第四天学习总结:C++ 文件系统 × Linux 自动化 × Makefile 工程化
一、学习目标概览
| 阶段 | 模块 | 目标 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 现代 C++ 文件系统操作 | 学会用 <filesystem> 遍历、判断、操作文件 |
| 2 | 文件流读写 | 掌握 ifstream / ofstream / getline 读取与写入文件 |
| 3 | Shell 自动化脚本 | 实现自动编译、备份、日志记录的 AutoBuild.sh |
| 4 | Makefile 工程管理 | 用 Makefile 让项目可自动增量编译和清理 |
| 5 | 项目整合 | 把前面所有内容串联成一个「能自己编译」的小型项目 |
二、现代 C++ 文件系统(std::filesystem)
核心概念
std::filesystem 是 C++17 引入的文件系统操作库。
它让你能像用命令行一样,用 C++ 代码操作文件夹、路径、文件。
常用函数与作用
| 函数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
fs::current_path() | 获取当前工作路径 |
fs::directory_iterator(path) | 遍历某个目录中的文件 |
fs::exists(path) | 判断文件是否存在 |
fs::is_directory(path) | 判断是否是文件夹 |
fs::remove(path) | 删除文件 |
fs::file_size(path) | 获取文件大小(字节) |
fs::copy(src, dst) | 拷贝文件 |
实例:文件扫描与行数统计
#include <iostream>
#include <filesystem>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
namespace fs = filesystem;int main() {int totalLines = 0;for (auto const &entry : fs::directory_iterator(".")) {if (entry.path().extension() == ".cpp") {ifstream file(entry.path());string line;int count = 0;while (getline(file, line))++count;cout << entry.path().filename() << " :" << count << " 行" << endl;totalLines += count;}}cout << "总行数:" << totalLines << endl;
}
输出示例:
main.cpp :54 行
fileManger.cpp :76 行
总行数:130
你在这里掌握了:
如何遍历目录;
如何读取文件;
如何统计数据;
如何整合路径信息。
三、文件流操作(ifstream / ofstream)
读取文件(ifstream)
ifstream file("log.txt");
string line;
while (getline(file, line)) {cout << line << endl;
}
功能:一行一行读取文本文件内容。
写入文件(ofstream)
ofstream fout("output.txt");
fout << "Hello File!" << endl;
fout.close();
功能:创建或覆盖文件,写入内容。
关键函数
| 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
getline(stream, str) | 从输入流中读取一整行到 str |
file.is_open() | 判断文件是否成功打开 |
file.close() | 关闭文件流 |
小项目:mini_file_manager
#ifndef FILE_MANGER_H
#define FILE_MANGER_H#include <iostream>
#include <filesystem>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
class FileManger{
public:void listFileDetail();void findStatic(std::string keyword);void copy(std::ifstream &File, std::ofstream &targetFile);void deleteTargetFile(std::string filename);void stat();void exitManger(){exit();};
private:int choose = 0;std::string userPath;std::filesystem::path Path;void exit(){return;}
};#endif
#include "fileManger.h"using namespace std;void FileManger::listFileDetail(){std::cin >> choose;if(choose == 0){std::filesystem::path Path = std::filesystem::current_path();}else {std::cout << "please input your path" << std::endl;std::cin >> userPath;std::filesystem::path Path = userPath;}for (auto const &entry : std::filesystem::directory_iterator(Path)){auto size = std::filesystem::is_regular_file(entry.path()) ?std::filesystem::file_size(entry.path()) : 0;auto time = std::filesystem::last_write_time(entry.path());std::cout << entry.path().filename() << std::endl<< size << std::endl;}
}
void FileManger::findStatic(string keyword){Path = std::filesystem::current_path();for (auto const &entry : std::filesystem::directory_iterator(Path)){if (entry.path().extension() == ".cpp" ||entry.path().extension() == ".h"){ifstream file(entry.path());string line;int lineNumber = 0;while (getline(file, line)){++lineNumber;if(line.find(keyword) != string::npos){cout << entry.path().filename() << ":" << lineNumber << "->" << line << endl;}}}}
}void FileManger::copy(std::ifstream &File, std::ofstream &targetFile){string line;while(getline(File, line)){targetFile << line << endl;}}void FileManger::deleteTargetFile(std::string filename){filesystem::path path = filesystem::current_path();for(auto const &entry : filesystem::recursive_directory_iterator(path)){if (entry.path().filename() == filename){filesystem::remove(filename);}else continue;}
}void FileManger::stat(){int filecount = 0;int fileAllsize = 0;int CppLine;for(auto const &entry : filesystem::recursive_directory_iterator(filesystem::current_path())){++filecount;auto size = filesystem::is_regular_file(entry.path()) ? filesystem::file_size(entry.path()) : 0;fileAllsize += size;if (entry.path().extension() == ".cpp"){string line;ifstream file(entry.path());while(getline(file, line)){++CppLine;}}}
}
#include "fileManger.h"using namespace std;void printMenu() {cout << "\n================= 📂 Mini File Manager =================\n";cout << " 0️⃣ Exit Manager (退出程序)\n";cout << " 1️⃣ List files with detail (列出文件详细信息)\n";cout << " 2️⃣ Delete a file (删除文件)\n";cout << " 3️⃣ Find keyword in files (搜索关键字)\n";cout << " 4️⃣ Show statistics (统计文件信息)\n";cout << " 5️⃣ Copy file (复制文件)\n";cout << "========================================================\n";cout << " Please input function number: ";
}int main() {FileManger myfileManegr;while (true) {printMenu(); // 打印菜单int switchFunc = -1;cin >> switchFunc;cout << "=============\n";switch (switchFunc) {case 0:myfileManegr.exitManger();return 0; // 退出整个程序case 1:myfileManegr.listFileDetail();break;case 2: {string filename;cout << "please input filename\n"; cin >> filename;myfileManegr.deleteTargetFile(filename);break;}case 3: {string keyword;cout << "please input keyword\n"; cin >> keyword;myfileManegr.findStatic(keyword);break;}case 4:myfileManegr.stat();break;case 5: {string file_0;string file_1;cout << "please input which file you want to copy?\n"; cin >> file_0;cout << "please input the new file name you want to use?\n"; cin >> file_1;ifstream inputfile(file_0);ofstream outfile(file_1);myfileManegr.copy(inputfile, outfile);break;}default:cout << "Invalid choice! Please input 0-5.\n";break;}}
}
运行结果:
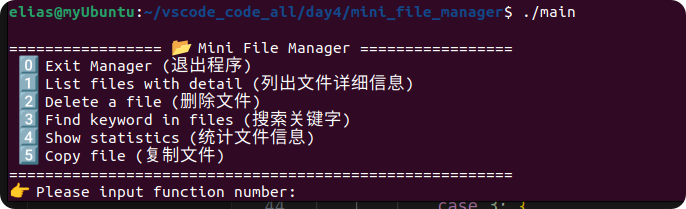
四、Linux 自动化脚本 AutoBuild.sh
目标
让项目能“一键编译 + 自动备份 + 自动运行 + 写日志”。
脚本内容
#!/bin/bashDATE=$(date +"%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
BACKUP_DIR="./backup/$DATE"
LOG_FILE="./build.log"
TARGET="./main"mkdir -p "$BACKUP_DIR"echo "==============================" >> $LOG_FILE
echo "编译开始时间: $DATE" >> $LOG_FILE# 备份旧版本
if [ -f "$TARGET" ]; thencp "$TARGET" "$BACKUP_DIR/"echo "已备份旧版本 -> $BACKUP_DIR/" >> $LOG_FILE
fi# 编译
echo "开始编译..." | tee -a $LOG_FILE
g++ -std=c++17 -Wall *.cpp -o main 2>> $LOG_FILEif [ $? -eq 0 ]; thenecho "编译成功!" | tee -a $LOG_FILE
elseecho "编译失败,请查看 build.log" | tee -a $LOG_FILEexit 1
fi# 运行
echo "运行程序..." | tee -a $LOG_FILE
./main
echo "编译结束时间: $(date +"%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")" >> $LOG_FILE
echo "==============================" >> $LOG_FILE
执行步骤
chmod +x AutoBuild.sh
./AutoBuild.sh
自动生成:
backup/└── 20251102_145800/└── main
build.log
main
学会了:
用脚本自动完成备份、编译、运行、日志记录。
五、Makefile —— C++ 工程化的核心
基本结构
目标: 依赖命令
实用模板
CXX = g++
CXXFLAGS = -std=c++17 -Wall -gSRC = $(wildcard *.cpp)
OBJ = $(SRC:.cpp=.o)
TARGET = main$(TARGET): $(OBJ)$(CXX) $(CXXFLAGS) $(OBJ) -o $(TARGET)%.o: %.cpp$(CXX) $(CXXFLAGS) -c $< -o $@clean:rm -f $(OBJ) $(TARGET).PHONY: clean
编译参数解释
| 参数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
-std=c++17 | 使用 C++17 标准 |
-Wall | 打开所有警告信息 |
-g | 生成调试信息(用于 gdb 调试) |
编译与执行
编译:
make
会自动:
编译
.cpp→.o链接所有
.o→ main清理:
make clean
清除所有 .o 与 main 文件。
增量编译:
只改了 fileManger.cpp → 只重新编译这一部分。
Makefile 优势总结
| 优点 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 自动化 | 一条命令搞定所有编译步骤 |
| 高效率 | 只重新编译改过的文件 |
| 可维护 | 支持多文件、多目录结构 |
| 专业标准 | 几乎所有大型 C++ 项目都用它 |
六、编译选项详解:-Wall -g
| 参数 | 含义 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
-Wall | 打开所有常见警告 | 检查变量未初始化、隐式转换等 |
-g | 向程序中写入调试信息 | 让 gdb 能定位代码行号、变量值 |
示例:
g++ -std=c++17 -Wall -g main.cpp -o main
含义:
用 C++17 编译,显示警告,保留调试符号。
七、今日产出成果
| 模块 | 文件 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| C++ 文件操作 | fileTest.cpp | 遍历、读取、复制、统计文件 |
| Shell 自动化 | AutoBuild.sh | 自动编译 + 日志 + 运行 |
| Makefile | Makefile | 工程自动化构建 |
| 日志系统 | build.log | 记录编译与运行过程 |
| 备份目录 | /backup/日期 | 版本备份 |
