【学习嵌入式day23-Linux编程-文件IO】
目录
使用fgets和fputs实现文件拷贝
整体思路:
fwrite
fread
使用fread和fwrite完成对图片的拷贝
整体思路:
流的定位
概念:
fseek
ftell
rewind
从终端输入文件名,得到文件的长度
读取BMP图片的宽度和高度
文件IO
概念
系统调用与库函数
文件IO函数接口
函数接口
文件打开
关闭文件描述符
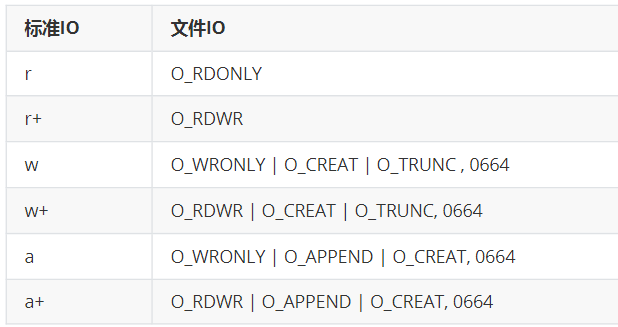
标准IO对应的文件IO的打开方式
文件IO读写
write
read
使用read和write完成对图片的拷贝
文件描述符偏移量的定位
lseek
文件IO与标准IO互相转换的函数
fileno
fdopen
feof
ferror
目录IO
操作方式
函数接口
opendir
closedir
readdir
getcwd:获得当前工作目录的绝对路径
chdir:切换当前的工作路径
递归实现目录的遍历
队列实现目录的广度遍历
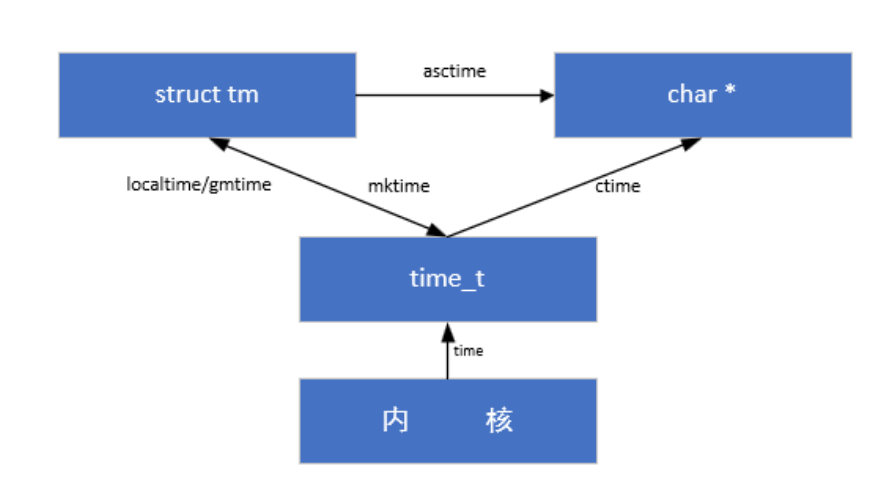
时间相关的函数接口
时间类型分类
time_t类型时间
struct tm类型时间
char *字符串类型时间
函数接口
time
localtime:将秒数转换为结构体时间
mktime:将结构体时间转换为time_t类型
ctime将Time_t转换为字符型时间
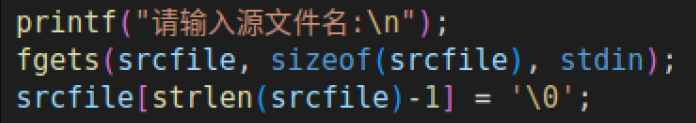
等价于gets的功能
使用fgets和fputs实现文件拷贝
整体思路:
fgets完成从流中接收一行数据到文件中
fputs完成从文件中写入字符串
- 使用fgets从终端接收源文件和目的文件
- 打开fopen源文件和目的文件
- 使用while(1)循环从源文件读数据fgets,往目的文件写数据fputs
- 关闭源文件和目的文件
//使用fgets和fputs实现文件拷贝#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>void copy_file_content(char *pdst, char *psrc)
{FILE *fsrc = NULL;FILE *fdst = NULL;char tmpbuff[256] = {0};char *pret = NULL;
//打开两个文件fsrc = fopen(psrc, "r");if(NULL == fsrc){perror("fail to fopen");return;}fdst = fopen(pdst, "w");if(NULL == fdst){perror("fail to fopen");return;}while (1){pret = fgets(tmpbuff, sizeof(tmpbuff), fsrc);if(NULL == pret){break;}fputs(tmpbuff, fdst);}fclose(fsrc);fclose(fdst);return;
}int main(void)
{char srcfile[256] = {0};char dstfile[256] = {0};printf("请输入源文件:\n");//gets(srcfile);//也可以使用fgetsfgets(srcfile, sizeof(srcfile), stdin);srcfile[strlen(srcfile)-1] = '\0';printf("请输入目的文件:\n");//gets(dstfile);//也可以使用fgersfgets(dstfile, sizeof(dstfile), stdin);dstfile[strlen(dstfile)-1] = '\0';copy_file_content(dstfile, srcfile);printf("拷贝完成\n");return 0;
}
fwrite
往文件里写二进制数据
#include <stdio.h>typedef struct student
{char name[32];char sex;int age;int score;
}stu_t;int main(void)
