Cell-cultured meat: The new favorite on the future dining table
What is Cultivated Meat?
Cultivated meat refers to edible animal muscle tissue produced in vitro using cell culture engineering and tissue engineering technologies. The concept dates back to the 1930s, but it wasn’t until the late 1990s and early 2000s that related patents began to emerge abroad. In 2013, Dutch scientist Mark Post organized the world’s first public tasting event for a cultivated beef burger and disclosed the technical details, marking the official entry of cultivated meat into the public eye.

The Development Process of Cultivated Meat
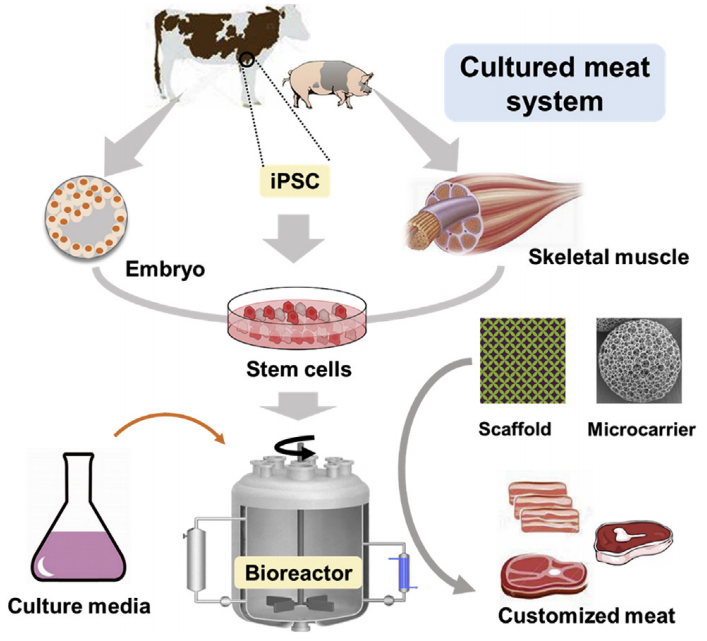
Source: Trends in Food Science & Technology
-
Cell Extraction: A small number of cells are extracted from an animal to serve as "seeds," forming the starting point for the cultivation and expansion of cultivated meat. These cells are typically myosatellite cells or mesenchymal stem cells, which have the potential to be induced into a "myogenic cell fate."
-
Cultivation and Expansion: The extracted cells are placed in a bioreactor that simulates the growth environment inside an animal, providing them with sufficient nutrients to achieve exponential proliferation. During this process, the cells are cultured on a large scale in a sterile environment, avoiding the diseases and contamination issues associated with traditional farming.
The production process requires various growth factors to support cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, and tissue formation. Below are some key growth factors that may be needed in cultivated meat production:
-
Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF): Commonly used to promote the proliferation and differentiation of mesenchymal, epithelial, and other cell types.
-
Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF): Plays an important role in the expansion and maturation of bovine myoblasts.
-
Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF): Used to maintain or derive certain types of stem cells.
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 (FGF-basic): Critical for the proliferation of many cell lines and the maintenance of stem cell pluripotency.
-
Transforming Growth Factor Beta 3 (TGF-β3): Used for the maintenance of mesenchymal stem cells and the differentiation of myoblasts.
-
Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB (PDGF-BB): A potent mitogen that promotes cell proliferation and increases cell mass.
Additionally, cultivated meat production involves other growth factors and nutrients, including amino acids, lipids, and vitamins, which are essential for cell proliferation and differentiation.
-
Structure Formation: Using scaffolds or 3D printing technology, the cells are guided to form the organizational structure of meat. These scaffolds are made of biodegradable polymer materials that facilitate directional cell growth and differentiation.
-
Final Meat Product: Food science techniques are applied to replicate the taste, texture, and nutritional value of traditional meat, making cultivated meat comparable in flavor, mouthfeel, and nutritional content.
