区块链论文速读 CCF A--USENIX Security 2025(4)

Conference:34th USENIX Security Symposium
CCF level:CCF A
Year:2025
Conference time:August 13–15, 2025 Seattle, WA, USA
区块链可投会议CCF A--Security 2026 截止2.5 附录用率
区块链论文速读 CCF A--USENIX Security 2025(1)
区块链论文速读 CCF A--USENIX Security 2025(2)
区块链论文速读 CCF A--USENIX Security 2025(3)
11
Title:
On the Atomicity and Efficiency of Blockchain Payment Channels
论区块链支付通道的原子性和效率
Authors:

Abstract:
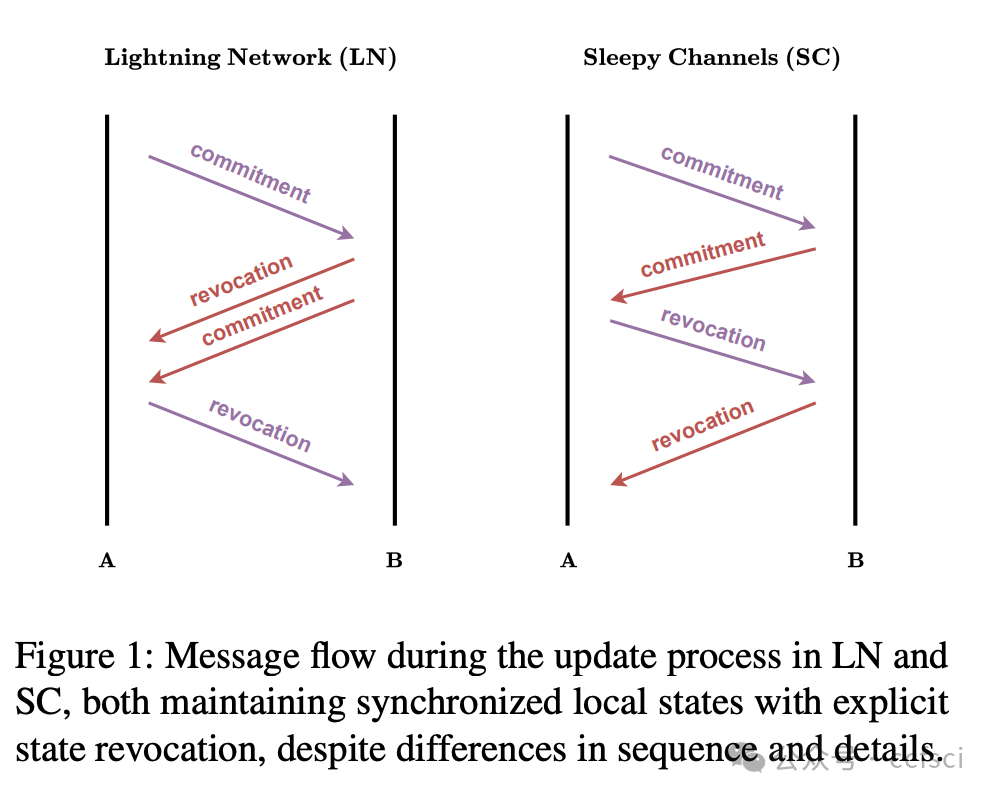
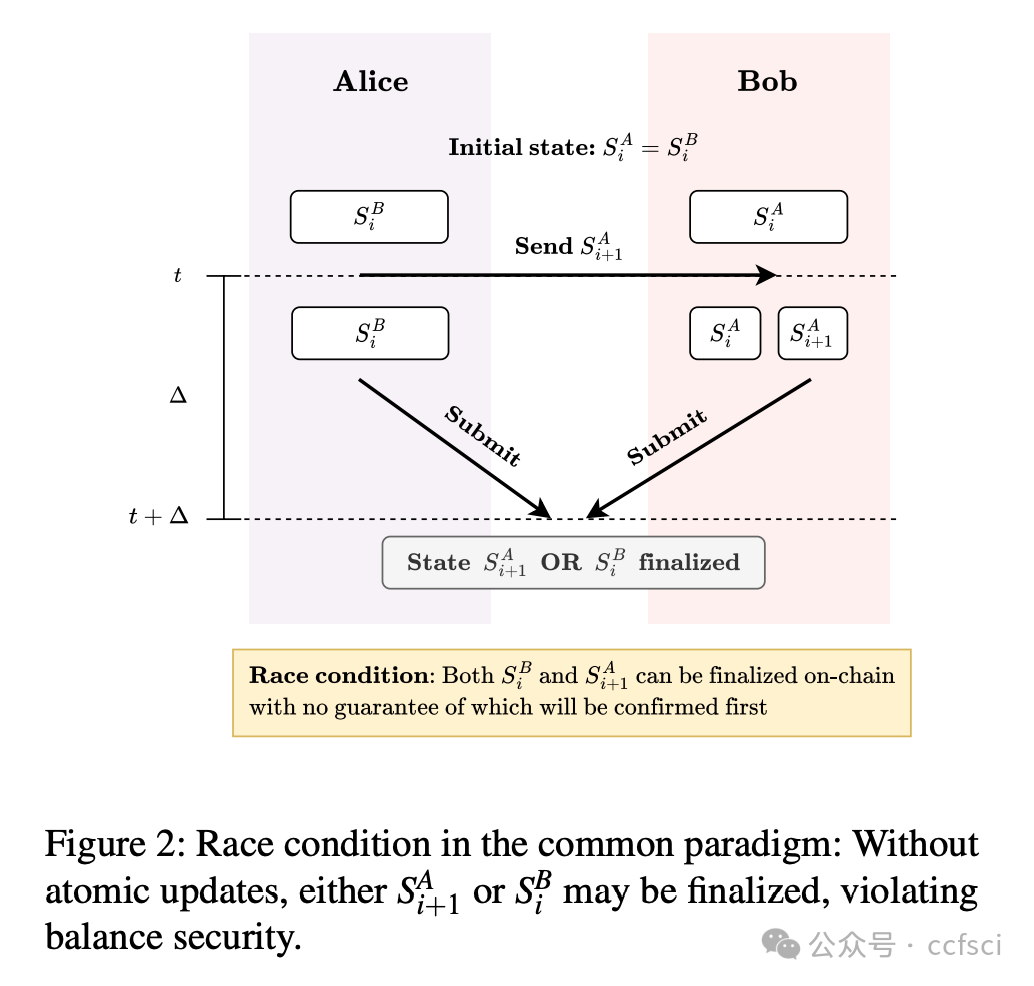
Payment channels are a promising solution for scaling cryptocurrency payments by enabling secure off-chain transactions. However, existing protocols, including the widely-deployed Lightning Network and the state-of-the-art Sleepy Channels, suffer from a fundamental flaw: non-atomic state transitions can result in multiple valid states coexisting, introducing race conditions and ambiguity in protocol execution. This ambiguity can be exploited to cause unexpected financial loss. We first formalize existing protocols into a common paradigm and prove that such flaws are inherent to their design, preventing balance security. To overcome this, we propose an atomic paradigm that guarantees atomic state transitions while preserving all desired functionality. Based on this paradigm, we design Ultraviolet, the first payment channel protocol that achieves atomicity by introducing the novel Resolve Mechanism. We formally prove that Ultraviolet satisfies balance security under the Universal Composability framework. In addition, Ultraviolet reduces the number of required messages per transaction by half compared to existing solutions. Our evaluation across multiple regions shows that Ultraviolet reduces latency by 37% and 52% compared to the Lightning Network and Sleepy Channels, respectively, and achieves comparable throughput to the Lightning Network and 2× that of Sleepy Channels.
支付通道通过实现安全的链下交易,为扩展加密货币支付提供了一种极具前景的解决方案。然而,包括广泛部署的闪电网络和最先进的Sleepy Channels在内的现有协议都存在一个根本缺陷:非原子状态转换可能导致多个有效状态共存,从而引入竞争条件和协议执行中的歧义。这种歧义可能被利用,造成意外的经济损失。我们首先将现有协议形式化为一个通用范式,并证明此类缺陷是其设计固有的,从而阻碍了余额安全。为了克服这一缺陷,我们提出了一种原子范式,该范式在保证所有所需功能的同时,确保了原子状态转换。基于此范式,我们设计了Ultraviolet,这是第一个通过引入新颖的Resolve机制实现原子性的支付通道协议。我们形式化地证明了Ultraviolet在通用可组合性框架下满足余额安全要求。此外,与现有解决方案相比,Ultraviolet将每笔交易所需的消息数量减少了一半。我们在多个地区的评估表明,与 Lightning Network 和 Sleepy Channels 相比,Ultraviolet 分别降低了 37% 和 52% 的延迟,并实现了与 Lightning Network 相当的吞吐量,是 Sleepy Channels 的 2 倍。


Pdf下载链接:
https://www.usenix.org/system/files/usenixsecurity25-wu-di.pdf
12
Title:
Parallelizing Universal Atomic Swaps for Multi-Chain Cryptocurrency Exchanges
面向多链加密货币交易所的通用原子交换并行化
Authors:

Abstract:
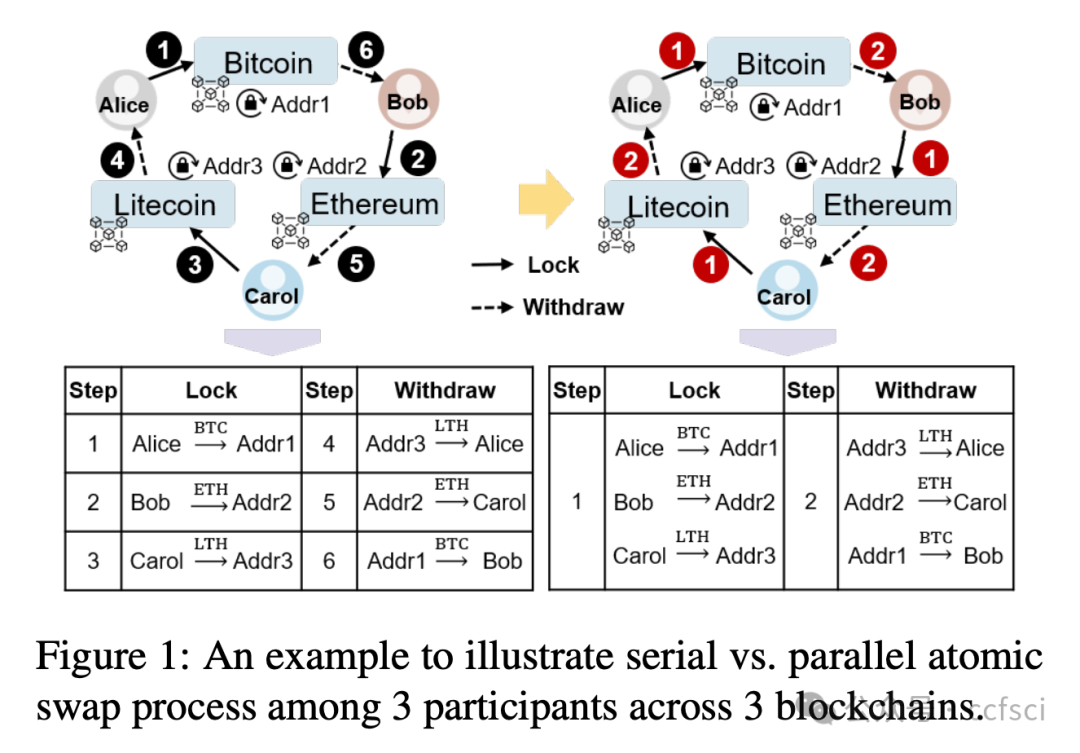
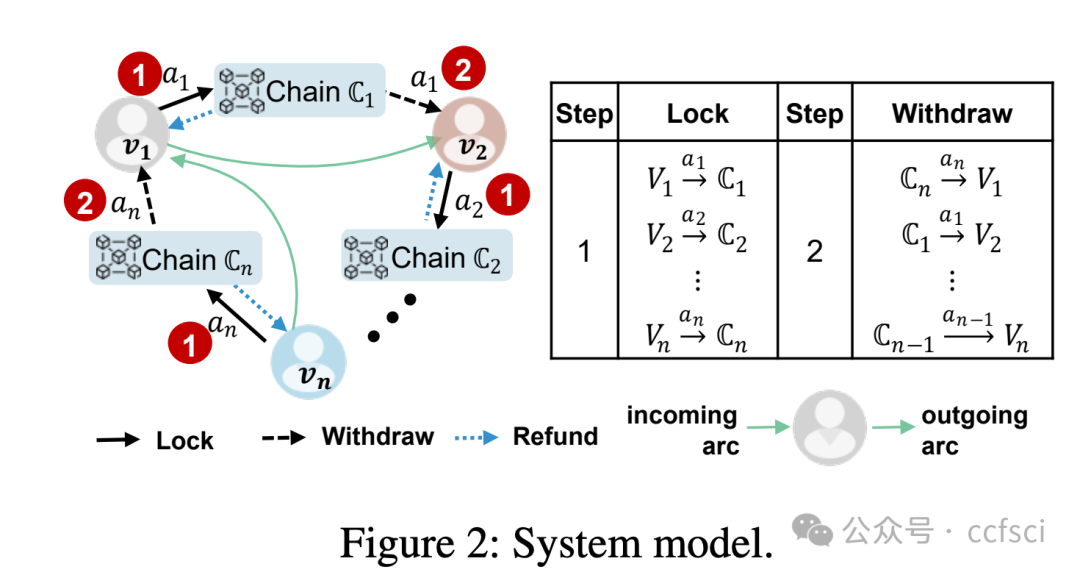
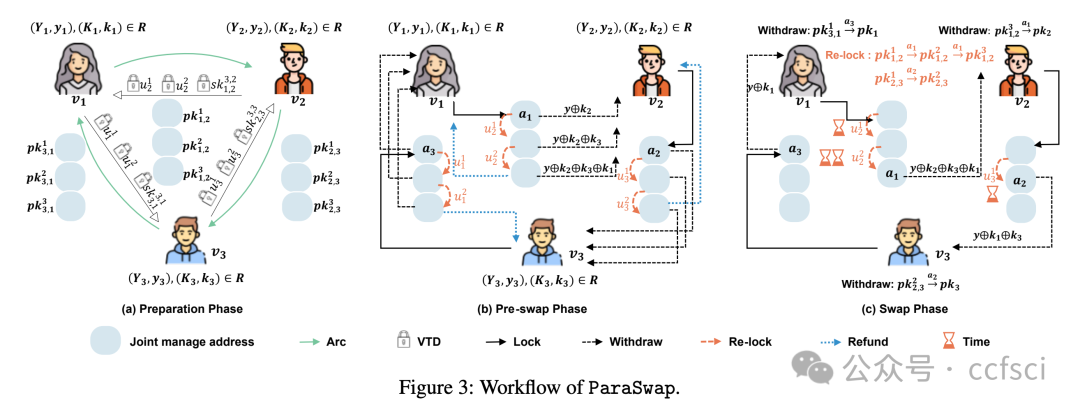
Universal atomic swap is an emerging technique for secure cryptocurrency exchanges across diverse blockchains, eliminating the need for custom scripting language support from blockchains. While existing schemes primarily focus on exchanges among two users, extending these to multiple users across multiple blockchains incurs significant overheads due to the need for performing multiple two-party swaps serially. An intuitive insight is to parallelize the universal processes, but this idea still faces two technical challenges: (i) avoid asset theft during parallel asset locking; (ii) ensure atomicity by preventing partial execution of transactions with a uniform refund time used to avoid asset deadlock in parallel.
In this paper, we present ParaSwap, the first framework to parallelize universal atomic swaps for cryptocurrency exchanges among multiple users across multiple blockchains. We replace the serial multiple two-party swaps with a concurrent mechanism, where each participant concurrently locks and withdraws coins, achieving parallel execution. To prevent asset theft, the necessary witness for swaps is collaboratively determined by all participants. Then we introduce a novel re-lock approach to ensure atomicity with a uniform refund time, allowing participants to re-lock their assets to new addresses when the remaining time is insufficient to complete their withdrawal. Notably, ParaSwap employs adaptor signatures and verifiable timed discrete logarithm (VTD) technology, relying only on the bare minimum ability of blockchain to verify transaction signatures. We implement ParaSwap on four public blockchain test networks: Bitcoin, Ethereum, Avalanche, and Binance Smart Chain. Our evaluation demonstrates that ParaSwap reduces the exchange time complexity from O(n) to O(1), where n is the number of participants, and lowers gas costs by 26.2x to 46.8x, compared to existing methods.
通用原子交换是一种新兴技术,用于在不同区块链上安全地进行加密货币交易,无需区块链提供自定义脚本语言支持。现有方案主要关注两个用户之间的交易,但将其扩展到跨多个区块链的多用户交易时,由于需要串行执行多个双边交换,会产生显著的开销。一个直观的思路是并行化这些通用流程,但这一思路仍然面临两个技术挑战:(i) 避免并行锁定资产期间的资产盗窃;(ii) 通过防止交易部分执行来确保原子性,并使用统一的退款时间来避免并行资产死锁。
本文提出了 ParaSwap,这是第一个用于并行化跨多个区块链的多用户加密货币交易通用原子交换的框架。我们用并发机制取代了串行的多双边交换,其中每个参与者同时锁定和提取代币,从而实现并行执行。为了防止资产盗窃,交换所需的见证人由所有参与者共同确定。然后,我们引入了一种新颖的重锁机制,以确保原子性并采用统一的退款时间。当剩余时间不足以完成提现时,参与者可以将资产重新锁定到新的地址。值得注意的是,ParaSwap 采用适配器签名和可验证时间离散对数 (VTD) 技术,仅依赖于区块链验证交易签名的最基本能力。我们在四个公共区块链测试网络上实现了 ParaSwap:比特币、以太坊、Avalanche 和币安智能链。我们的评估表明,与现有方法相比,ParaSwap 将交易时间复杂度从 O(n) 降低到 O(1)(其中 n 为参与者数量),并将 gas 成本降低了 26.2 倍至 46.8 倍。

Pdf下载链接:
https://www.usenix.org/system/files/usenixsecurity25-xiao-danlei.pdf
13
Title:
Automated Soundness and Completeness Vetting of Polygon zkEVM
Polygon zkEVM 的自动化健全性和完整性审查
Authors:

Abstract:
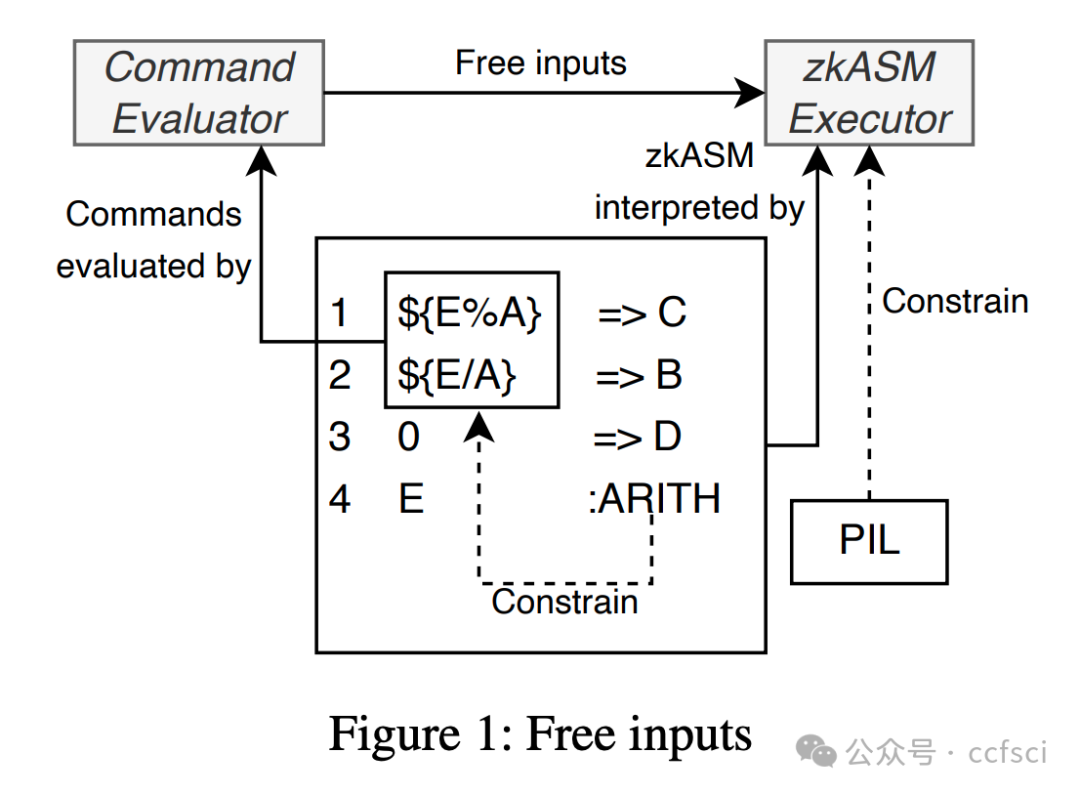
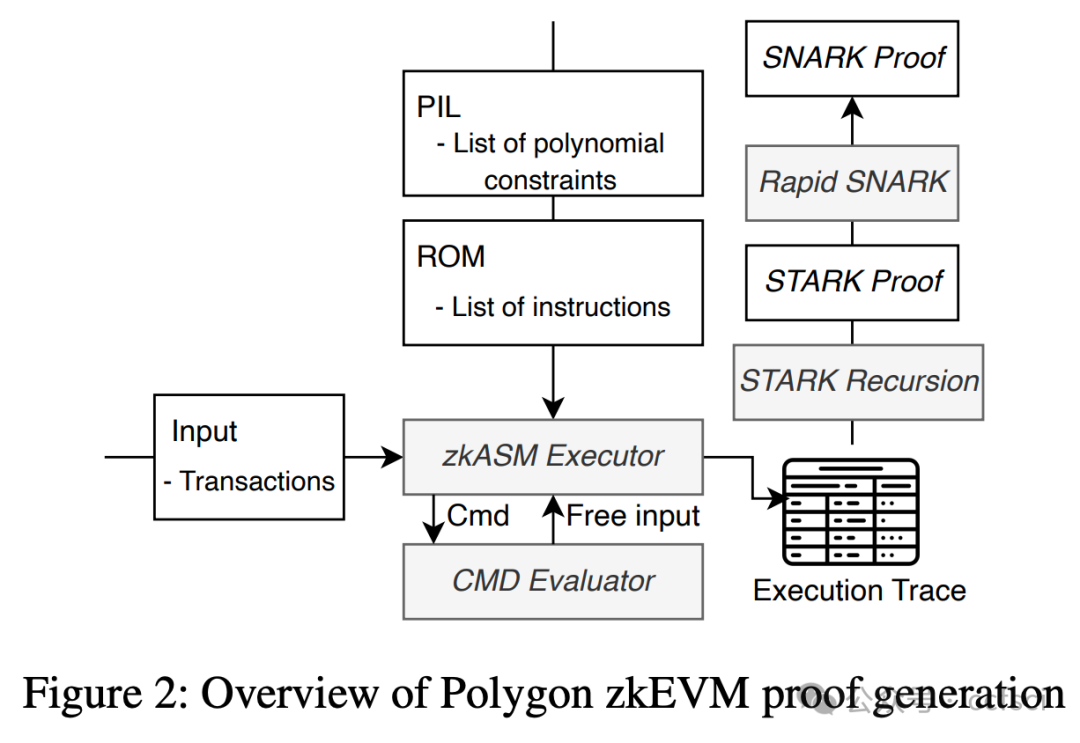
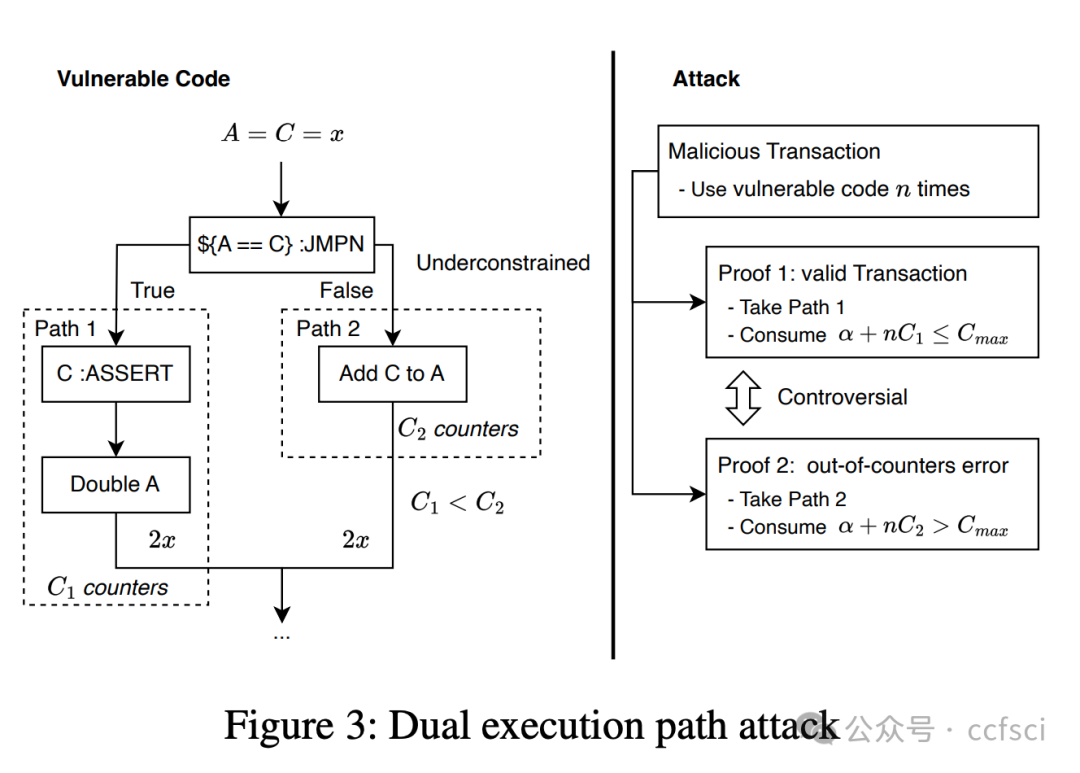
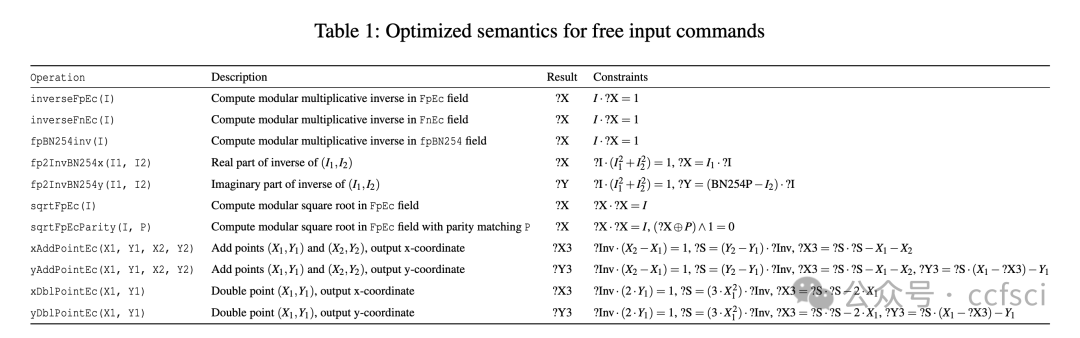
Zero-knowledge rollups have emerged as popular layer 2 scaling solutions for blockchains. Polygon zkEVM, a leading deployment of zk rollups, leverages non-deterministic execution to derive free inputs from an unconstrained command evaluator when implementing the zkEVM. This mechanism significantly simplifies the design of zkEVM and enhances the performance of proof generation. However, it introduces the challenge of requiring developers to define constraints for free inputs, a task that demands strong mathematical expertise and is prone to errors. As a component of the layer-2 infrastructure, the zkEVM's vulnerabilities could lead to powerful attacks. However, despite their importance, the security of free inputs in zkEVM remains unexplored.
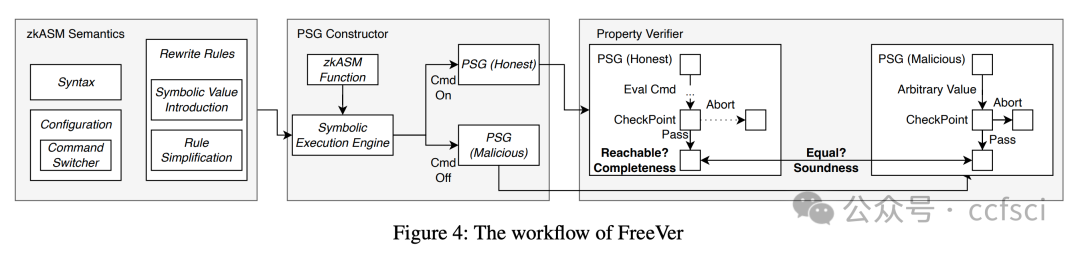
In this paper, we present the first systematic exploration of free inputs in Polygon zkEVM. Our study reveals critical soundness and completeness issues with them. In particular, we uncover a new attack surface, termed the dual execution path attack, which targets unsound implementations of free inputs and can lead to chain splits. Moreover, we design the first tool, FreeVer, which facilitates the verification of the soundness and completeness of free inputs with formal semantics. Additionally, it automatically generates formal specifications for correct constraints by constructing prover state graphs that model both the behaviors of malicious and honest provers. It then uses the states from the honest prover as specifications to assist in the verification of states from the malicious one. FreeVer also adopts optimization strategies to reduce the complexity of constraints for effective verification. Our evaluation results show that FreeVer can correctly identify all previously disclosed free input related vulnerabilities and detect 7 new vulnerabilities in Polygon zkEVM. All detected bugs are submitted through the bug bounty program and are confirmed as high impact vulnerabilities.
Zero-knowledge rollups(ZKR)已成为区块链二层扩容方案的热门选择。Polygon zkEVM 作为 ZKR 的领先部署方案,在实现 ZKEVM 时利用非确定性执行,从无约束命令评估器中导出自由输入。这种机制显著简化了 ZKEVM 的设计,并提升了证明生成的性能。然而,这也带来了新的挑战:开发者需要为自由输入定义约束,而这项任务需要深厚的数学专业知识,且极易出错。作为二层基础设施的一部分,ZKEVM 的漏洞可能导致强大的攻击。尽管自由输入至关重要,但其安全性仍未得到充分研究。
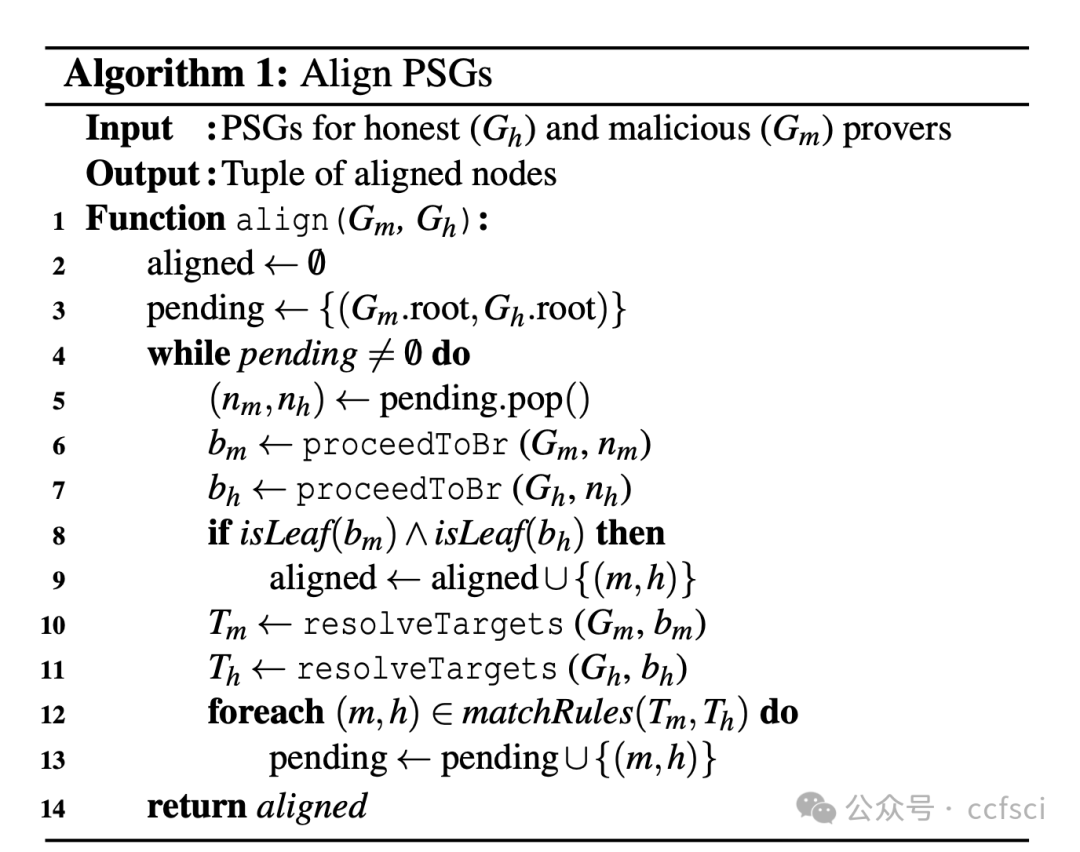
本文首次系统地探索了 Polygon zkEVM 中的自由输入。我们的研究揭示了其关键的可靠性和完备性问题。尤其值得一提的是,我们发现了一个新的攻击面,称为双执行路径攻击,该攻击针对自由输入的不可靠实现,并可能导致链分裂。此外,我们设计了首个工具 FreeVer,它能够利用形式语义验证自由输入的可靠性和完整性。FreeVer 通过构建证明者状态图,自动生成正确约束的形式化规范,该状态图同时模拟了恶意证明者和诚实证明者的行为。然后,它利用诚实证明者的状态作为规范,辅助验证恶意证明者的状态。FreeVer 还采用了优化策略来降低约束的复杂度,从而实现有效的验证。我们的评估结果表明,FreeVer 能够正确识别所有先前已披露的与自由输入相关的漏洞,并在 Polygon zkEVM 中检测到 7 个新的漏洞。所有检测到的漏洞均已通过漏洞赏金计划提交,并被确认为高影响漏洞。

Pdf下载链接:
https://www.usenix.org/system/files/usenixsecurity25-peng-xinghao.pdf
