学Java第四十三天——Map双列集合
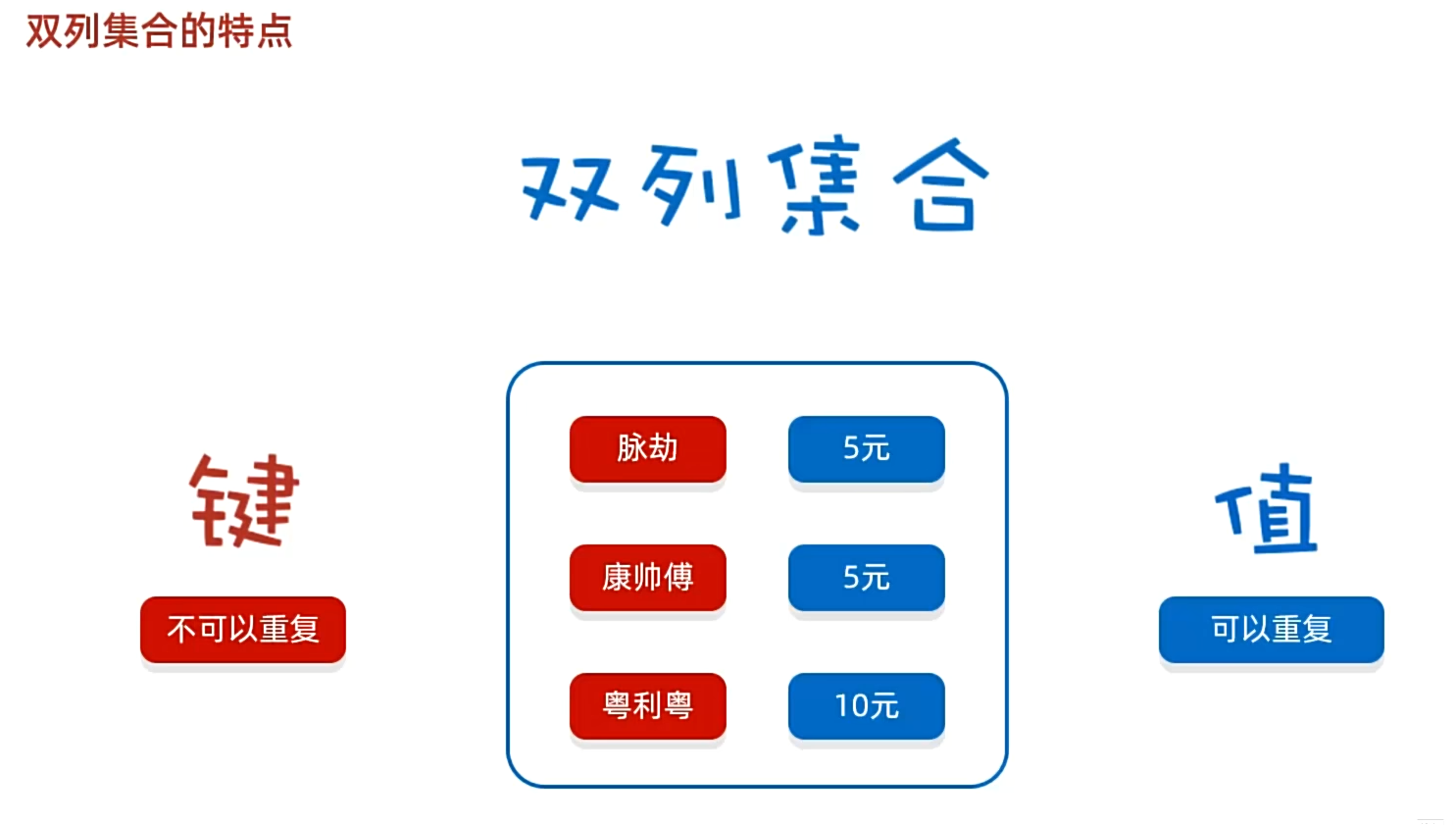
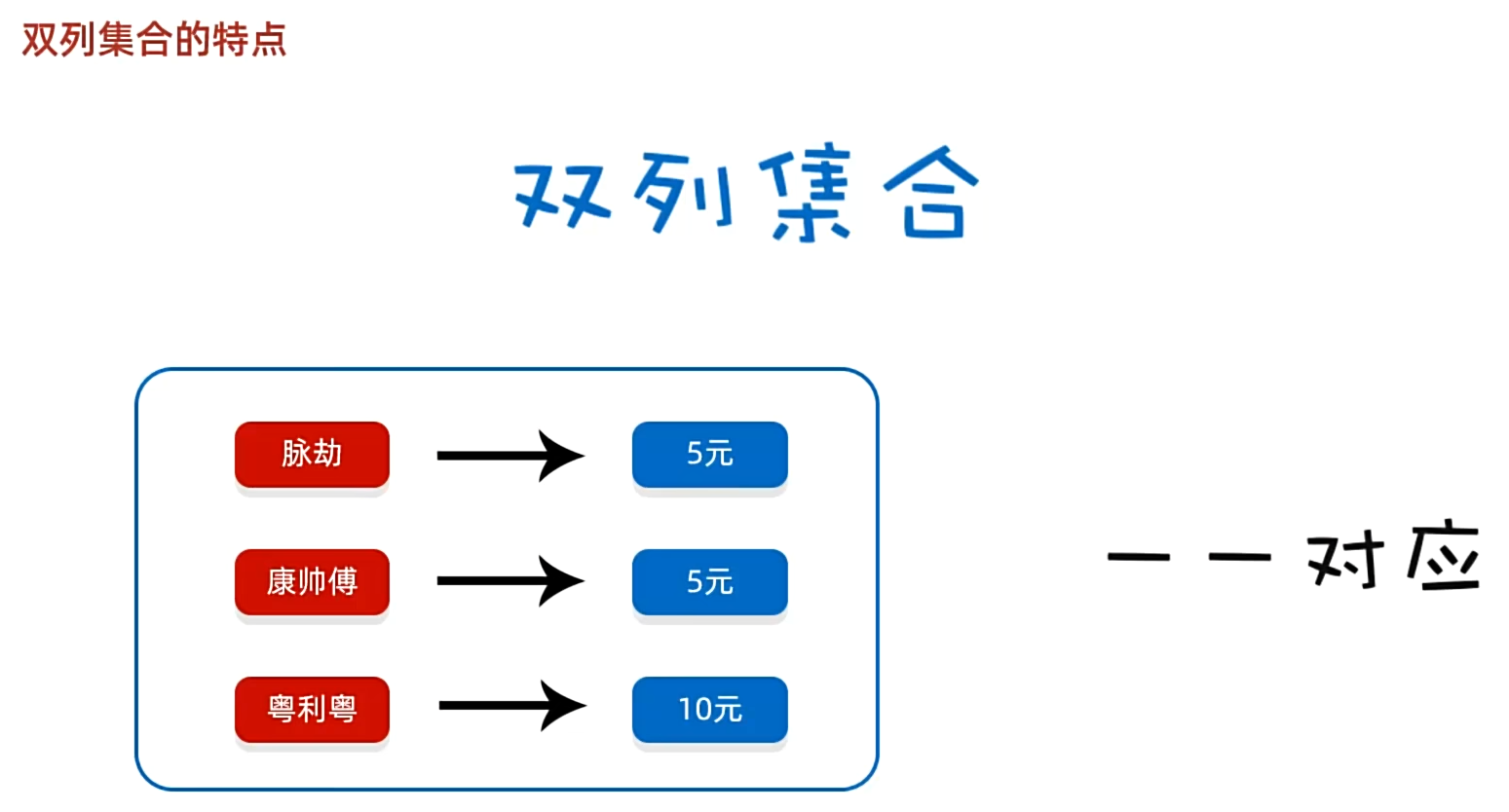
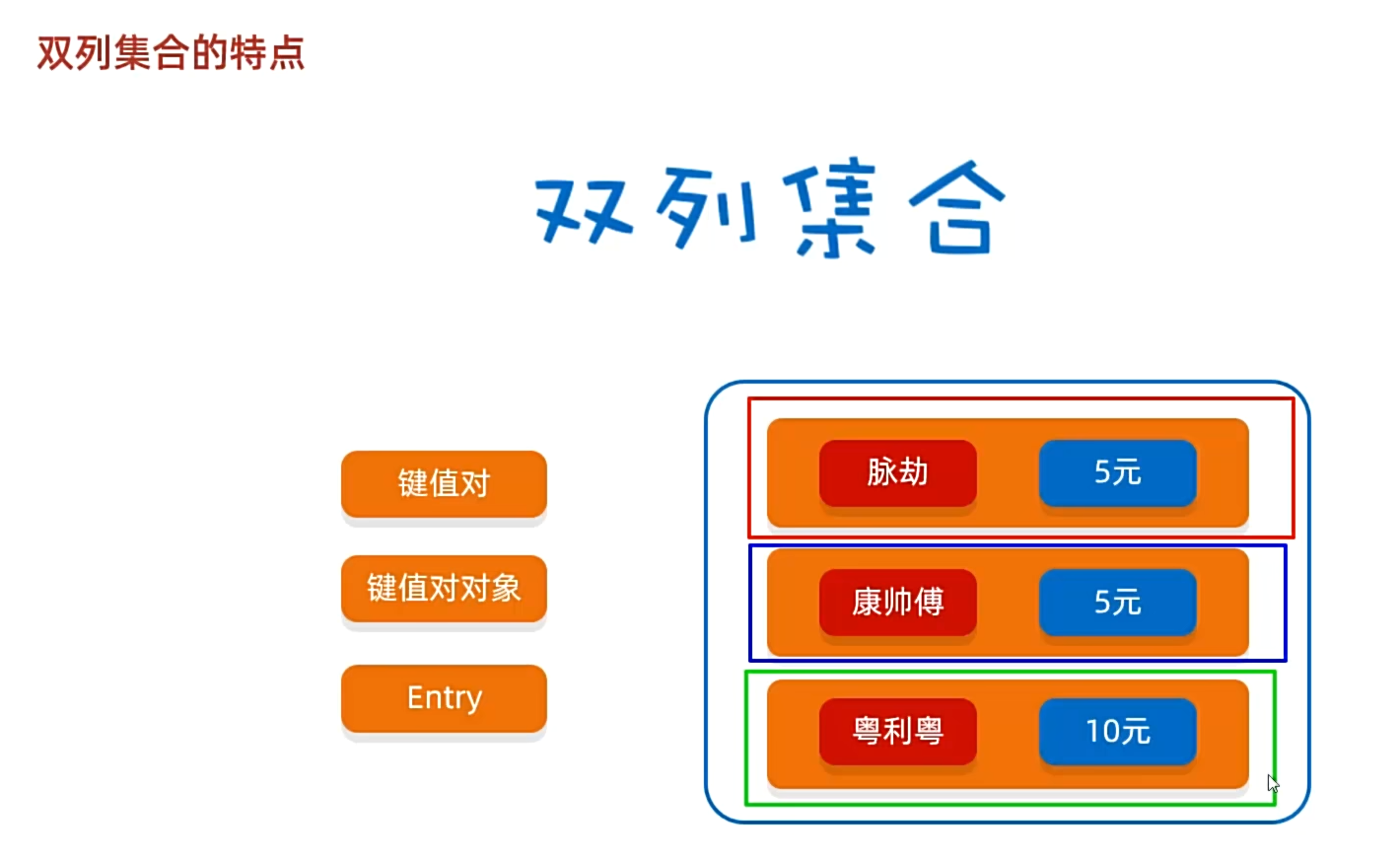
双列集合概念
每次都添加一对,map更像一个字典,可以把它想象成字典

双列集合Map接口 常用方法
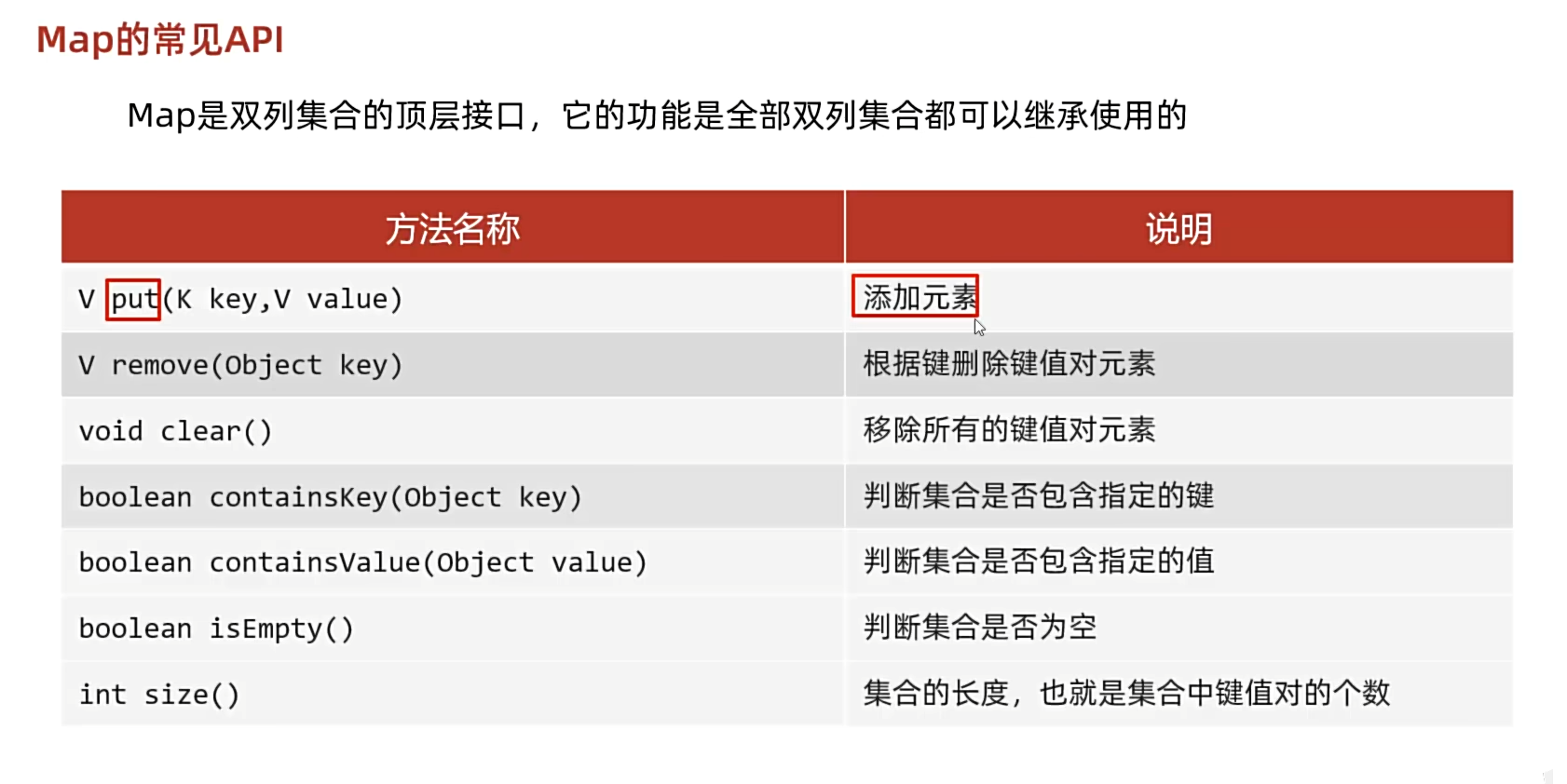
重点是put():添加 / 覆盖
- 在添加数据的时候,如果键不存在,就直接把键值对对象添加到map集合当中,方法返回null
- 在添加数据的时候,如果键存在,那就会把原有的键值对对象覆盖,会把被覆盖的值进行返回
代码:
package com.Map_exe;import java.util.HashMap;public class map_method {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建Map集合的对象HashMap<String,String> m=new HashMap<>();//添加元素m.put("黄晓明","baby");m.put("李晨","范冰冰");m.put("鹿晗","关晓彤");//覆盖String s = m.put("黄晓明", "lican");System.out.println(s);System.out.println(m);//删除,删除某个键,返回键对应的值String s1 = m.remove("李晨");System.out.println(s1);System.out.println(m);//m.clear();//System.out.println(m);boolean b = m.containsKey("李晨");System.out.println(b);boolean b1 = m.containsValue("关晓彤");System.out.println(b1);System.out.println(m.isEmpty());System.out.println(m.size());}
}
Map的遍历方式

1、键找值
用集合名调用KeySet方法,得到一个只包含 键 的集合,返回的是一个集合
代码:
package com.Map_exe;import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.function.Consumer;public class Map_bianli_1 {public static void main(String[] args) {Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<>();map.put("黄晓明","baby");map.put("李晨","范冰冰");map.put("张若昀","唐艺昕");map.put("鹿晗","关晓彤");Set<String> keys = map.keySet();for (String key : keys) {String value = map.get(key);System.out.println(key+"="+value);}System.out.println("----------------");Iterator<String> it = keys.iterator();while (it.hasNext()){String key = it.next();String value=map.get(key);System.out.println(key+"="+value);}System.out.println("----------------");keys.forEach(key-> {String value = map.get(key);System.out.println(key+"="+value);});}
}
2、键值对
这次的 集合名.EntrySet()会得到一个Map.Entry<String,String>类型的集合,所以里面的每一个元素都是Map.Entry<String,String>类型的。
代码:
package com.Map_exe;import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.function.Consumer;public class Map_bianli_2 {public static void main(String[] args) {Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<>();map.put("黄晓明","baby");map.put("李晨","范冰冰");map.put("张若昀","唐艺昕");map.put("鹿晗","关晓彤");//键值对遍历Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> entries = map.entrySet();for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : entries) {String key=entry.getKey();String value =entry.getValue();System.out.println(key+"="+value);}System.out.println("----------------");entries.forEach(new Consumer<Map.Entry<String, String>>() {@Overridepublic void accept(Map.Entry<String, String> entry) {String key=entry.getKey();String value=entry.getValue();System.out.println(key+"="+value);}});System.out.println("--------------------");Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> it = entries.iterator();while (it.hasNext()){Map.Entry<String, String> entry = it.next();String key = entry.getKey();String value = entry.getValue();System.out.println(key+"="+value);}}
}
3、lambda表达式
forEach方法里面是 增强for循环
代码:
package com.Map_exe;import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.function.BiConsumer;
import java.util.function.Consumer;public class Map_bianli_3 {public static void main(String[] args) {Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<>();map.put("黄晓明","baby");map.put("李晨","范冰冰");map.put("张若昀","唐艺昕");map.put("鹿晗","关晓彤");map.forEach(new BiConsumer<String, String>() {@Overridepublic void accept(String key, String value) {System.out.println(key+"="+value);}});}
}
HashMap
特点

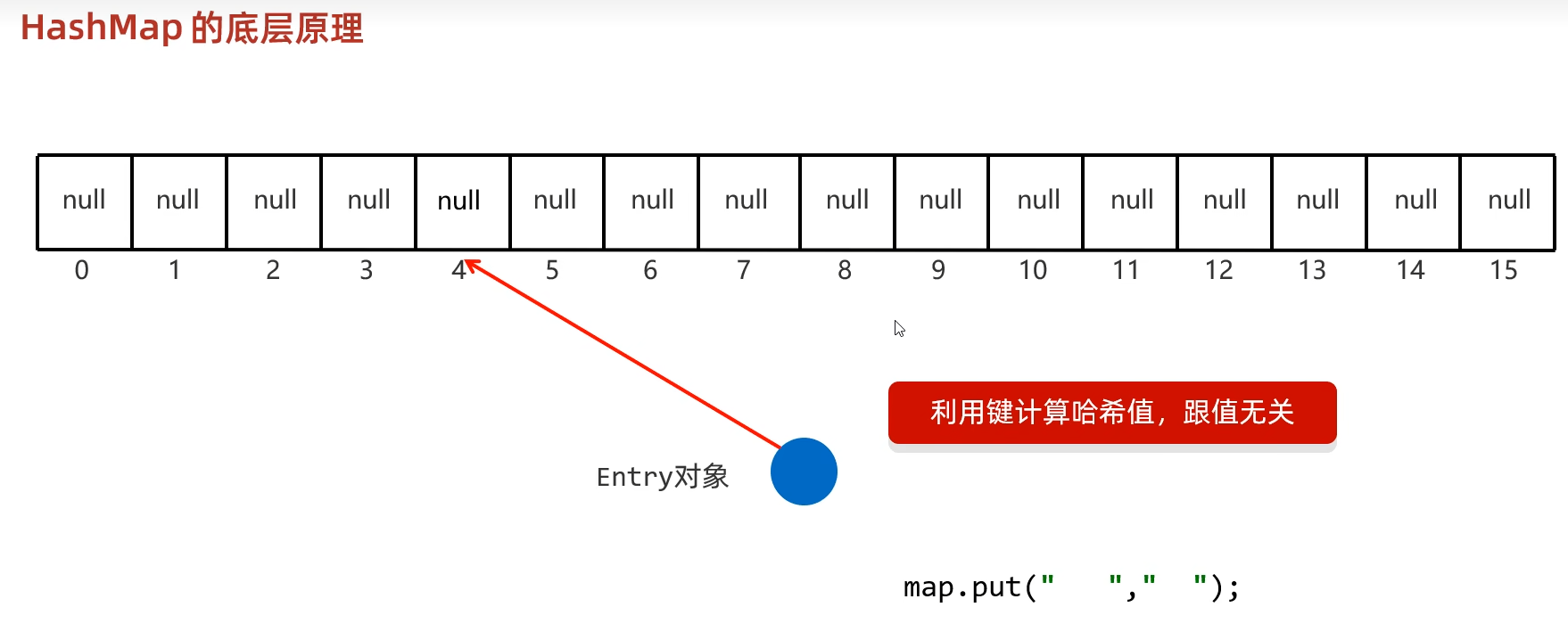

- 计算存储在哈希表数组上的索引是利用的'(数组长度)和(键的属性值的哈希值)来决定的,当要添加的位置上已经有元素值时,用equals方法比较,如果相同,就进行覆盖,而不是和HashSet一样抛弃。
- map.put方法会先将key和value构成entry对象,之后再拿键进行计算索引并比较。
代码练习题

package com.Map_exe;import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.function.BiConsumer;public class HashMap_exe01 {public static void