哈希表特性与unordered_map/unordered_set实现分析

目录
一、哈希表核心特性总结
1.开放地址法
2.链地址法
二、unordered_map/unordered_set实现要点分析
1. 哈希表核心实现(HashTable2.h)
(1) 哈希函数处理
(2) 链地址法实现
(3) 迭代器设计
(4) hashtable设计
2. unordered_map实现要点
3. unordered_map实现要点
一、哈希表核心特性总结
哈希表有两种表 : 一种是闭散列(开放地址法),一种是开散列(链地址法),我将用画图来带大家理解这两种方法的思路
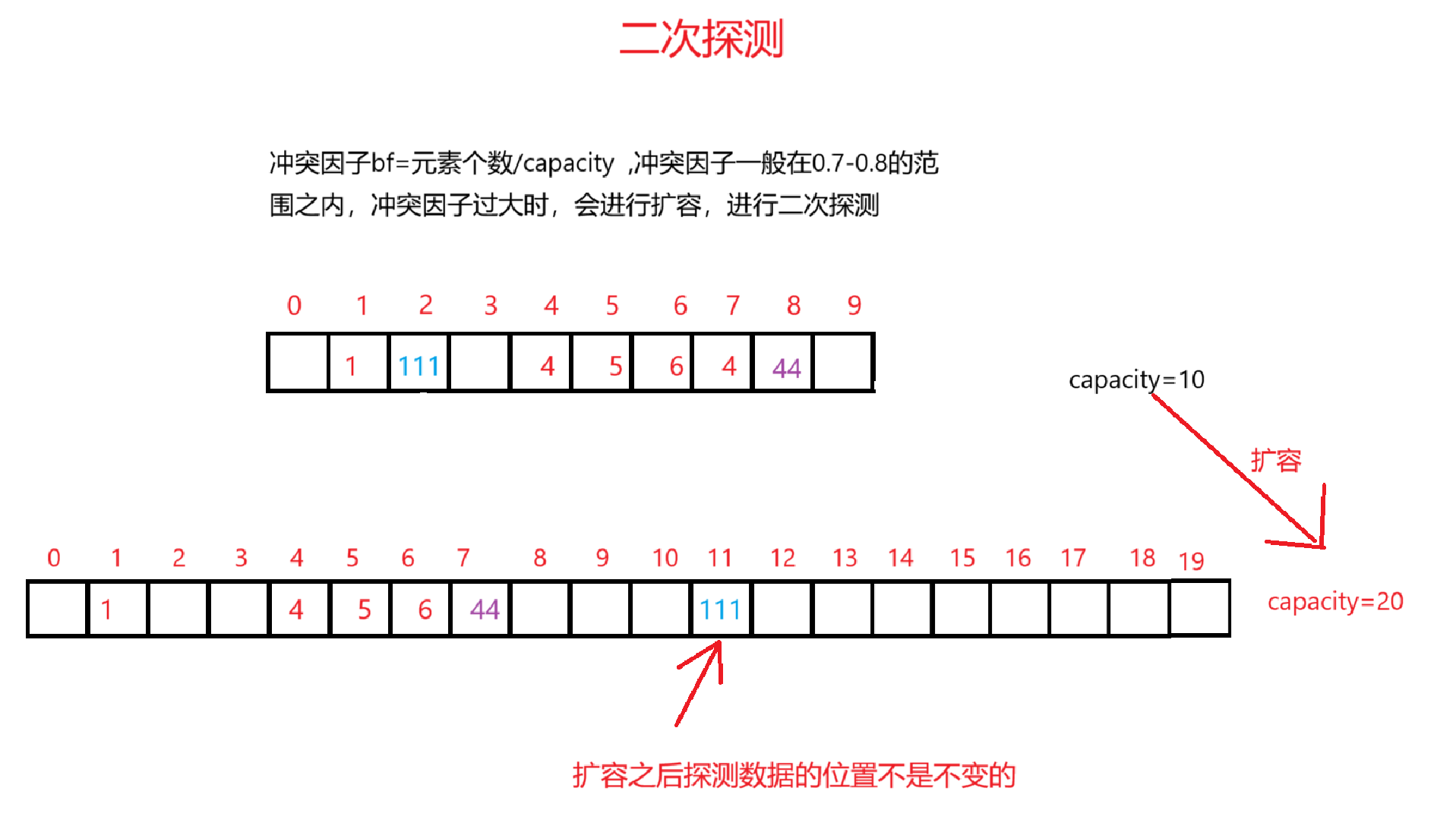
1.开放地址法
线性探测
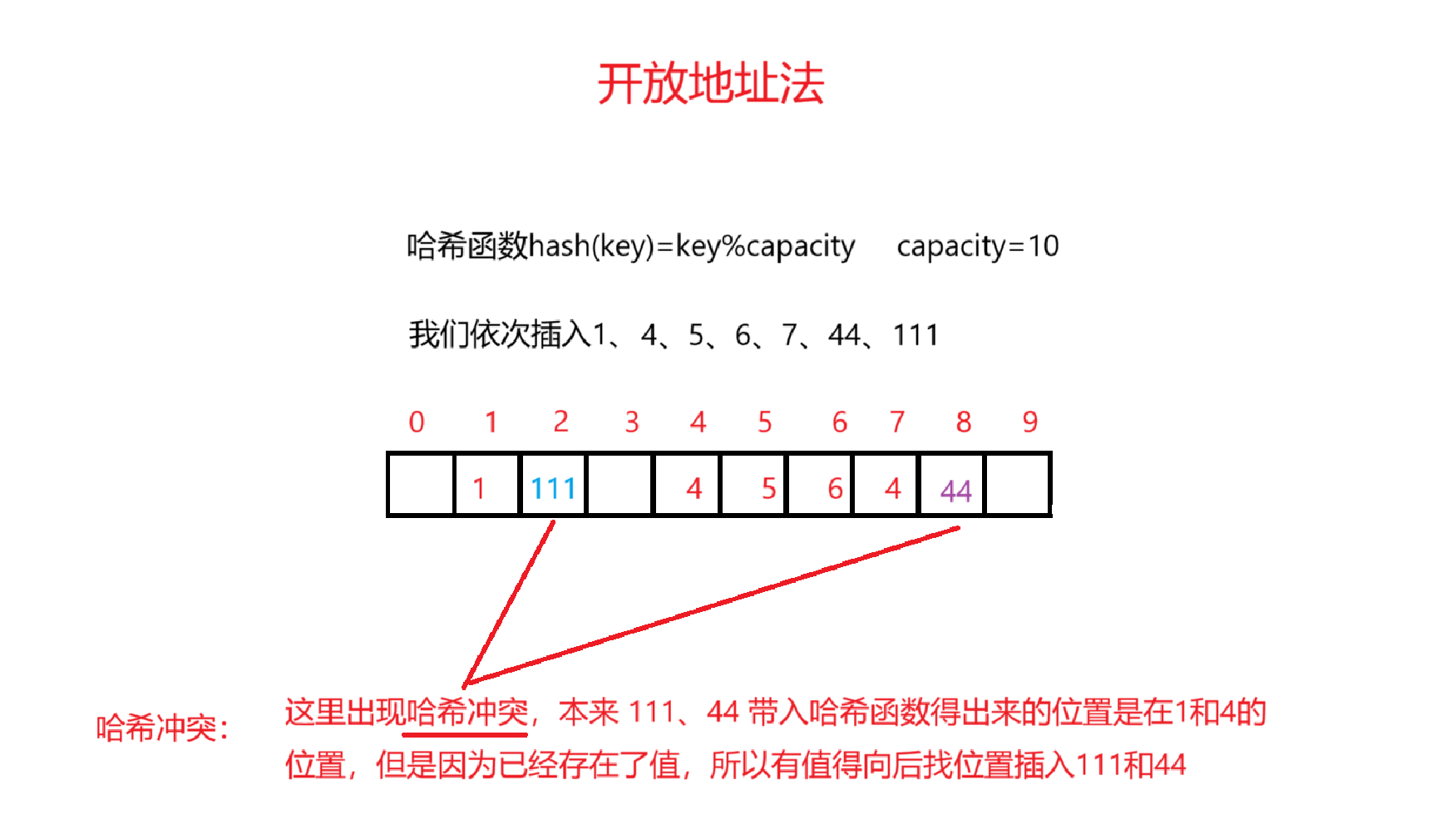
v
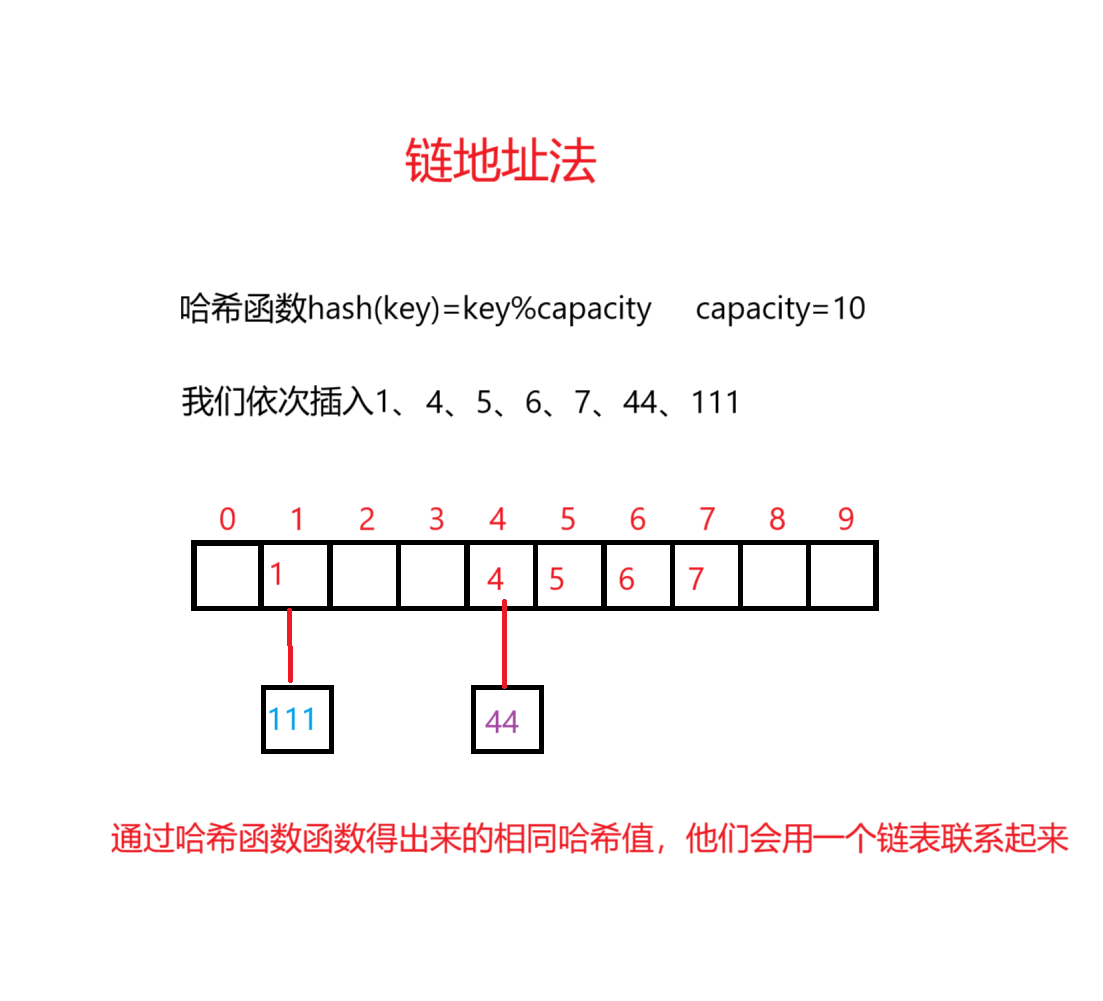
2.链地址法
二、unordered_map/unordered_set实现要点分析
1. 哈希表核心实现(HashTable2.h)
(1) 哈希函数处理
仅使用首字符会导致大量冲突(如所有以相同字母开头的字符串),使用BKDR哈希,通过累乘质数和字符值获得更好分布
// 默认哈希函数(直接类型转换)
template<class K>
struct DefaultHashFunc {size_t operator()(const K& key) {return (size_t)key;}
};// 字符串特化版本
template<>
struct DefaultHashFunc<string> {size_t operator()(const string& str) {size_t hash = 0;for(auto ch : str) {hash += 131;hash += ch;}return hash;}
};
(2) 链地址法实现
template<class T>
struct HashNode
{T _data;HashNode<T>* next;HashNode(const T& data):_data(data), next(nullptr){}
};(3) 迭代器设计
//前置申明,告诉Iterator,申明了哈希表
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class HashFunc >
class HashTable;template<class K, class T,class Ptr,class Ref, class KeyOfT, class HashFunc>
struct HTIterator
