Java119 反射使用
反射
方法
getMethod();
public class ReflectionExample2 {public static void main(String[] args) {try {
Class classstudent=Class.forName("student");classstudent.getMethod();} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}
}import java.lang.reflect.Method;public class ReflectionExample2 {public static void main(String[] args) {try {// 使用正确的类名(假设有一个Student类)Class<?> studentClass = Class.forName("Student");// 获取一个无参数的公共方法,比如"getName"Method method = studentClass.getMethod("getName");System.out.println("成功获取方法: " + method.getName());} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {System.err.println("找不到Student类,请确保该类存在");e.printStackTrace();} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {System.err.println("找不到指定的方法");e.printStackTrace();} catch (Exception e) {System.err.println("发生其他错误");e.printStackTrace();}}
}
import java.lang.reflect.Method;public class ReflectionExample2 {public static void main(String[] args) {try {
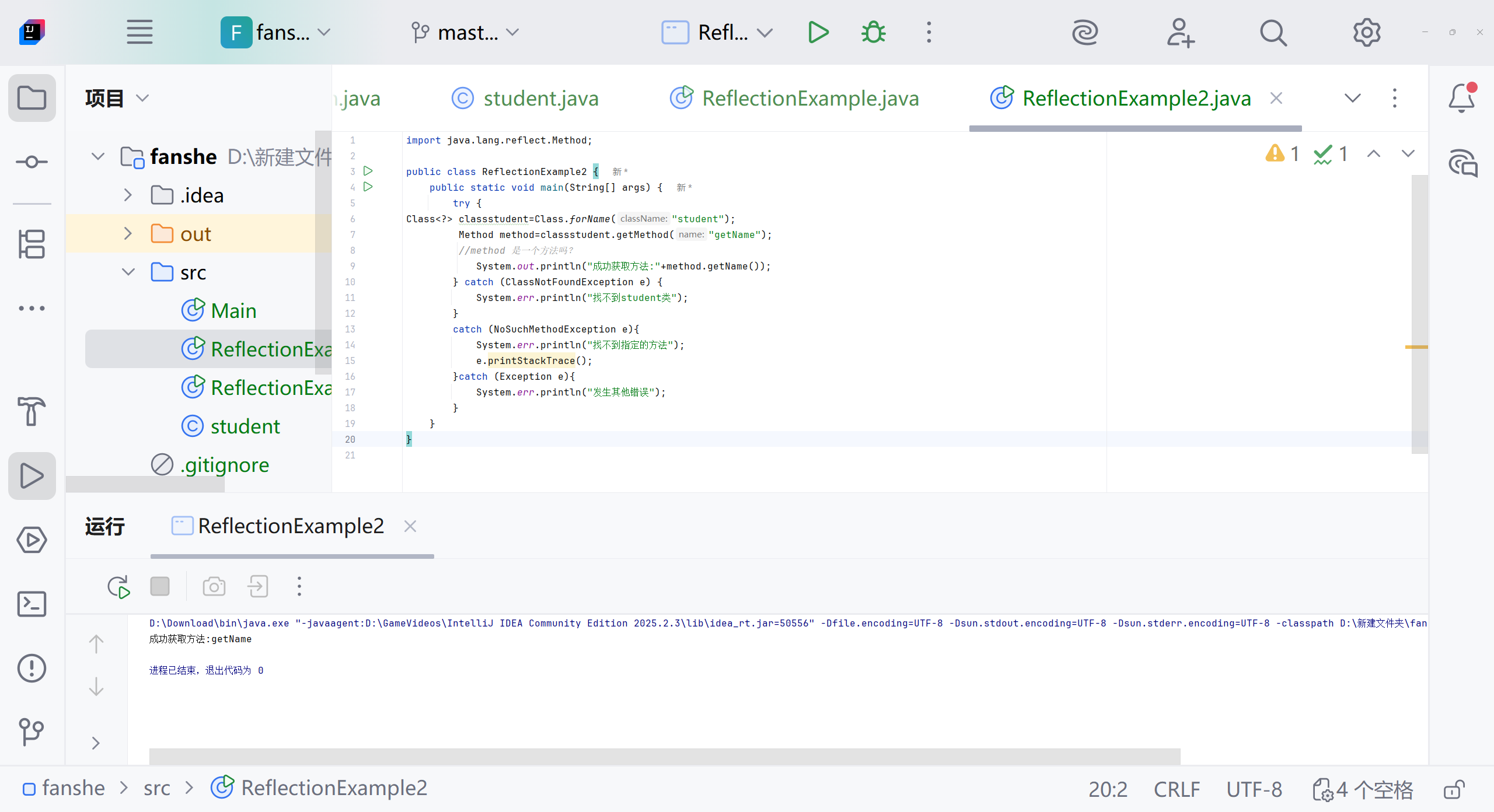
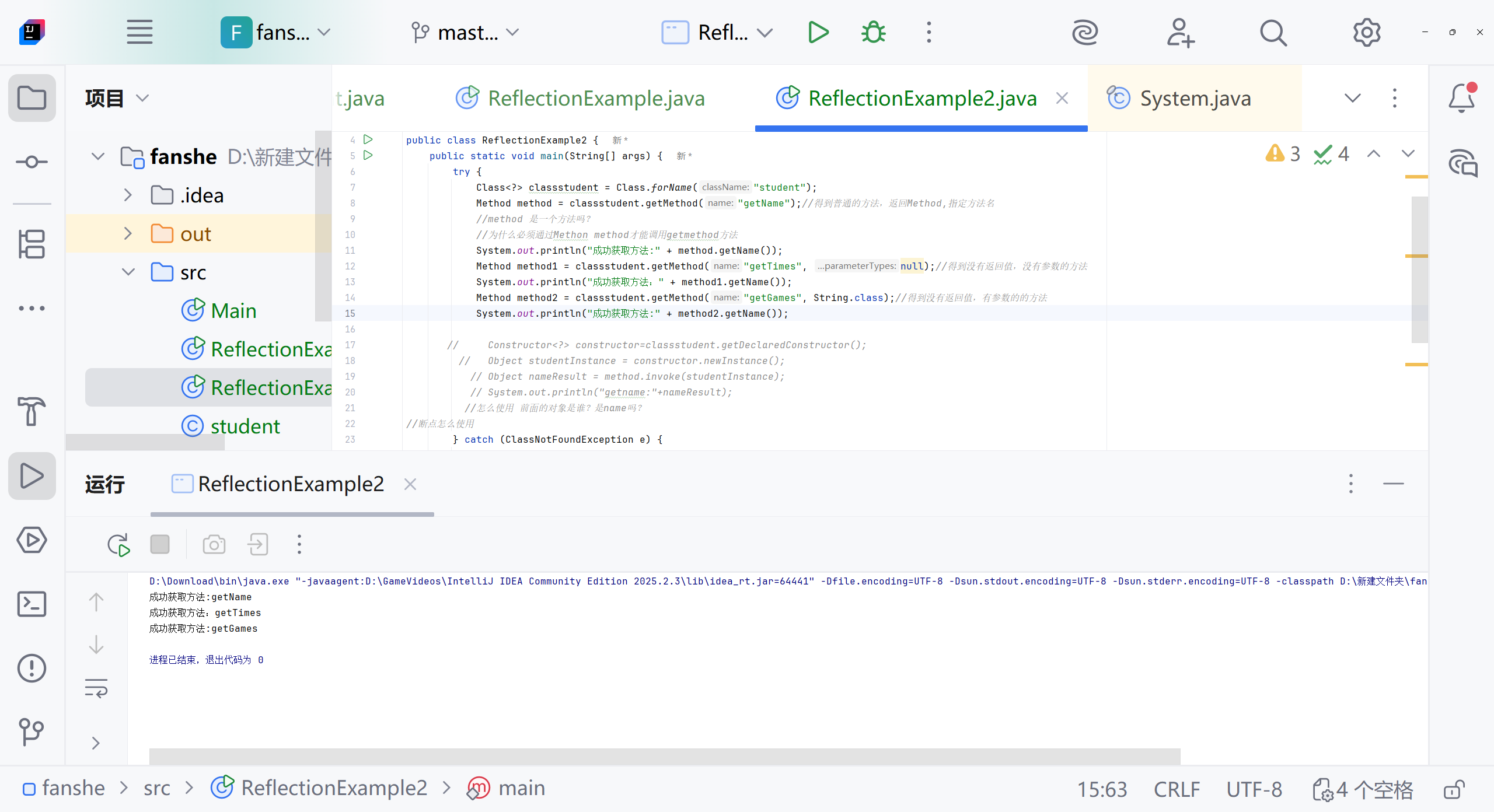
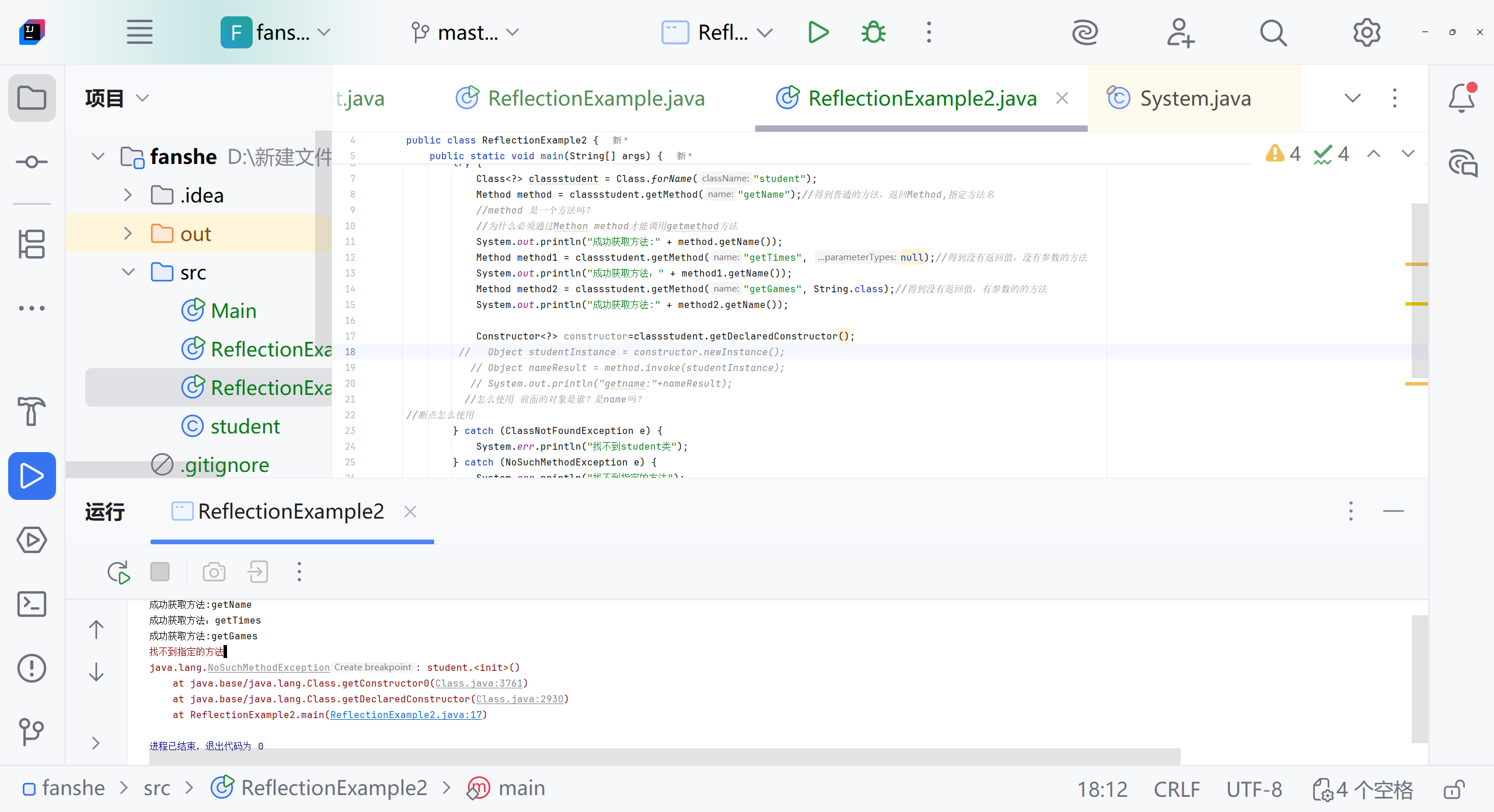
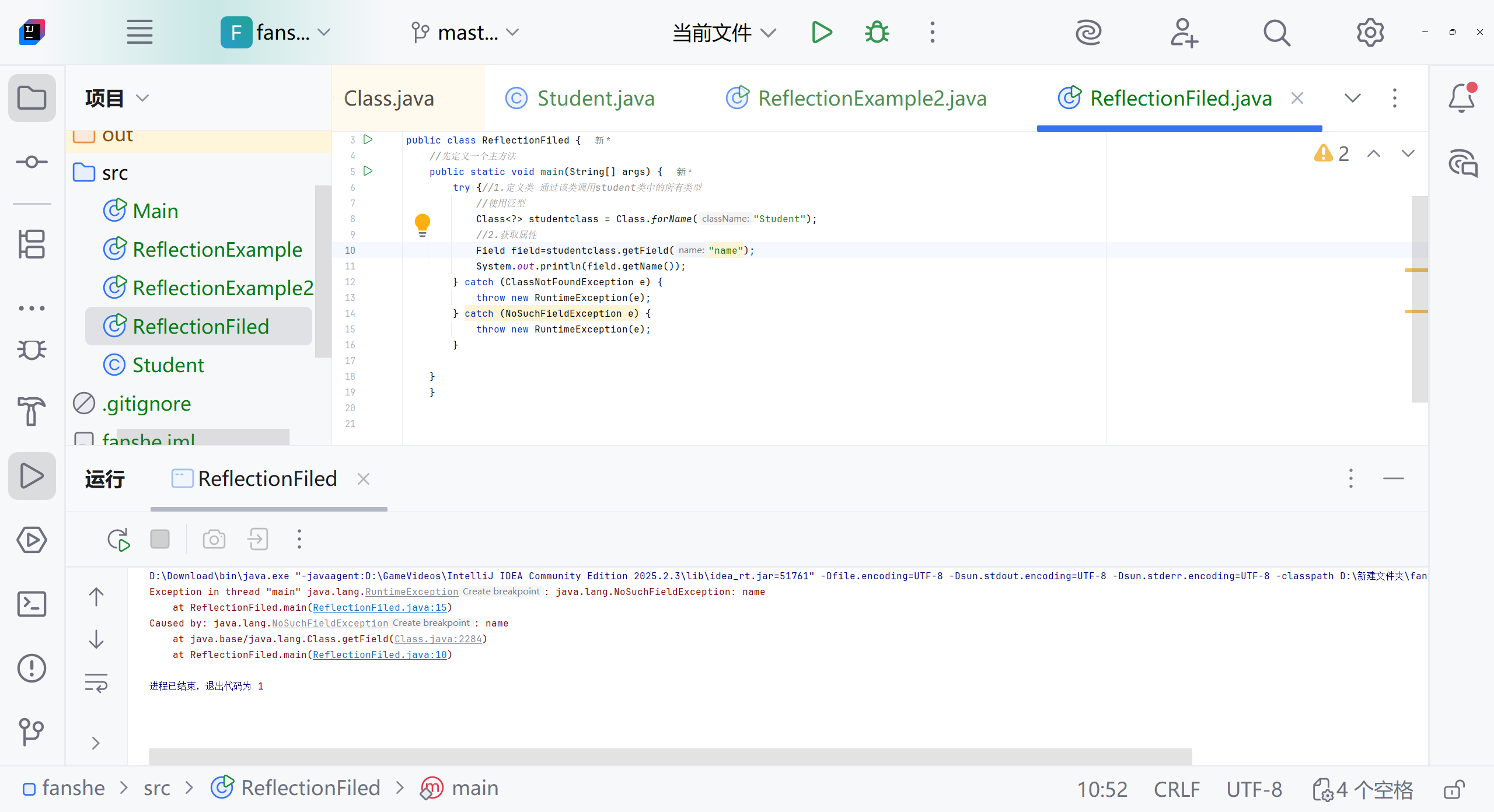
Class<?> classstudent=Class.forName("student");Method method=classstudent.getMethod("getName");//method 是一个方法吗?System.out.println("成功获取方法:"+method.getName());} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {System.err.println("找不到student类");}catch (NoSuchMethodException e){System.err.println("找不到指定的方法");e.printStackTrace();}catch (Exception e){System.err.println("发生其他错误");}}
}
import java.lang.reflect.Method;public class ReflectionExample2 {public static void main(String[] args) {try {
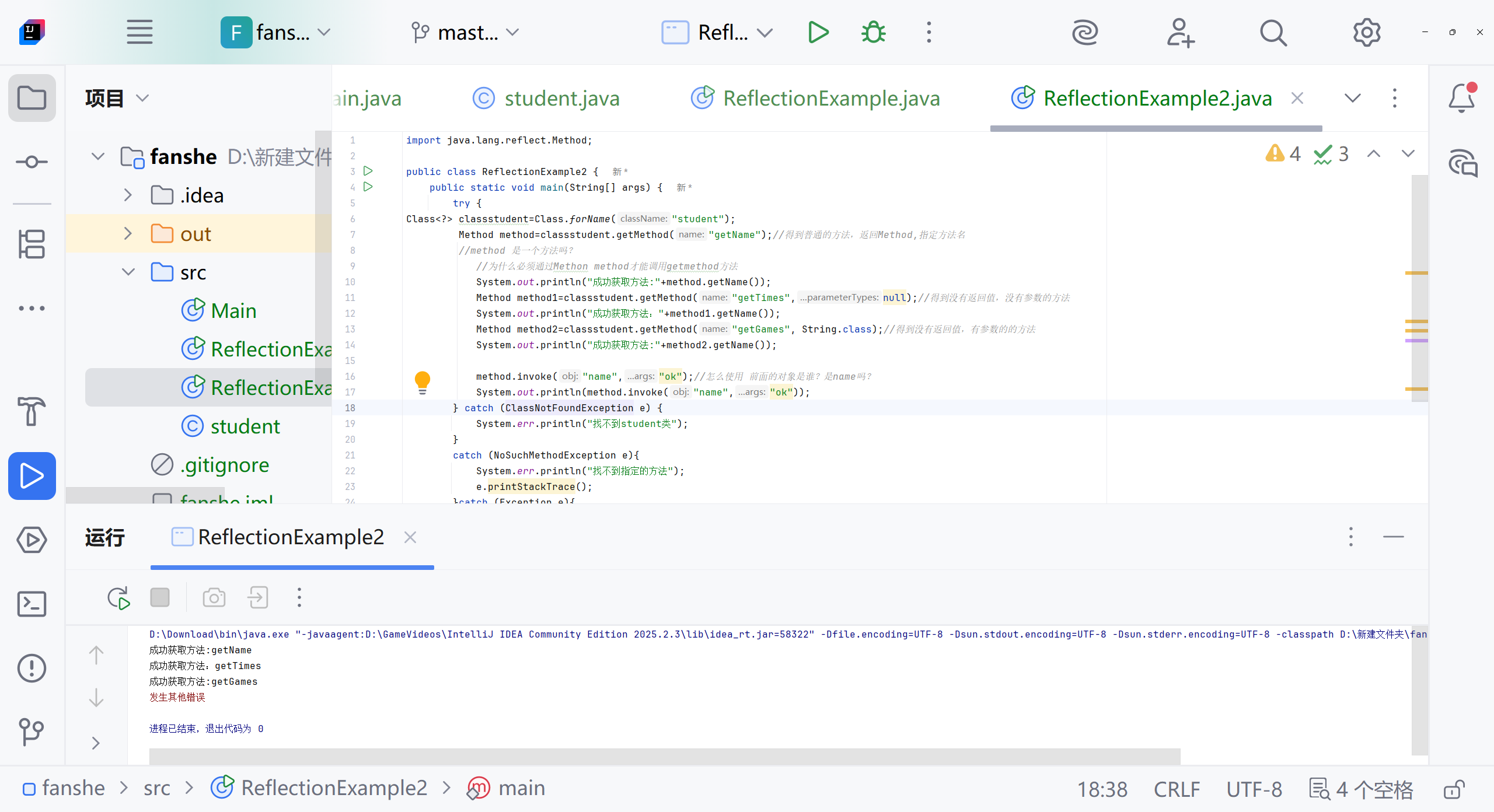
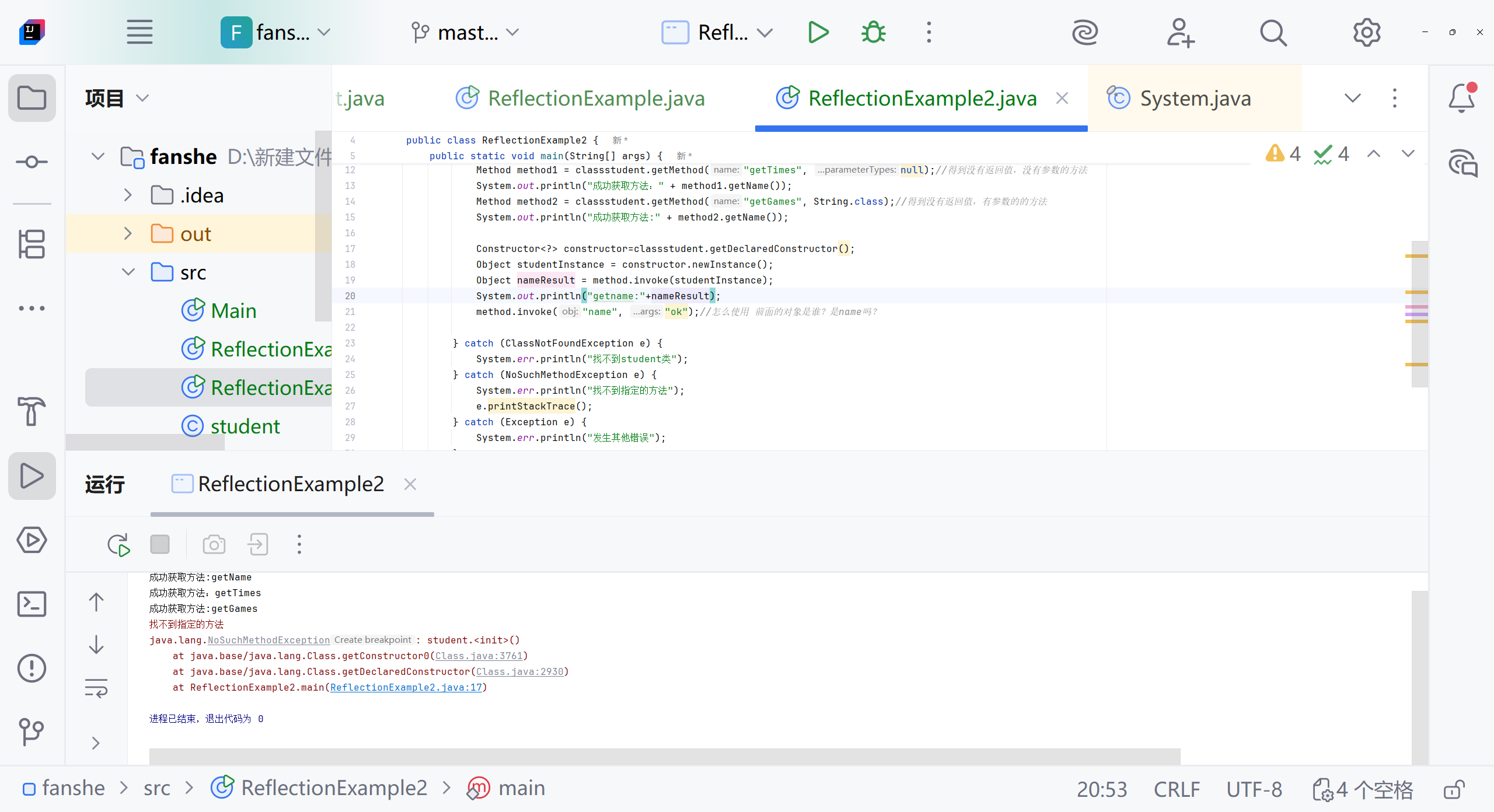
Class<?> classstudent=Class.forName("student");Method method=classstudent.getMethod("getName");//得到普通的方法,返回Method,指定方法名//method 是一个方法吗?//为什么必须通过Methon method才能调用getmethod方法System.out.println("成功获取方法:"+method.getName());Method method1=classstudent.getMethod("getTimes",null);//得到没有返回值,没有参数的方法System.out.println("成功获取方法:"+method1.getName());Method method2=classstudent.getMethod("getGames", String.class);//得到没有返回值,有参数的的方法System.out.println("成功获取方法:"+method2.getName());method.invoke("name","ok");//怎么使用 前面的对象是谁?是name吗?System.out.println(method.invoke("name","ok"));} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {System.err.println("找不到student类");}catch (NoSuchMethodException e){System.err.println("找不到指定的方法");e.printStackTrace();}catch (Exception e){System.err.println("发生其他错误");}}
}
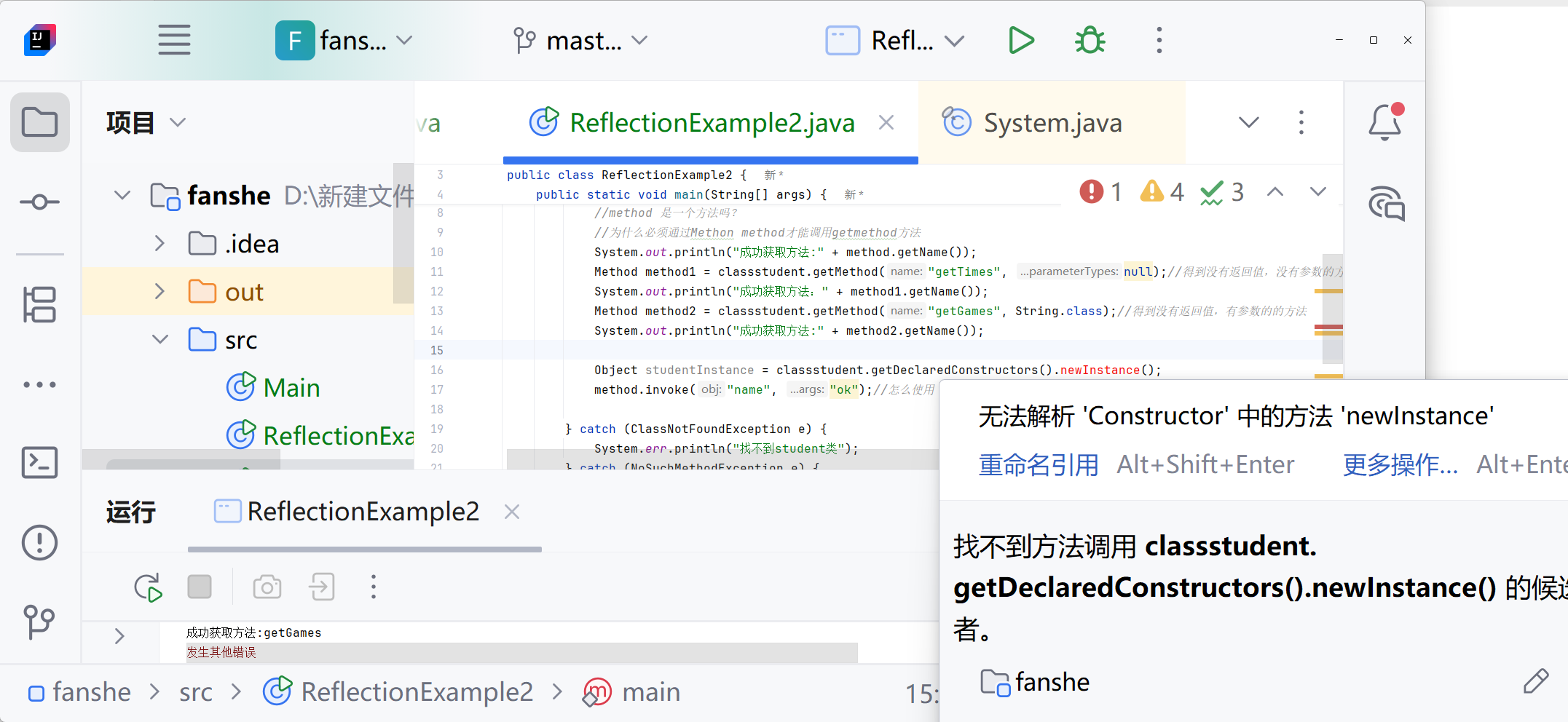
主要问题:student类缺少无参构造函数,导致无法创建实例。
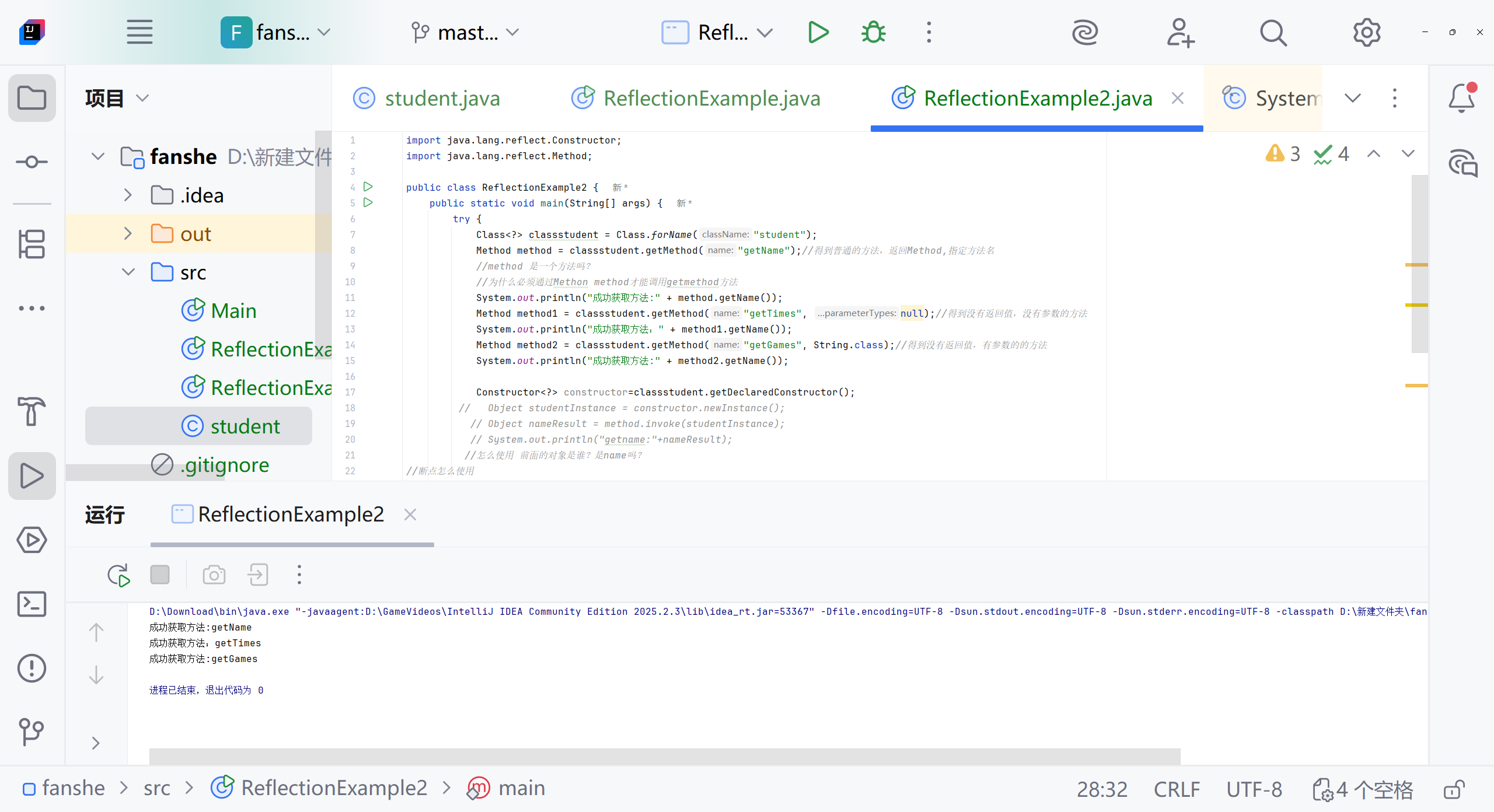
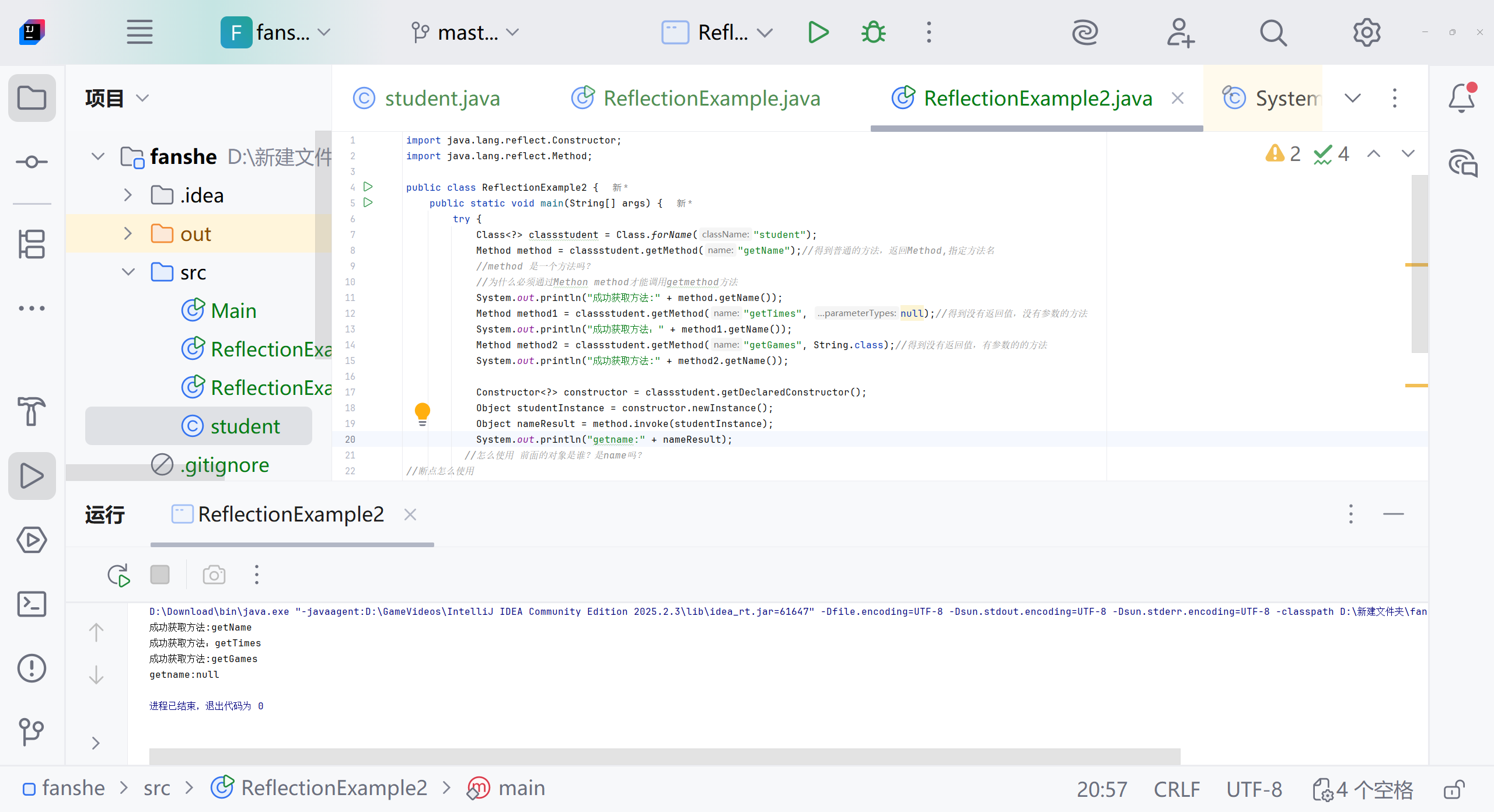
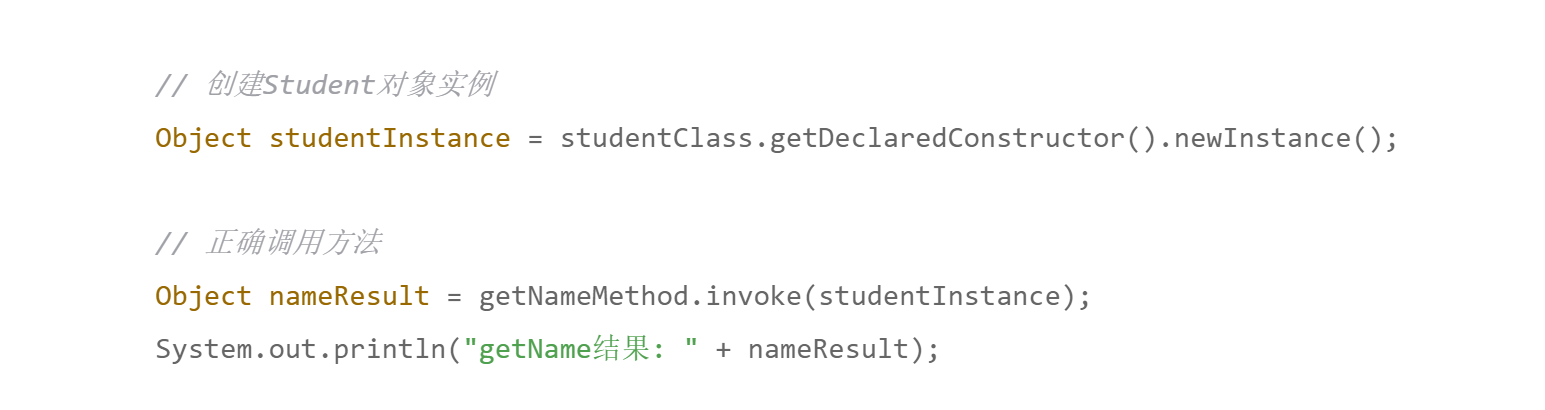
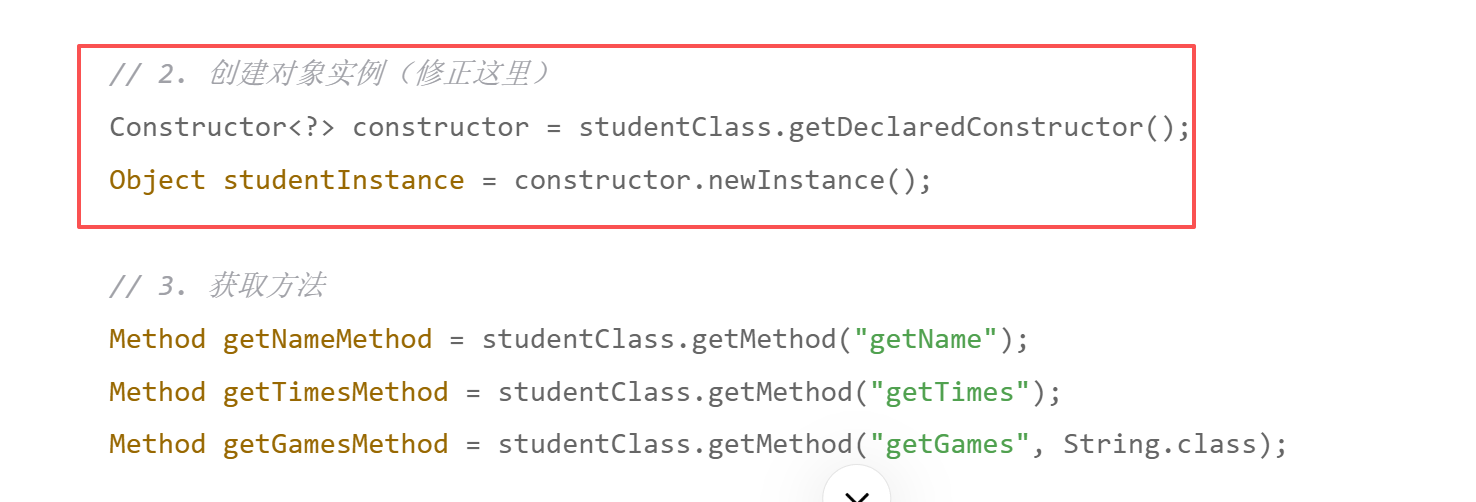
Constructor<?> constructor = classstudent.getDeclaredConstructor();Object studentInstance = constructor.newInstance();Object nameResult = method.invoke(studentInstance);System.out.println("getname:" + nameResult);
什么意思
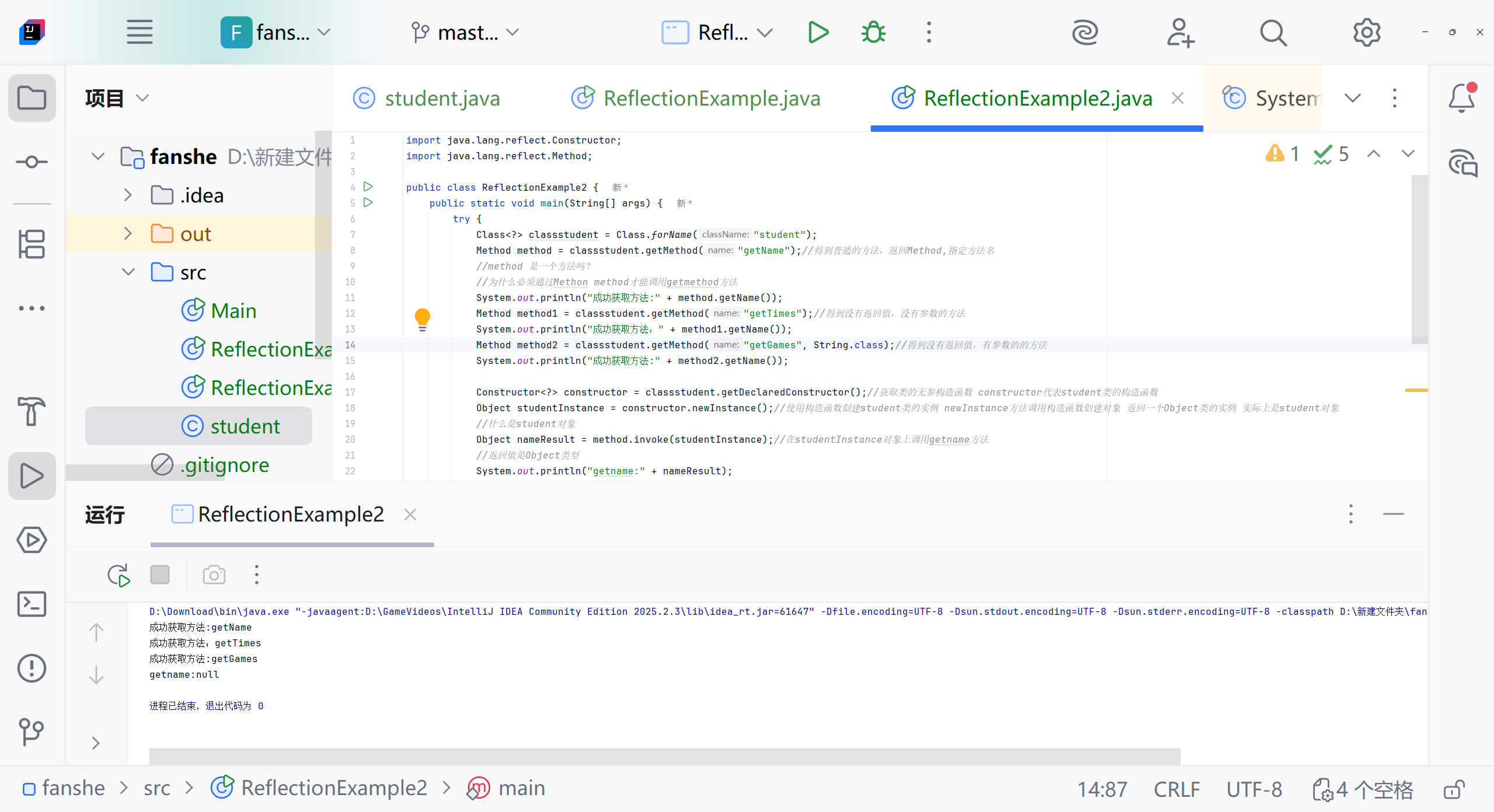
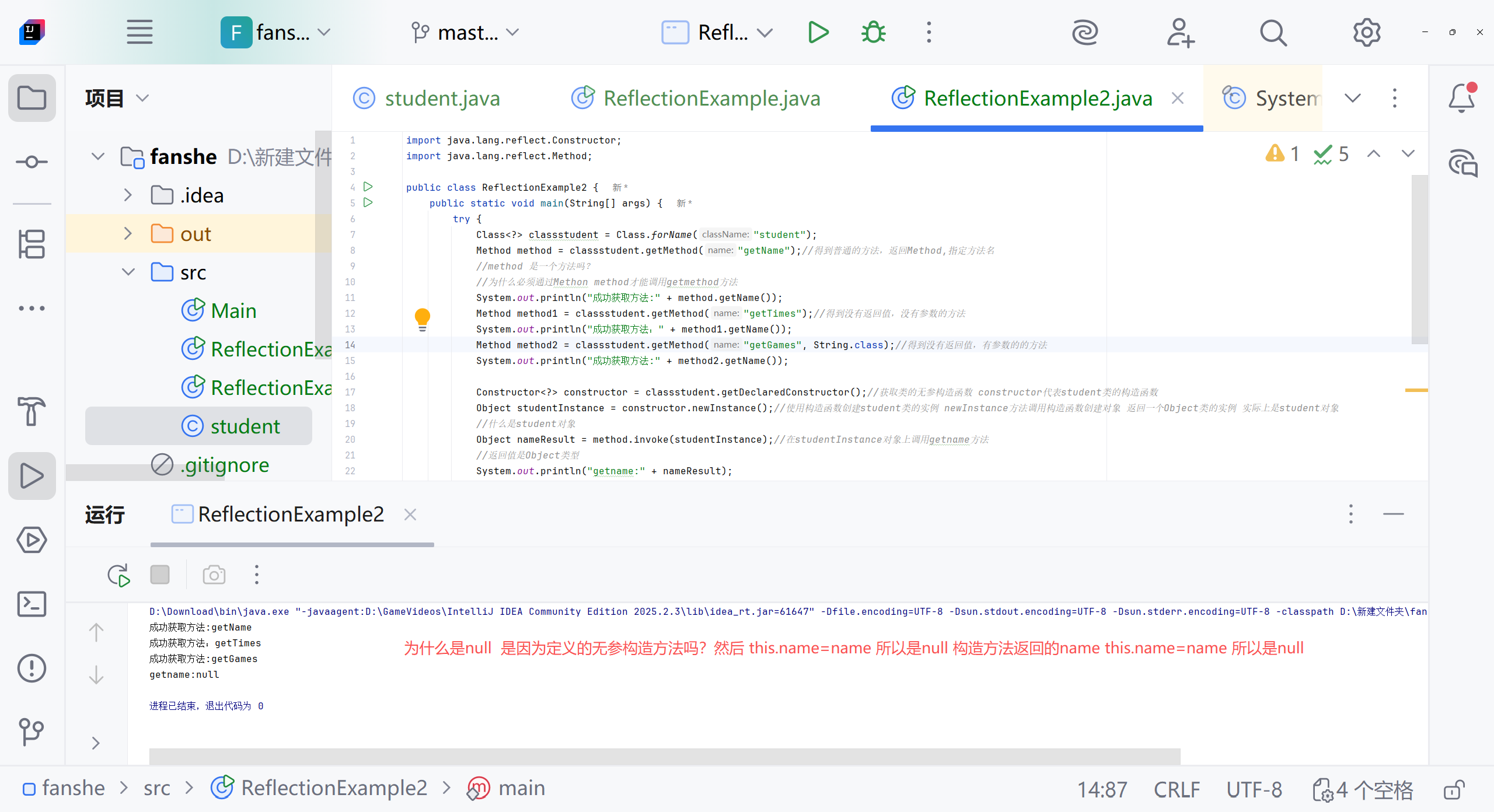
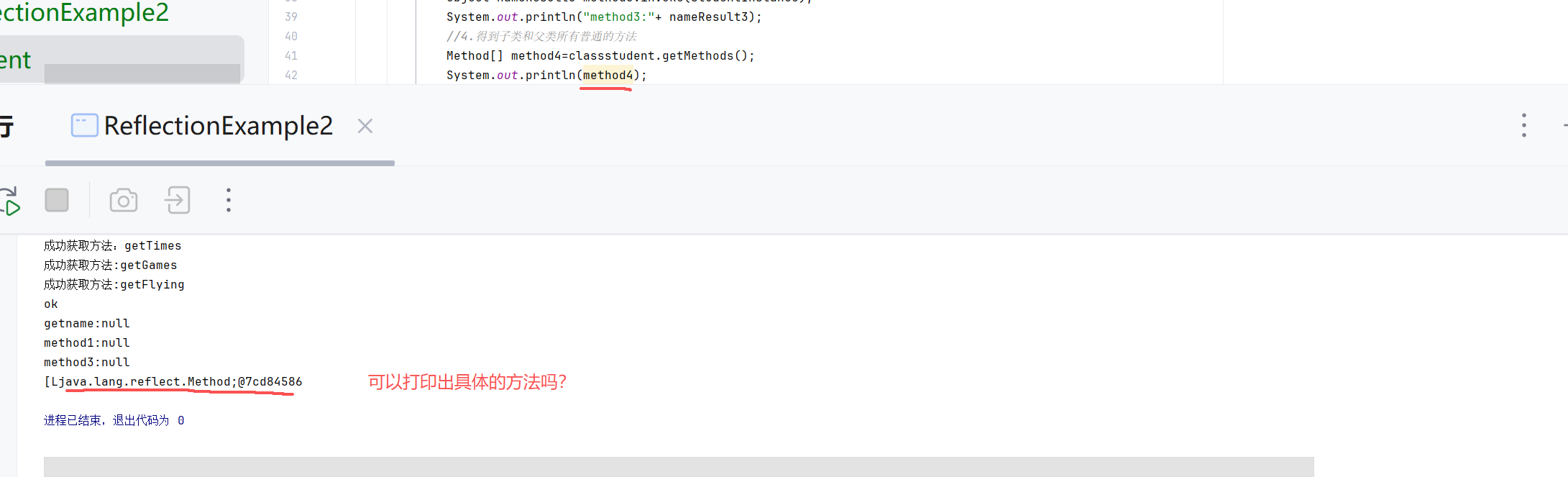
如何打印

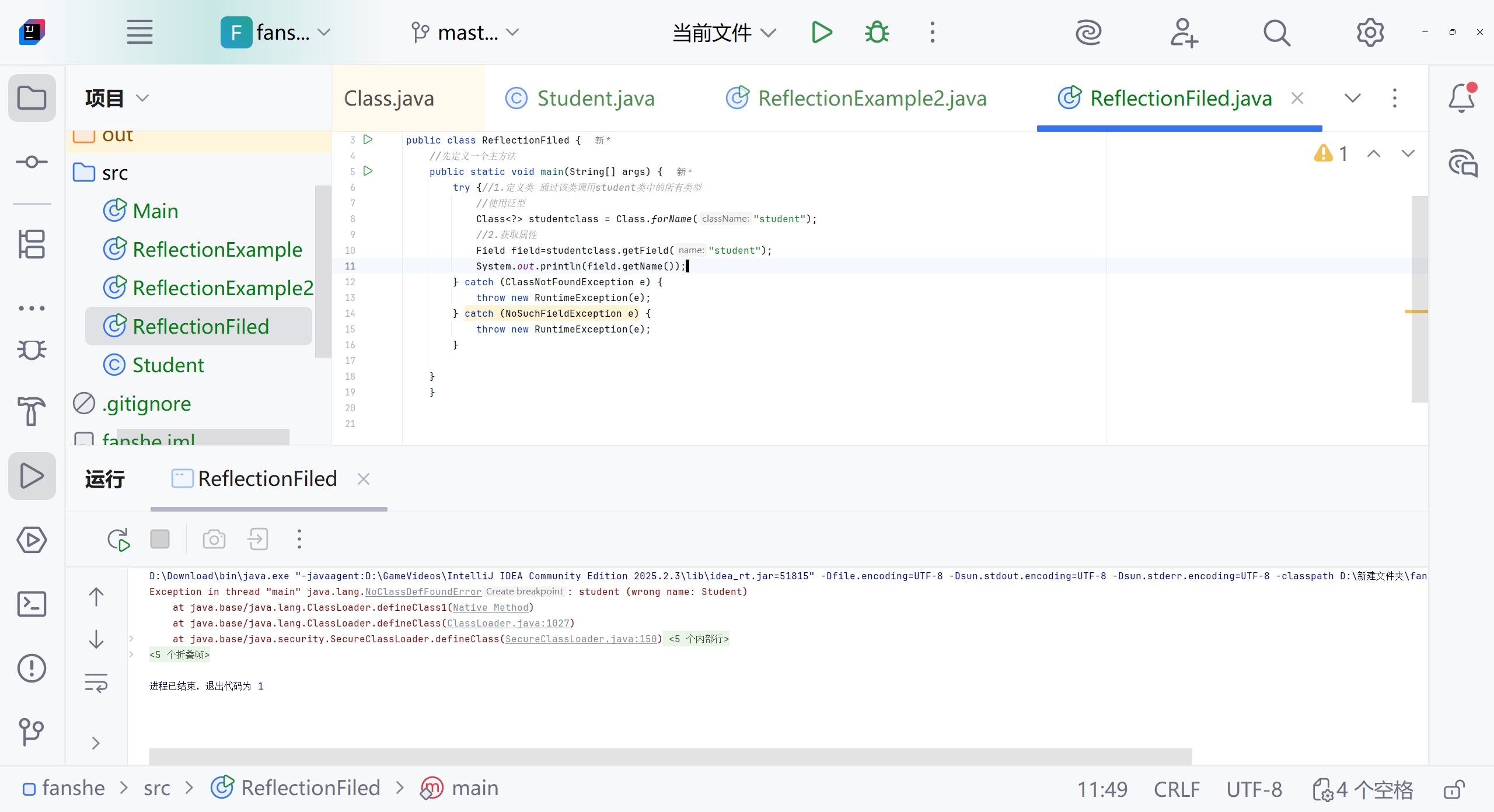
找不到目标构造函数报错
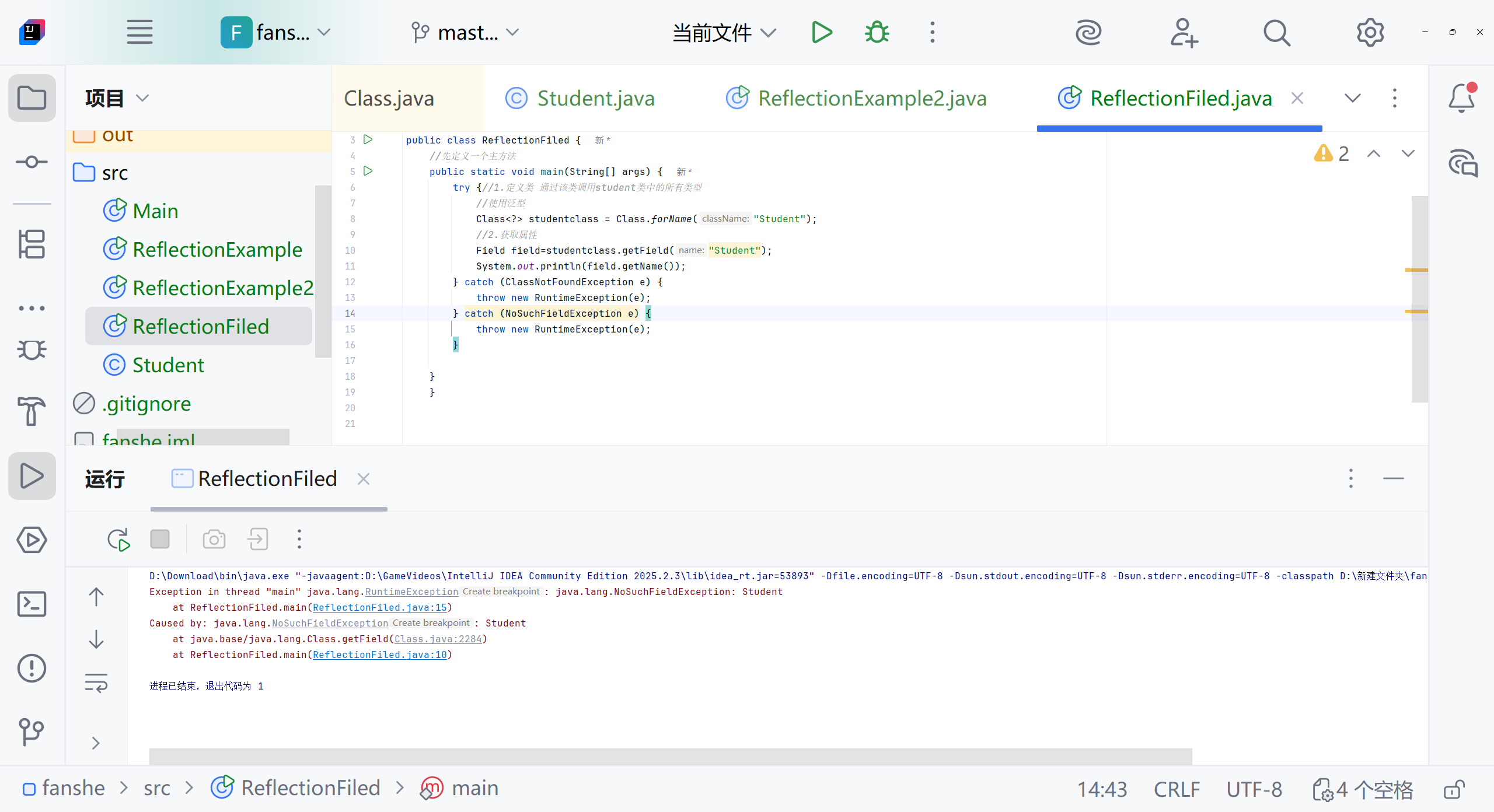
需要student类 构造方法加上public
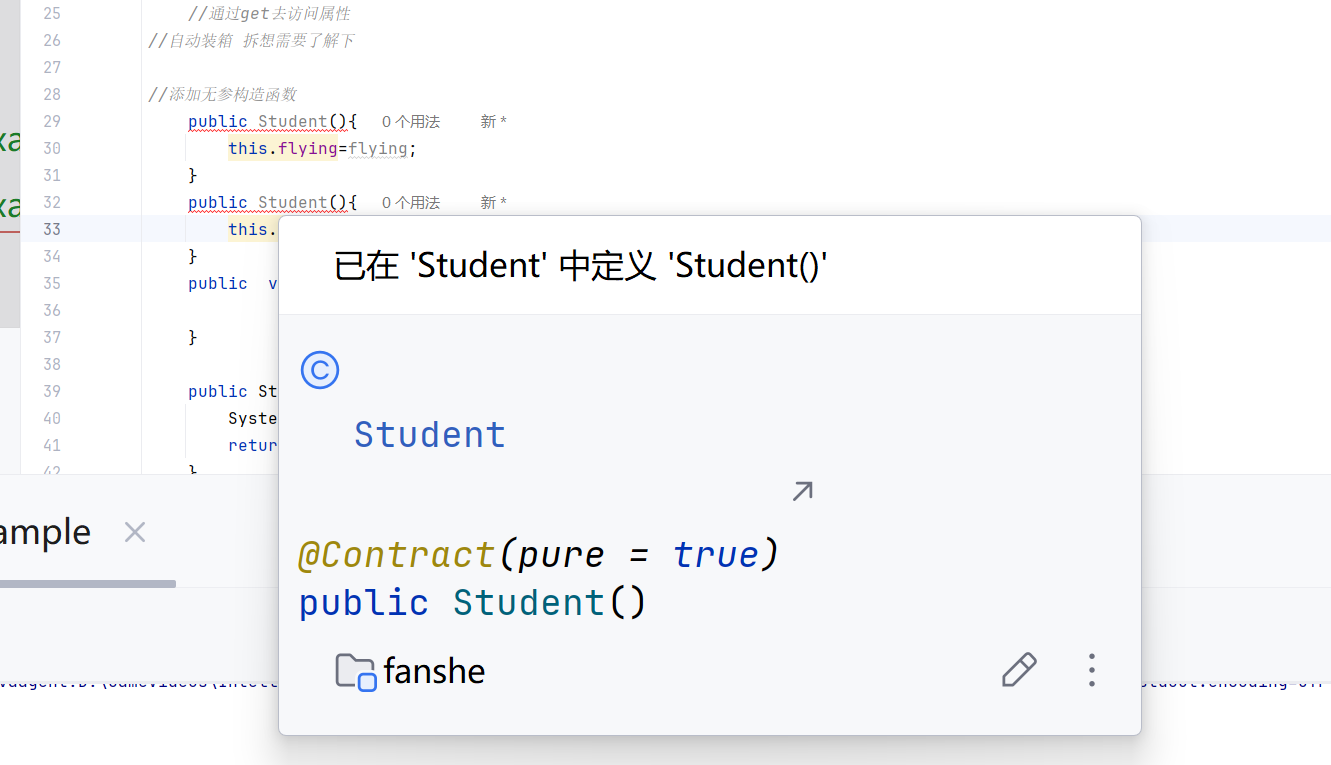
从图片中可以看到,您的 Student类中重复定义了无参构造函数,导致编译错误。


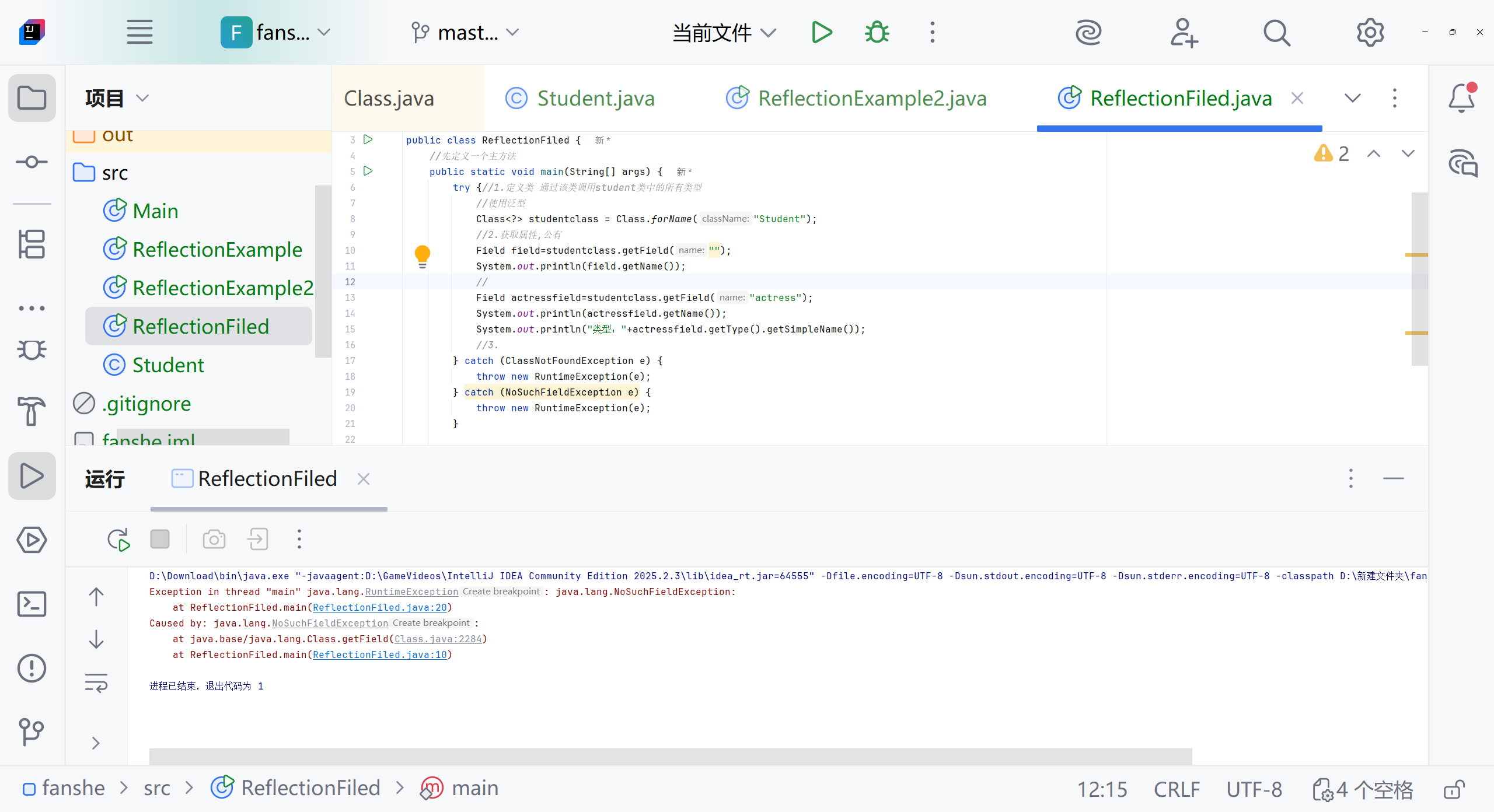
// studentclass 代表的是"学生类"的概念(蓝图)
Class<?> studentclass = Class.forName("Student");// studentInstance 代表的是"具体的学生对象"(根据蓝图建造的房子)
Object studentInstance = studentclass.getConstructor().newInstance();
// 类比:一个班级(Class)有多个学生(Object实例)
Class<?> studentClass = Class.forName("Student"); // 班级定义Object student1 = studentClass.newInstance(); // 学生1
Object student2 = studentClass.newInstance(); // 学生2// 两个学生有各自的名字
actressfield.set(student1, "张三");
actressfield.set(student2, "李四");

使用反射
在一个类中,可以创建另外一个类的对象,调用其的属性和方法,无论那个类是否被创建了。
如何理解:无论那个类是否被创建了
这句话的意思是:使用反射,你可以在运行时动态地操作一个类,而不需要事先在代码中显式地引用或创建这个类。
// 反射方式:运行时才决定要操作哪个类
// 不需要import,编译时不需要知道Student类的存在
Class<?> studentClass = Class.forName("Student"); // 运行时动态加载
Object student = studentClass.newInstance();
Method getNameMethod = studentClass.getMethod("getName");
Object result = getNameMethod.invoke(student);
类在编译时不存
// 你可以写这样的代码,即使编译时Student类还不存在
String className = "Student"; // 类名可以是动态的,从配置文件读取
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className); // 运行时才检查类是否存在
情况2:类在代码中没有直接引用
java
// 主程序完全不知道Student类的存在
// 但可以通过反射动态创建和调用
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {// 从配置文件读取要操作的类名和方法名String className = loadFromConfig("target.class");String methodName = loadFromConfig("target.method");// 运行时动态操作(编译时不需要知道具体类)Class<?> targetClass = Class.forName(className);Object instance = targetClass.newInstance();Method method = targetClass.getMethod(methodName);method.invoke(instance);}
}
情况3:类的信息在运行时才确定
java
// 框架代码示例:可以在不知道具体类的情况下操作
public void processObject(String className) {// 编译时不知道具体是哪个类Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className); // 运行时确定// 创建实例Object obj = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();// 调用方法(方法名也可以是运行时确定的)Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();for (Method method : methods) {if (method.getName().startsWith("get")) {Object value = method.invoke(obj);System.out.println(method.getName() + ": " + value);}}
}
创建一个类对象
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
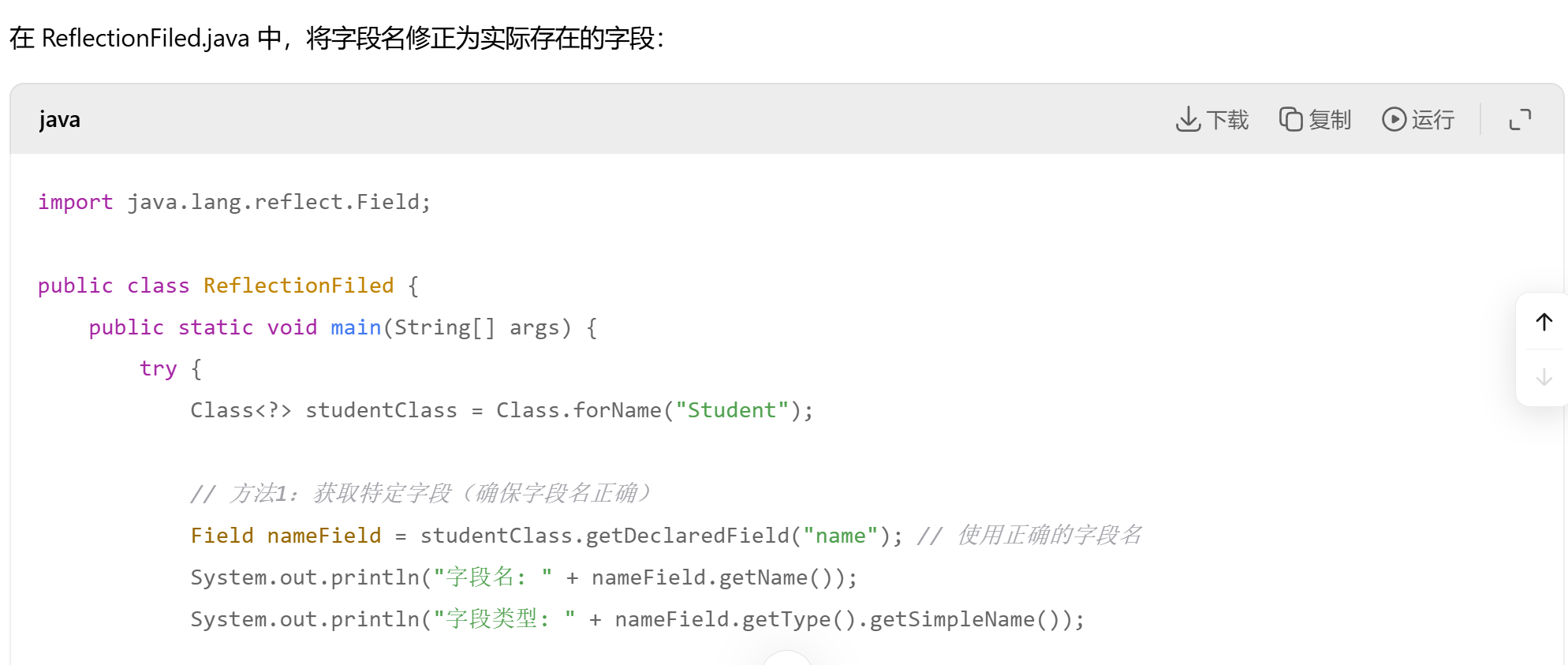
import java.lang.reflect.Method;public class ReflectionExample2 {public static void main(String[] args) {try {//1.定义类Class<?> classstudent = Class.forName("Student");//Class<?> 泛型语法代表一个未知的Class类对象// C.forname 静态方法,用于动态加载类 运行时查找并加载"student"类 如果找到并成功加载,返回student类的class对象 这个对象可以得到类中的所有信息。//classstudent 存储获取到的class类对象 通过classstudent 可以访问类中的所有信息//泛型了解下。异常了解下}catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {System.err.println("找不到student类");} }
}
构造方法
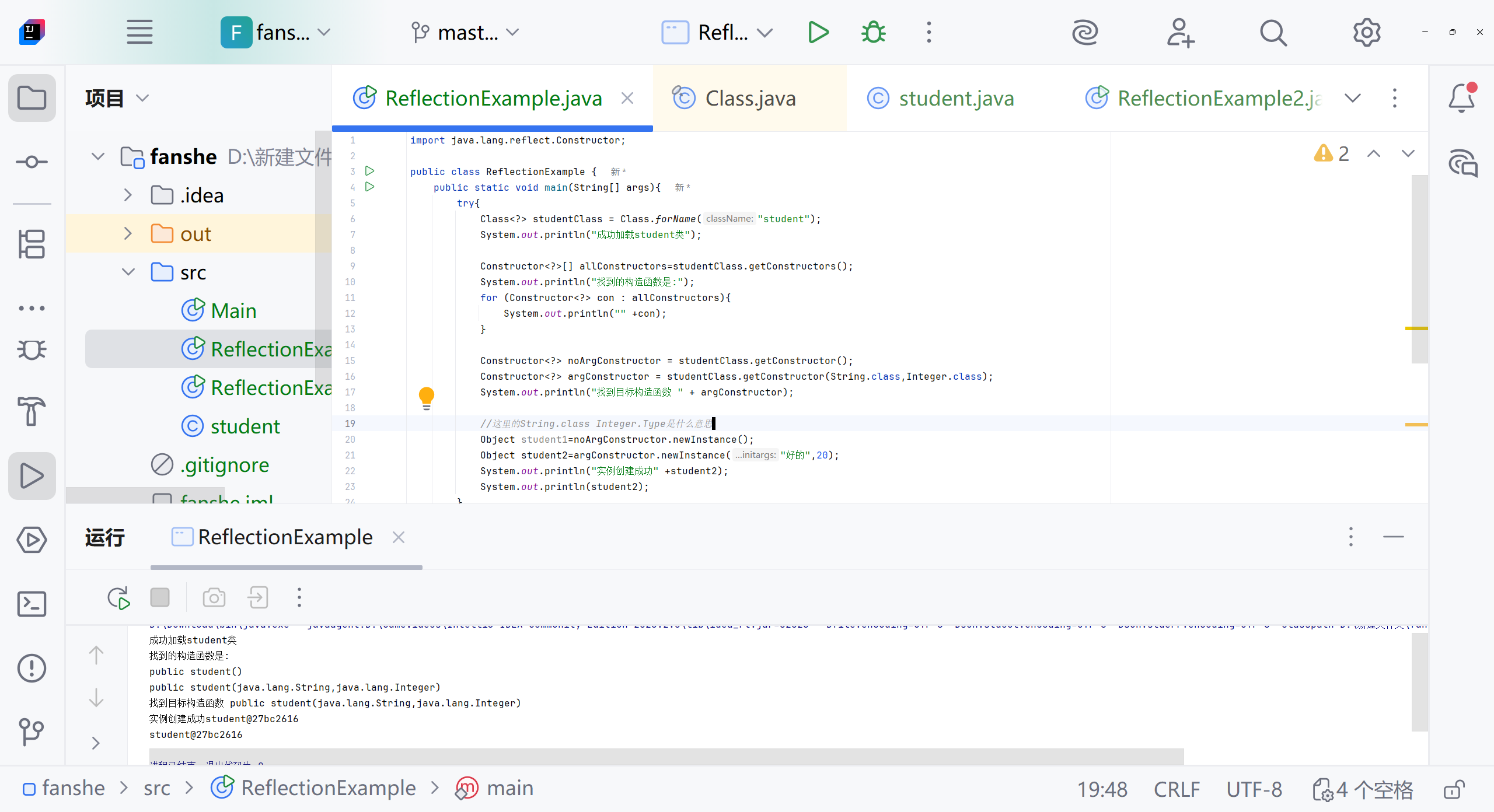
public class ReflectionExample {public static void main(String[] args){try{Class<?> studentClass = Class.forName("Student");System.out.println("成功加载student类");Constructor<?>[] allConstructors=studentClass.getConstructors();System.out.println("找到的构造函数是:");for (Constructor<?> con : allConstructors){System.out.println("" +con);}Constructor<?> noArgConstructor = studentClass.getConstructor();Constructor<?> argConstructor = studentClass.getConstructor(String.class,Integer.class);System.out.println("找到目标构造函数 " + argConstructor);//这里的String.class Integer.Type是什么意思Object student1=noArgConstructor.newInstance();Object student2=argConstructor.newInstance("好的",20);System.out.println("实例创建成功" +student2);System.out.println(student2);}catch (ClassNotFoundException e){System.out.println("类未找到"+e.getMessage());}catch (NoSuchMethodException e){System.out.println("构造函数未找到:"+e.getMessage());}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}
}方法
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
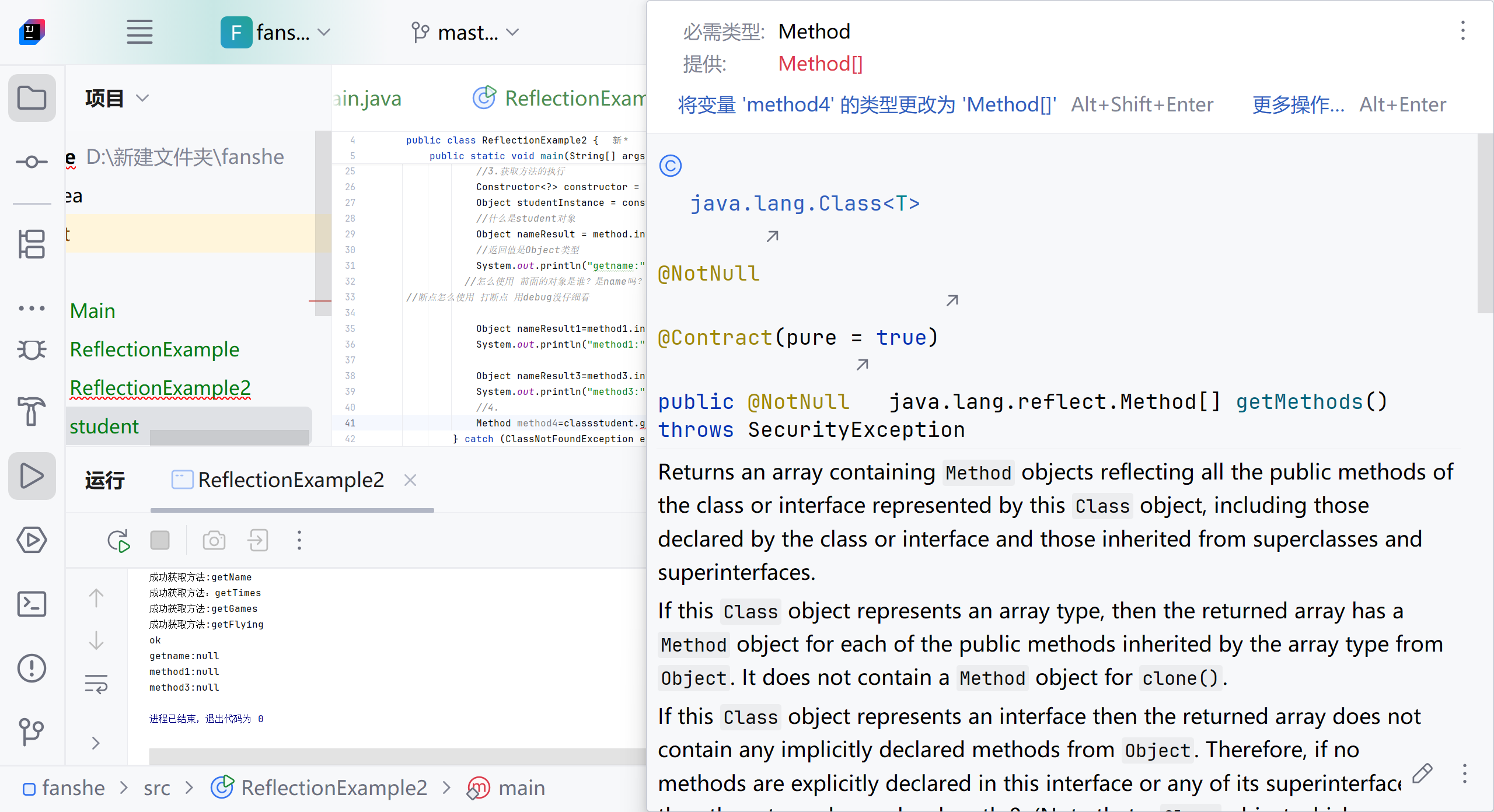
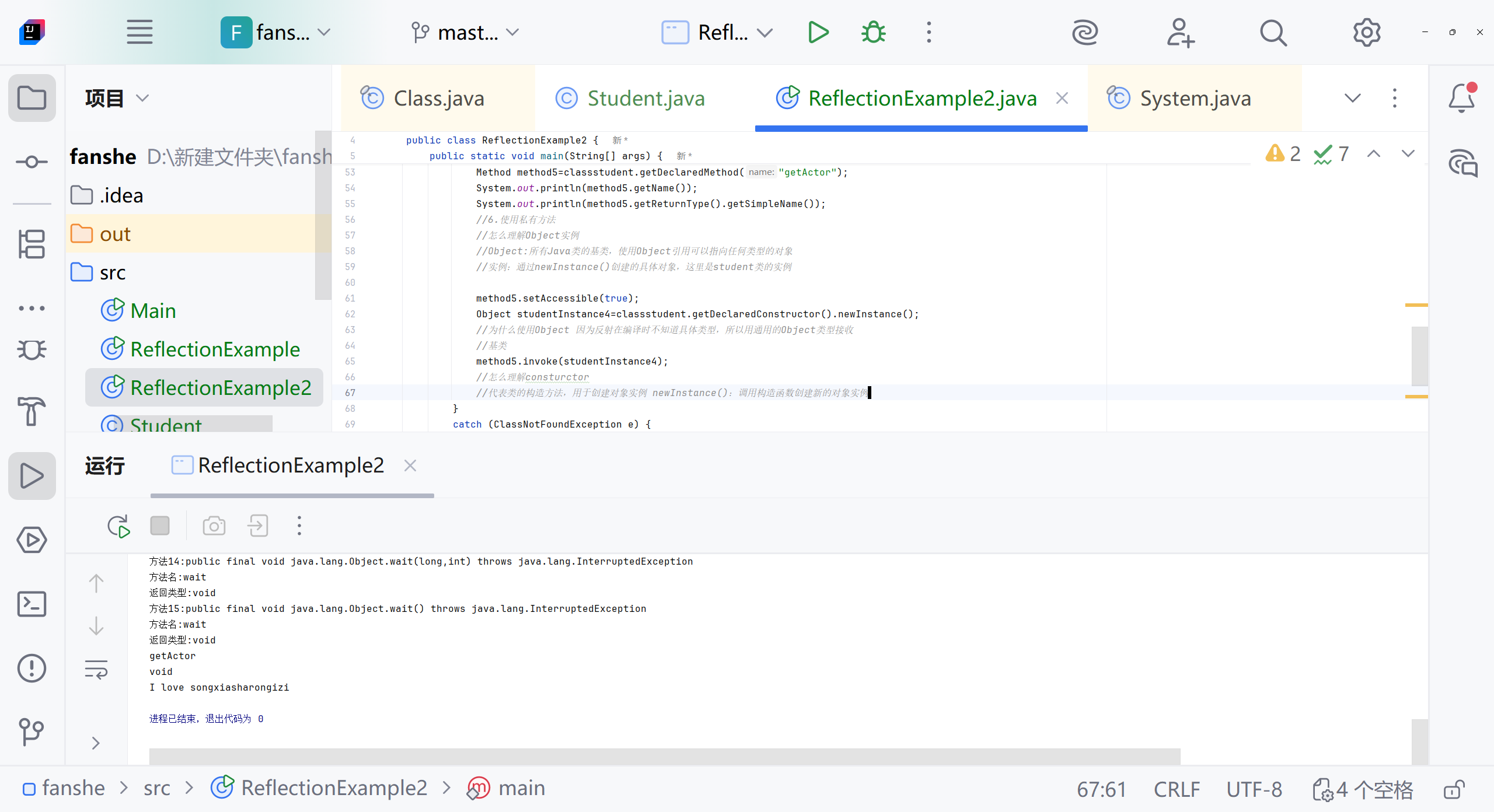
import java.lang.reflect.Method;public class ReflectionExample2 {public static void main(String[] args) {try {//1.定义类Class<?> classstudent = Class.forName("Student");//Class<?> 泛型语法代表一个未知的Class类对象// C.forname 静态方法,用于动态加载类 运行时查找并加载"student"类 如果找到并成功加载,返回student类的class对象 这个对象可以得到类中的所有信息。//classstudent 存储获取到的class类对象 通过classstudent 可以访问类中的所有信息//泛型了解下。异常了解下//2.获取方法Method method = classstudent.getMethod("getName");//得到普通的方法,返回Method,指定方法名//method 是一个方法吗?//为什么必须通过Methon method才能调用getmethod方法//method是Method类的一个对象实例 代表student类中的getName方法 通过Method对象 可以在运行时动态调用实际的方法//getMethod()是class类的方法,用于获取方法的元信息,返回一个Method对象,这个对象封装方法的所有信息System.out.println("成功获取方法:" + method.getName());Method method1 = classstudent.getMethod("getTimes");//得到没有返回值,没有参数的方法System.out.println("成功获取方法:" + method1.getName());Method method2 = classstudent.getMethod("getGames", String.class);//得到没有返回值,有参数的的方法System.out.println("成功获取方法:" + method2.getName());Method method3=classstudent.getMethod("getFlying");System.out.println("成功获取方法:"+method3.getName());//3.获取方法的执行Constructor<?> constructor = classstudent.getDeclaredConstructor();//获取类的无参构造函数 constructor代表student类的构造函数Object studentInstance = constructor.newInstance();//使用构造函数创建student类的实例 newInstance方法调用构造函数创建对象 返回一个Object类的实例 实际上是student对象//什么是student对象Object nameResult = method.invoke(studentInstance);//在studentInstance对象上调用getname方法//返回值是Object类型System.out.println("getname:" + nameResult);//怎么使用 前面的对象是谁?是name吗?
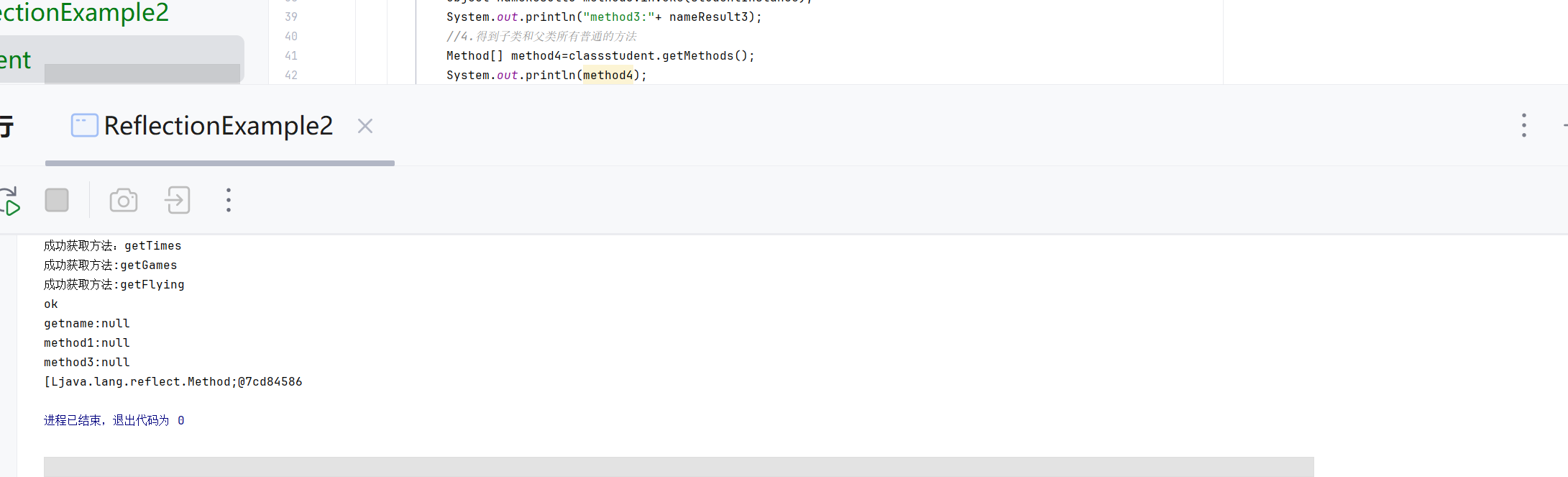
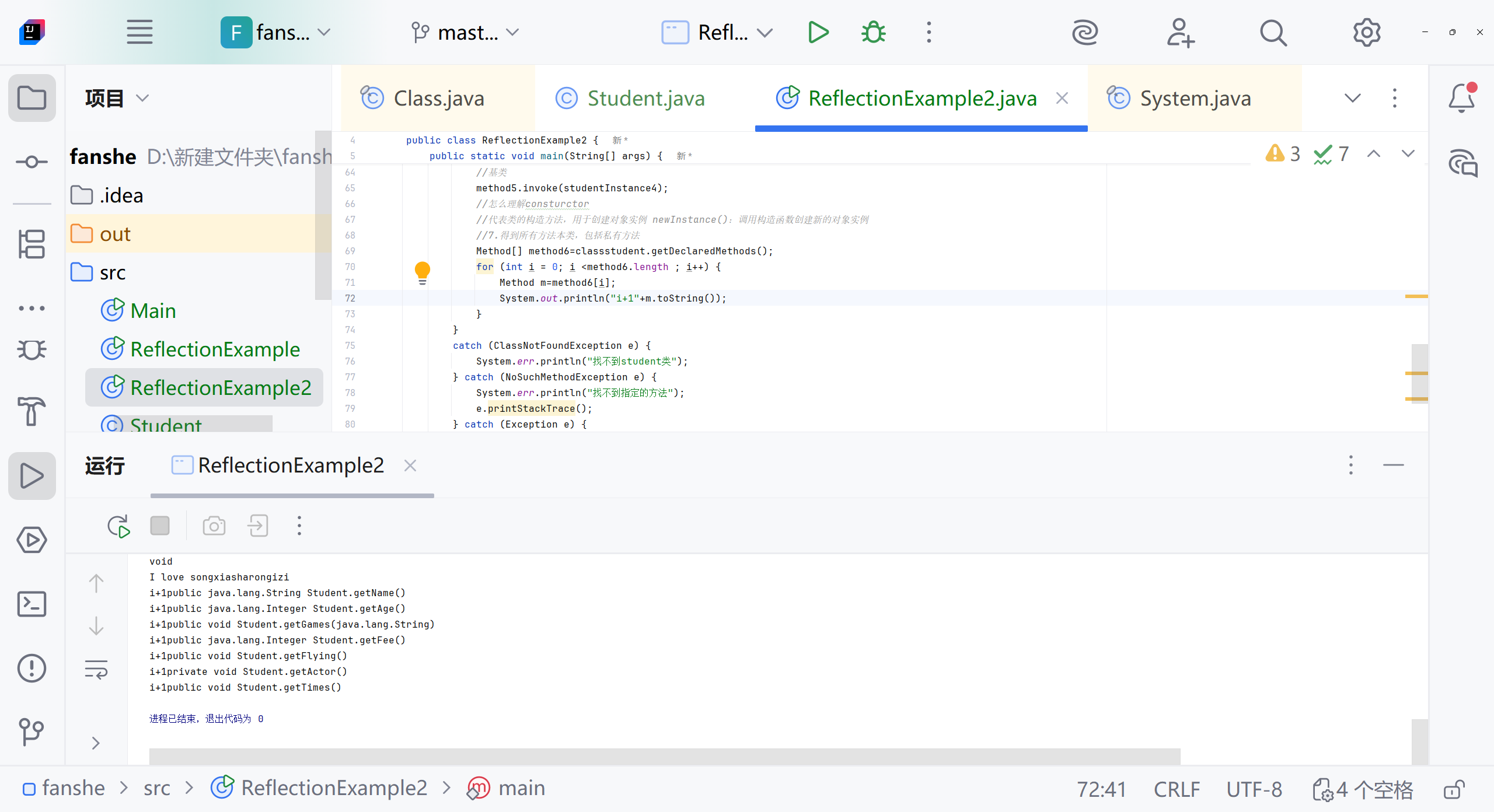
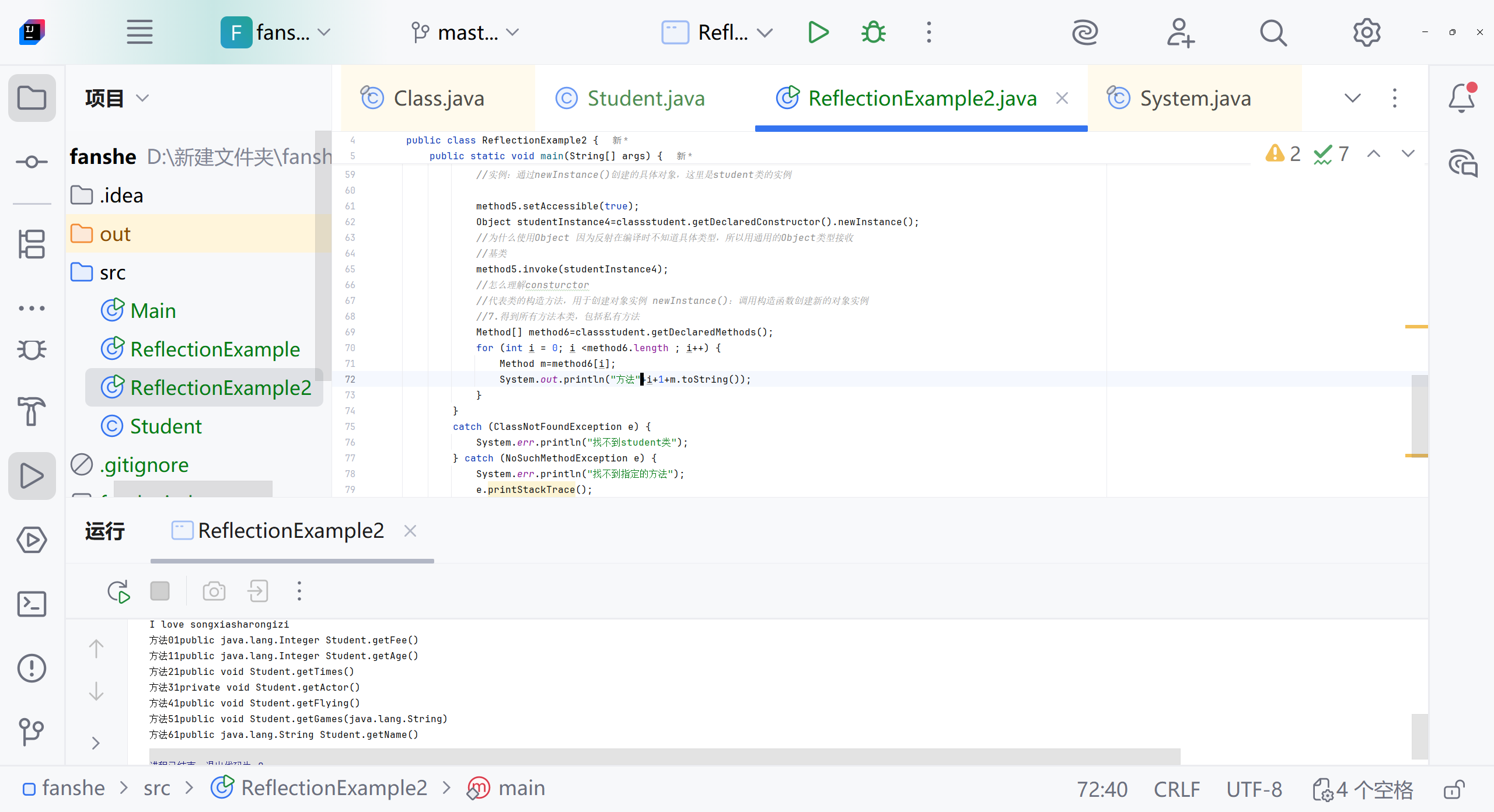
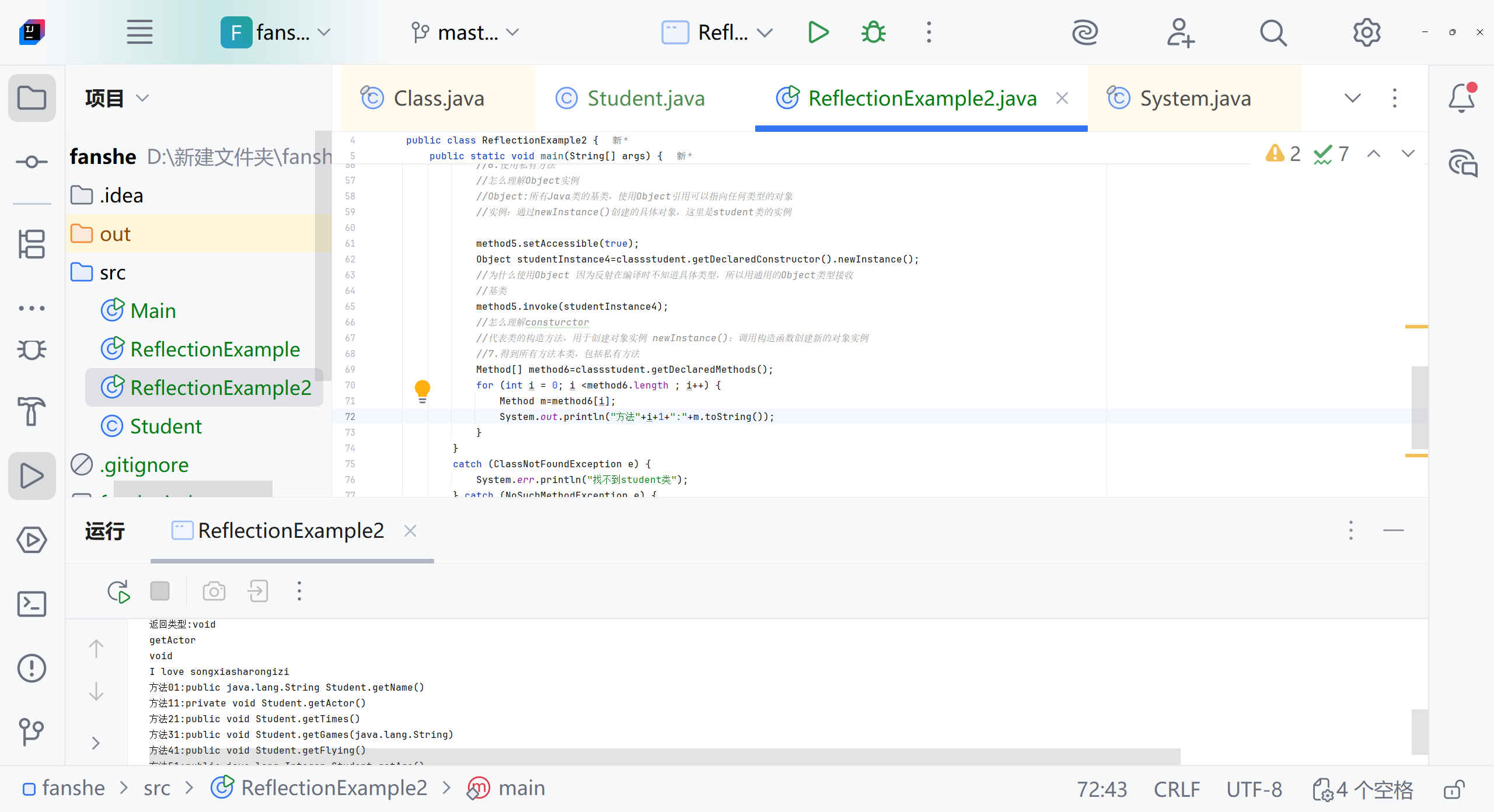
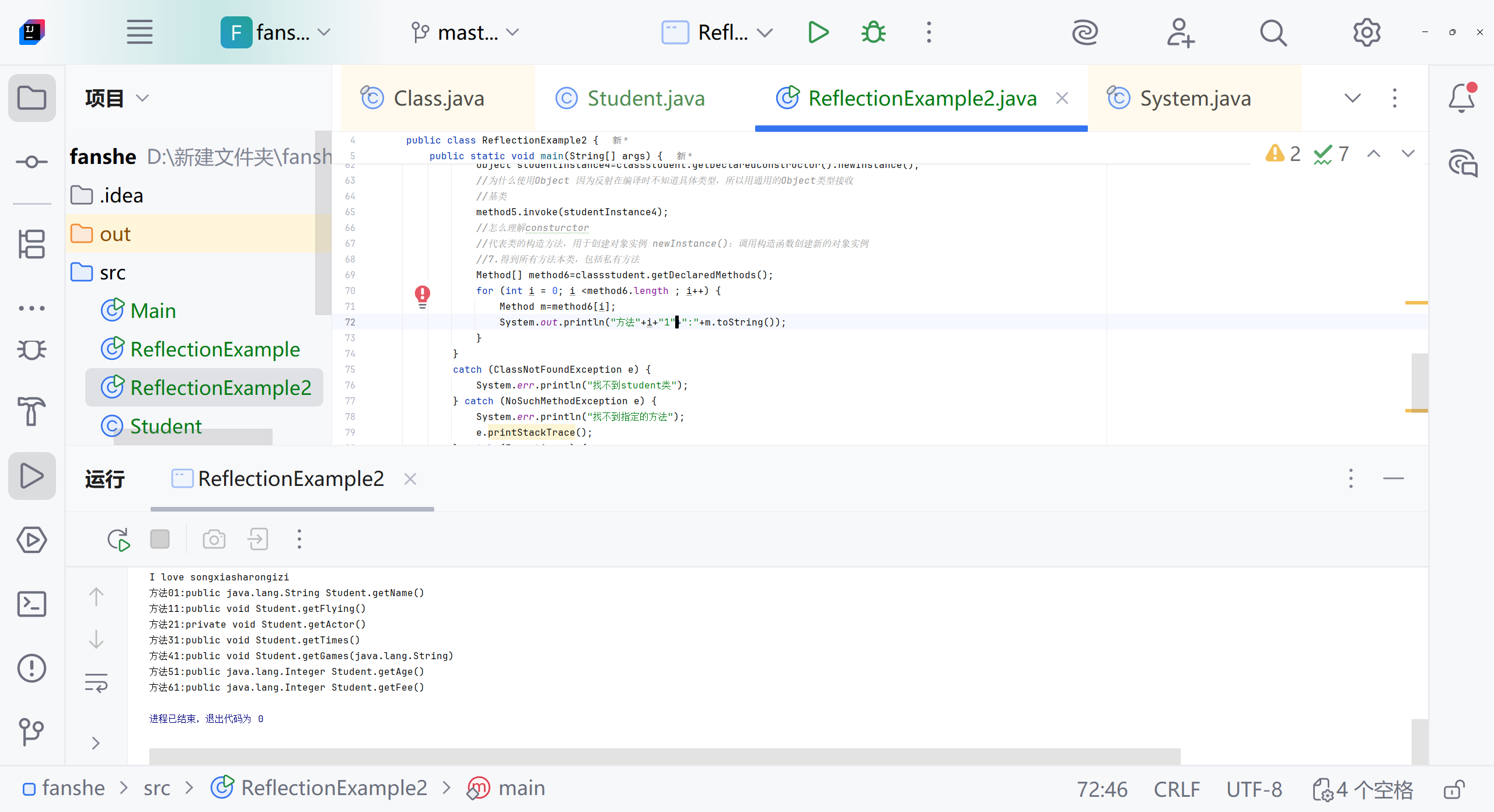
//断点怎么使用 打断点 用debug没仔细看Object nameResult1=method1.invoke(studentInstance);System.out.println("method1:"+ nameResult1);Object nameResult3=method3.invoke(studentInstance);System.out.println("method3:"+ nameResult3);//4.得到子类和父类所有普通的方法 包括继承的方法Method[] method4=classstudent.getMethods();System.out.println(method4);for (int i=0;i<method4.length;i++) {Method m=method4[i];System.out.println("方法"+(i+1)+":"+m.toString());//怎么理解i+1 m.toString//因为遍历从0开始 方法从1开始计算//toString是Method类的方法 包括返回方法的完整签名,包括:修饰符、返回类型、方法名、参数类型System.out.println("方法名:"+m.getName());System.out.println("返回类型:"+m.getReturnType().getSimpleName());}//5.得到私有的方法Method method5=classstudent.getDeclaredMethod("getActor");System.out.println(method5.getName());System.out.println(method5.getReturnType().getSimpleName());//6.使用私有方法//怎么理解Object实例//Object:所有Java类的基类,使用Object引用可以指向任何类型的对象//实例:通过newInstance()创建的具体对象,这里是student类的实例method5.setAccessible(true);Object studentInstance4=classstudent.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();//为什么使用Object 因为反射在编译时不知道具体类型,所以用通用的Object类型接收//基类method5.invoke(studentInstance4);//怎么理解consturctor//代表类的构造方法,用于创建对象实例 newInstance():调用构造函数创建新的对象实例//7.得到所有方法本类,包括私有方法Method[] method6=classstudent.getDeclaredMethods();for (int i = 0; i <method6.length ; i++) {Method m=method6[i];System.out.println("方法"+(i+1)+":"+m.toString());System.out.println("方法名:"+m.getName());System.out.println("返回类型是:"+m.getReturnType().getSimpleName());}//studentinstance是一个实例,字段值属于对象实例 修正 字段值存储在对象实例中//studentclass是class对象,每个类只有一个}catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {System.err.println("找不到student类");} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {System.err.println("找不到指定的方法");e.printStackTrace();} catch (Exception e) {System.err.println("发生其他错误");}}
}属性
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;public class ReflectionFiled {//先定义一个主方法public static void main(String[] args) {try {//1.定义类 通过该类调用student类中的所有类型//使用泛型Class<?> studentclass = Class.forName("Student");//2.获取属性,公有Field[] field=studentclass.getFields();//怎么会报错,必须指定//修正 getFieldsfor (int i = 0; i < field.length ; i++) {Field e=field[i];System.out.println("属性"+(i+1)+":"+e.getName());System.out.println("类型:"+e.getType().getSimpleName());}//3.获取特定字段的属性//为什么每次都要Field act=studentclass. 是因为存储不同的东西吗?Field actressfield=studentclass.getField("actress");System.out.println(actressfield.getName());System.out.println("类型:"+actressfield.getType().getSimpleName());//4.设置字段值Object studentInstance=studentclass.getConstructor().newInstance();//.set方法怎么进行//获取studentclass的值 返回给studentInstance?//为什么不用Field studentInstance= 为什么要单独定义一个studentInstance 因为要靠他调用吗?为什么不能用studentclass直接调用呢?//不是有actressfile吗?为什么不能直接使用set方法,一定要使用studentInstance这个object?//查阅后解释:studentclass相当于蓝图,不能在图纸上设置 studentInstance相当于根据图纸设计好的房子,字段值actress相当于房子内的物品,只能在实际房子内放物品actressfield.set(studentInstance,"dasd");//5.获取字段值Object value=actressfield.get(studentInstance);System.out.println("设置后的值:"+value);//6.获取所有属性[]studentclass.getDeclaredFields();Field[] declaredFields=studentclass.getDeclaredFields();for (int i = 0; i <declaredFields.length ; i++) {Field field2=declaredFields[i];System.out.println("属性"+(i+1)+":"+field2.getName()+"[类型:"+field2.getType().getSimpleName()+",修饰符:" +java.lang.reflect.Modifier.toString(field2.getModifiers())+ "]");}//怎么理解// System.out.println(studentclass.getDeclaredFields());//7.获取所有属性,修正:获取属性 指定属性名// System.out.println(studentclass.getDeclaredField("fee"));Object value1=studentclass.getDeclaredField("fee");System.out.println(value1);//8.获取特定私有属性并操作Field feeField=studentclass.getDeclaredField("fee");feeField.setAccessible(true);feeField.set(studentInstance,200);studentclass.getDeclaredField("fee");Object value2=studentclass.getDeclaredField("fee");System.out.println("fee的值"+value2);Object value3=feeField.get(studentInstance);//feeFiled不是代表fee吗?为什么还要get studentInstanceSystem.out.println("fee的值"+value3);//这句话是什么意思} catch (ClassNotFoundException | InvocationTargetException | InstantiationException | NoSuchFieldException |IllegalAccessException | NoSuchMethodException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}//怎么理解反射的优点 缺点
需要关注基类 泛型 异常