{FILE *fp = NULL;size_t nret = 0;stu_t s = {"zhangsan", 'm', 18, 90};stu_t s1 = {"lisi", 'f', 19, 85};//定义一个结构体数组stu_t stu[3] = {{"wangwu", 'm', 20, 95},{"xiaozhang", 'f', 19, 80},{"xiaowu", 'm', 18, 75},};fp = fopen("a.txt", "w");if(NULL == fp){perror("fail to fopen");return -1;}nret = fwrite(&s, sizeof(s), 1, fp);printf("nret = %ld\n", nret);nret = fwrite(&s1, sizeof(s1), 1, fp);printf("nret = %ld\n", nret);nret = fwrite(stu, sizeof(stu_t), 3, fp);printf("nret = %ld\n", nret);fclose(fp);return 0;
}Makefile文件
#要生成的文件名
OBJ=a.out#依赖的所有文件
OBJS+=main.c$(OBJ):$(OBJS)gcc $^ -o $@fread
从文件里读二进制数据
#include <stdio.h>typedef struct student{char name[32];char sex;int age;int score;
}stu_t;int main(void)
{FILE *fp = NULL;stu_t s;stu_t stu[10];size_t nret = 0;int i = 0;fp = fopen("a.txt", "r");if(NULL == fp){perror("fail to fopen");return -1;}//一次读所有的nretnret = fread(stu, sizeof(stu_t), 10, fp);printf("nret = %ld\n", nret);for(i = 0; i < nret; i++){printf("姓名:%s\n", stu[i].name);printf("性别:%c\n", stu[i].sex);printf("年龄:%d\n", stu[i].age);printf("分数:%d\n", stu[i].score);}printf("===============");//一次只读一个nret
/*while(1){nret = fread(&s, sizeof(s), 1, fp);if(0 == nret){break;}printf("nret = %ld\n", nret);printf("姓名:%s\n", s.name);printf("性别:%c\n", s.sex);printf("年龄:%d\n", s.age);printf("分数:%d\n", s.score);}
*/fclose(fp);return 0;
}
使用fread和fwrite完成对图片的拷贝
整体思路:
- 使用只读方式,打开原图片( fopen )
- 使用读写方式,打开目的图片( fopen )
- fread读原图片,参数:每次读一个字节,读4096个对象,循环完成
- fwrite写,往目的图片文件里写 所读到的内容。参数:每次读一个字节,读nret(fread的返回值)个对象。
- 关闭原图片和目的图片
#include <stdio.h>int main(void)
{FILE *fp_src = NULL;FILE *fp_dst = NULL;
//定义缓存区的大小char tmpbuff[4096] = {0};size_t nret = 0;//只读方式,打开原图片fp_src = fopen("1.png", "r");if(NULL == fp_src){perror("fail to fopen");return -1;}
//读写方式,打开目的图片fp_dst = fopen("2.png", "w");if(NULL == fp_dst){perror("fail to fopen");return -1;}while(1){//第二个参数:每次读一个字节。第三个参数:4096个对象//每次只读一个字节,读4096个对象,循环nret = fread(tmpbuff, 1, sizeof(tmpbuff), fp_src);if(0 == nret){break;}//第三个参数:读nret个对象fwrite(tmpbuff, 1, nret, fp_dst);}fclose(fp_src);fclose(fp_dst);return 0;
}流的定位
概念:
设置流的偏移量
fseek

