Java(HashMap和HashTable和Properties)
HashMap:

HashMap底层原理分析:
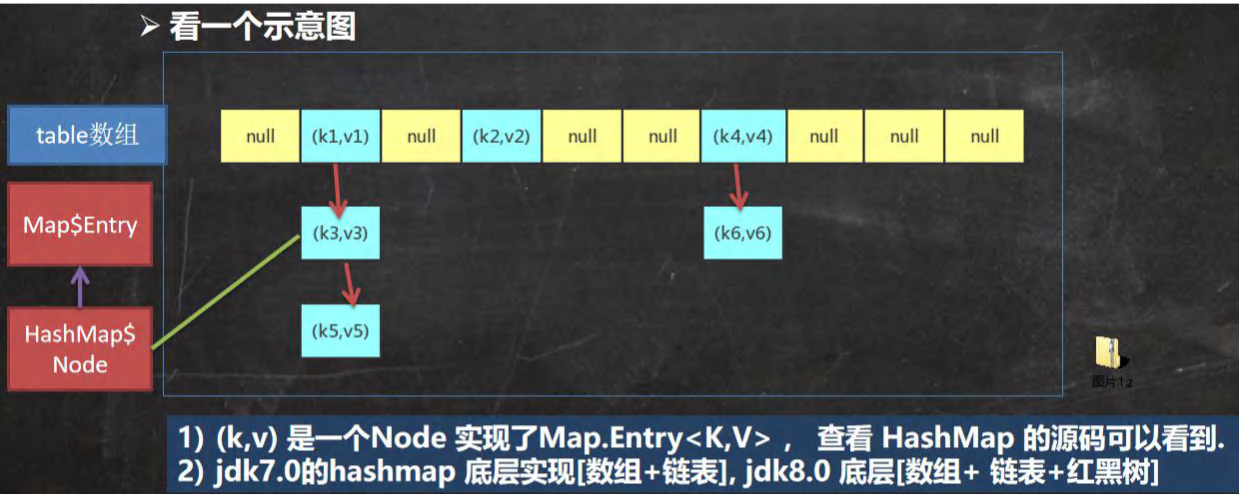

源码:
1.执行构造器 new HashMap()
初始化加载因子 loadfactor = 0.75
HashMap$Node[] table = null
2. 执行 put 调用 hash 方法,计算 key 的 hash 值 (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16)
public V put(K key, V value) {//K = "java" value = 10
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
3. 执行 putVal
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;//辅助变量
//如果底层的 table 数组为 null, 或者 length =0 , 就扩容到 16
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
//取出 hash 值对应的 table 的索引位置的 Node, 如果为 null, 就直接把加入的 k-v
//, 创建成一个 Node ,加入该位置即可
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;//辅助变量
// 如果 table 的索引位置的 key 的 hash 相同和新的 key 的 hash 值相同,
// 并 满足(table 现有的结点的 key 和准备添加的 key 是同一个对象 || equals 返回真)
// 就认为不能加入新的 k-v
if (p.hash == hash &&((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)//如果当前的 table 的已有的 Node 是红黑树,就按照红黑树的方式处
理
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
//如果找到的结点,后面是链表,就循环比较
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {//死循环
if ((e = p.next) == null) {//如果整个链表,没有和他相同,就加到该链表的最后
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
//加入后,判断当前链表的个数,是否已经到 8 个,到 8 个,后
//就调用 treeifyBin 方法进行红黑树的转换
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash && //如果在循环比较过程中,发现有相同,就 break,就只是替换 value
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value; //替换,key 对应 value
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;//每增加一个 Node ,就 size++
if (++size > threshold[12-24-48])//如 size > 临界值,就扩容
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
5. 关于树化(转成红黑树)
//如果 table 为 null ,或者大小还没有到 64,暂时不树化,而是进行扩容.
//否则才会真正的树化 -> 剪枝
final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) {
int n, index; Node<K,V> e;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)
resize();
}
}
}
HashTable 的基本介绍:
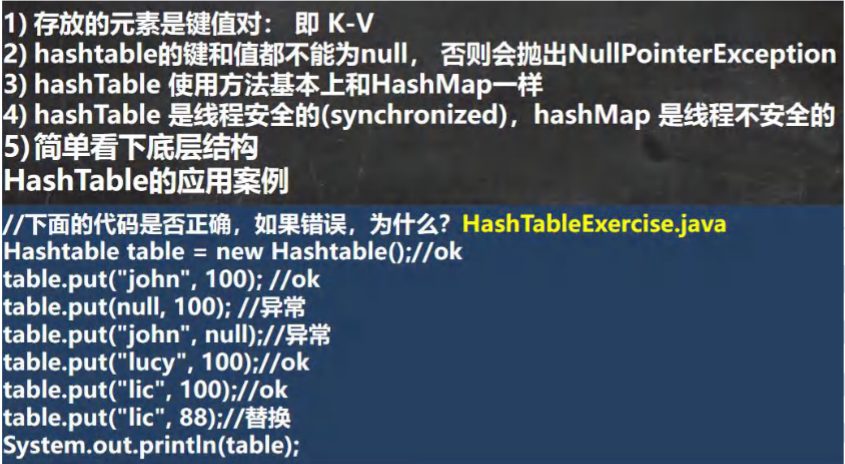
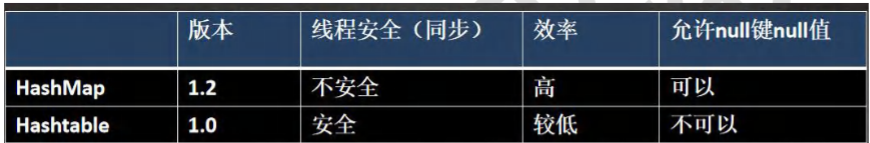
Hashtable 和 HashMap 对比:
Properties:

Properties的方法:
put():添加/修改
remove():删除
开发中如何选择集合实现类:

TreeSet:
//1. 当我们使用无参构造器,创建 TreeSet 时,仍然是无序的
//2. 老师希望添加的元素,按照字符串大小来排序
//3. 使用 TreeSet 提供的一个构造器,可以传入一个比较器(匿名内部类)
// 并指定排序规则
源码:
1. 构造器把传入的比较器对象,赋给了 TreeSet 的底层的 TreeMap 的属性 this.comparator
public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
2. 在 调用 treeSet.add("tom"), 在底层会执行到
if (cpr != null) {//cpr 就是我们的匿名内部类(对象)
do {
parent = t;
//动态绑定到我们的匿名内部类(对象)compare
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else //如果相等,即返回 0,这个 Key 就没有加入
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
TreeMap:
1. 构造器. 把传入的实现了 Comparator 接口的匿名内部类(对象),传给给 TreeMap 的 comparator
public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
2. 调用 put 方法
2.1 第一次添加, 把 k-v 封装到 Entry 对象,放入 root
Entry<K,V> t = root;
if (t == null) {
compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
2.2 以后添加
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
do { //遍历所有的 key , 给当前 key 找到适当位置
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);//动态绑定到我们的匿名内部类的 compare
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else //如果遍历过程中,发现准备添加 Key 和当前已有的 Key 相等,就不添加
eturn t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
}
}