{typedef HashNode<T> Node; typedef HTIterator<K, T,Ptr,Ref, KeyOfT, HashFunc> Self;//这是什么鬼??typedef HTIterator<K, T, T*, T&, KeyOfT, HashFunc> Iterator;Node* _node;//就是不能改*phtconst HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, HashFunc>* _pht;//为什么需要节点的指针和哈希的指针/*HTIterator(Node * node,HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, HashFunc>* pht):_node(node),_pht(pht){}*///这个_pht加了const的重载HTIterator(Node* node,const HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, HashFunc>* pht):_node(node), _pht(pht){}//普通迭代器时,它是拷贝构造//const迭代器时,它是构造HTIterator(const Iterator & it):_node(it._node), _pht(it._pht){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}Self& operator++(){if (_node->next){//当前桶还没完_node = _node->next;}else{KeyOfT kot;HashFunc hf;size_t hashi = hf(kot(_node->_data)) % _pht->_table.size();//从下一个位置,查找不为空的桶++hashi;while (hashi < _pht->_table.size()){if (_pht->_table[hashi]){//不为空就退出_node = _pht->_table[hashi];return (*this);}else{//为空继续加 ++hashi;}}_node = nullptr;}return *this;}bool operator!=(const Self& s){return _node != s._node;}bool operator==(const Self& s){return _node == s._node;}
};(4) hashtable设计
template<class K, class T,class KeyOfT, class HashFunc = DefaultHashFunc<K>>class HashTable{typedef HashNode<T> Node;////友元声明,类模版需要把模版参数带上template<class K, class T,class Ptr,class Ref ,class KeyOfT, class HashFunc >friend struct HTIterator; public:typedef HTIterator<K, T,T*,T&, KeyOfT, HashFunc> iterator;typedef HTIterator<K, T,const T*,const T&, KeyOfT, HashFunc> const_iterator;iterator begin(){//找第一个桶for (size_t i =0 ;i < _table.size();i++){Node* cur = _table[i];if (cur){//这里为什么传this ??? 