使用 FastAPI 的 WebSockets 和 Elasticsearch 来构建实时应用
作者:来自 Elastic Jeffrey Rengifo
学习如何使用 FastAPI WebSockets 和 Elasticsearch 构建实时应用程序。
更多阅读:使用 FastAPI 构建 Elasticsearch API
想要获得 Elastic 认证吗?看看下一次 Elasticsearch Engineer 培训什么时候开始!
Elasticsearch 拥有许多新功能,可以帮助你为你的使用场景构建最佳搜索解决方案。深入学习我们的示例笔记本,了解更多内容,开始免费的云试用,或者立即在本地机器上尝试 Elastic。
WebSockets 是一种同时双向通信协议。它的理念是客户端和服务器可以保持一个打开的连接,同时互相发送消息,从而尽可能降低延迟。这种方式常见于实时应用,比如聊天、活动通知或交易平台,在这些场景中延迟是关键,并且存在持续的信息交换。
想象一下你创建了一个消息应用,想在用户收到新消息时通知他们。你可以每隔 5 或 10 秒通过发送 HTTP 请求轮询服务器,直到有新消息,或者你可以保持一个 WebSockets 连接,让服务器推送一个事件,客户端监听后在消息到达时立即显示通知标记。
在这种情况下,Elasticsearch 能够在数据集上实现快速而灵活的搜索,使其非常适合需要即时结果的实时应用。
在这篇文章中,我们将使用 FastAPI 的 WebSockets 功能和 Elasticsearch 创建一个实时应用程序。
先决条件
- Python 版本 3.x
- 一个 Elasticsearch 实例(自托管或 Elastic Cloud 上)
- 一个具有写权限的 Elasticsearch API key
本文使用的所有代码可以在这里找到。
使用场景
为了向你展示如何将 WebSockets 与 FastAPI 和 Elasticsearch 一起使用,我们将采用一个使用场景:作为店主的你,想在某个查询被执行时通知所有用户,以吸引他们的注意力。这模拟了搜索驱动应用中的实时互动,比如促销活动或产品兴趣提醒。
在这个使用场景中,我们将构建一个应用,客户可以搜索产品,并在其他用户执行了在监控列表中的搜索时收到通知。
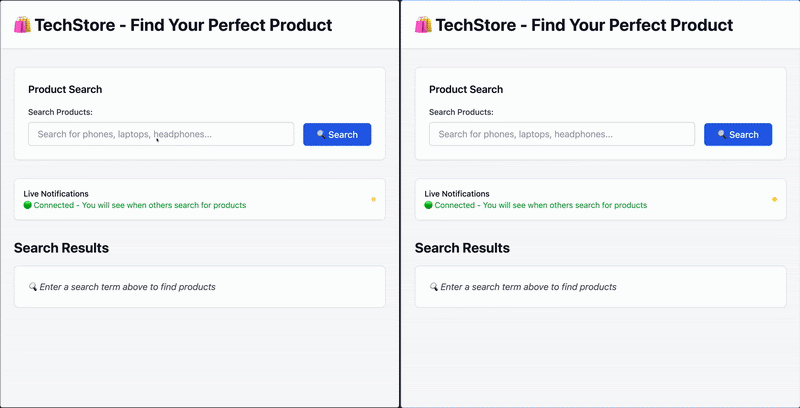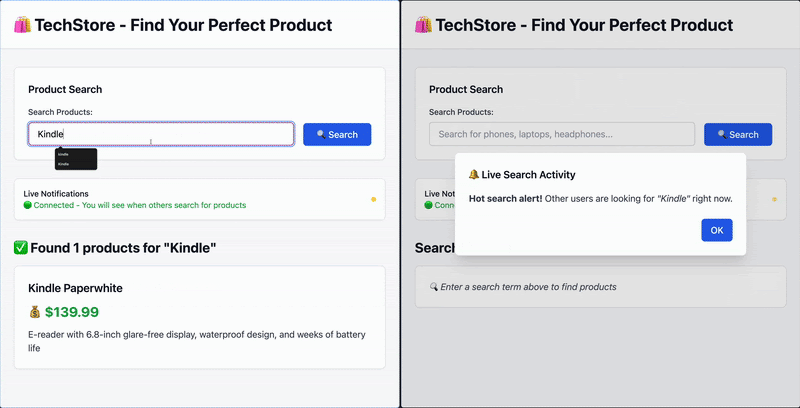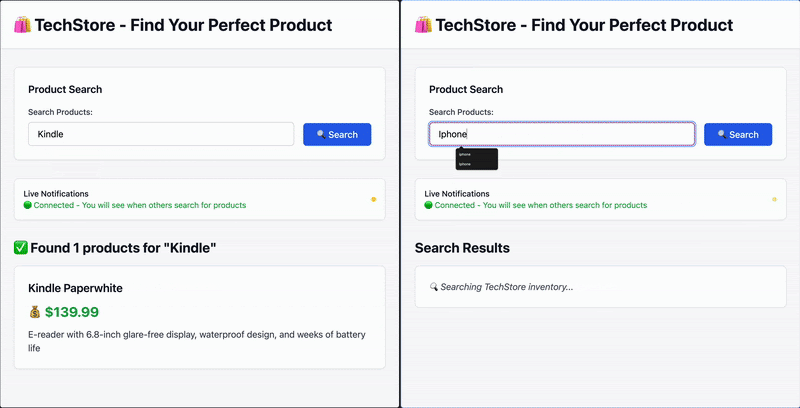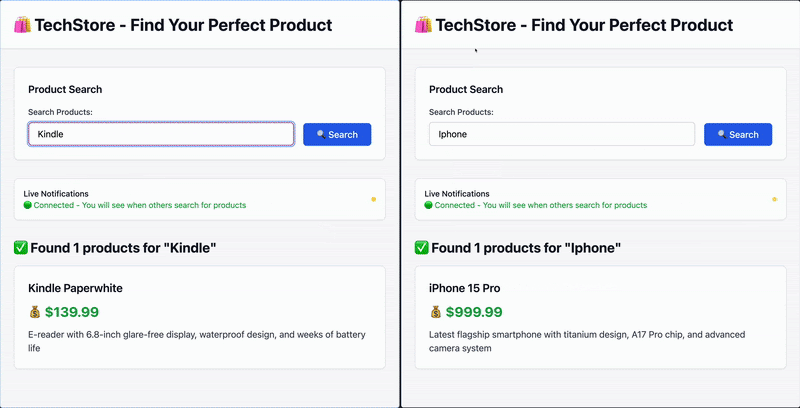
用户 A 搜索 “Kindle”,用户 B 会实时收到通知。
数据摄取
在这一部分,我们将创建索引映射,并使用一个 Python 脚本摄取所需的数据。你可以在博客仓库中找到以下脚本。
摄取脚本
创建一个名为 ingest_data.py 的新文件,其中包含用于处理数据摄取的 Python 逻辑。
安装 Elasticsearch 库以处理对 Elasticsearch 的请求:
pip install elasticsearch -q现在导入依赖,并使用 API key 和 Elasticsearch 端点 URL 初始化 Elasticsearch 客户端。
import json
import osfrom elasticsearch import Elasticsearches_client = Elasticsearch(hosts=[os.environ["ELASTICSEARCH_ENDPOINT"]],api_key=os.environ["ELASTICSEARCH_API_KEY"],
)创建一个方法,在名为 “products” 的索引下设置索引映射。
