0824 MLIR和AST相关资料
- 简单直观的理解:【编译原理:构建抽象语法树】
编译原理:构建抽象语法树_哔哩哔哩_bilibili - 程序转为AST可视化:https://astexplorer.net/
- MLIR的博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/YuanZiming/p/18956253
- 学习MLIR的仓库:https://github.com/KEKE046/mlir-tutorial
- for循环:https://blog.csdn.net/ReadyShowShow/article/details/137275857
- if判断
DIST-IR中有用的测试用例
test/test_sequential_executor.py中的两个元素加法
test/test_simulator.py中的两个连续的矩阵乘法_test_data_parallel
test/test_pytorch_backend.py中的Send函数测试:test_send_recv
test/test_prettyprint.py中的两个连续的矩阵乘法:IR
tensor乘法simulator.py
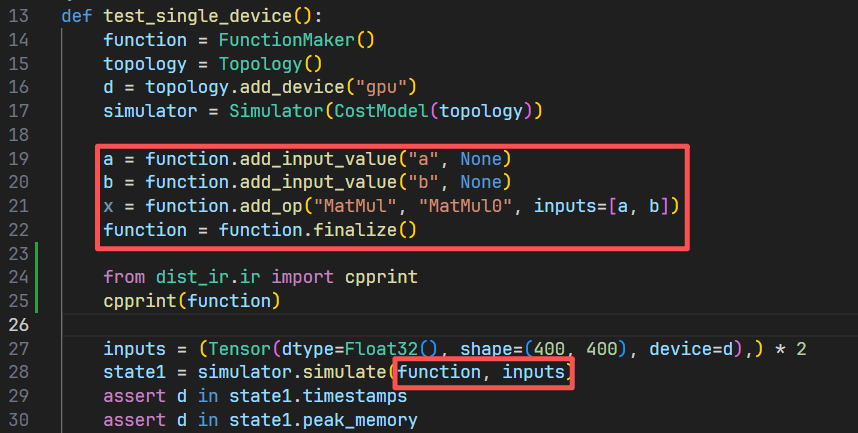
完成图的构建,在这里采用了手写中间表示的方式
FunctionMaker中包含四个重要函数
- add_op:参数为:操作码、输入、属性、子函数
- add_input_value:添加输入值
- set_outputs:设置元组输出
- finalize:根据上面的参数构造
Function类
IR的格式
大萨
simulator的实现
类型
Function = {# Invariant: ops are in topological orderops: List[Op]inputs: List[Value]outputs: List[Value]
}Device = {device_id: Int# Unique device IDdevice_type: String# Device type (e.g. "gpu")
}Op = {name: String# Do we need this to be unique in a function? Across all functions?op_type: OpType# The type of operatorin_edges: List[Value]# Pointer to a Value object either in Function.inputs or another Op.out_edgesout_edges: List[Value]# To support ops that have more than one outputattributes: Dict[String, Any]# Constant data for ops, e.g. stride of convolution or devices to scattersubfunctions: List[Function]
}OpType = | MatMul | Add | Relu | ...| MatMulGrad | ReluGrad | ...| N11Loss | SGDOptimizer | ...| Pmap | AllReduce | ...Value = {name: String# Again, does it need to be unique in a function?type: Typedevice: DeviceID# Which device this value lives on# TODO pointer to source op that generated this value?
}Type =| Tensor{shape: Optional[Shape], dtype: Type, device: Device}| Float | Int | ...| TupleType{elems: List[Type]}Topology = {devices: List[Device]# The list of all devices in the topology.bandwidths: Dict[Device, Dict[Device, Float]]# The bandwidth between each device.
}
dispatch是如何绑定的
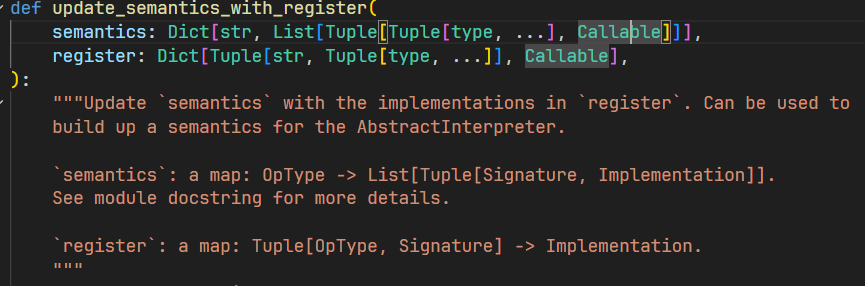
更新字典的函数
-
操作码类型推断:
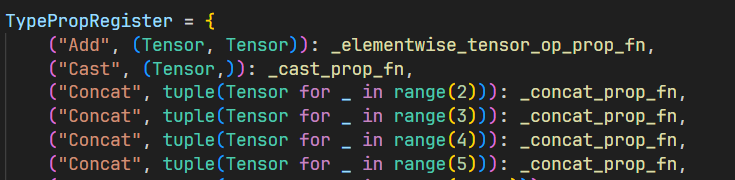
-
混合输入的操作码类型推断:
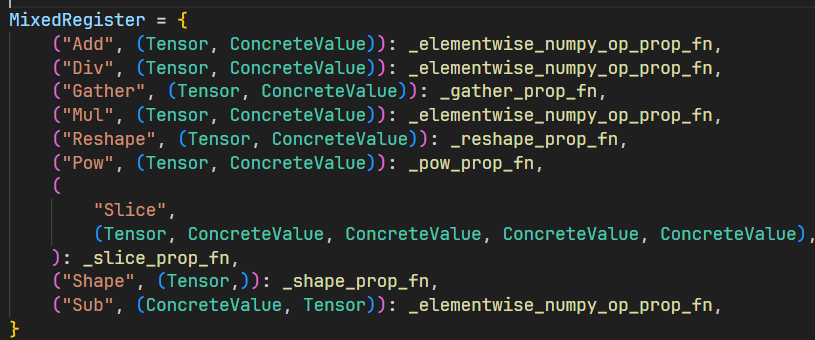
-
实际操作码计算
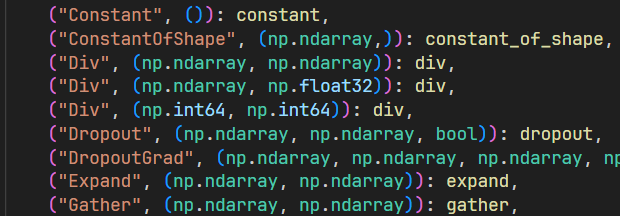
-
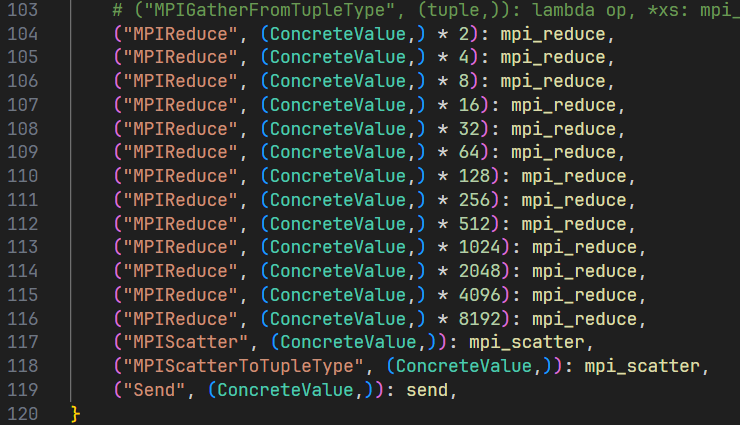
通信类型操作码: