质数时间(二分查找)
题目描述
如果把一年之中的某个时间写作 a 月 b 日 c 时 d 分 e 秒的形式,当这五个数都为质数时,我们把这样的时间叫做质数时间,现已知起始时刻是 2022 年的 a 月 b 日 c 时 d 分 e 秒,终止时刻是 2022 年的 u 月 v 日 w 时 x 分 y 秒,请你统计在这段时间中有多少个质数时间?
输入
输入共 (2∗T+1) 行。第一行一个整数 T ,代表共有 T 组查询。
接下来2∗T 行,对于每组查询,先输入一行五个整数a、b、c、d、e ,代表起始时刻是 a 月 b 日 c 时 d 分 e 秒。再输入一行五个整数u、v、w、x、y,代表终止时刻是 u 月 v 日 w 时 x 分 y 秒。
对于每组查询保证输入的起始时刻不晚于终止时刻。
输出
输出共 T 行,一行一个整数,表示对于每组查询输入统计到的从 a 月 b 日 c 时 d 分 e 秒到 u 月 v 日 w 时 x 分 y 秒中质数时间的个数。多组查询结果用换行分隔。
样例输入
3
3 3 3 3 0
3 3 3 5 59
7 2 6 45 32
7 29 15 30 54
2 6 2 45 32
12 3 16 56 8样例输出
34
24276
127449提示
对于所有数据,保证1≤T≤105 且1≤a,u≤12, 1≤b, 1≤b,v≤31, 0≤c,w<24, 0≤d,x<60 ,0≤e,y<60。
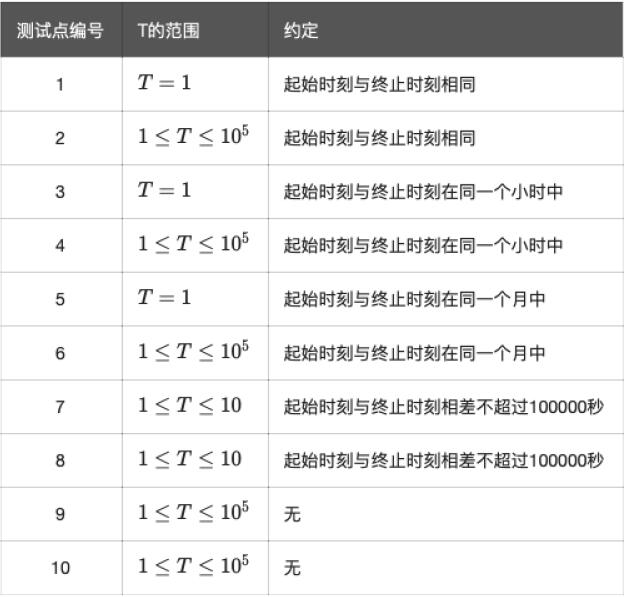
每个测试点的数据规模及特点如下表所示。
思路分析
1.预处理所有质数时间,转化为秒,存入数组。
2.读入数据,同样地,将起止时间转化为秒,二分查找。(起点对应lower_bound,终点对应upper_bound。lower_bound返回第一个指向不小于value的数的位置的迭代器,upper_bound返回第一个指向大于value的数的位置的迭代器。)
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
ll T;
vector<int>month={2,3,5,7,11};
vector<int>day={2,3,5,7,11,13,17,19,23,29,31};
vector<int>hour={2,3,5,7,11,13,17,19,23};
vector<int>ms={2,3,5,7,11,13,17,19,23,29,31,37,41,43,47,53,59};
vector<ll>p;
int main(){ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);vector<int>v={31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};vector<vector<int>>data(15,vector<int>(35,0));ll k=0;for(int i=0;i<12;i++){for(int j=1;j<=v[i];j++){data[i+1][j]=k;k++;}}for(int i=0;i<5;i++){for(int j=0;j<11;j++){if(month[i]==2&&day[j]>28)break;if(month[i]==11&&day[j]>30)break;for(int k=0;k<9;k++){for(int m=0;m<17;m++){for(int n=0;n<17;n++){ll t=data[month[i]][day[j]]*24*60*60+hour[k]*60*60+ms[m]*60+ms[n];p.push_back(t);}}}}}cin>>T;while(T--){ll t,ans=0;int a,b,c,d,e,u,v,w,x,y;cin>>a>>b>>c>>d>>e;cin>>u>>v>>w>>x>>y;ll st=data[a][b]*24*60*60+c*60*60+d*60+e;ll ed=data[u][v]*24*60*60+w*60*60+x*60+y;auto it=lower_bound(p.begin(),p.end(),st);auto id=upper_bound(p.begin(),p.end(),ed);ans=id-it;cout<<ans<<"\n";}return 0;
}(若定义vector<ll> p(35000000,0);p数组的大小为35000000个long long,每个long long8字节,总大小约35000000*8=280,000,000字节,即280MB)