Technological Advantages of Cultivated Meat
-
High Efficiency and Environmental Friendliness: Cultivated meat bypasses the traditional livestock farming and slaughter processes, directly producing animal protein from cells, significantly reducing resource consumption and environmental pollution. Estimates suggest that if cultivated meat reaches mass production, it could reduce energy use by 7%–45%, lower greenhouse gas emissions by 78%–96%, decrease land use by 99%, and cut water consumption by 82%–96%.
-
Safety and Health: Cultivated meat is produced in a sterile environment, avoiding hormones, antibiotics, and pathogens that may be present in traditional farming, thereby improving food safety. Additionally, by adjusting cell culture conditions, healthier meat products with lower fat and higher protein content can be produced.
-
Customizable Production: Cultivated meat can be tailored to consumer preferences, such as adjusting protein and fat levels or adding vitamins and other functional ingredients to meet diverse nutritional needs.
-
Reduced Harm to Animals: Cultivated meat does not rely on live animals, achieving zero harm to animals and reducing the risk of animal diseases and foodborne illnesses.
Challenges
-
Cost Issues: Currently, the production cost of cultivated meat is relatively high, requiring further technological breakthroughs and scaled-up production to reduce costs.
-
Consumer Acceptance: The level of consumer acceptance for this new type of meat product remains uncertain, necessitating education and marketing efforts to raise awareness.
-
Regulation and Legislation: As an emerging food product, cultivated meat requires a corresponding regulatory framework and legal standards to ensure its safety and legitimacy.
Future Prospects
Although cultivated meat technology is still in development, its prospects are promising. With continuous technological advancements and gradual cost reductions, cultivated meat is expected to achieve commercial-scale production in the coming years, serving as an important complement to traditional meat.
To realize this goal, collaborative efforts from research institutions, businesses, and governments are needed. On one hand, increased investment in R&D is required to overcome technical bottlenecks and improve production efficiency. On the other hand, a robust regulatory system and market mechanisms must be established to ensure product safety and competitiveness.
Additionally, public awareness and education about cultivated meat must be strengthened to address consumer concerns. Through science communication, tasting events, and other initiatives, consumers can learn about the benefits of cultivated meat, gradually accepting and embracing this innovative product.
In conclusion, as a new, efficient, and environmentally friendly method of meat production, cultivated meat has broad development prospects and enormous market potential. We have every reason to believe that in the near future, cultivated meat will become a new favorite on our dining tables, contributing to human health and sustainable development.
Product Information
| Gatalog Num | Product Name | Product Parameters | Price |
| UA040313-AF | EGF Protein, Porcine (Animal Free) | Host : Porcine | Inquiry |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040349-AF | EGF Protein, Bovine (Animal Free) | Host : Bovine | $80 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040003 | EGF Protein, Human | Host : Human | $48 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040283-AF | HGF(NK1) Protein, Bovine (Animal Free) | Host : Bovine | $330 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040284-AF | HGF(NK1) Protein, Porcine (Animal Free) | Host : Porcine | $330 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040194 | HGF Protein, Human | Host : Human | $120 |
| Expression System : CHO | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040280-AF | LIF Protein, Porcine (Animal Free) | Host : Porcine | $376 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040277 | LIF Protein, Bovine | Host : Bovine | $576 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040023 | LIF Protein, Human | Host : Human | $760 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040318 | FGF-basic Protein(146aa), Porcine | Host : Porcine | $60 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040197 | FGF-basic Protein, Bovine | Host : Bovine | $80 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040276 | FGF-basic(145aa) Protein, Human | Host : Human | $80 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040145 | FGF-basic(146aa) Protein, Human | Host : Human | $80 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040007 | FGF-basic(154aa) Protein, Human | Host : Human | $216 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040294 | TGF-β3 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $240 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040014 | PDGF-BB Protein, Human | Host : Human | $240 |
| Expression System : Yeast | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated |
Source of the article:Cell-cultured meat: The new favorite on the future dining table.
