Go的GRPC框架:Kitex
文章目录
- 1.概览
- 2.环境准备
- 3.Demo
- 3.1 创建项目目录
- 3.2 编写 IDL
- 3.3 代码生成
- 3.4 拉取依赖
- 3.5 编写商品服务逻辑
- 3.7 运行 API 服务
- 3.8 运行库存服务
- 3.9 补充商品服务
1.概览
基于 Thrift 的 RPC 服务开发,通常包括如下过程:
- 编写 IDL,定义服务 (Service) 接口。
- IDL 全称是 Interface Definition Language,接口定义语言。
- 使用 thrift(或者等价的生成代码工具,如 kitex 等)生成客户端、服务端的支持代码。
- 服务端开发者编写 handler ,即请求的处理逻辑。
- 服务端开发者运行服务监听端口,处理请求。
- 客户端开发者编写客户端程序,经过服务发现连接上服务端程序,发起请求并接收响应。
2.环境准备
kitex 是 Kitex 框架提供的用于生成代码的一个命令行工具。目前,kitex 支持 thrift 和 protobuf 的 IDL,并支持生成一个服务端项目的骨架。
go install github.com/cloudwego/kitex/tool/cmd/kitex@latest
kitex --version
3.Demo
模拟一个简单的电商场景,包括商品服务、库存服务与 API 服务,商品服务调用库存服务查询库存,API 服务调用商品服务查询商品信息,对前端或用户暴露 HTTP 接口供查询商品信息。
3.1 创建项目目录
mkdir example_shop
cd example_shop
go mod init example_shop
3.2 编写 IDL
按照开发流程,我们首先需要编写 thrift IDL
创建 idl 目录用于存放项目 idl 文件
mkdir idlcd idl

后面不再以指令的形式进行,直接在GoLand里进行开发
一般不同的服务都会使用不同的 IDL,所以我们这里创建
- item.thrift 商品服务接口
- stock.thrift 库存服务接口
- base.thrift 定义公共数据结构
base.thrift
namespace go example.shop.basestruct BaseResp {1: string code2: string msg
}
item.thrift
namespace go example.shop.iteminclude "base.thrift"struct Item {1: i64 id2: string title3: string description4: i64 stock
}struct GetItemReq {1: required i64 id
}struct GetItemResp {1: Item item255: base.BaseResp baseResp
}service ItemService{GetItemResp GetItem(1: GetItemReq req)
}stock.thrift
namespace go example.shop.stockinclude "base.thrift"struct GetItemStockReq {1: required i64 item_id
}struct GetItemStockResp {1: i64 stock255: base.BaseResp BaseResp
}service StockService {GetItemStockResp GetItemStock(1:GetItemStockReq req)
}3.3 代码生成
有了 IDL 以后我们便可以通过 kitex 工具生成项目代码了,我们在先回到项目的根目录即 example_shop。因为我们有两个 IDL 定义了服务,所以执行两次 kitex 命令:
kitex -module example_shop idl/item.thriftkitex -module example_shop idl/stock.thrift
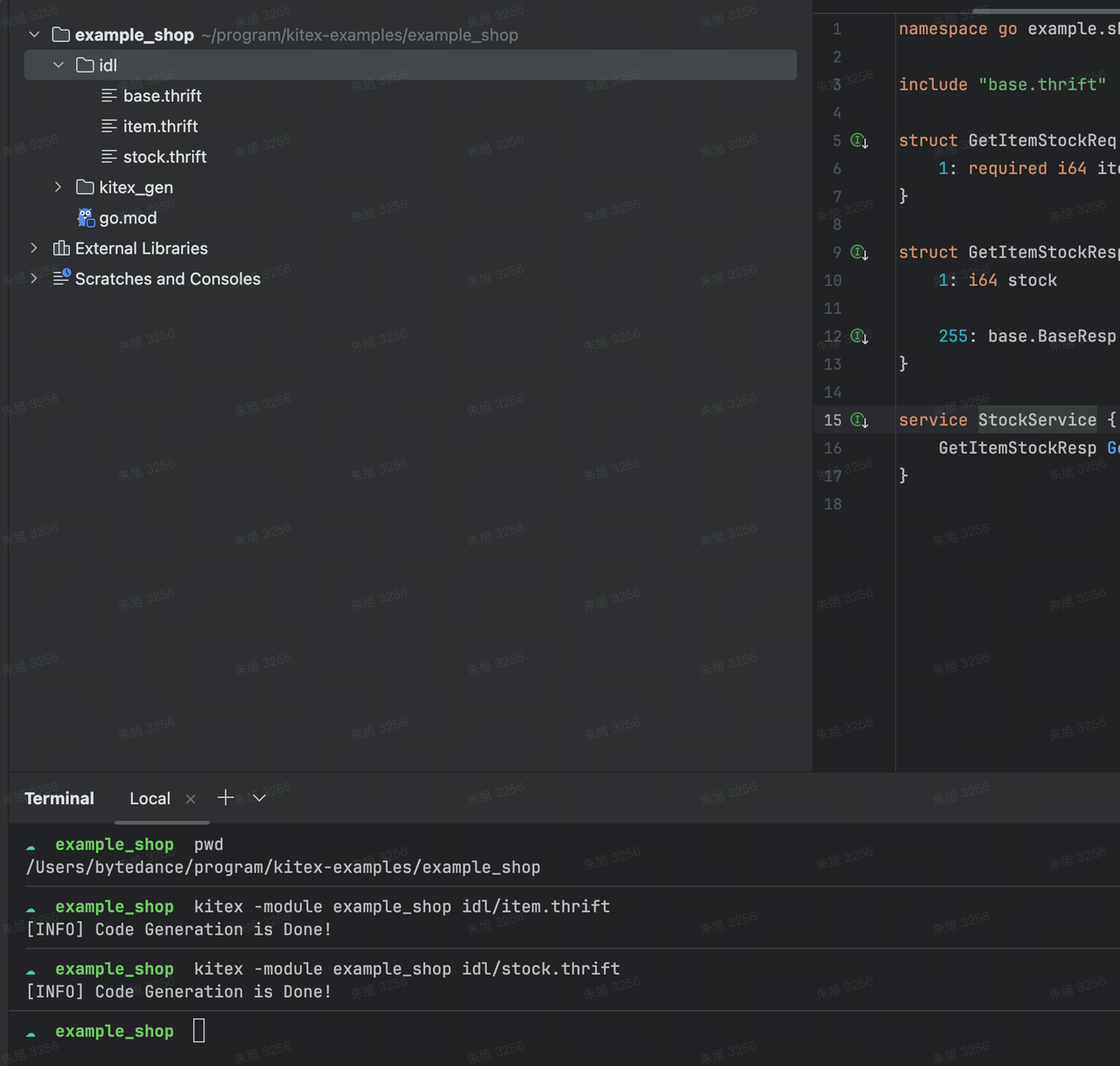
生成的代码分两部分,一部分是结构体的编解码序列化代码,由 IDL 编译器生成;另一部分由 kitex 工具在前者产物上叠加,生成用于创建和发起 RPC 调用的桩代码。它们默认都在 kitex_gen 目录下。
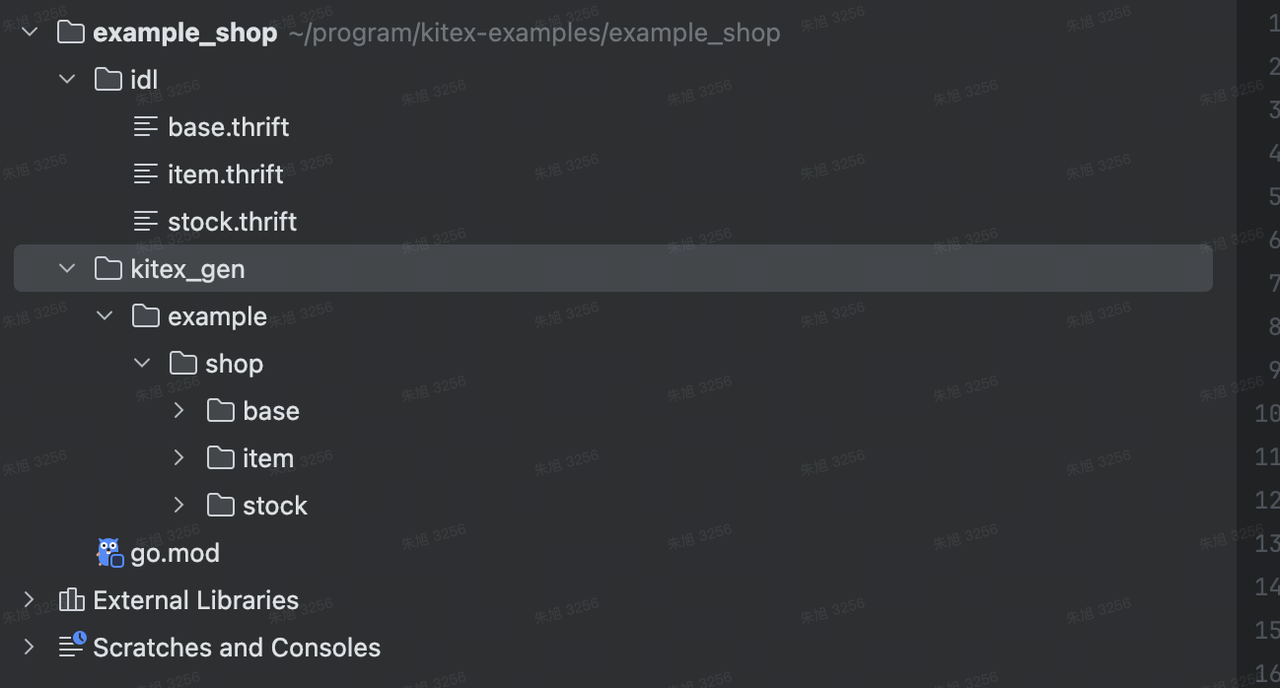
上面生成的代码并不能直接运行,需要自己完成 NewClient 和 NewServer 的构建。kitex 命令行工具提供了
-service 参数能直接生成带有脚手架的代码,接下来让我们为商品服务和库存服务分别生成脚手架。
mkdir -p rpc/item rpc/stock
再分别进入各自的目录中,执行如下命令生成代码:
// item 目录下执行
kitex -module example_shop -service example.shop.item -use example_shop/kitex_gen ../../idl/item.thrift// stock 目录下执行
kitex -module example_shop -service example.shop.stock -use example_shop/kitex_gen ../../idl/stock.thrift
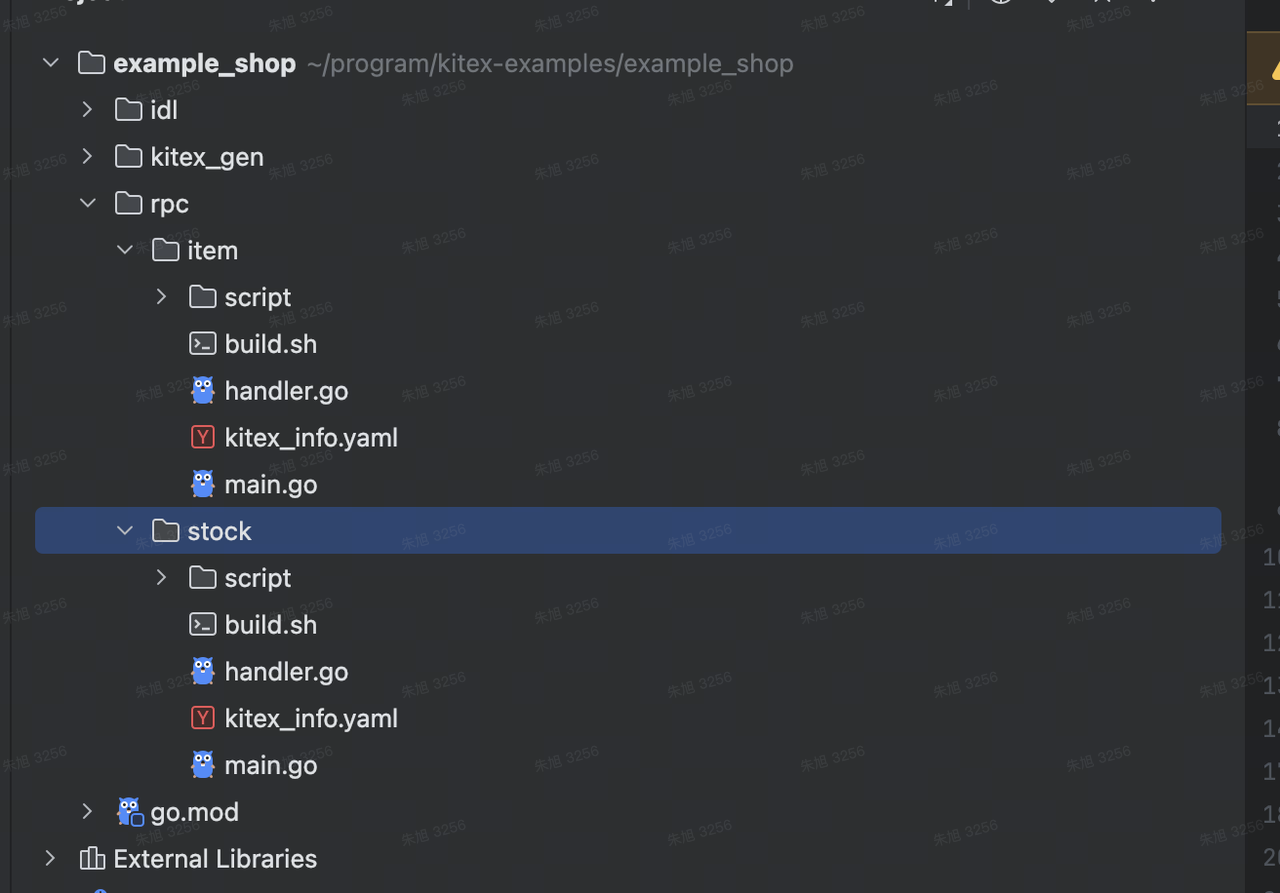
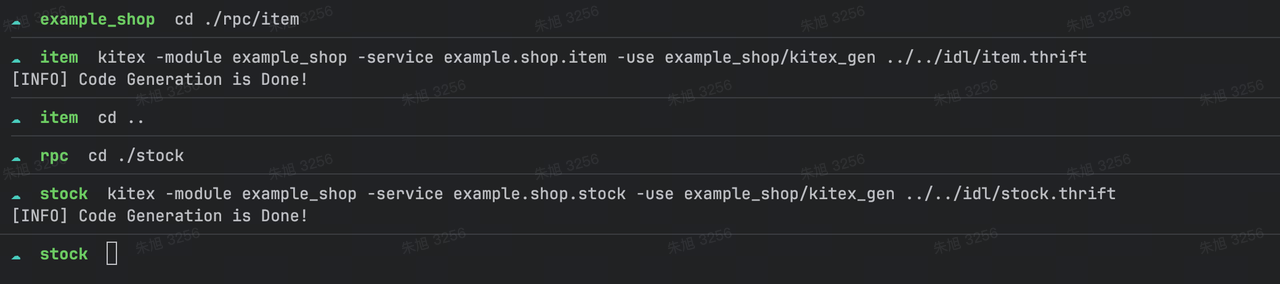
kitex 默认会将代码生成到执行命令的目录下,kitex 的命令中:
- -module 参数表明生成代码的 go mod 中的 module name,在本例中为 example_shop
- -service 参数表明我们要生成脚手架代码,后面紧跟的 example.shop.item 或 example.shop.stock 为该服务的名字。
- -use 参数表示让 kitex 不生成 kitex_gen 目录,而使用该选项给出的 import path。在本例中因为第一次已经生成 kitex_gen 目录了,后面都可以复用。
- 最后一个参数则为该服务的 IDL 文件
3.4 拉取依赖
完成代码生成后,我们回到项目根目录,即 example_shop。 使用 go mod tidy 命令拉取项目依赖
3.5 编写商品服务逻辑
我们需要编写的服务端逻辑都在 handler.go 这个文件中,目前我们有两个服务,对应了两个 handler.go,他们的结构都是类似的,我们先看看商品服务的服务端逻辑 rpc/item/handler.go
package mainimport ("context"item "example_shop/kitex_gen/example/shop/item"
)// ItemServiceImpl implements the last service interface defined in the IDL.
type ItemServiceImpl struct{}// GetItem implements the ItemServiceImpl interface.
func (s *ItemServiceImpl) GetItem(ctx context.Context, req *item.GetItemReq) (resp *item.GetItemResp, err error) {// TODO: Your code here...return
}这里的 GetItem 函数就对应了我们之前在 item.thrift IDL 中定义的 GetItem 方法。
现在让我们修改一下服务端逻辑,本项目仅仅演示使用方法,重点不在于业务逻辑,故简单处理后返回。
package mainimport ("context"item "example_shop/kitex_gen/example/shop/item"
)// ItemServiceImpl implements the last service interface defined in the IDL.
type ItemServiceImpl struct{}// GetItem implements the ItemServiceImpl interface.
func (s *ItemServiceImpl) GetItem(ctx context.Context, req *item.GetItemReq) (resp *item.GetItemResp, err error) {resp = item.NewGetItemResp()resp.Item = item.NewItem()resp.Item.Id = req.GetId()resp.Item.Title = "Kitex"resp.Item.Description = "Kitex is an excellent framework!"return
}
除了 handler.go 外,我们还需关心 main.go 文件,可以看看 main.go 中做了什么事情:
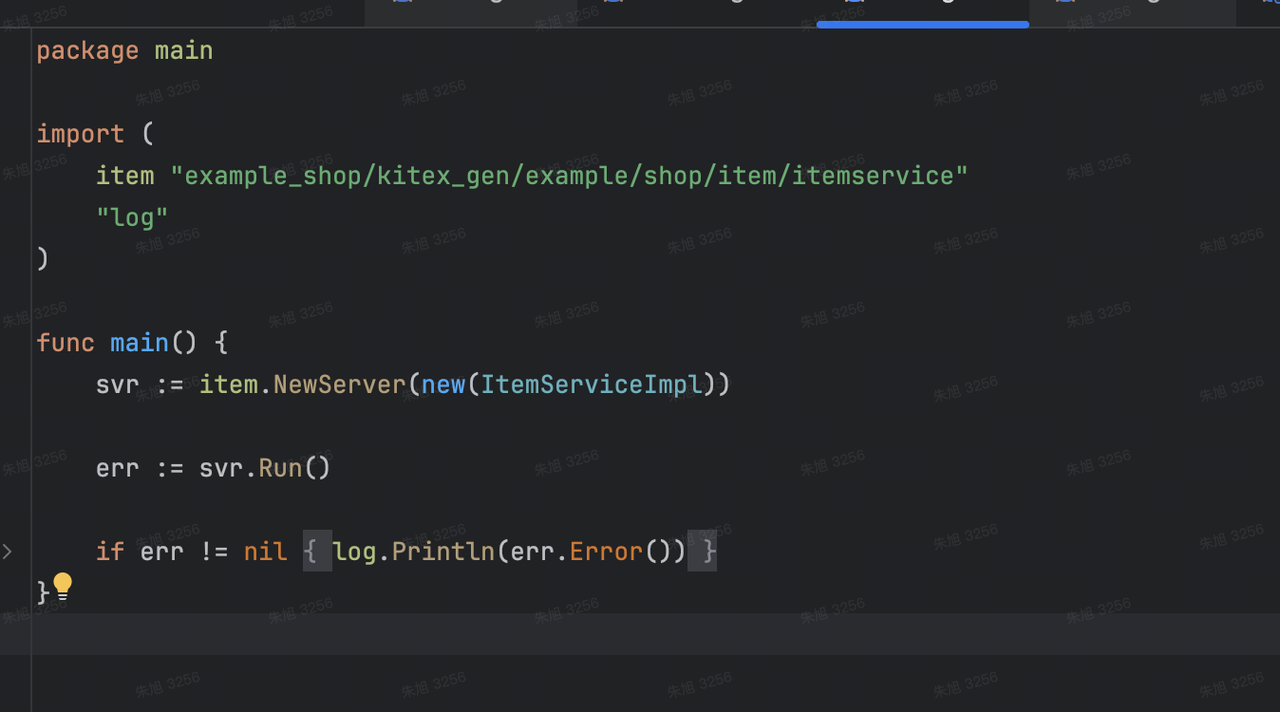
main.go 中的代码很简单,即使用 kitex 生成的代码创建一个 server 服务端,并调用其 Run 方法开始运行。通常使用 main.go 进行一些项目初始化,如加载配置等。
运行商品服务
至此,我们便可以开始运行商品服务了,kitex 也为我们生成了编译脚本,即 build.sh:
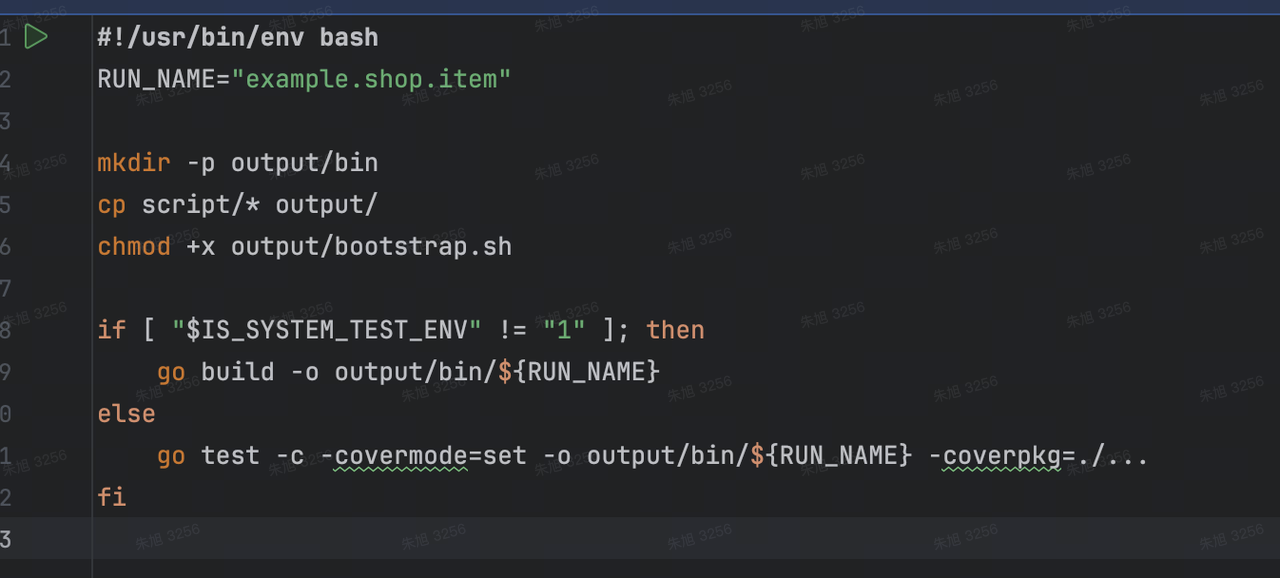
在 build.sh 主要做了以下事情:
- 定义了一个变量 RUN_NAME,用于指定生成的可执行文件的名称,值为我们在 IDL 中指定的 namespace。本例中为 example.shop.item
- 创建 output 目录,此后的编译出的二进制文件放在 output/bin 下。同时将 script 目录下的项目启动脚本复制进去
- 根据环境变量 IS_SYSTEM_TEST_ENV 的值判断生成普通可执行文件或测试可执行文件。值为 1 则代表使用 go test -c 生成测试文件,否则正常使用 go build 命令编译。
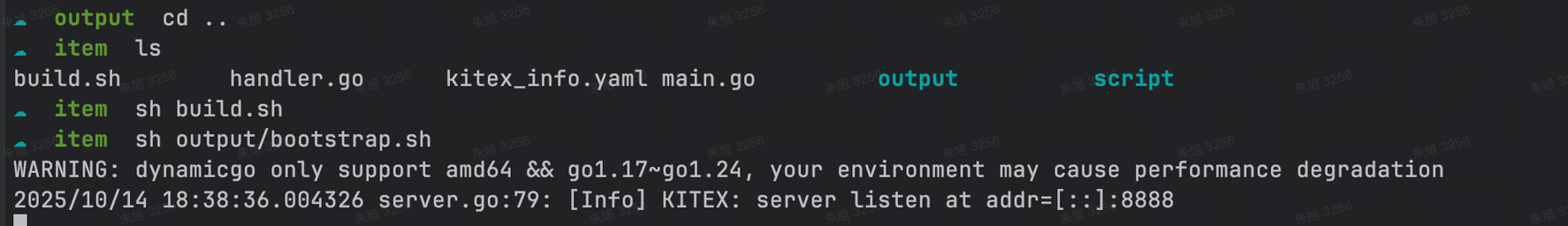
直接执行 sh build.sh 即可编译项目。
编译成功后,生成 output 目录:
执行 sh output/bootstrap.sh 即可启动编译后的二进制文件。
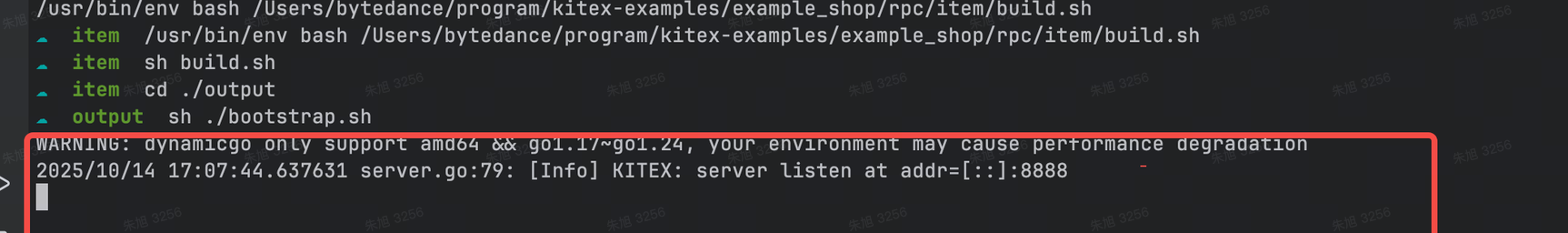
输出类似上图所示信息,代表运行成功
在上面的日志输出中,addr=[::]:8888 代表我们的服务运行在本地的 8888 端口,此参数可以在创建 server 时传入 option 配置来修改,更多服务端配置见 Server Option。
3.7 运行 API 服务
有了商品服务后,接下来就让我们编写 API 服务用于调用刚刚运行起来的商品服务,并对外暴露 HTTP 接口。
首先,同样的,我们回到项目根目录先创建一个目录用于存放我们的代码,然后创建一个 main.go 文件,就可以开始编写代码了。
接下来就可以在main.go里开发接口使其可以被外部的请求通过Http进行访问
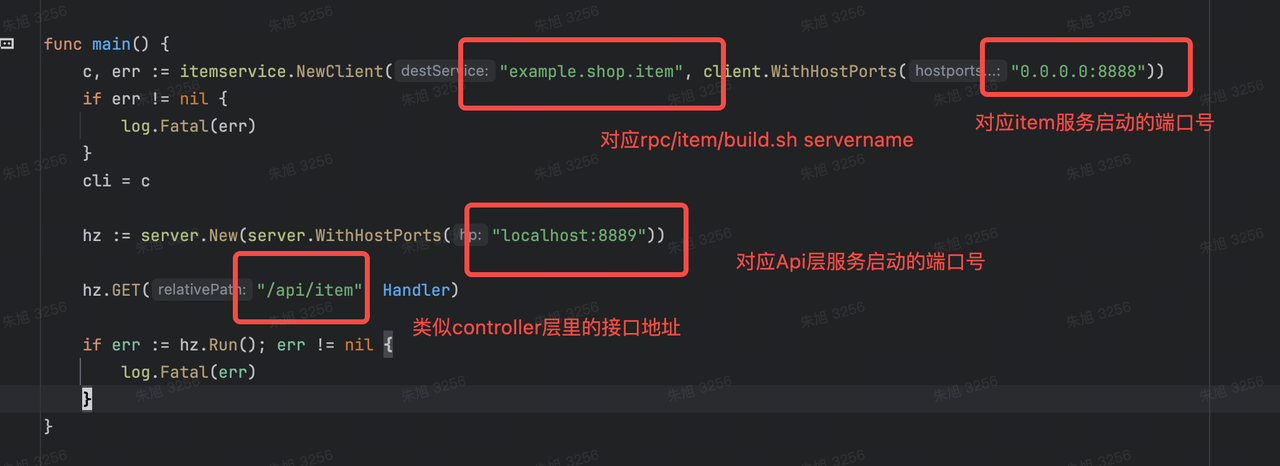
package mainimport ("context""log""time""example_shop/kitex_gen/example/shop/item""example_shop/kitex_gen/example/shop/item/itemservice""github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app""github.com/cloudwego/hertz/pkg/app/server""github.com/cloudwego/kitex/client""github.com/cloudwego/kitex/client/callopt"
)var (cli itemservice.Client
)func main() {c, err := itemservice.NewClient("example.shop.item", client.WithHostPorts("0.0.0.0:8888"))if err != nil {log.Fatal(err)}cli = chz := server.New(server.WithHostPorts("localhost:8889"))hz.GET("/api/item", Handler)if err := hz.Run(); err != nil {log.Fatal(err)}
}func Handler(ctx context.Context, c *app.RequestContext) {req := item.NewGetItemReq()req.Id = 1024resp, err := cli.GetItem(context.Background(), req, callopt.WithRPCTimeout(3*time.Second))if err != nil {log.Fatal(err)}c.String(200, resp.String())
}
启动接口层api服务
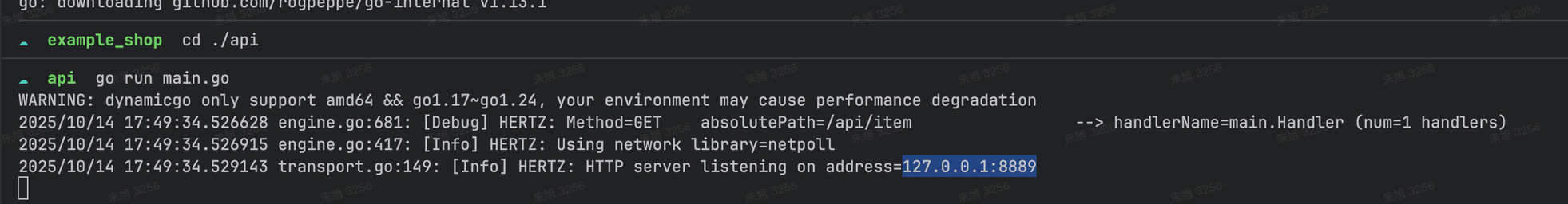
访问:http://127.0.0.1:8889/api/item即可
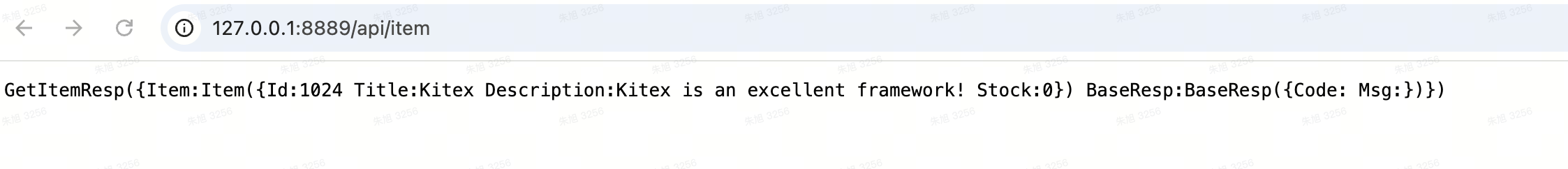
3.8 运行库存服务
在上面的示例中,我们已经完成了一次 RPC 调用,但在更常见的场景下,一次 RPC 调用远不能实现业务需求,故我们再添加库存服务,模拟更常见的场景。
库存服务的代码我们已经生成,只需要补充业务逻辑即可,与商品服务类似,业务代码位于 rpc/stock/handler.go,我们补充以下逻辑:
package mainimport ("context"stock "example_shop/kitex_gen/example/shop/stock"
)// StockServiceImpl implements the last service interface defined in the IDL.
type StockServiceImpl struct{}// GetItemStock implements the StockServiceImpl interface.
func (s *StockServiceImpl) GetItemStock(ctx context.Context, req *stock.GetItemStockReq) (resp *stock.GetItemStockResp, err error) {resp = stock.NewGetItemStockResp()resp.Stock = req.GetItemId() * 100return resp, nil
}
由于之前的商品服务和 API 服务分别占用了 8888 和 8889 端口,故我们在库存服务的 main.go 中修改监听的端口:
package mainimport ("log""net"stock "example_shop/kitex_gen/example/shop/stock/stockservice""github.com/cloudwego/kitex/server"
)func main() {addr, _ := net.ResolveTCPAddr("tcp", "127.0.0.1:8890")svr := stock.NewServer(new(StockServiceImpl), server.WithServiceAddr(addr))err := svr.Run()if err != nil {log.Println(err.Error())}
}
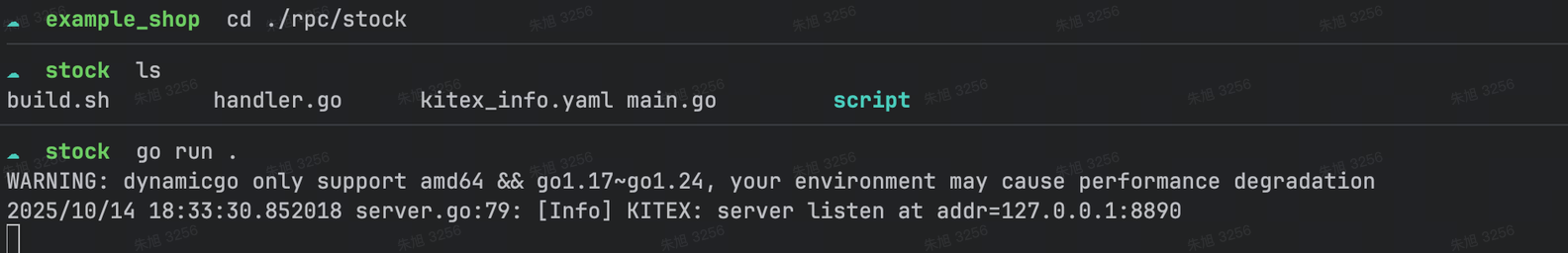
执行在/rpc/stock 目录下执行go run .
3.9 补充商品服务
我们已经成功运行了库存服务,接下来我们补充商品服务,实现对库存服务的调用,与 API 服务类似,我们只需要创建客户端后构造参数发起调用即可,为了实现 client 的复用,我们在 ItemServiceImpl 中补充字段 stockservice.Client ,在 rpc/item/handler.go 中我们补充以下方法:
package mainimport ("context"item "example_shop/kitex_gen/example/shop/item""example_shop/kitex_gen/example/shop/stock""example_shop/kitex_gen/example/shop/stock/stockservice""log""github.com/cloudwego/kitex/client"
)// ItemServiceImpl implements the last service interface defined in the IDL.
type ItemServiceImpl struct {stockCli stockservice.Client
}func NewStockClient(addr string) (stockservice.Client, error) {return stockservice.NewClient("example.shop.stock", client.WithHostPorts(addr))
}// GetItem implements the ItemServiceImpl interface.
func (s *ItemServiceImpl) GetItem(ctx context.Context, req *item.GetItemReq) (resp *item.GetItemResp, err error) {resp = item.NewGetItemResp()resp.Item = item.NewItem()resp.Item.Id = req.GetId()resp.Item.Title = "Kitex"resp.Item.Description = "Kitex is an excellent framework!"stockReq := stock.NewGetItemStockReq()stockReq.ItemId = req.GetId()stockRsp, err := s.stockCli.GetItemStock(ctx, stockReq)if err != nil {log.Println(err)stockRsp.Stock = 0}resp.Item.Stock = stockRsp.Stockreturn resp, nil}
为 ItemServiceImpl 补充了库存服务的客户端,我们需要初始化后才能使用,我们在 rpc/item/main.go 中完成初始化操作:
package mainimport ("log"item "example_shop/kitex_gen/example/shop/item/itemservice"
)func main() {itemServiceImpl := new(ItemServiceImpl)stockCli, err := NewStockClient("0.0.0.0:8890")if err != nil {log.Fatal(err)}itemServiceImpl.stockCli = stockClisvr := item.NewServer(itemServiceImpl)err = svr.Run()if err != nil {log.Println(err.Error())}
}
至此,商品服务代码编写完整,参照上文重新编译并启动商品服务,具体命令如下:
sh build.sh
sh output/bootstrap.sh