Android Build系列专题【篇五:构建系统主入口文件build/core/makefile】
这里我们主要介绍一下android构建系统的主入口文件build/core/makefile,它承担着整个编译的启动和调度工作。该文件作为构建系统的起点,负责初始化编译环境并包含所有必要的子模块文件。具体功能包括:
- 版本检查:确保使用的 make 版本符合要求(通常需要 3.81 或更高)
- 环境设置:定义 BUILD_SYSTEM 等关键环境变量
- 核心配置:包含 config.mk、definitions.mk 等基础定义文件
- 目标管理:根据 MAKECMDGOALS 和 TARGET_BUILD_VARIANT 设置不同的编译目标
- 模块调度:协调整个构建系统的执行流程
Android构建系统采用模块化设计,位于build/core/目录下,由makefile和多个mk文件组成。makefile作为启动入口,main.mk作为核心流程文件,通过包含关系组织起整个构建框架。由于整个流程过于复杂,这里只记录我跟读过的一些模块。
1、sysprop.mk构建默认属性文件
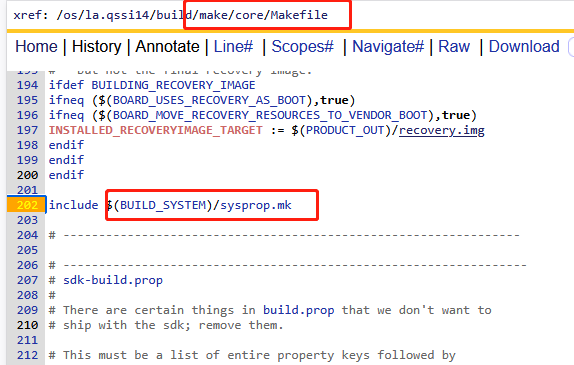
sysprop.mk文件在build/make/core/Makefile文件中直接include包含编译进去。sysprop.mk的主要目的就是为各个分区创建默认的build.prop文件,build.prop文件在init进程中的属性服务线程里面有去读取build.prop文件并把该文件中的键值对加载到内存中。由此系统属性才能被正式使用。
1)build-properties函数
build-properties函数主要目的是用来为各个分区创建build.prop文件,其定义如下:
# la.qssi16/build/core/sysprop.mk
# 函数功能:为各个分区partition创建etc/build.prop文件 Rule for generating <partition>/[etc/]build.prop file
# $(1): 分区名称,通常参数为system/product/vendor/odm
# $(2): 输出路径,通常为product/etc/build.prop
# $(3): 输入属性文件路径,此文件的内容通常为键值对直接输出到$(2)中, path to the input *.prop files. The contents of the files are directly emitted to the output
# $(4): 包含键值对格式属性的变量名列表,这些键值对直接输出到$(2)中, list of variable names each of which contains name=value pairs
# $(5): 可选的要强制移除的属性名列表,可以移除$3和$4的一些键值对,optional list of prop names to force remove from the output. Properties from both $(3) and (4) are affected
# $(6): 可选的要追加到文件末尾的文件列表,optional list of files to append at the end. The content of each file is emitted to the output
# $(7): 可选的跳过公共属性生成的标志,optional flag to skip common properties generation
# 函数名称:build-properties
define build-properties# 流程1:把输出文件安装到系统中,即product/etc/build.prop安装到系统中生效能过被init进程解读
ALL_DEFAULT_INSTALLED_MODULES += $(2)
# 流程2:$4指定的键值对直接输出到product/etc/build.prop文件中
$(eval # Properties can be assigned using `prop ?= value` or `prop = value` syntax.)
$(eval # Eliminate spaces around the ?= and = separators.)
$(foreach name,$(strip $(4)),\$(eval _temp := $$(call collapse-pairs,$$($(name)),?=))\$(eval _resolved_$(name) := $$(call collapse-pairs,$$(_temp),=))\
)
$(eval # Implement the legacy behavior when BUILD_BROKEN_DUP_SYSPROP is on.)