航哥说这里this是哈希表的指针return iterator(cur, this);}}//没有找到return iterator(nullptr, this);}iterator end(){return iterator(nullptr,this);}const_iterator begin()const{//找第一个桶for (size_t i = 0;i < _table.size();i++){Node* cur = _table[i];if (cur){return const_iterator(cur, this);}}//没有找到return const_iterator(nullptr, this);}const_iterator end()const{return const_iterator(nullptr, this);}HashTable(){//先把size开到10,然后把剩余的位置另存为空指针_table.resize(10, nullptr);}~HashTable(){for (size_t i = 0;i < _table.size();i++){Node* cur = _table[i];while (cur){Node* next = cur->next;delete cur;// free cur;cur = next;}//因为cur是野指针,如果不置空,那么他有可能还会指向原来的节点cur = nullptr;}}pair<iterator,bool> insert(const T& data){KeyOfT kot;HashFunc hf;iterator it = Find(kot(data));//在这里是证明有相同的内容if (it!=end()){return make_pair(it,false);}//负载因子到一就扩容if (_n == _table.size()){size_t newSize = _table.size() * 2;//创建新表HashTable<K,T,KeyOfT,HashFunc> newht;//这个需要开新节点,而且销毁也麻烦//for (size_t i = 0;i < _table.size();i++)//{// //.......