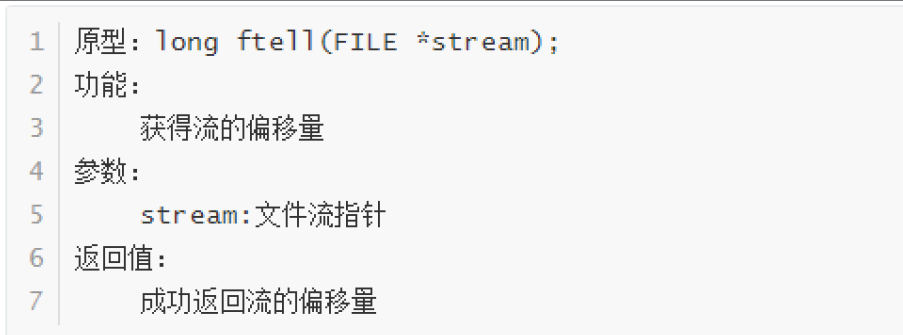
ftell
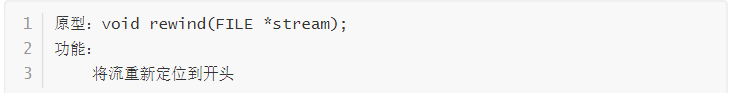
rewind
重新回到开头
从终端输入文件名,得到文件的长度
整体思路
- fgets函数,终端接收文件名
- fopen打开文件
- fseek定位到文件末尾位置
- ftell得到此时的len长度
- 输出len长度
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>int main(void)
{FILE *fp = NULL;char filename[256] = {0};long len = 0;printf("请输入文件名:\n");fgets(filename, sizeof(filename), stdin);filename[strlen(filename)-1] = '\0';fp = fopen(filename, "r");if(NULL == fp){perror("fail to fopen");return -1;}fseek(fp, 0, SEEK_END);len = ftell(fp);printf("len = %ld\n", len);fclose(fp);return 0;
}读取BMP图片的宽度和高度
整体思路:
- fopen打开bmp图片
- fseek偏移18个字节到宽度位置
- fread读取宽度和高度
- 输出宽度和高度
#include <stdio.h>int main(void)
{FILE *fp = NULL;int width = 0;int height = 0;fp = fopen("test.bmp", "r");if(NULL == fp){perror("fail to fopen");return -1;}fseek(fp, 18, SEEK_SET);fread(&width, 1, sizeof(width), fp);fread(&height, 1, sizeof(height), fp);printf("width = %d, height = %d\n", width, height);return 0;
}文件IO
概念
标准IO是由缓存的IO,文件IO没有缓存,适合于通信、硬件设备操作
标准IO是库函数,文件IO是系统调用
系统调用与库函数
系统调用:是linux内核中的代码,只能在linux系统中使用
库函数:是对系统调用的封装,可以在不同的操作系统中安装并使用,库函数最终还是要调用系统调用完成对应功能
文件IO函数接口
函数接口

文件打开

有三个特殊的文件描述符:
标准输入(0)、标准输出(1)、标准错误(2)
文件描述符特点:
- 非负整数
- 取 尚未被占用的最小的非负整数
- 文件描述符是由上限的,到达上限后再打开会报错
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>int main(void)
{int fd = 0;//r —— O_RDONLY//r+ —— O_RDWR 文件存在读写打开,文件不存在报错fd = open("a,txt", O_RDWR);if(-1 == fd){perror("fail to open");return -1;}close(fd);return 0;
}关闭文件描述符

标准IO对应的文件IO的打开方式
文件IO读写
write

#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>int main(void)
{int fd = 0;char tmpbuff[4096] = {"hello world"};ssize_t nret = 0;fd = open("a.txt", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0664);if (-1 == fd){perror("fail to open");return -1;}nret = write(fd, tmpbuff, strlen(tmpbuff));printf("实际写入:%ld\n", nret);close(fd);return 0;
}read

需要打印时,才对siezof(tmpbuff)-1
#include "../head.h"int main(void)
{int fd = 0;char tmpbuff[4096] = {0};ssize_t nret = 0;fd = open("/usr/include/stdio.h", O_RDONLY);if(-1 == fd){perror("fail to open");return -1;}nret = read(fd, tmpbuff, sizeof(tmpbuff)-1);printf("实际接收%ld字节,内容:%s\n", nret, tmpbuff);close(fd);return 0;
}使用read和write完成对图片的拷贝
#include "../head.h"int main(void)
{int fsrc = 0;int fdst = 0;char tmpbuff[4096] = {0};ssize_t nret = 0;//实际读到的字节数fsrc = open("1.png", O_RDONLY);if(-1 == fsrc){perror("fail to open");return -1;}fdst = open("2.png", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0664);if(-1 == fdst){perror("fail to open");return -1;}while (1){nret = read(fsrc, tmpbuff, sizeof(tmpbuff));if(nret <= 0){break;}//第二个参数:缓存区指针;第三个参数:实际读到的字节数write(fdst, tmpbuff, nret);}close(fsrc);close(fdst);return 0;
}文件描述符偏移量的定位
lseek

#include "../head.h"int main(void)
{FILE ;int fd = 0;char ch = 0;off_t len = 0;fd = open("a.txt", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT, 0664);if (-1 == fd){perror("fail to open");return -1;}len = lseek(fd, 10, SEEK_SET);printf("偏移量:%ld\n", len);ch = 'a';write(fd, &ch, 1);len = lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_CUR);printf("偏移量:%ld\n", len);len = lseek(fd, -5, SEEK_CUR);printf("偏移量:%ld\n", len);ch = 'b';write(fd, &ch, 1);len = lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_SET);printf("偏移量:%ld\n", len);ch = 'c';write(fd, &ch, 1); close(fd);return 0;
}文件IO与标准IO互相转换的函数
fileno
根据文件流指针获得文件描述符
fdopen
根据已经打开的文件描述符获得文件流指针
feof
判断文件流指针是否到达末尾
ferror
判断文件流指针是否出错
目录IO
操作方式
- 打开目录文件
- 读取目录文件中的没目录想
- 关闭目录文件
函数接口
opendir
要加上头文件 #include <dirent.h>

closedir

readdir

#include "../head.h"int main(void)
{DIR *dp = NULL;struct dirent *pp = NULL;dp = opendir(".");if(NULL == dp){perror("fail to opendir");return -1;}while (1){pp = readdir(dp);if(NULL == pp){break;}if('.' == pp->d_name[0]){continue;}switch(pp->d_type){case DT_BLK:printf("块设备文件");break;case DT_CHR:printf("字符设备文件");break;case DT_DIR:printf("目录文件");break;case DT_FIFO:printf("管道文件");break;case DT_LNK:printf("链接文件");break;case DT_REG:printf("普通文件");break;case DT_SOCK:printf("套接字文件");break;}printf("\t\t%s\n", pp->d_name);}closedir(dp);return 0;
}getcwd:获得当前工作目录的绝对路径

chdir:切换当前的工作路径

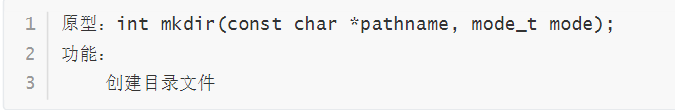
mkdir
- r : 读权限,决定用户是否能够查看目录下所有文件名
- w :写权限,决定用户是否能够在目录下新建文件
- x:执行权限,决定用户是否能够进入目录
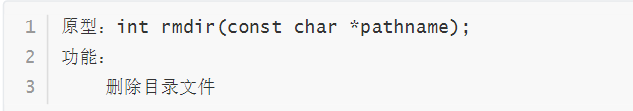
rmdir
递归实现目录的遍历
//遍历所有目录下的子文件
#include "../head.h"void listdir(char *dirpath)
{DIR *dp = NULL;struct dirent *pp = NULL;char tmpbuff[4096] = {0};dp = opendir(dirpath);if(NULL == dp){perror("fail to opendir");printf("failed:%s\n", dirpath);return;}while(1){pp = readdir(dp);if(NULL == pp){break;}if('.' == pp->d_name[0]){continue;}sprintf(tmpbuff, "%s/%s", dirpath, pp->d_name);printf("%s\n", tmpbuff);if(pp->d_type == DT_DIR){listdir(tmpbuff);}}closedir(dp);return;
}int main(void)
{listdir("/home/linux");return 0;
}队列实现目录的广度遍历
#include "../head.h"
#include "linkqueue.h"void listdir(char *dirpath)
{linknode *plinkqueue = NULL;char tmppath[256] = {0};char filepath[1024] = {0};DIR *dp = NULL;struct dirent *pp = NULL;plinkqueue = create_empty_linkqueue();enter_linkqueue(plinkqueue, dirpath);while (!is_empty_linkqueue(plinkqueue)){quit_linkqueue(plinkqueue, tmppath);dp = opendir(tmppath);if (NULL == dp){perror("fail to opendir");printf("%s\n", tmppath);return;}while (1){pp = readdir(dp);if (NULL == pp){break;}if ('.' == pp->d_name[0]){continue;}sprintf(filepath, "%s/%s", tmppath, pp->d_name);printf("%s\n", filepath);if (pp->d_type == DT_DIR){enter_linkqueue(plinkqueue, filepath);}}}destroy_linkqueue(&plinkqueue);return;
}int main(void)
{listdir("/home/linux");return 0;
}时间相关的函数接口
时间类型分类
-
time_t类型时间
- 1970-1-1到现在的秒数
- 用于时间计算相关逻辑
-
struct tm类型时间
- 包含年月日时分秒信息
-
char *字符串类型时间
- 由时间拼接的字符串
函数接口
time

localtime:将秒数转换为结构体时间

#include "../head.h"int main(void)
{time_t t;struct tm *ptm = NULL;time_t ret;char *pstr = NULL;//time(&t);t = time(NULL);//获得当前时间的秒数,从1970年开始printf("t = %ld\n", t);ptm = localtime(&t);printf("%04d-%02d-%02d %02d-%02d-%02d\n", ptm->tm_year+1900, ptm->tm_mon+1, ptm->tm_mday,ptm->tm_hour, ptm->tm_min, ptm->tm_sec);ret = mktime(ptm); printf("ret = %ld\n", ret);pstr = ctime(&ret);printf("pstr = %s\n", pstr);return 0;
}mktime:将结构体时间转换为time_t类型

ctime将Time_t转换为字符型时间