PRODUCTS_INDEX = "products"def create_products_index():try:mapping = {"mappings": {"properties": {"product_name": {"type": "text"},"price": {"type": "float"},"description": {"type": "text"},}}}es_client.indices.create(index=PRODUCTS_INDEX, body=mapping)print(f"Index {PRODUCTS_INDEX} created successfully")except Exception as e:print(f"Error creating index: {e}")现在使用 bulk API 加载产品文档,将它们推送到 Elasticsearch。数据将位于项目仓库中的 NDJSON 文件中。
def load_products_from_ndjson():try:if not os.path.exists("products.ndjson"):print("Error: products.ndjson file not found!")returnproducts_loaded = 0with open("products.ndjson", "r") as f:for line in f:if line.strip():product_data = json.loads(line.strip())es_client.index(index=PRODUCTS_INDEX, body=product_data)products_loaded += 1print(f"Successfully loaded {products_loaded} products into Elasticsearch")except Exception as e:print(f"Error loading products: {e}")最后,调用已创建的方法。
if __name__ == "__main__":create_products_index()load_products_from_ndjson()在终端中使用以下命令运行脚本。
python ingest_data.py完成后,让我们继续构建应用。
Index products created successfully
Successfully loaded 25 products into ElasticsearchWebSockets 应用
为了提高可读性,应用的界面将简化。完整的应用仓库可以在这里找到。
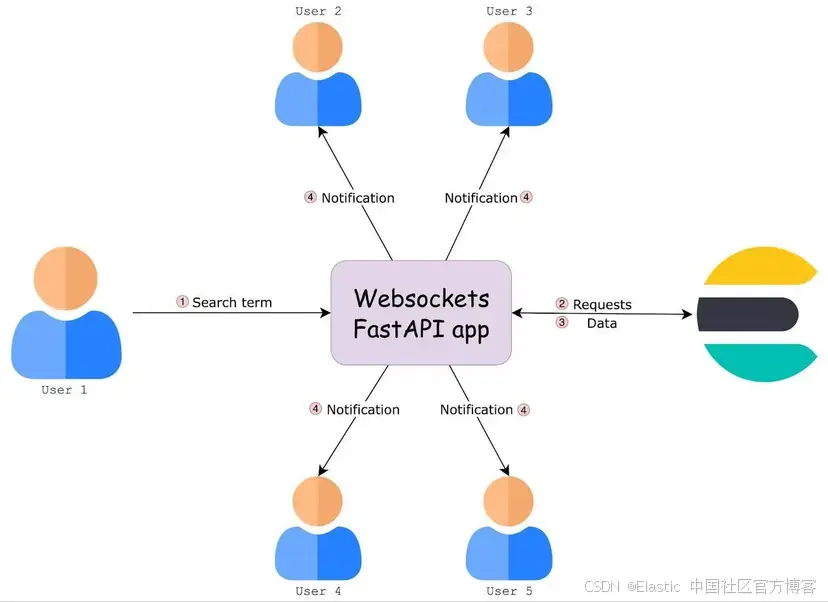
该图展示了 WebSocket 应用如何与 Elasticsearch 和多个用户交互的高级概览。
应用结构
|-- websockets_elasticsearch_app
|-- ingest_data.py
|-- index.html
|-- main.py安装并导入依赖
安装 FastAPI 和 WebSocket 支持。Uvicorn 将作为本地服务器,Pydantic 用于定义数据模型,Elasticsearch 客户端允许脚本连接到集群并发送数据。
pip install websockets fastapi pydantic uvicorn -qFastAPI 提供了易用、轻量且高性能的工具来构建 web 应用,而 Uvicorn 作为 ASGI 服务器来运行它。Pydantic 在 FastAPI 内部用于数据验证和解析,使定义结构化数据更容易。WebSockets 提供了低级协议支持,使服务器和客户端之间能够实现实时双向通信。之前安装的 Elasticsearch Python 库将在此应用中用于处理数据检索。
现在,导入构建后端所需的库。
import json
import os
import uvicorn
from datetime import datetime
from typing import Dict, Listfrom elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException, WebSocket, WebSocketDisconnect
from fastapi.responses import FileResponse
from pydantic import BaseModel, FieldElasticsearch 客户端
定义 Elasticsearch 端点和 API key 的环境变量,并实例化一个 Elasticsearch 客户端来处理与 Elasticsearch 集群的连接。
os.environ["ELASTICSEARCH_ENDPOINT"] = getpass("Insert the Elasticsearch endpoint here: "
)
os.environ["ELASTICSEARCH_API_KEY"] = getpass("Insert the Elasticsearch API key here: ")es_client = Elasticsearch(hosts=[os.environ["ELASTICSEARCH_ENDPOINT"]],api_key=os.environ["ELASTICSEARCH_API_KEY"],
)PRODUCTS_INDEX = "products"数据模型和应用设置
现在是创建 FastAPI 实例的时候了,它将处理 REST API 和 WebSocket 路由。然后,我们将使用 Pydantic 定义几个数据模型。
- Product 模型描述每个产品的结构。
- SearchNotification 模型定义我们将发送给其他用户的消息。
- SearchResponse 模型定义 Elasticsearch 结果的返回方式。
这些模型有助于在整个应用中保持一致性和可读性,并在代码 IDE 中提供数据验证、默认值和自动补全。
app = FastAPI(title="Elasticsearch - FastAPI with websockets")class Product(BaseModel):product_name: strprice: floatdescription: strclass SearchNotification(BaseModel):session_id: strquery: strtimestamp: datetime = Field(default_factory=datetime.now)class SearchResponse(BaseModel):query: strresults: List[Dict]total: intWebSockets 端点设置
当用户连接到 /ws 端点时,WebSocket 连接会保持打开状态并添加到全局列表中。这允许服务器即时向所有连接的客户端广播消息。如果用户断开连接,他们的连接将被移除。
# Store active WebSocket connections
connections: List[WebSocket] = []@app.websocket("/ws")
async def websocket_endpoint(websocket: WebSocket):await websocket.accept()connections.append(websocket)print(f"Client connected. Total connections: {len(connections)}")try:while True:await websocket.receive_text()except WebSocketDisconnect:connections.remove(websocket)print(f"Client disconnected. Total connections: {len(connections)}")搜索端点
现在让我们查看发生实时交互的代码。
当用户执行搜索时,会查询 Elasticsearch 并返回结果。同时,如果查询在全局监控列表中,所有其他已连接用户会收到通知,提示有人找到了其中的某个产品。通知中包含查询内容。
session_id 参数用于避免将通知发送回发起搜索的用户。
@app.get("/search")
async def search_products(q: str, session_id: str = "unknown"):# List of search terms that should trigger a notificationWATCH_LIST = ["iphone", "kindle"]try:query_body = {"query": {"bool": {"should": [{"match": {"product_name": q}},{"match_phrase": {"description": q}},],"minimum_should_match": 1,}},"size": 20,}response = es_client.search(index=PRODUCTS_INDEX, body=query_body)results = []for hit in response["hits"]["hits"]:product = hit["_source"]product["score"] = hit["_score"]results.append(product)results_count = response["hits"]["total"]["value"]# Only send notification if the search term matchesif q.lower() in WATCH_LIST:notification = SearchNotification(session_id=session_id, query=q, results_count=results_count)for connection in connections.copy():try:await connection.send_text(json.dumps({"type": "search","session_id": session_id,"query": q,"timestamp": notification.timestamp.isoformat(),}))except:connections.remove(connection)return SearchResponse(query=q, results=results, total=results_count)except Exception as e:status_code = getattr(e, "status_code", 500)return HTTPException(status_code=status_code, detail=str(e))注意:session_id 仅基于当前时间戳以简化处理 —— 在生产环境中,你需要使用更可靠的方法。
客户端
为了展示应用流程,创建一个前端页面,使用简单的 HTML,包括搜索输入框、结果区域和用于通知的对话框。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en"><body><h1>🛍️ TechStore - Find Your Perfect Product</h1><form onsubmit="event.preventDefault(); searchProducts();"><p><label for="searchQuery">Search Products:</label><br /><inputtype="text"id="searchQuery"placeholder="Search for phones, laptops, headphones..."size="50"required /><button type="submit">🔍 Search</button></p></form><!-- HTML Dialog for notifications --><dialog id="notificationDialog"><div><h2>🔔 Live Search Activity</h2><p id="notificationMessage"></p><p><button onclick="closeNotification()" autofocus>OK</button></p></div></dialog><div id="searchResults"><h2>Search Results</h2></div><script>...</script></body>
</html>通知使用了 元素用于演示,但在真实应用中,你可能会使用 toast 或小徽章来显示。在实际场景中,这类通知可用于显示有多少用户正在搜索某些产品、提供库存实时更新,或突出显示返回成功结果的热门搜索查询。
Script 标签
在 标签内,包含将前端连接到后端 WebSocket 端点的逻辑。让我们看看下面的代码片段。
let ws = null;
let sessionId = null;window.onload = function () {sessionId = "session_" + Date.now();connectWebSocket();
};页面加载时,会生成一个唯一的 session ID 并连接到 WebSocket。
function connectWebSocket() {ws = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:8000/ws");ws.onopen = function () {console.log("Connected to WebSocket");};ws.onmessage = function (event) {try {const notification = JSON.parse(event.data);if (notification.type === "search") {showSearchNotification(notification);}} catch (error) {console.error("Error parsing notification:", error);}};ws.onclose = function () {console.log("Disconnected from WebSocket");};ws.onerror = function (error) {console.error("WebSocket error:", error);};
}函数 connectWebSocket 使用 ws = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:8000/ws") 建立 WebSocket 连接。语句 ws.onopen 通知后端已创建新连接。然后,ws.onmessage 监听其他用户在商店中搜索时发送的通知。
function showSearchNotification(notification) {// Skip notifications from the same session (same browser window)if (notification.session_id === sessionId) {return;}const dialog = document.getElementById("notificationDialog");const messageElement = document.getElementById("notificationMessage");messageElement.innerHTML = `<p><strong>Hot search alert!</strong> Other users are looking for <em>"${notification.query}"</em> right now.</p>`;// Show the notification dialogdialog.showModal();
}function closeNotification() {const dialog = document.getElementById("notificationDialog");dialog.close();
}函数 showSearchNotification 在屏幕上显示通过 WebSockets 接收到的通知,而 closeNotification 函数用于关闭 showSearchNotification 显示的消息。
async function searchProducts() {const query = document.getElementById("searchQuery").value.trim();const response = await fetch(`/search?q=${encodeURIComponent(query)}&session_id=${encodeURIComponent(sessionId)}`);const data = await response.json();if (response.ok) {displaySearchResults(data);} else {throw new Error(data.error || "Search failed");}
}function displaySearchResults(data) {const resultsDiv = document.getElementById("searchResults");let html = `<h2>Found ${data.total} products for "${data.query}"</h2>`;data.results.forEach((product) => {html += `<ul><li><strong>${product.product_name}</strong></li><li>💰 $${product.price.toFixed(2)}</li><li>${product.description}</li>
</ul>`;});resultsDiv.innerHTML = html;
}searchProducts() 函数将用户的查询发送到后端,并通过调用 displaySearchResults 函数更新结果区域中匹配的产品。
渲染视图和主方法
最后,在浏览器访问应用时渲染 HTML 页面并启动服务器。
@app.get("/")
async def get_main_page():return FileResponse("index.html")if __name__ == "__main__":uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8000)运行应用
