【Linux 进程】进程程序替换
文章目录
- 1.进程替换的六个库函数
- 2.execl
1.进程替换的六个库函数
-
使用
man 3 execl进行查询,3表示 Linux 中的3号手册,即为库函数(例如C标准库中的库函数,printf,malloc) -
man 1: 用户命令(在shell中可以执行的命令,如ls, cp) -
man 2: 系统调用(由内核提供的接口,如open, read, fork)
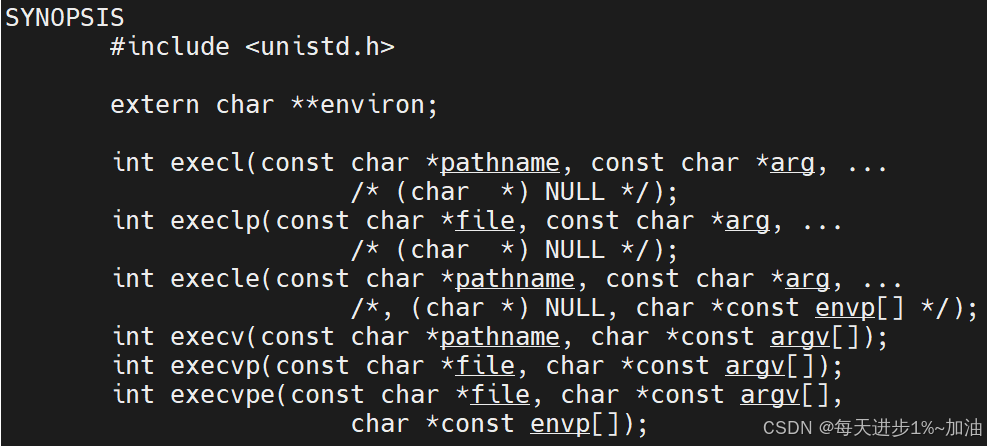
2.execl
🍎参数介绍:
pathname:表示要替换程序的路径(绝对路径或者相对路径都可);
arg:命令行参数的第一个参数,一般是程序名本身;
...:表示可变参数,按照要求填写命令行参数即可;
注意:结尾一定要以 NULL,表示结束标志;
execl的返回值我们不用关心,因为只要程序替换成功,旧的代码将不再执行,如果后续的代码执行了,说明替换失败。
int execl(const char *pathname, const char *arg, .../* (char *) NULL */);

- ⚽小案例:使用
ls -a -l来替换程序代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>int main()
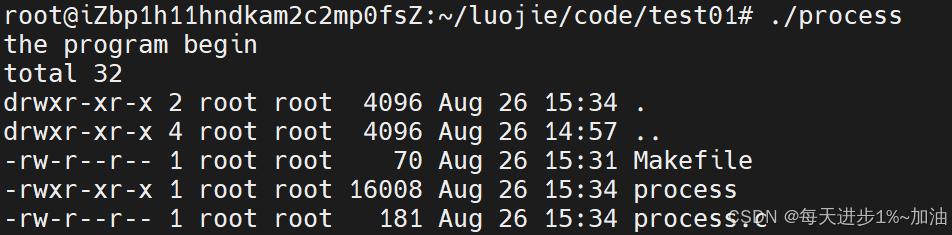
{printf("the program begin\n");execl("/usr/bin/ls", "ls", "-a","-l", NULL);printf("the program end\n");return 0;
}》运行结果如下:
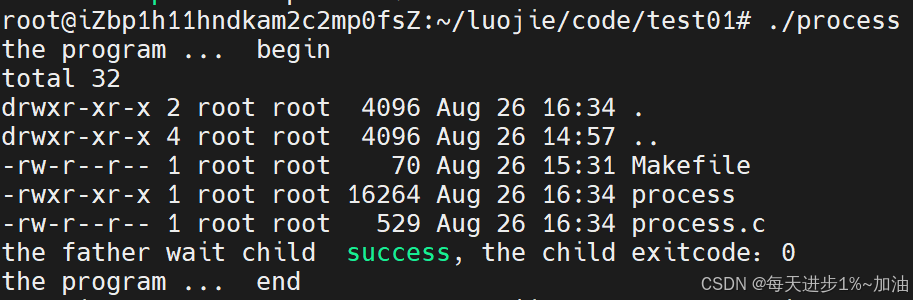
程序替换成功,原来的程序代码 the program end 已经被替换成为 ls -a -l
- ⚽多进程版本:子进程中进行程序替换,父进程正常执行
下面这个代码案例说明,虽然刚开始父子进程是共享同一块代码的内存区域的,但是当子进程发生程序替换要对代码进行修改时,此时OS会发生写时拷贝,在物理内存上新建一块内存区域,首先把父进程的代码进行复制,然后再把子进程要替换的代码加载进来。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <stdlib.h>int main()
{printf("the program ... begin\n");pid_t id =fork();// child processif (id == 0){sleep(2);execl("/usr/bin/ls", "ls", "-l", "-a", NULL);exit(123);}// father processint status = 0;pid_t wid = waitpid(id, &status, 0);if (wid > 0){printf("the father wait child success, the child exitcode:%d\n", WEXITSTATUS(status));}printf("the program ... end\n");return 0;
}》运行结果如下: