Linux重定向和缓冲区
前提知识:
获取文件信息
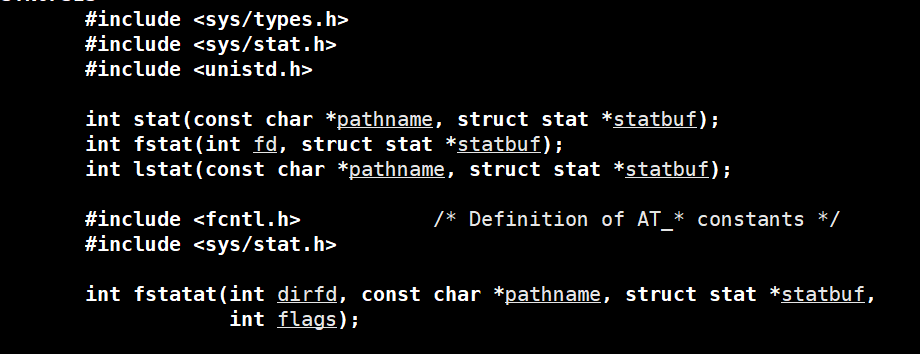 struct stat:
struct stat:
struct stat {dev_t st_dev; /* ID of device containing file */ino_t st_ino; /* Inode number */mode_t st_mode; /* File type and mode */nlink_t st_nlink; /* Number of hard links */uid_t st_uid; /* User ID of owner */gid_t st_gid; /* Group ID of owner */dev_t st_rdev; /* Device ID (if special file) */off_t st_size; /* Total size, in bytes */blksize_t st_blksize; /* Block size for filesystem I/O */blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* Number of 512B blocks allocated *//* Since Linux 2.6, the kernel supports nanosecondprecision for the following timestamp fields.For the details before Linux 2.6, see NOTES. */struct timespec st_atim; /* Time of last access */struct timespec st_mtim; /* Time of last modification */struct timespec st_ctim; /* Time of last status change */#define st_atime st_atim.tv_sec /* Backward compatibility */#define st_mtime st_mtim.tv_sec#define st_ctime st_ctim.tv_sec};
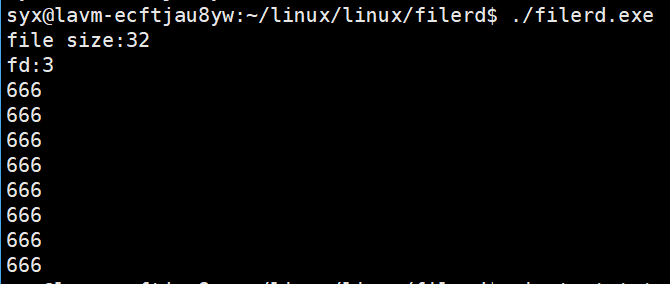
读取文件及获取文件大小代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<malloc.h>
int main()
{struct stat st;int n = stat("test.txt",&st);if(n<0)return 1;printf("file size:%lu\n",st.st_size);int fd = open("test.txt",O_RDONLY);if(fd<0){perror("open");return 2;}printf("fd:%d\n",fd);char* buffer = (char*)malloc(st.st_size + 1);n = read(fd,buffer,st.st_size);if(n>0){buffer[n] = '\0';printf("%s",buffer);}free(buffer);close(fd);return 0;
}
重定向
本质:是在内核中改变文件描述符表特定下表的内容,和上层无关。
现有如下代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
int main()
{close(1);int fd = open("file.txt",O_WRONLY | O_CREAT,0666);printf("printf,fd:%d\n",fd);fprintf(stdout,"666\n");fprintf(stdout,"888\n");fflush(stdout);close(fd);return 0;
}
运行
但是什么都没有打印,查看file.txt文件,发现所有信息在该文件里
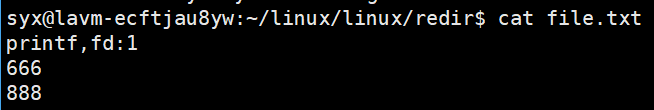
说明stdout里封装的fd永远是1,但是我们将这个1下标指向的内容改为文件流了,所以输出在文件里,这就是重定向。
但是,如果把fflush注释掉,会发现不会写在文件里,这是因为fflush会把语言级别的缓冲区刷新到内核级别的文件缓冲区,然后写在磁盘上,如果没有这个刷新操作,该文件关闭之后数据也就丢失了。
dup2
描述符表数组下标内容的拷贝,把oldfd的下表的内容拷贝到newfd对应内容,只剩下oldfd。
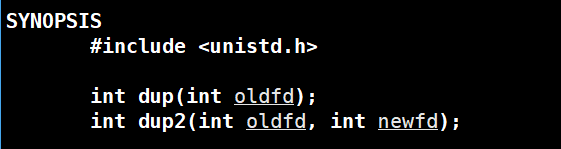
int fd = open("file.txt",O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC,0666);dup2(fd,1);fprintf(stdout,"666\n");fprintf(stdout,"888\n");
结果输出在file.txt里。
缓冲区
缓冲区就是一段内存空间,给上层提供高效的IO体验,间接提高整体效率。
缓冲区好处:解耦,提高效率(使用者效率,IO刷新效率)。
刷新策略:
1.立即刷新。fflush,fsync
2.行刷新。显示器
3.全缓冲。写满才刷新,普通文件
特殊情况:
进程退出,缓冲区自动刷新。
强制刷新。
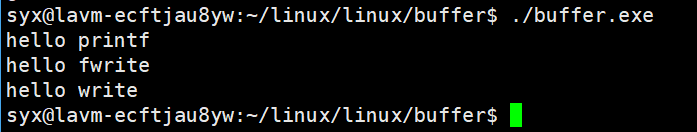
现有代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{const char *msg0="hello printf\n";const char *msg1="hello fwrite\n";const char *msg2="hello write\n";printf("%s", msg0);fwrite(msg1, strlen(msg0), 1, stdout);write(1, msg2, strlen(msg2));fork();return 0;
}
运行:
没有任何问题,但是重定向后结果却不同:
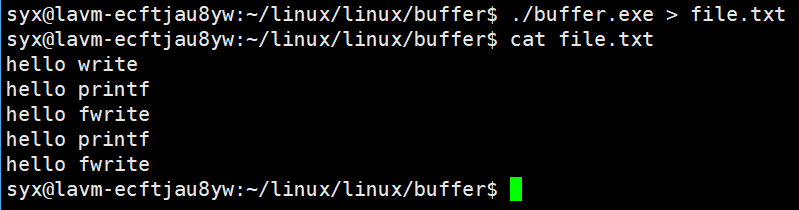
这是因为子进程的stdout用户级别缓冲区也刷新到文件里了,而父子进程拥有一样的缓冲区内容。
FILE结构体源码
struct _IO_FILE {int _flags; /* High-order word is _IO_MAGIC; rest is flags. */
#define _IO_file_flags _flags//缓冲区相关/* The following pointers correspond to the C++ streambuf protocol. *//* Note: Tk uses the _IO_read_ptr and _IO_read_end fields directly. */char* _IO_read_ptr; /* Current read pointer */char* _IO_read_end; /* End of get area. */char* _IO_read_base; /* Start of putback+get area. */char* _IO_write_base; /* Start of put area. */
char* _IO_write_ptr; /* Current put pointer. */char* _IO_write_end; /* End of put area. */char* _IO_buf_base; /* Start of reserve area. */char* _IO_buf_end; /* End of reserve area. *//* The following fields are used to support backing up and undo. */char *_IO_save_base; /* Pointer to start of non-current get area. */char *_IO_backup_base; /* Pointer to first valid character of backup area */char *_IO_save_end; /* Pointer to end of non-current get area. */struct _IO_marker *_markers;struct _IO_FILE *_chain;int _fileno; //封装的文件描述符
#if 0int _blksize;
#elseint _flags2;
#endif_IO_off_t _old_offset; /* This used to be _offset but it's too small. */#define __HAVE_COLUMN /* temporary *//* 1+column number of pbase(); 0 is unknown. */unsigned short _cur_column;signed char _vtable_offset;char _shortbuf[1];/* char* _save_gptr; char* _save_egptr; */_IO_lock_t *_lock;
#ifdef _IO_USE_OLD_IO_FILE
};