// ht.insert();//}vector<Node*> newTable;newTable.resize(newSize, nullptr);//便利旧表,顺手牵羊,把节点签下来挂到新表for (size_t i = 0;i < _table.size();i++){Node* cur = _table[i];while (cur){Node* next = cur->next;//头插新表size_t hashi = hf(kot(cur->_data)) % newSize;cur->next = newTable[hashi];newTable[hashi] = cur;cur = next;}_table[i] = nullptr;}_table.swap(newTable);}size_t hashi = hf(kot(data)) % _table.size();//头插,这个没看懂Node* newnode = new Node(data);newnode->next = _table[hashi];_table[hashi] = newnode;++_n;return make_pair(iterator(newnode,this), true);}iterator Find(const K& key){HashFunc hf;KeyOfT kot;size_t hashi = hf(key) % _table.size();Node* cur = _table[hashi];while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) == key){return iterator(cur,this);}cur = cur->next;}return iterator(nullptr,this);}void Print(){for (size_t i = 0;i < _table.size();i++){printf("[%d]->", i);Node* cur = _table[i];while (cur){cout << cur->_kv.first << "->" << cur->_kv.second << "->";cur = cur->next;}printf("NULL\n");}}bool Erase(const K& key){HashFunc hf;KeyOfT kot;size_t hashi = hf(key) % _table.size();Node* cur = _table[hashi];Node* prev = nullptr;while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) == key){if (prev == nullptr){_table[hashi] = cur->next;}else{prev->next = cur->next;}delete cur;return true;}prev = cur;cur = cur->next;}--_n;return false;}private:vector<Node*> _table;//指针数组size_t _n = 0;};2. unordered_map实现要点
template<class K,class V>
class unordered_map
{struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K,V>& kv){return kv.first;}};
public:typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;pair<iterator,bool> insert(const pair<K,V>& kv){return _ht.insert(kv);}iterator begin(){return _ht.begin();}iterator end(){return _ht.end();}const_iterator begin()const{return _ht.begin();}const_iterator end()const{return _ht.end();}V& operator[](const K& key){pair<iterator,bool> ret=_ht.insert(make_pair(key,V()));return ret.first->second;}
private://这种const的特殊属性,一般是自己设置hash_bucket::HashTable<K,pair<const K,V>,MapKeyOfT > _ht;
};3. unordered_map实现要点
template<class K>
class unordered_set
{struct SetKeyOfT{const K & operator()(const K & key){return key;}};public:typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K,K,SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator iterator;typedef typename hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;iterator begin()const
{return _ht.begin();
}iterator end()const
{return _ht.end();
}
pair<iterator,bool> insert(const K& key)
{//这样写是错的,因为这里接受的是const_iterator,返回的是iteratorpair<hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::iterator, bool> ret = _ht.insert(key);return make_pair(ret.first, ret.second);
}private:hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K,SetKeyOfT> _ht;
};