$(eval # Optional assignments are all converted to normal assignments and)
$(eval # when their duplicates the first one wins)
$(if $(filter true,$(BUILD_BROKEN_DUP_SYSPROP)),\$(foreach name,$(strip $(4)),\$(eval _temp := $$(subst ?=,=,$$(_resolved_$(name))))\$(eval _resolved_$(name) := $$(call uniq-pairs-by-first-component,$$(_resolved_$(name)),=))\)\$(eval _option := --allow-dup)\
)
# 流程3:清空或者创建输出文件,即通过touch指令创建product/etc/build.prop文件
$(2): $(POST_PROCESS_PROPS) $(INTERNAL_BUILD_ID_MAKEFILE) $(3) $(6) $(BUILT_KERNEL_VERSION_FILE_FOR_UFFD_GC)$(hide) echo Building $$@$(hide) mkdir -p $$(dir $$@)$(hide) rm -f $$@ && touch $$@
# 流程4:如果$7不是true,调用generate-common-build-props函数,生成通用键值对到product/etc/build.prop文件中
ifneq ($(strip $(7)), true)$(hide) $$(call generate-common-build-props,$(call to-lower,$(strip $(1))),$$@)
endif
# 流程5:遍历所有输入属性文件,添加分隔符和注释并输出到product/etc/build.prop文件中# Make and Soong use different intermediate files to build vendor/build.prop.# Although the sysprop contents are same, the absolute paths of android-info.prop are different.# Print the filename for the intermediate files (files in OUT_DIR).# This helps with validating mk->soong migration of android partitions.$(hide) $(foreach file,$(strip $(3)),\if [ -f "$(file)" ]; then\echo "" >> $$@;\echo "####################################" >> $$@;\$(if $(filter $(OUT_DIR)/%,$(file)), \echo "# from $(notdir $(file))" >> $$@;\,\echo "# from $(file)" >> $$@;\)\echo "####################################" >> $$@;\cat $(file) >> $$@;\fi;)$(hide) $(foreach name,$(strip $(4)),\echo "" >> $$@;\echo "####################################" >> $$@;\echo "# from variable $(name)" >> $$@;\echo "####################################" >> $$@;\$$(foreach line,$$(_resolved_$(name)),\echo "$$(line)" >> $$@;\)\)
# 流程6:追加SDK版本等信息和文件结束符$(hide) $(POST_PROCESS_PROPS) $$(_option) \--sdk-version $(PLATFORM_SDK_VERSION) \--kernel-version-file-for-uffd-gc "$(BUILT_KERNEL_VERSION_FILE_FOR_UFFD_GC)" \$$@ $(5)$(hide) $(foreach file,$(strip $(6)),\if [ -f "$(file)" ]; then\cat $(file) >> $$@;\fi;)$(hide) echo "# end of file" >> $$@
$(call declare-1p-target,$(2))
endef函数功能:为各个分区partition创建etc/build.prop文件
- $(1): 分区名称,通常参数为system/product/vendor/odm
- $(2): 输出路径,通常为product/etc/build.prop
- $(3): 输入属性文件路径,此文件的内容通常为键值对直接输出到$(2)中, path to the input *.prop files. The contents of the files are directly emitted to the output
- $(4): 包含键值对格式属性的变量名列表,这些键值对直接输出到$(2)中, list of variable names each of which contains name=value pairs
- $(5): 可选的要强制移除的属性名列表,可以移除$3和$4的一些键值对,optional list of prop names to force remove from the output. Properties from both $(3) and (4) are affected
- $(6): 可选的要追加到文件末尾的文件列表,optional list of files to append at the end. The content of each file is emitted to the output
- $(7): 可选的跳过公共属性生成的标志,optional flag to skip common properties generation
函数名称:build-properties
- 流程1:把输出文件安装到系统中,即product/etc/build.prop安装到系统中生效能过被init进程解读
- 流程2:$4指定的键值对直接输出到product/etc/build.prop文件中
- 流程3:清空或者创建输出文件,即通过touch指令创建product/etc/build.prop文件
- 流程4:如果$7不是true,调用generate-common-build-props函数,生成通用键值对到product/etc/build.prop文件中
- 流程5:遍历所有输入属性文件,添加分隔符和注释并输出到product/etc/build.prop文件中
- 流程6:追加SDK版本等信息和文件结束符
2)A14如何通过build-properties创建etc/build.prop默认文件?
A system分区
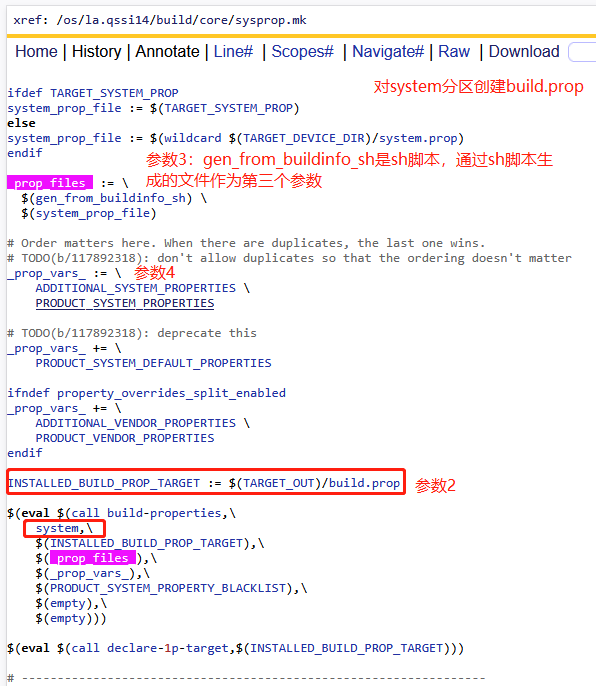
B vendor分区
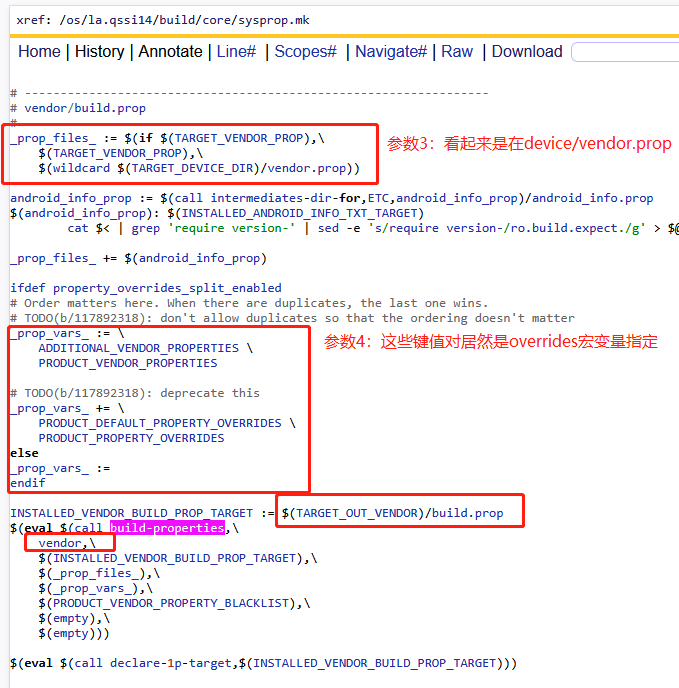
C product分区
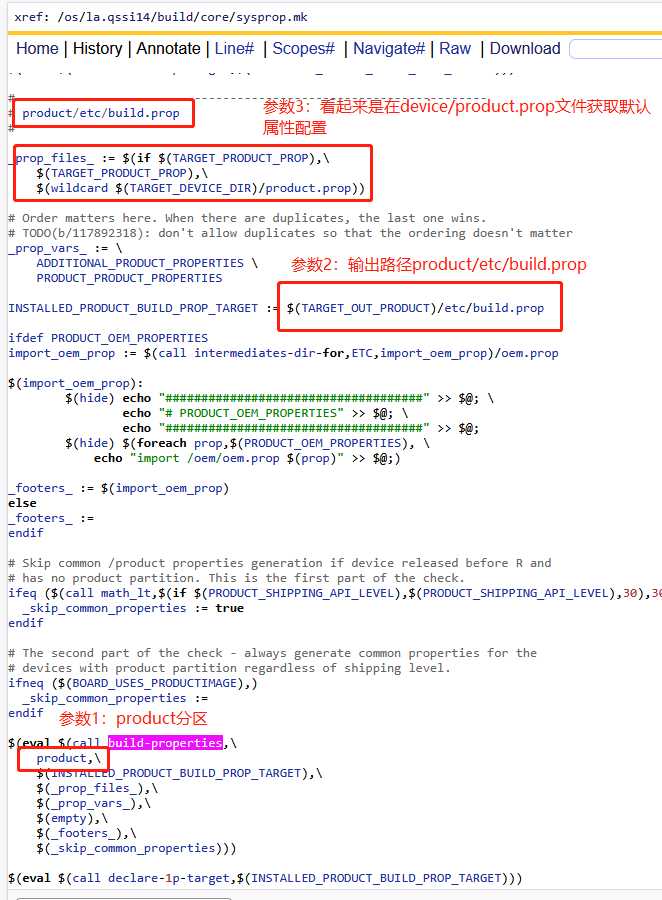
D odm和其他分区
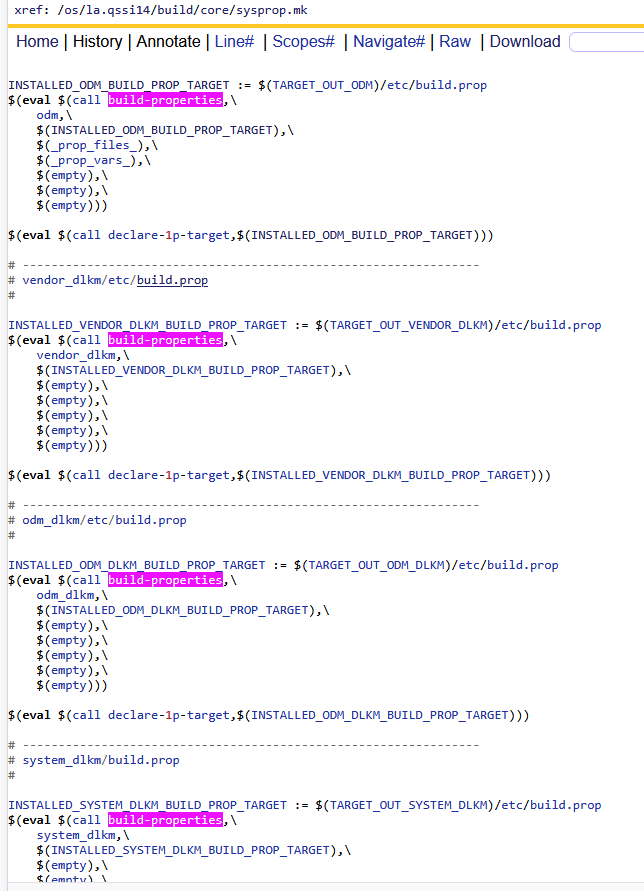
3)A16如何通过build-properties创建etc/build.prop默认文件?
A16对这块内容有所变更,主要是针对system/product/odm等分区的build.prop创建方式有变化,从代码来看vendor分区还是按照之前
A vendor分区
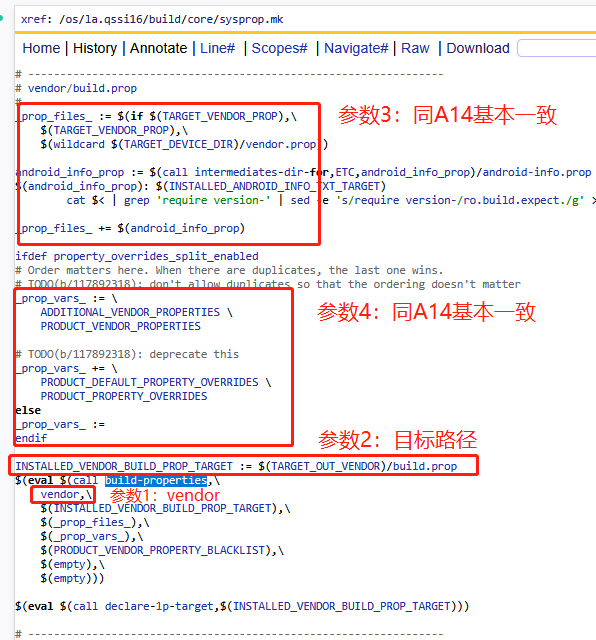
B system & product & odm分区
# la.qssi16/build/core/sysprop.mk
# -----------------------------------------------------------------
# system/build.prop
#
# system/build.prop is built by Soong. See system-build.prop module in
# build/soong/Android.bp.INSTALLED_BUILD_PROP_TARGET := $(TARGET_OUT)/build.prop
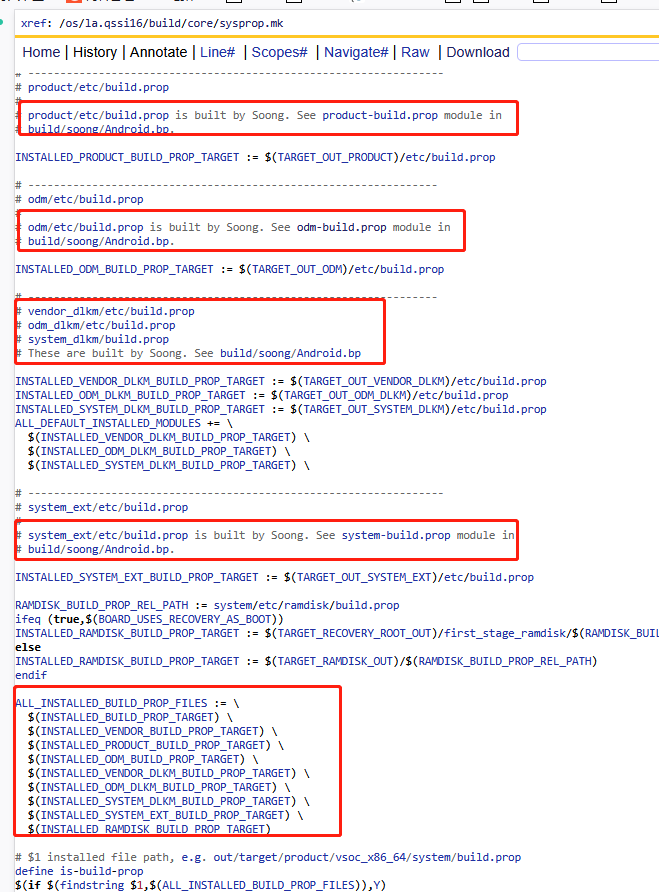
如上system/product/odm分区并没有在mk文件中调用build-properties函数进行创建build.prop文件,而是定义了输出路径,然后备注See system-build.prop module in build/soong/Android.bp.
Android 16 在构建系统上继续强化了 Soong 的作用。10 在您之前分析的 Android 14 中,我们看到了详细的 Makefile 规则来生成 build.prop 文件,但在这里,我们看到的是对 Soong 构建系统的引用,这表明:
Soong 主导:system/build.prop 的生成已从传统的 Makefile 规则迁移到 Soong 构建系统。
模块化定义:具体的生成规则现在定义在 build/soong/Android.bp 文件中的 system-build.prop 模块。