main(String[] args) {HashMap<Student,String> hm=new HashMap<>();hm.put(new Student("zhangsan",18),"henan");hm.put(new Student("lisi",19),"anhui");hm.put(new Student("wangwu",20),"beijing");hm.forEach((student, jiguan) ->System.out.println(student+"="+jiguan));}
}

package com.Map_exe;import java.util.*;
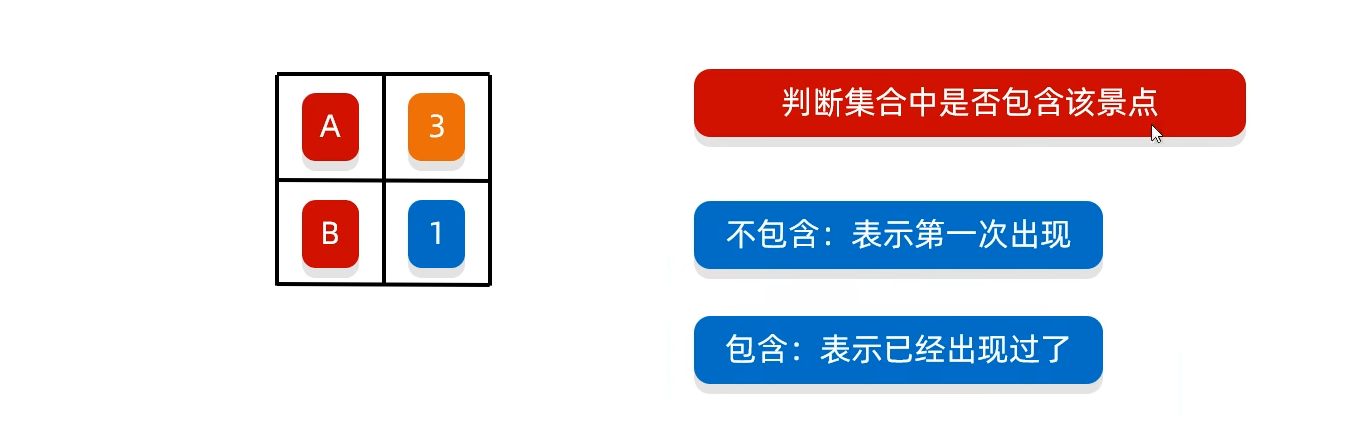
import java.util.function.BiConsumer;public class HashMap_exe02 {public static void main(String[] args) {//1、先让同学们投票//定义一个数组,存储4个景点ABCDString []arr={"A","B","C","D"};//利用随机数模拟80个学生的投票,并用集合把结果存储起来ArrayList<String> list=new ArrayList<>();Random r=new Random();for (int i = 0; i < 80; i++) {list.add(arr[r.nextInt(arr.length)]);}System.out.println(list);//用map集合,利用集合进行统计HashMap<String,Integer> hm=new HashMap<>();for (String s : list) {if(hm.containsKey(s)){ //如果map集合里面存在某个景点,value就+1Integer i = hm.get(s);i=i+1;hm.put(s,i);}else{//如果不存在,value=1hm.put(s,1);}}System.out.println(hm);//3、求最大值,遍历hashmapint sum=0;Set<String> keys = hm.keySet();for (String key : keys) {int count=hm.get(key);if(count>sum){sum=count;}}//4、看看哪个景点对应的是最大值Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entries = hm.entrySet();for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : entries) {if(entry.getValue()==sum){System.out.println(entry.getKey());}}}}匿名内部类不能访问外部的变量,只能访问外部不能改变的量,即被final修饰的变量。
LinkedHashMap
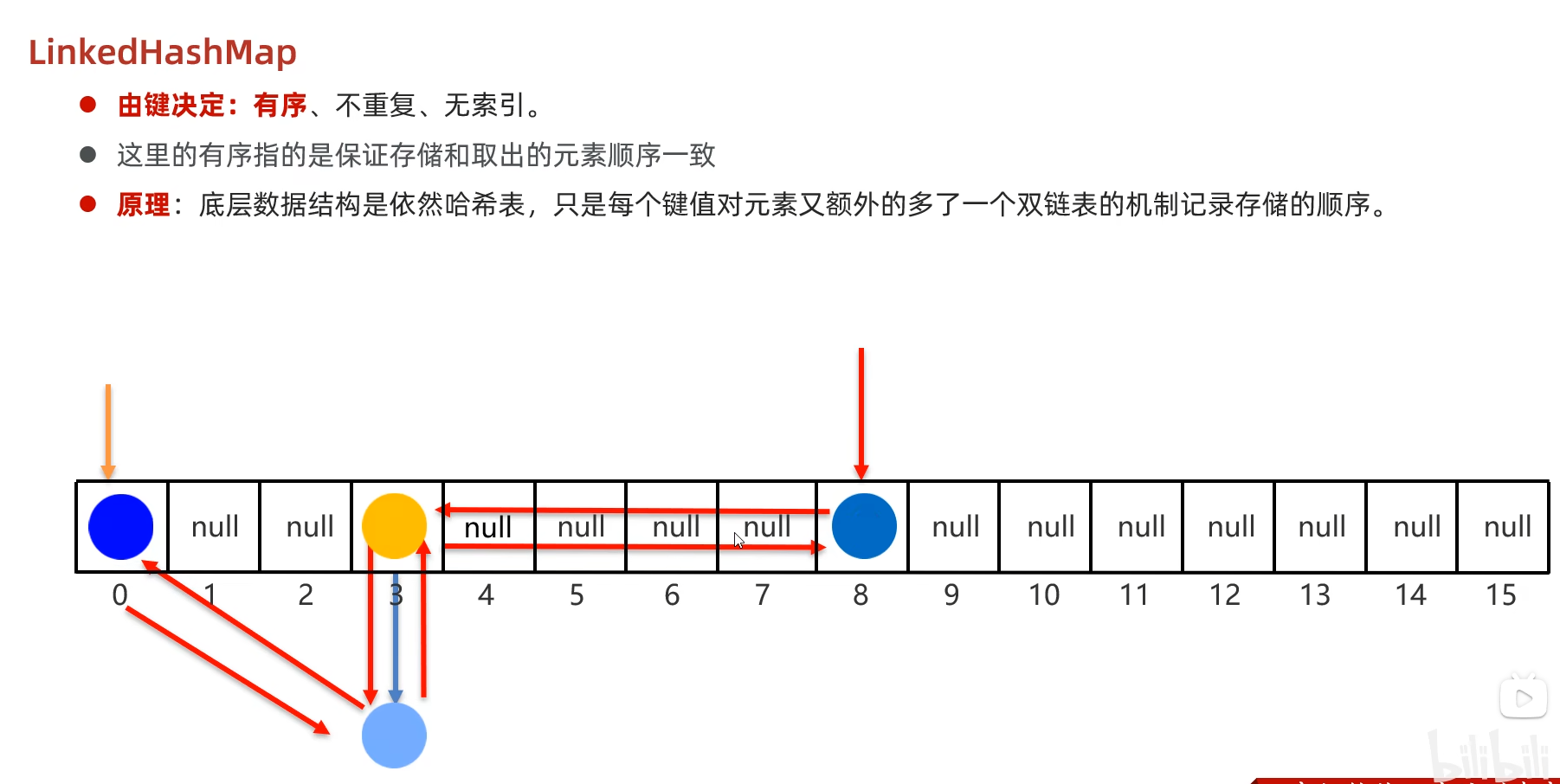
特点就是存和取的顺序一致
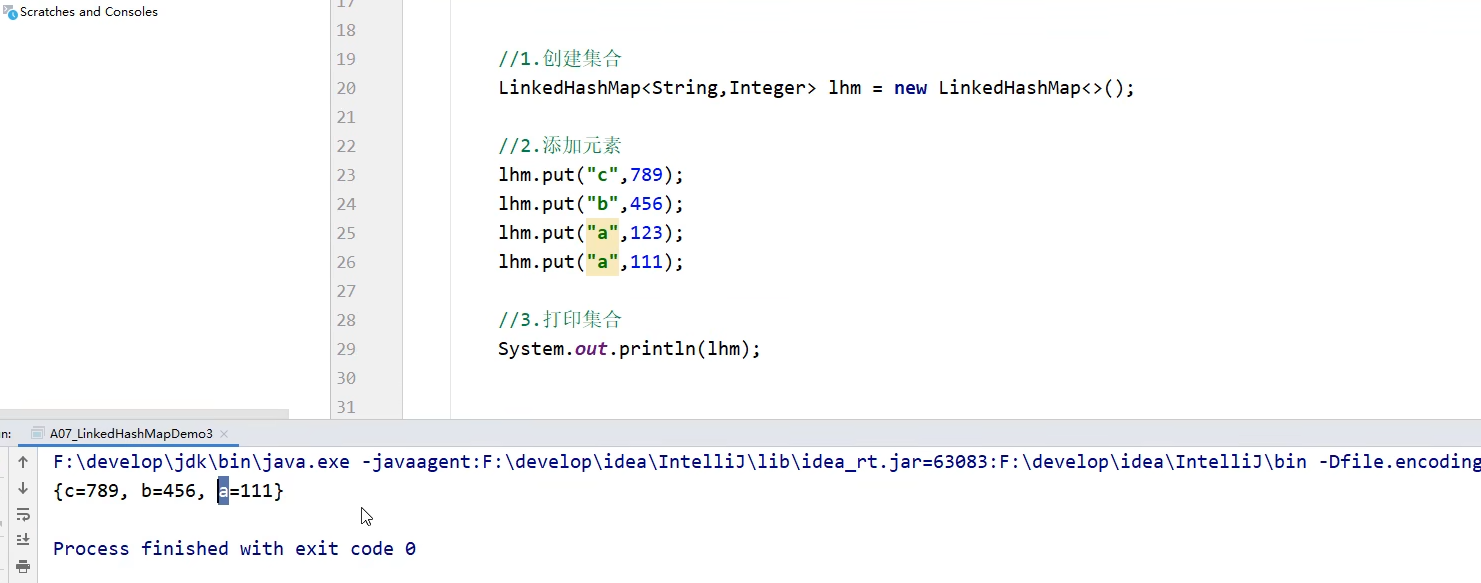
代码
TreeMap
特点

代码练习

需求1
升序:默认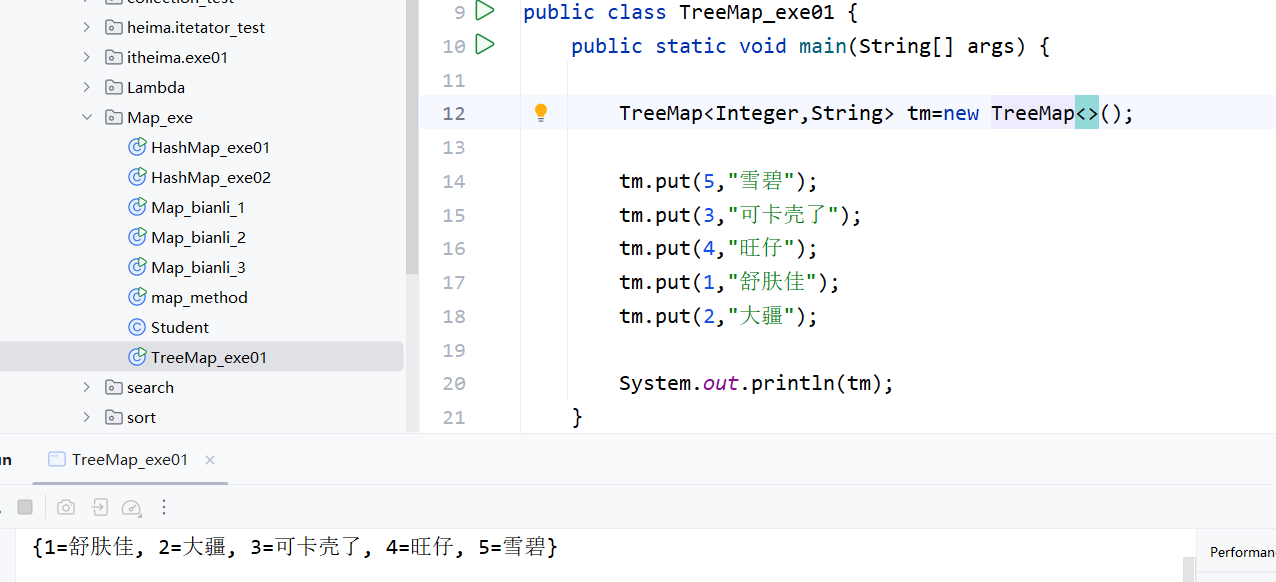
降序:利用比较器
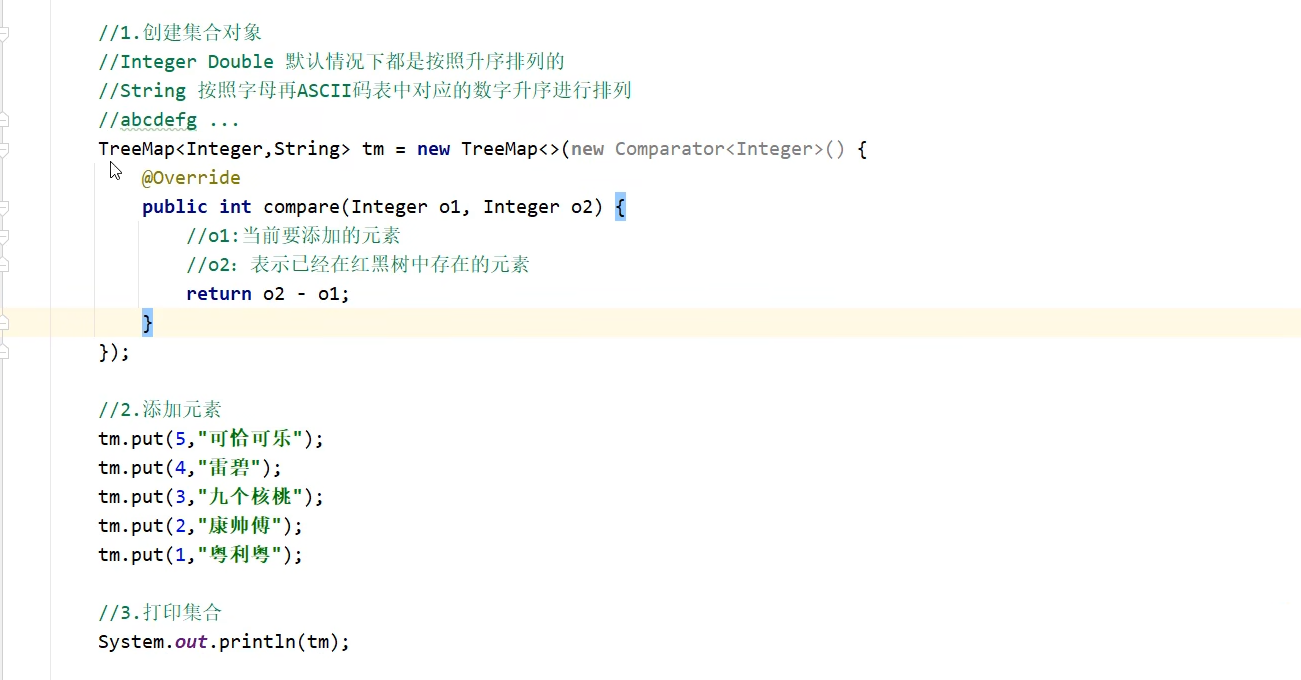
需求2:
测试类:
package com.Map_exe;import java.util.TreeMap;public class TreeMap_exe02 {public static void main(String[] args) {TreeMap<Student,String> tm=new TreeMap<>();Student s1=new Student("小王",25);Student s2=new Student("小sun",24);Student s3=new Student("小li",28);Student s4=new Student("小peng",21);tm.put(s1,"河南");tm.put(s2,"北京");tm.put(s3,"上海");tm.put(s4,"天津");System.out.println(tm);}
}
student javabean类
package com.Map_exe;import java.util.Objects;public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{private String name;private int age;public Student() {}public Student(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}/*** 获取* @return name*/public String getName() {return name;}/*** 设置* @param name*/public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}/*** 获取* @return age*/public int getAge() {return age;}/*** 设置* @param age*/public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object o) {if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;Student student = (Student) o;return age == student.age && Objects.equals(name, student.name);}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return Objects.hash(name, age);}public String toString() {return "Student{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + "}";}@Overridepublic int compareTo(Student o) {//this代表当前要添加的元素//o代表已经在红黑树里面的元素int i = this.getAge() - o.getAge();i=i==0?this.getName().compareTo(o.getName()):i;return i;}
}
综合代码练习:

package com.Map_exe;import java.util.TreeMap;
import java.util.function.BiConsumer;public class TreeMap_exe03 {public static void main(String[] args) {//1、定义字符串String s="aaabbcddbcbcdbcdadcbad";//2、定义一个treemap集合充当计数器TreeMap<Character,Integer> tm=new TreeMap<>();//3、遍历字符串for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {char c=s.charAt(i);if(tm.containsKey(c)){Integer count = tm.get(c);count++;tm.put(c,count);}else{tm.put(c,1);}}//4、打印//System.out.println(tm);StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();tm.forEach(new BiConsumer<Character, Integer>() {@Overridepublic void accept(Character c, Integer count) {sb.append(c).append("(").append(count).append(")");}});System.out.println(sb);}
}
代码思想
- 集合map,hashmap,treemap可以作为统计的计数器,当遍历某个对象(如数组、字符串)时,里面的元素就可以作为集合hashmap的键,而元素个数就可以作为hashmap的值。
- 遍历集合可以用keyset、entryset、lambda表达式方法,遍历的时候可以执行很多操作。

总结:

