Spring 源码阅读(二) 核心概念解析 ApplicationContext、类型转化
ApplicationContext
上面有分析到,ApplicationContext是个接口,实际上也是一个BeanFactory,不过比BeanFactory更加强大,比如:
- HierarchicalBeanFactory:拥有获取父BeanFactory的功能
- ListableBeanFactory:拥有获取beanNames的功能
- ResourcePatternResolver:资源加载器,可以一次性获取多个资源(文件资源等等)
- EnvironmentCapable:可以获取运行时环境(没有设置运行时环境功能)
- ApplicationEventPublisher:拥有广播事件的功能(没有添加事件监听器的功能)
- MessageSource:拥有国际化功能
具体的功能演示,后面会有。
我们先来看ApplicationContext两个比较重要的实现类:
- AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
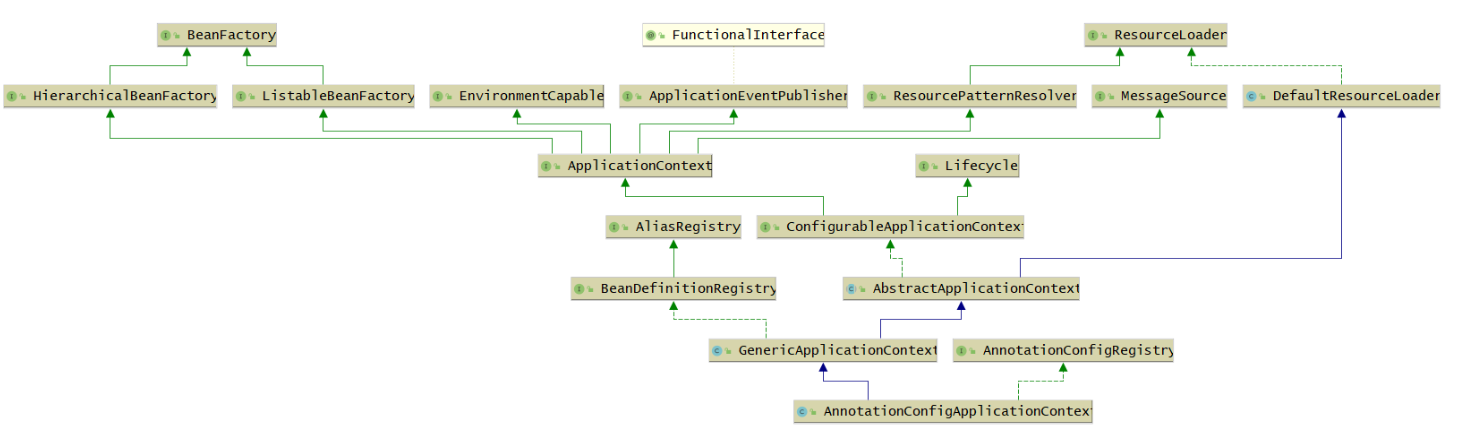
这部分现在看不懂没关系,源码熟悉一点后回来再来看都可以。
- ConfigurableApplicationContext:继承了ApplicationContext接口,增加了,添加事件监听器、添加BeanFactoryPostProcessor、设置Environment,获取ConfigurableListableBeanFactory等功能
- AbstractApplicationContext:实现了ConfigurableApplicationContext接口
- GenericApplicationContext:继承了AbstractApplicationContext,实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口,拥有了所有ApplicationContext的功能,并且可以注册BeanDefinition,注意这个类中有一个属性(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory)
- AnnotationConfigRegistry:可以单独注册某个为类为BeanDefinition(可以处理该类上的**@Configuration注解**,已经可以处理**@Bean注解**),同时可以扫描
- AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:继承了GenericApplicationContext,实现了AnnotationConfigRegistry接口,拥有了以上所有的功能
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
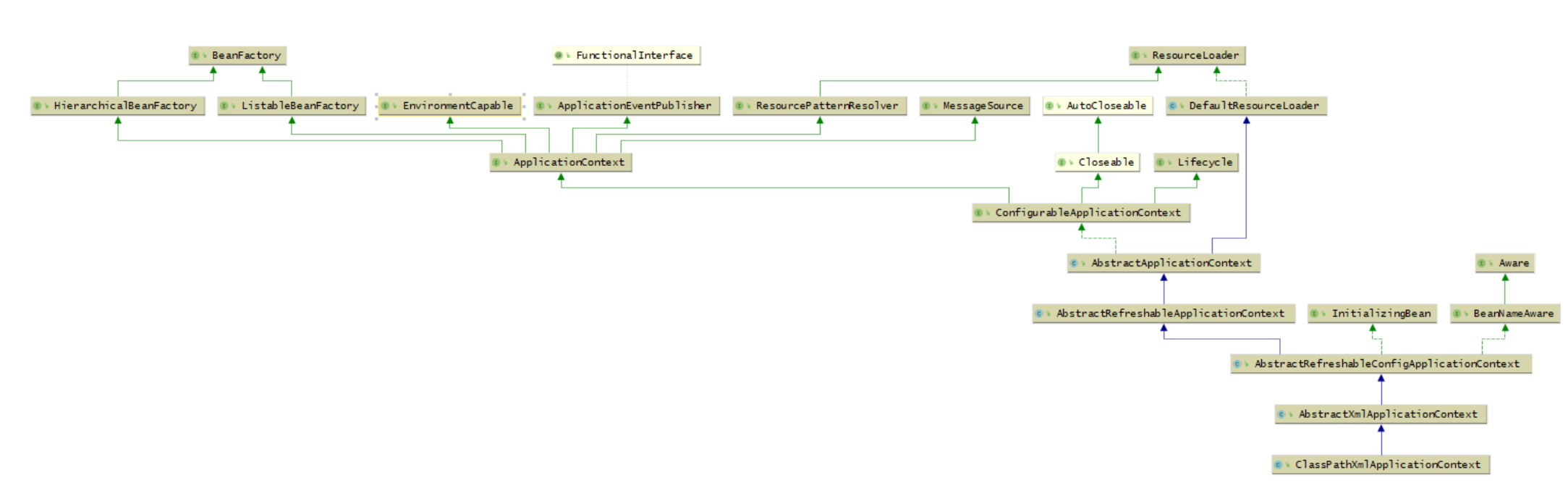
它也是继承了AbstractApplicationContext,但是相对于AnnotationConfigApplicationContext而言,功能没有AnnotationConfigApplicationContext强大,比如不能注册BeanDefinition
国际化
先定义一个MessageSource:
@Bean
public MessageSource messageSource() {ResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = new ResourceBundleMessageSource();messageSource.setBasename("messages");return messageSource;
}
有了这个Bean,你可以在你任意想要进行国际化的地方使用该MessageSource。
同时,因为ApplicationContext也拥有国家化的功能,所以可以直接这么用:
context.getMessage("test", null, new Locale("en_CN"))
资源加载
ApplicationContext还拥有资源加载的功能,比如,可以直接利用ApplicationContext获取某个文件的内容:
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);Resource resource = context.getResource("file://D:\\IdeaProjects\\spring-framework\\luban\\src\\main\\java\\com\\luban\\entity\\User.java");
System.out.println(resource.contentLength());
你可以想想,如果你不使用ApplicationContext,而是自己来实现这个功能,就比较费时间了。
还比如你可以:
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);Resource resource = context.getResource("file://D:\\IdeaProjects\\spring-framework-5.3.10\\tuling\\src\\main\\java\\com\\zhouyu\\service\\UserService.java");
System.out.println(resource.contentLength());
System.out.println(resource.getFilename());Resource resource1 = context.getResource("https://www.baidu.com");
System.out.println(resource1.contentLength());
System.out.println(resource1.getURL());Resource resource2 = context.getResource("classpath:spring.xml");
System.out.println(resource2.contentLength());
System.out.println(resource2.getURL());
还可以一次性获取多个:
Resource[] resources = context.getResources("classpath:com/zhouyu/*.class");
for (Resource resource : resources) {System.out.println(resource.contentLength());System.out.println(resource.getFilename());
}
获取运行时环境
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);Map<String, Object> systemEnvironment = context.getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment();
System.out.println(systemEnvironment);System.out.println("=======");Map<String, Object> systemProperties = context.getEnvironment().getSystemProperties();
System.out.println(systemProperties);System.out.println("=======");MutablePropertySources propertySources = context.getEnvironment().getPropertySources();
System.out.println(propertySources);System.out.println("=======");System.out.println(context.getEnvironment().getProperty("NO_PROXY"));
System.out.println(context.getEnvironment().getProperty("sun.jnu.encoding"));
System.out.println(context.getEnvironment().getProperty("zhouyu"));
注意,可以利用
@PropertySource("classpath:spring.properties")
来使得某个properties文件中的参数添加到运行时环境中
事件发布
先定义一个事件监听器
@Bean
public ApplicationListener applicationListener() {return new ApplicationListener() {@Overridepublic void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {System.out.println("接收到了一个事件");}};
}
然后发布一个事件:
context.publishEvent("kkk");
类型转化
在Spring源码中,有可能需要把String转成其他类型,所以在Spring源码中提供了一些技术来更方便的做对象的类型转化,关于类型转化的应用场景, 后续看源码的过程中会遇到很多。
PropertyEditor
这其实是JDK中提供的类型转化工具类
public class StringToUserPropertyEditor extends PropertyEditorSupport implements PropertyEditor {@Overridepublic void setAsText(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException {User user = new User();user.setName(text);this.setValue(user);}
}
StringToUserPropertyEditor propertyEditor = new StringToUserPropertyEditor();
propertyEditor.setAsText("1");
User value = (User) propertyEditor.getValue();
System.out.println(value);
如何向Spring中注册PropertyEditor:
@Bean
public CustomEditorConfigurer customEditorConfigurer() {CustomEditorConfigurer customEditorConfigurer = new CustomEditorConfigurer();Map<Class<?>, Class<? extends PropertyEditor>> propertyEditorMap = new HashMap<>();// 表示StringToUserPropertyEditor可以将String转化成User类型,在Spring源码中,如果发现当前对象是String,而需要的类型是User,就会使用该PropertyEditor来做类型转化propertyEditorMap.put(User.class, StringToUserPropertyEditor.class);customEditorConfigurer.setCustomEditors(propertyEditorMap);return customEditorConfigurer;
}
假设现在有如下Bean:
@Component
public class UserService {@Value("xxx")private User user;public void test() {System.out.println(user);}}
那么test属性就能正常的完成属性赋值
ConversionService
Spring中提供的类型转化服务,它比PropertyEditor更强大
public class StringToUserConverter implements ConditionalGenericConverter {@Overridepublic boolean matches(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {return sourceType.getType().equals(String.class) && targetType.getType().equals(User.class);}@Overridepublic Set<ConvertiblePair> getConvertibleTypes() {return Collections.singleton(new ConvertiblePair(String.class, User.class));}@Overridepublic Object convert(Object source, TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {User user = new User();user.setName((String)source);return user;}
}
DefaultConversionService conversionService = new DefaultConversionService();
conversionService.addConverter(new StringToUserConverter());
User value = conversionService.convert("1", User.class);
System.out.println(value);
如何向Spring中注册ConversionService:
@Bean
public ConversionServiceFactoryBean conversionService() {ConversionServiceFactoryBean conversionServiceFactoryBean = new ConversionServiceFactoryBean();conversionServiceFactoryBean.setConverters(Collections.singleton(new StringToUserConverter()));return conversionServiceFactoryBean;
}
TypeConverter
整合了PropertyEditor和ConversionService的功能,是Spring内部用的
SimpleTypeConverter typeConverter = new SimpleTypeConverter();
typeConverter.registerCustomEditor(User.class, new StringToUserPropertyEditor());
//typeConverter.setConversionService(conversionService);
User value = typeConverter.convertIfNecessary("1", User.class);
System.out.println(value);