使用 uvicorn 运行 FastAPI 应用。
uvicorn main:app --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000现在应用已上线!
INFO: Started server process [61820]
INFO: Waiting for application startup.
INFO: Application startup complete.测试应用
访问 localhost:8000/ 渲染应用视图,并观察控制台的情况:
INFO: 127.0.0.1:53422 - "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 OK
INFO: ('127.0.0.1', 53425) - "WebSocket /ws" [accepted]
Client connected. Total connections: 1
INFO: connection open当视图被打开时,服务器会收到一个 WebSocket 连接。每打开一个新页面,都会增加一个连接。例如,如果你在三个不同的浏览器标签中打开页面,你将在控制台看到三个连接:
INFO: ('127.0.0.1', 53503) - "WebSocket /ws" [accepted]
Client connected. Total connections: 2
INFO: connection open
INFO: ('127.0.0.1', 53511) - "WebSocket /ws" [accepted]
Client connected. Total connections: 3
INFO: connection open如果关闭一个标签,对应的连接也会关闭:
Client disconnected. Total connections: 2
INFO: connection closed当有多个活跃客户端连接时,如果一个用户搜索了某个产品,并且该搜索词在监控列表中,其他已连接的客户端将实时收到通知。
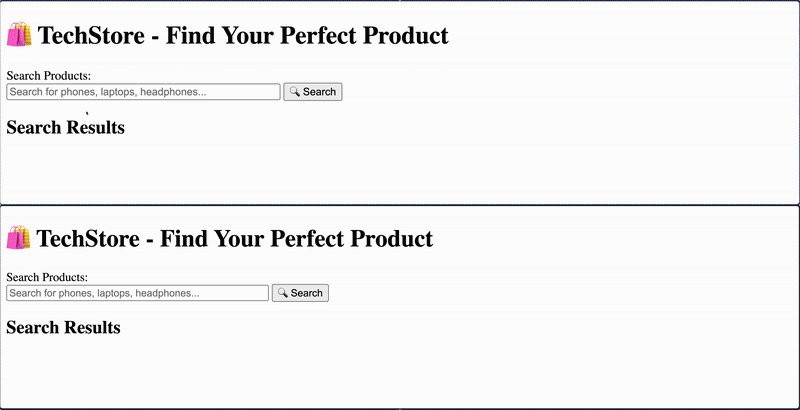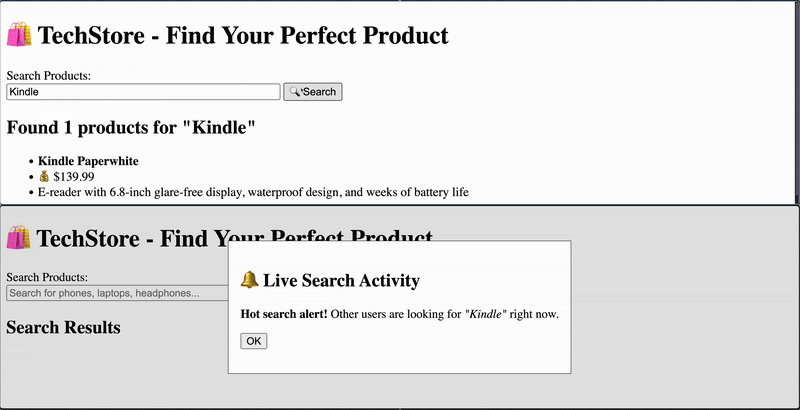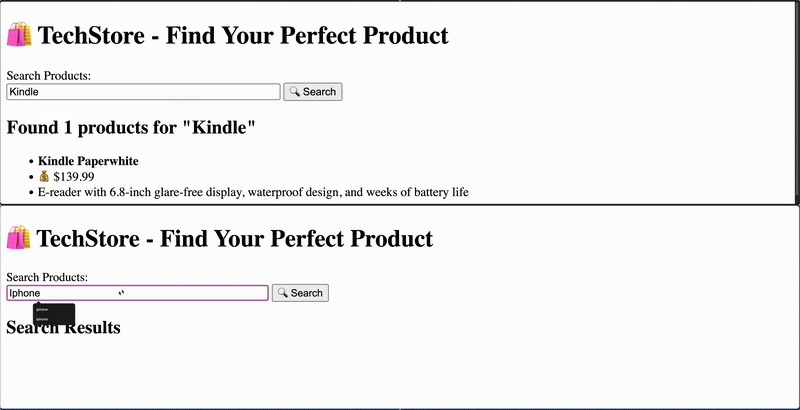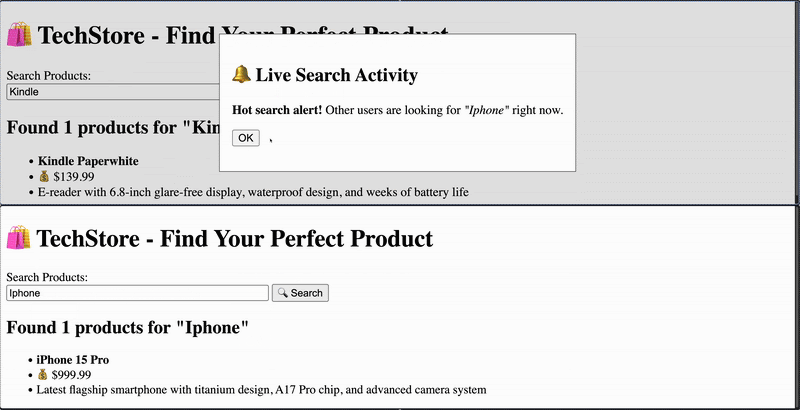
可选步骤是使用 Tailwind 应用一些样式。这可以改善 UI,使其看起来现代且视觉上更吸引人。完整的带有更新 UI 的代码可以在这里找到。
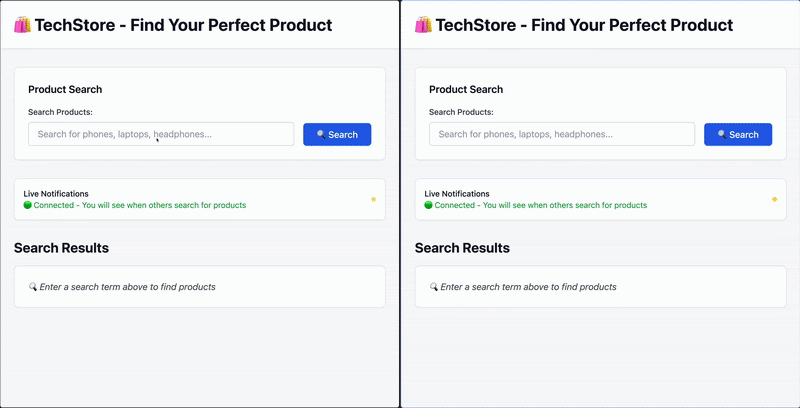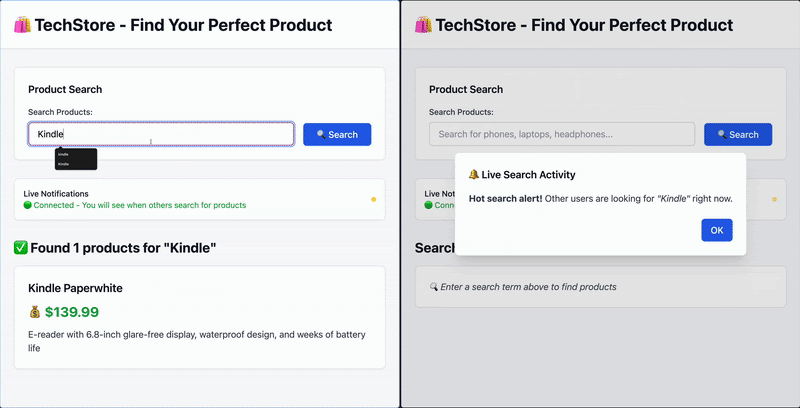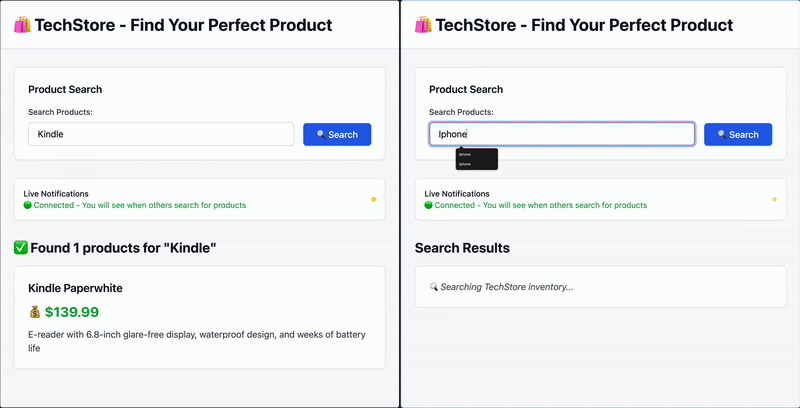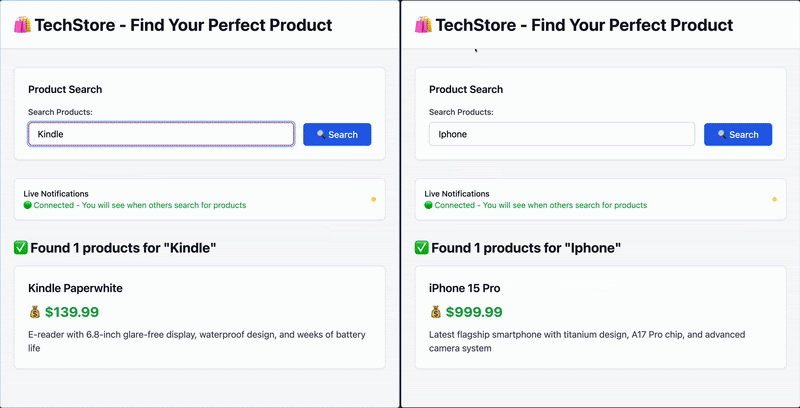
结论
在本文中,我们学习了如何使用 Elasticsearch 和 FastAPI 基于搜索创建实时通知。我们选择了一个固定的产品列表来发送通知,但你可以探索更多自定义流程,让用户选择自己想要接收通知的产品或查询,甚至使用 Elasticsearch 的 percolate 查询根据产品规格配置通知。
我们还尝试了一个接收通知的单用户池。使用 WebSockets,你可以选择向所有用户广播,或者选择特定用户。一个常见的模式是定义用户可以订阅的 “消息组”,就像群聊一样。
原文:Using FastAPI’s WebSockets and Elasticsearch to build a real-time app - Elasticsearch Labs
