int类型。
//类型转换Object age = context.getBeanFactory().getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(value, descriptor.getDependencyType());System.out.println(age.getClass());测试结果: