7.进程控制(三)
一.上集回顾
建议先学上篇博客,再向下学习,上篇博客的链接如下:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_60668256/article/details/154126973?fromshare=blogdetail&sharetype=blogdetail&sharerId=154126973&sharerefer=PC&sharesource=weixin_60668256&sharefrom=from_link
二.实现一个简易的shell
1.框架的实现
我们先将大框架搭出来
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>using namespace std;int main()
{while(true){PrintCommandLine(); //1.命令行提示符GetCommandLine(); //2.获取用户输入ParseCommandLine(); //3.分析命令ExecuteCommand(); //4.执行命令}return 0;
}2.命令行提示符的实现

#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
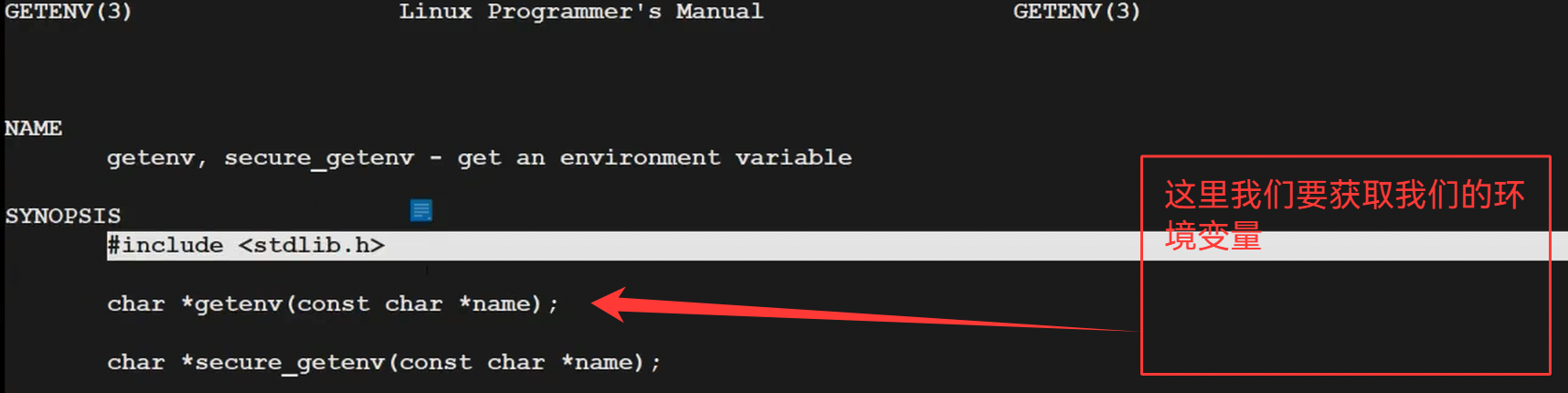
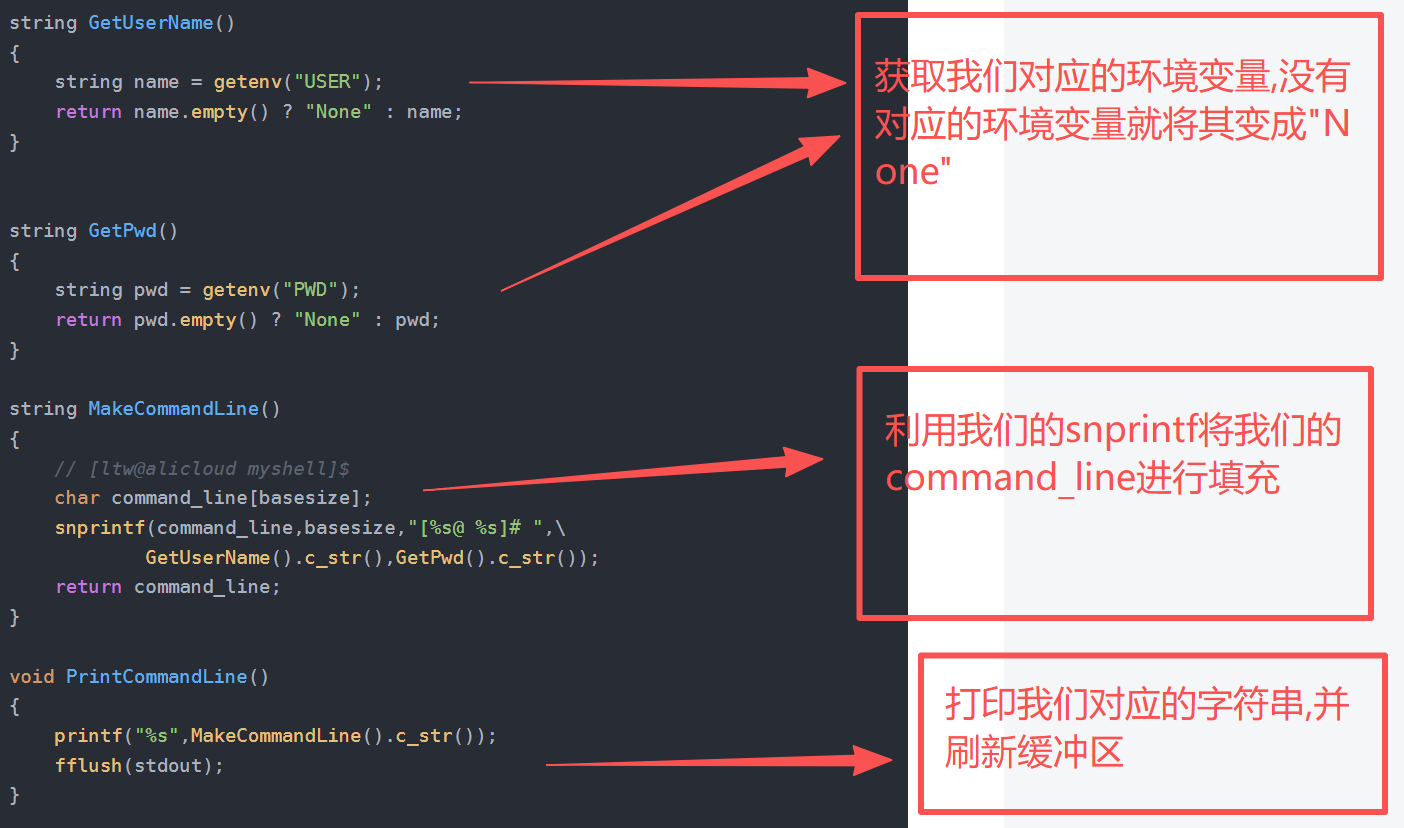
#include <unistd.h>using namespace std;const int basesize = 1024;string GetUserName()
{string name = getenv("USER");return name.empty() ? "None" : name;
}string GetPwd()
{string pwd = getenv("PWD");return pwd.empty() ? "None" : pwd;
}string MakeCommandLine()
{// [ltw@alicloud myshell]$char command_line[basesize];snprintf(command_line,basesize,"[%s@ %s]# ",\GetUserName().c_str(),GetPwd().c_str());return command_line;
}void PrintCommandLine()
{printf("%s",MakeCommandLine().c_str());fflush(stdout);
}int main()
{while(true){PrintCommandLine(); //1.命令行提示符printf("\n");sleep(1);//GetCommandLine(); //2.获取用户输入//ParseCommandLine(); //3.分析命令//ExecuteCommand(); //4.执行命令}return 0;
}
3.获取用户对应输入

#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>using namespace std;const int basesize = 1024;string GetUserName()
{string name = getenv("USER");return name.empty() ? "None" : name;
}string GetPwd()
{string pwd = getenv("PWD");return pwd.empty() ? "None" : pwd;
}string MakeCommandLine()
{// [ltw@alicloud myshell]$char command_line[basesize];snprintf(command_line,basesize,"[%s@ %s]# ",\GetUserName().c_str(),GetPwd().c_str());return command_line;
}void PrintCommandLine()
{printf("%s",MakeCommandLine().c_str());fflush(stdout);
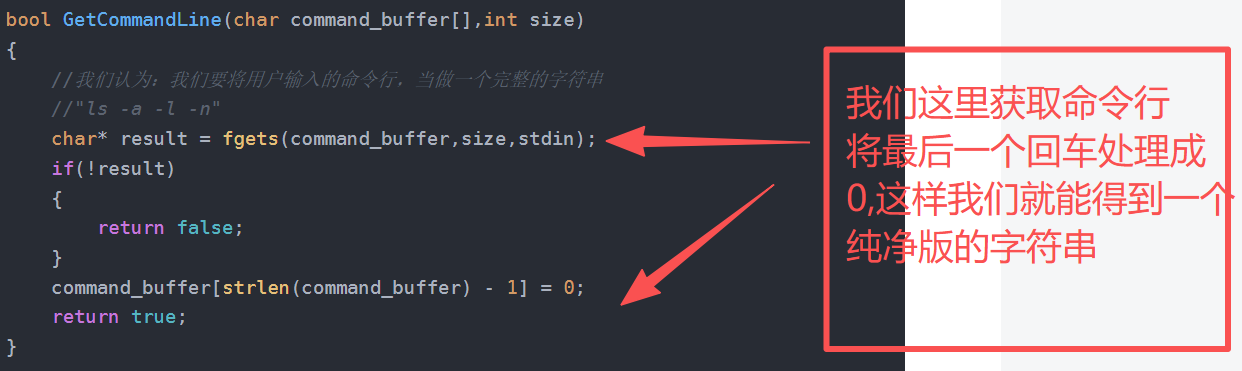
}bool GetCommandLine(char command_buffer[],int size)
{//我们认为:我们要将用户输入的命令行,当做一个完整的字符串//"ls -a -l -n"char* result = fgets(command_buffer,size,stdin);if(!result){return false;}command_buffer[strlen(command_buffer) - 1] = 0;return true;
}int main()
{char command_buffer[basesize];while(true){PrintCommandLine(); //1.命令行提示符if(!GetCommandLine(command_buffer,basesize)) //2.获取用户输入{continue;}printf("%s\n",command_buffer);//ParseCommandLine(); //3.分析命令//ExecuteCommand(); //4.执行命令}return 0;
}
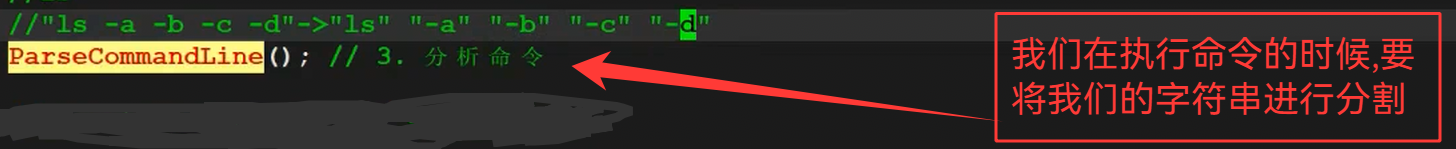
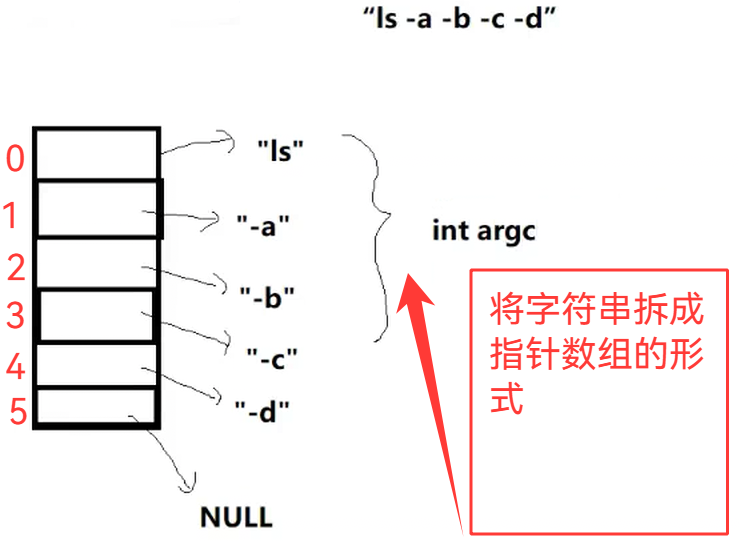
4.分析命令


#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>using namespace std;const int basesize = 1024;
const int argvnum = 64;
char* gargv[argvnum];
int gargc = 0;string GetUserName()
{string name = getenv("USER");return name.empty() ? "None" : name;
}string GetPwd()
{string pwd = getenv("PWD");return pwd.empty() ? "None" : pwd;
}string MakeCommandLine()
{// [ltw@alicloud myshell]$char command_line[basesize];snprintf(command_line,basesize,"[%s@ %s]# ",\GetUserName().c_str(),GetPwd().c_str());return command_line;
}void PrintCommandLine()
{printf("%s",MakeCommandLine().c_str());fflush(stdout);
}bool GetCommandLine(char command_buffer[],int size)
{//我们认为:我们要将用户输入的命令行,当做一个完整的字符串//"ls -a -l -n"char* result = fgets(command_buffer,size,stdin);if(!result){return false;}command_buffer[strlen(command_buffer) - 1] = 0;if(strlen(command_buffer) == 0){return false;}return true;
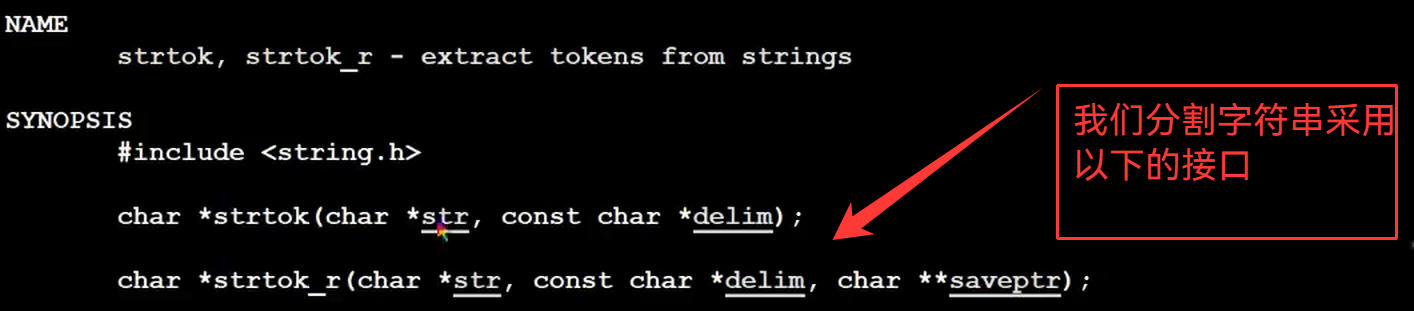
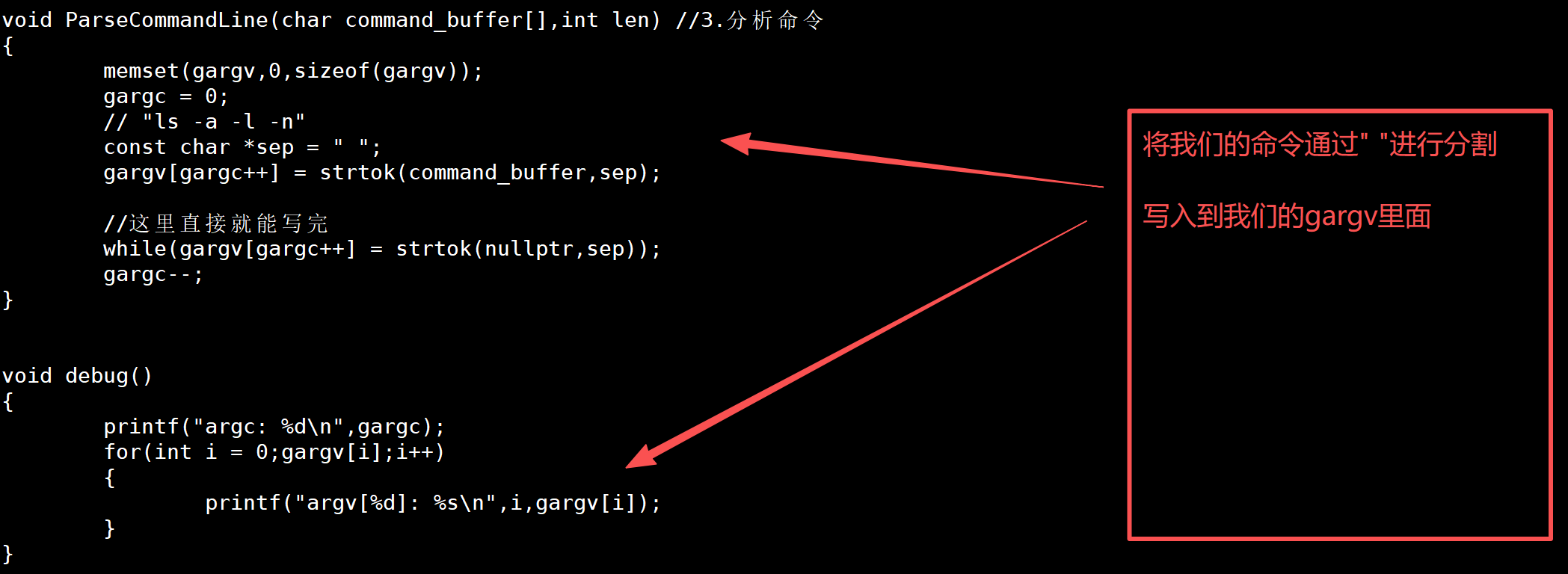
}void ParseCommandLine(char command_buffer[],int len) //3.分析命令
{memset(gargv,0,sizeof(gargv));gargc = 0;// "ls -a -l -n"const char *sep = " ";gargv[gargc++] = strtok(command_buffer,sep);//这里直接就能写完while(gargv[gargc++] = strtok(nullptr,sep));gargc--;
}void debug()
{printf("argc: %d\n",gargc);for(int i = 0;gargv[i];i++){printf("argv[%d]: %s\n",i,gargv[i]);}
}int main()
{char command_buffer[basesize];while(true){PrintCommandLine(); //1.命令行提示符if(!GetCommandLine(command_buffer,basesize)) //2.获取用户输入{continue;}printf("%s\n",command_buffer);ParseCommandLine(command_buffer,strlen(command_buffer)); //3.分debug();//ExecuteCommand(); //4.执行命令}return 0;
}
5.执行命令
我执行命令不能直接拿我们的主进程进行执行,我们要创建子进程来处理我们的任务
exec*的接口我们要选择哪一个呢?
![]()
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>using namespace std;const int basesize = 1024;
const int argvnum = 64;
char* gargv[argvnum];
int gargc = 0;string GetUserName()
{string name = getenv("USER");return name.empty() ? "None" : name;
}string GetPwd()
{string pwd = getenv("PWD");return pwd.empty() ? "None" : pwd;
}string MakeCommandLine()
{// [ltw@alicloud myshell]$char command_line[basesize];snprintf(command_line,basesize,"[%s@ %s]# ",\GetUserName().c_str(),GetPwd().c_str());return command_line;
}void PrintCommandLine()
{printf("%s",MakeCommandLine().c_str());fflush(stdout);
}bool GetCommandLine(char command_buffer[],int size)
{//我们认为:我们要将用户输入的命令行,当做一个完整的字符串//"ls -a -l -n"char* result = fgets(command_buffer,size,stdin);if(!result){return false;}command_buffer[strlen(command_buffer) - 1] = 0;if(strlen(command_buffer) == 0){return false;}return true;
}void ParseCommandLine(char command_buffer[],int len) //3.分析命令
{memset(gargv,0,sizeof(gargv));gargc = 0;// "ls -a -l -n"const char *sep = " ";gargv[gargc++] = strtok(command_buffer,sep);//这里直接就能写完while(gargv[gargc++] = strtok(nullptr,sep));gargc--;
}void debug()
{printf("argc: %d\n",gargc);for(int i = 0;gargv[i];i++){printf("argv[%d]: %s\n",i,gargv[i]);}
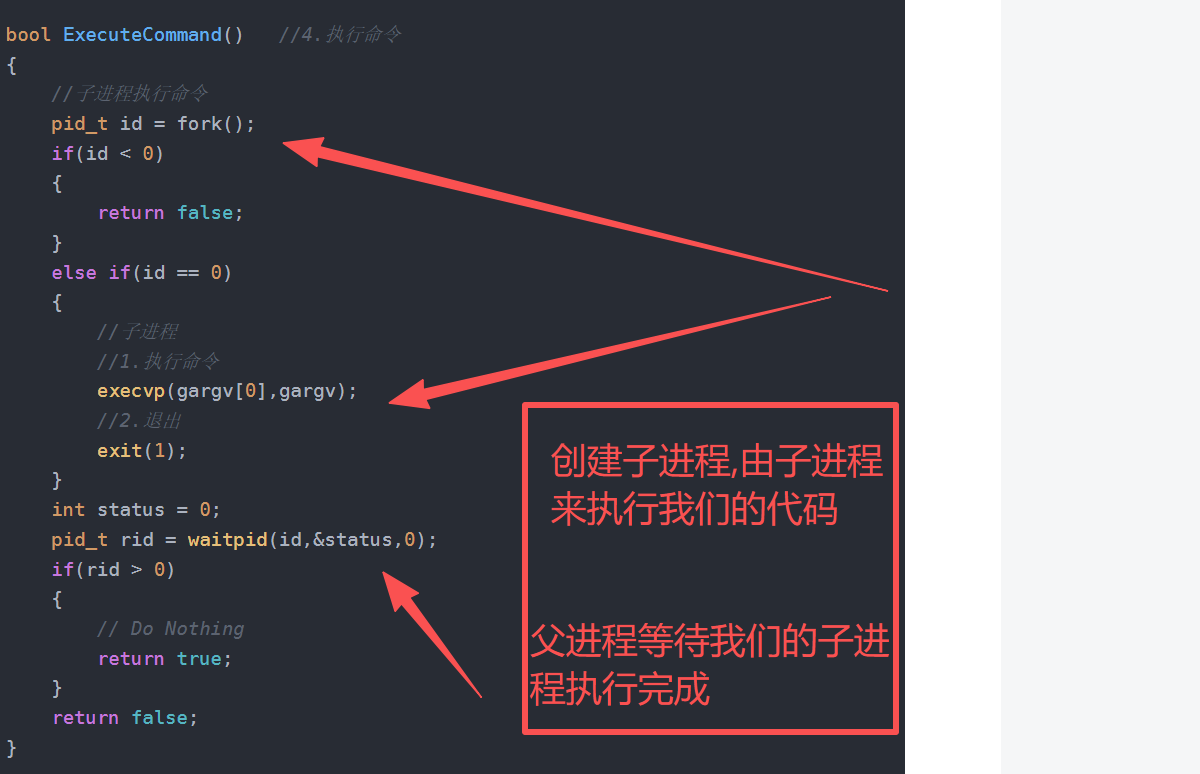
}bool ExecuteCommand() //4.执行命令
{//子进程执行命令pid_t id = fork();if(id < 0){return false;}else if(id == 0){//子进程//1.执行命令execvp(gargv[0],gargv);//2.退出exit(1);}int status = 0;pid_t rid = waitpid(id,&status,0);if(rid > 0){// Do Nothingreturn true;}return false;
}int main()
{char command_buffer[basesize];while(true){PrintCommandLine(); //1.命令行提示符if(!GetCommandLine(command_buffer,basesize)) //2.获取用户输入{continue;}//printf("%s\n",command_buffer);ParseCommandLine(command_buffer,strlen(command_buffer)); //3.分析命令//debug();ExecuteCommand(); //4.执行命令}return 0;
}
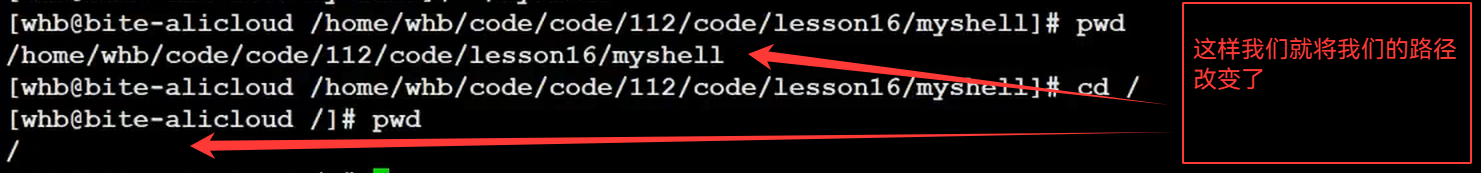
三.myshell修改
1.自己执行内建命令
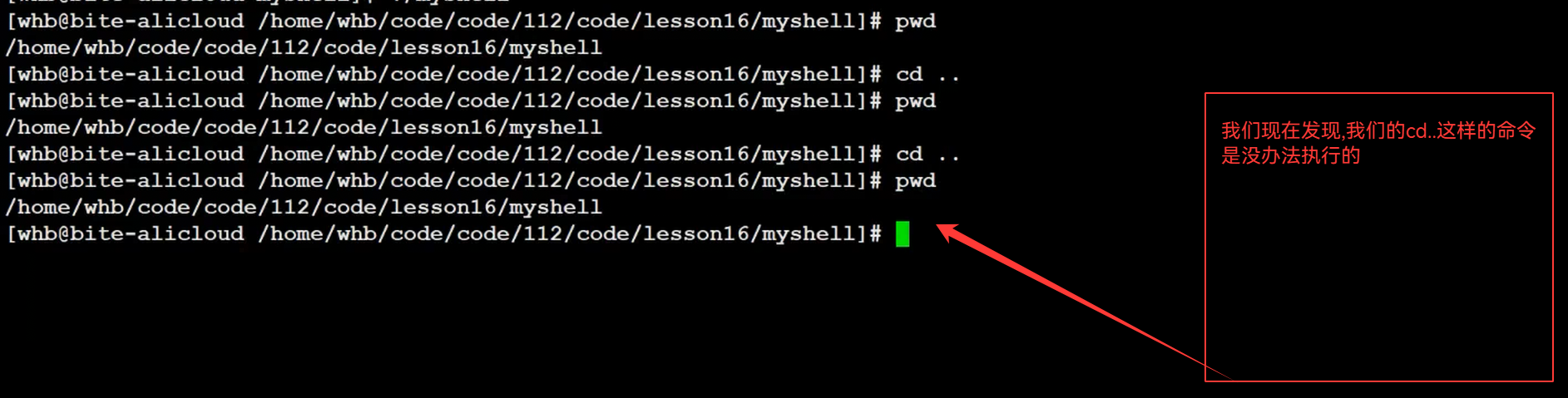

![]()
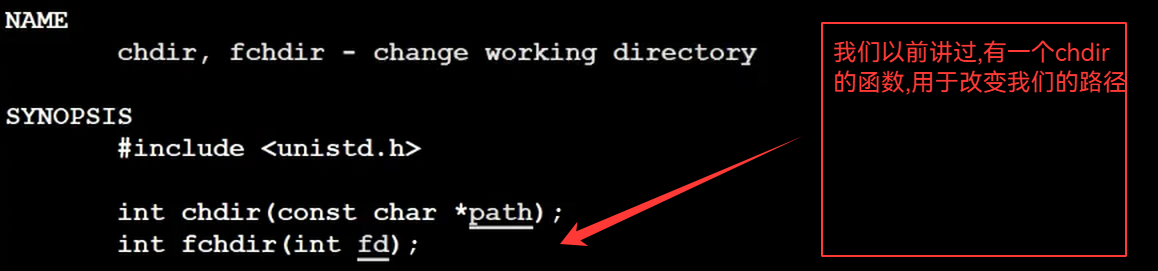
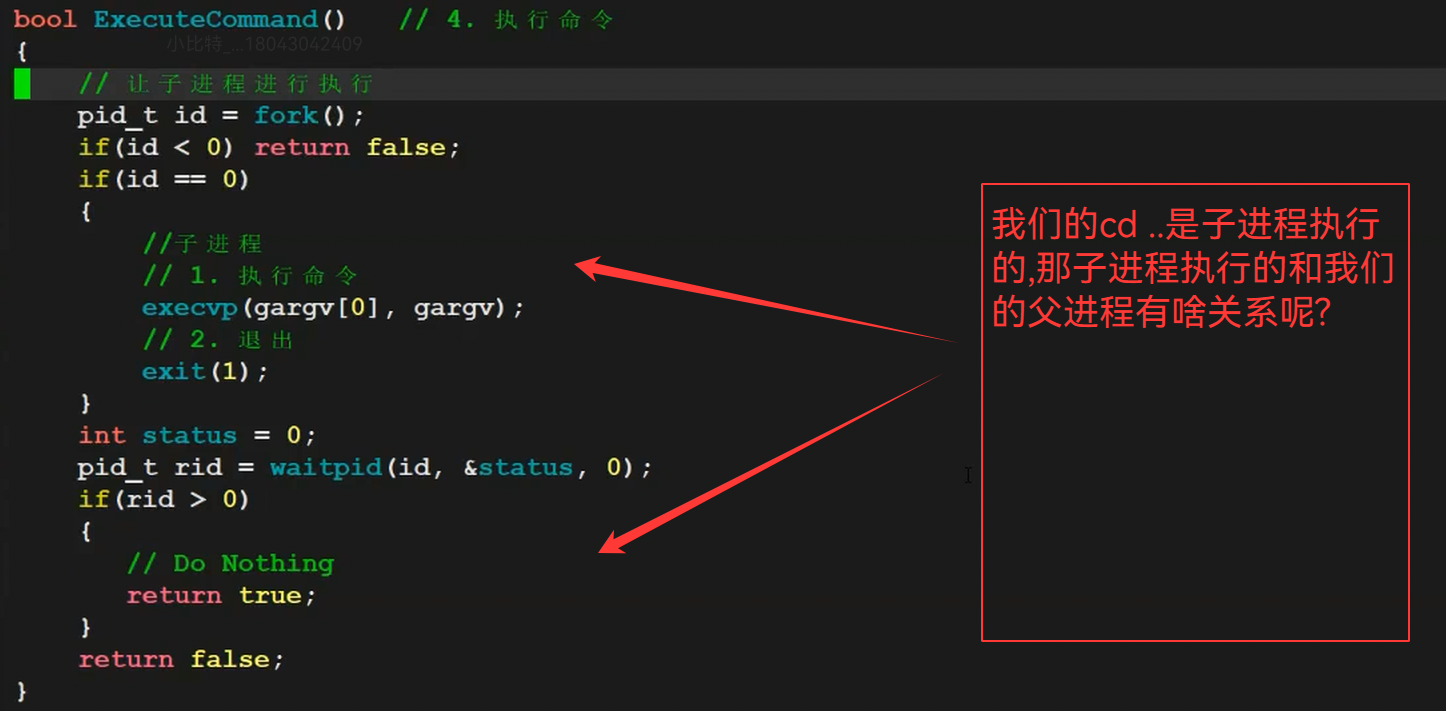
我们的cd ..要父进程自己执行

#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>using namespace std;const int basesize = 1024;
const int argvnum = 64;
char* gargv[argvnum];
int gargc = 0;string GetUserName()
{string name = getenv("USER");return name.empty() ? "None" : name;
}string GetPwd()
{string pwd = getenv("PWD");return pwd.empty() ? "None" : pwd;
}string MakeCommandLine()
{// [ltw@alicloud myshell]$char command_line[basesize];snprintf(command_line,basesize,"[%s@ %s]# ",\GetUserName().c_str(),GetPwd().c_str());return command_line;
}void PrintCommandLine()
{printf("%s",MakeCommandLine().c_str());fflush(stdout);
}bool GetCommandLine(char command_buffer[],int size)
{//我们认为:我们要将用户输入的命令行,当做一个完整的字符串//"ls -a -l -n"char* result = fgets(command_buffer,size,stdin);if(!result){return false;}command_buffer[strlen(command_buffer) - 1] = 0;if(strlen(command_buffer) == 0){return false;}return true;
}void ParseCommandLine(char command_buffer[],int len) //3.分析命令
{memset(gargv,0,sizeof(gargv));gargc = 0;// "ls -a -l -n"const char *sep = " ";gargv[gargc++] = strtok(command_buffer,sep);//这里直接就能写完while(gargv[gargc++] = strtok(nullptr,sep));gargc--;
}void debug()
{printf("argc: %d\n",gargc);for(int i = 0;gargv[i];i++){printf("argv[%d]: %s\n",i,gargv[i]);}
}bool ExecuteCommand() //4.执行命令
{//子进程执行命令pid_t id = fork();if(id < 0){return false;}else if(id == 0){//子进程//1.执行命令execvp(gargv[0],gargv);//2.退出exit(1);}int status = 0;pid_t rid = waitpid(id,&status,0);if(rid > 0){// Do Nothingreturn true;}return false;
}// shell自己执行命令,本质上是shell调用自己的函数
bool CheckAndExecBuiltCommand()
{if(strcmp(gargv[0],"cd") == 0){if(gargc == 2){chdir(gargv[1]);}return true;}return false;
}int main()
{char command_buffer[basesize];while(true){PrintCommandLine(); //1.命令行提示符if(!GetCommandLine(command_buffer,basesize)) //2.获取用户输入{continue;}//printf("%s\n",command_buffer);ParseCommandLine(command_buffer,strlen(command_buffer)); //3.分析命令//debug();if(CheckAndExecBuiltCommand()){continue;}ExecuteCommand(); //4.执行命令}return 0;
}
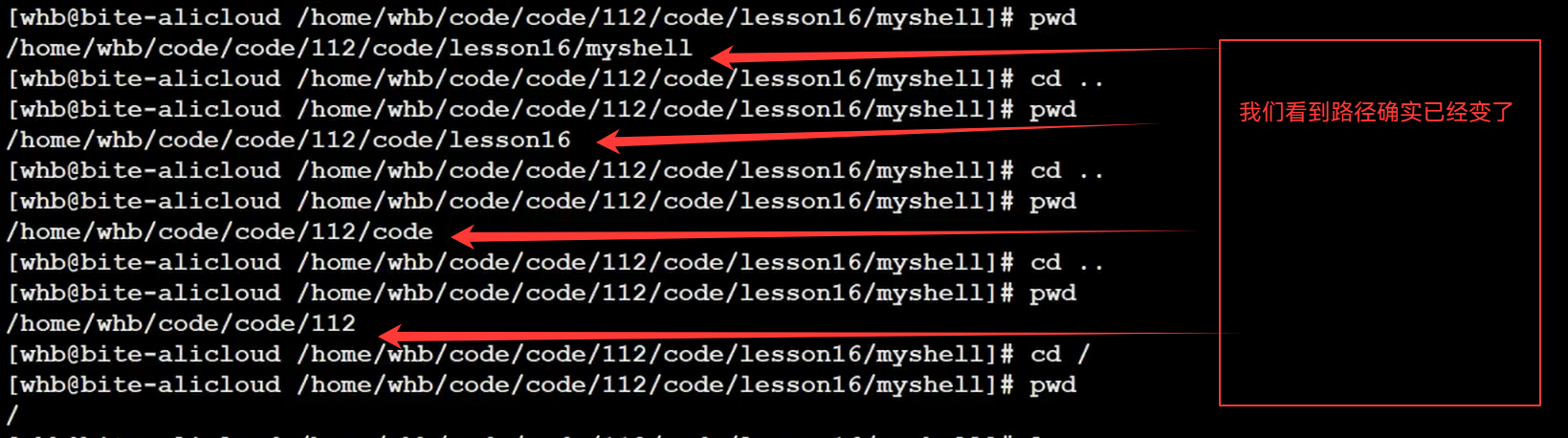
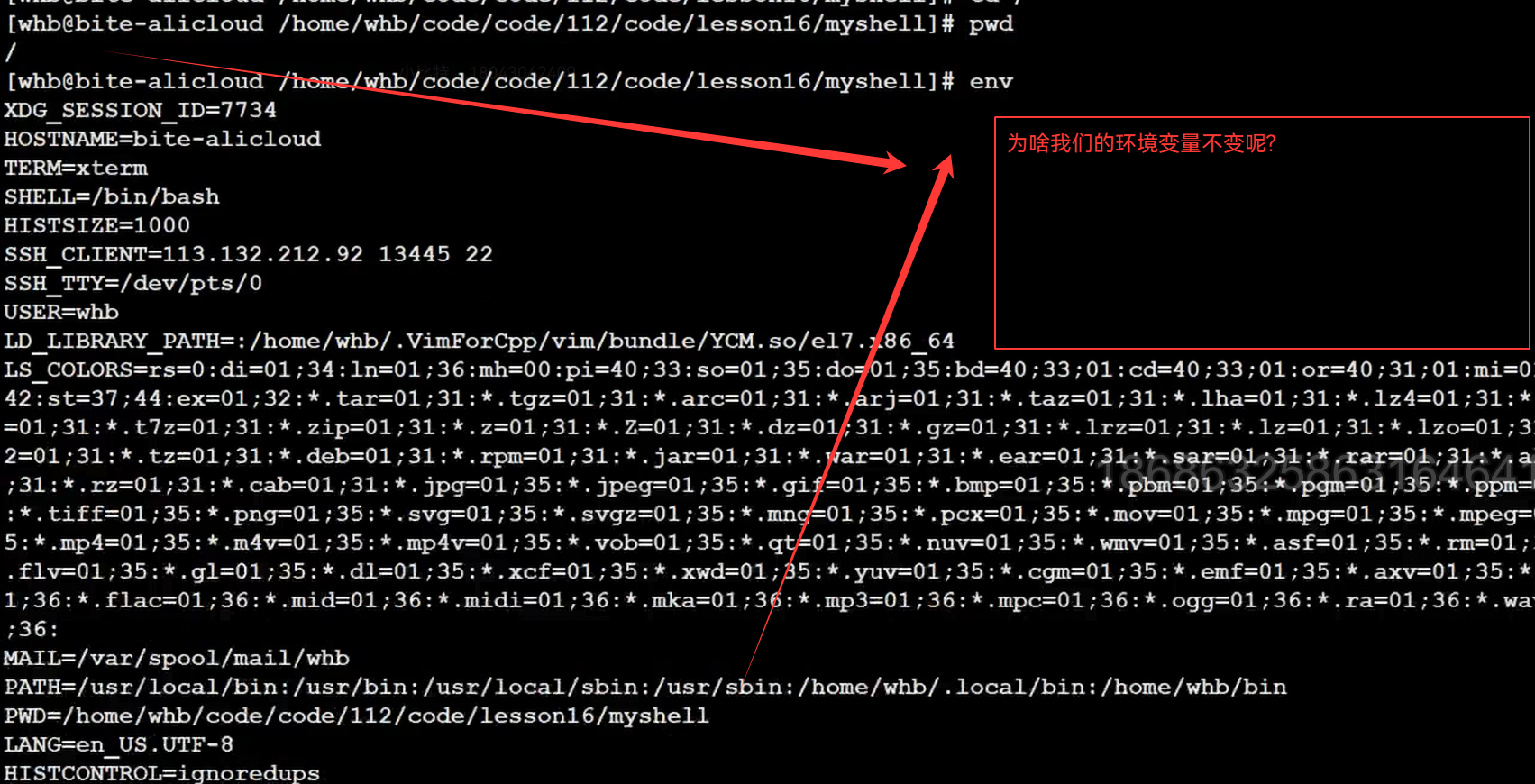
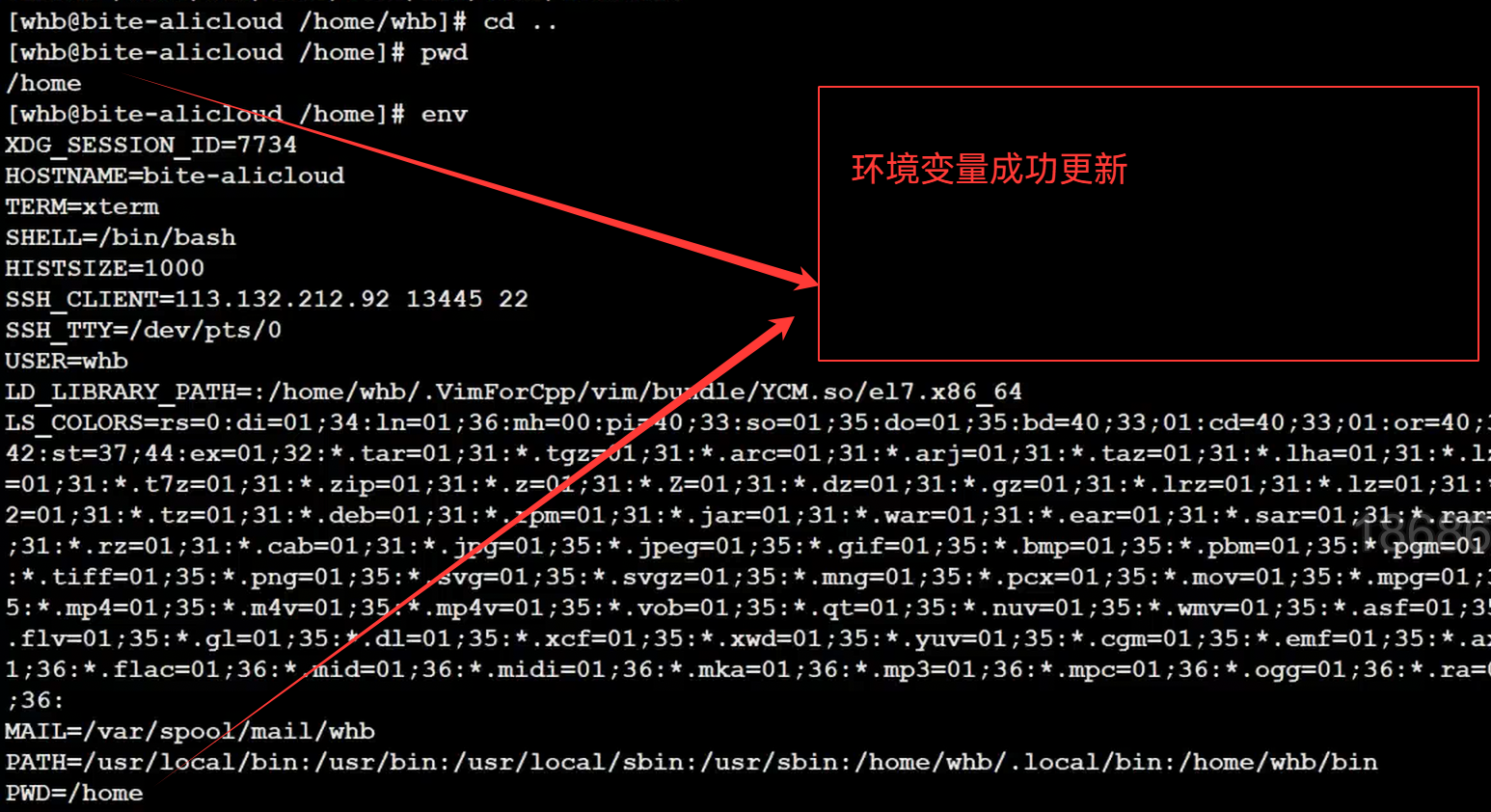
2.从系统中获取我们的PWD
因为我们的路径发生改变,但是环境变量没有变,所以我们要更新环境变量(环境变量是要进行维护的)

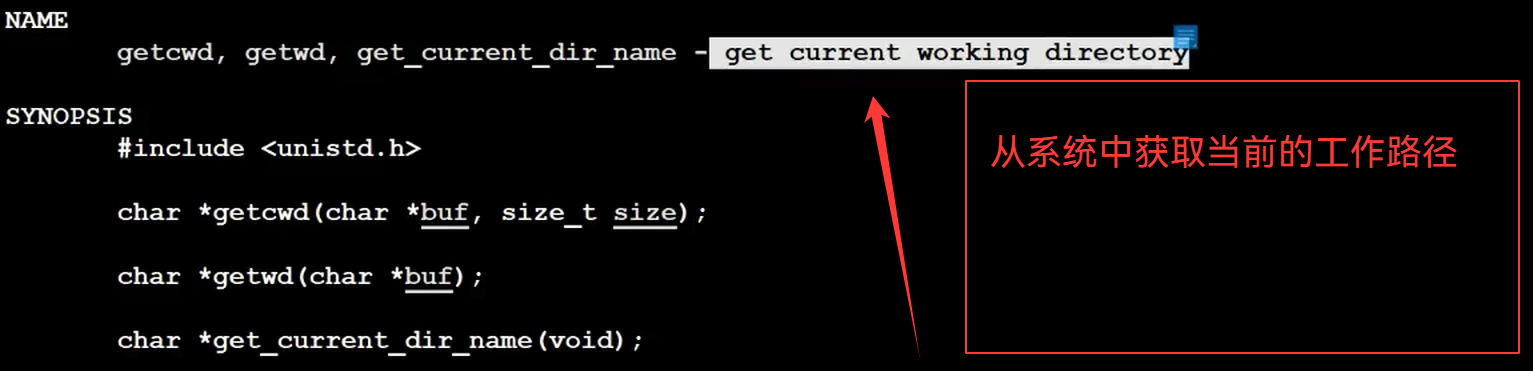
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>using namespace std;const int basesize = 1024;
const int argvnum = 64;//全局的命令行参数表
char* gargv[argvnum];
int gargc = 0;//全局的当前shell工作路径
char pwd[basesize];string GetUserName()
{string name = getenv("USER");return name.empty() ? "None" : name;
}string GetPwd()
{if(nullptr == getcwd(pwd,sizeof(pwd))){return "None";}return pwd;
}string MakeCommandLine()
{// [ltw@alicloud myshell]$char command_line[basesize];snprintf(command_line,basesize,"[%s@ %s]# ",\GetUserName().c_str(),GetPwd().c_str());return command_line;
}void PrintCommandLine()
{printf("%s",MakeCommandLine().c_str());fflush(stdout);
}bool GetCommandLine(char command_buffer[],int size)
{//我们认为:我们要将用户输入的命令行,当做一个完整的字符串//"ls -a -l -n"char* result = fgets(command_buffer,size,stdin);if(!result){return false;}command_buffer[strlen(command_buffer) - 1] = 0;if(strlen(command_buffer) == 0){return false;}return true;
}void ParseCommandLine(char command_buffer[],int len) //3.分析命令
{memset(gargv,0,sizeof(gargv));gargc = 0;// "ls -a -l -n"const char *sep = " ";gargv[gargc++] = strtok(command_buffer,sep);//这里直接就能写完while(gargv[gargc++] = strtok(nullptr,sep));gargc--;
}void debug()
{printf("argc: %d\n",gargc);for(int i = 0;gargv[i];i++){printf("argv[%d]: %s\n",i,gargv[i]);}
}bool ExecuteCommand() //4.执行命令
{//子进程执行命令pid_t id = fork();if(id < 0){return false;}else if(id == 0){//子进程//1.执行命令execvp(gargv[0],gargv);//2.退出exit(1);}int status = 0;pid_t rid = waitpid(id,&status,0);if(rid > 0){// Do Nothingreturn true;}return false;
}// shell自己执行命令,本质上是shell调用自己的函数
bool CheckAndExecBuiltCommand()
{if(strcmp(gargv[0],"cd") == 0){if(gargc == 2){chdir(gargv[1]);}return true;}return false;
}int main()
{char command_buffer[basesize];while(true){PrintCommandLine(); //1.命令行提示符if(!GetCommandLine(command_buffer,basesize)) //2.获取用户输入{continue;}//printf("%s\n",command_buffer);ParseCommandLine(command_buffer,strlen(command_buffer)); //3.分析命令//debug();if(CheckAndExecBuiltCommand()){continue;}ExecuteCommand(); //4.执行命令}return 0;
}
3.更新我们的环境变量
但是我们的环境变量还是没有进行修改

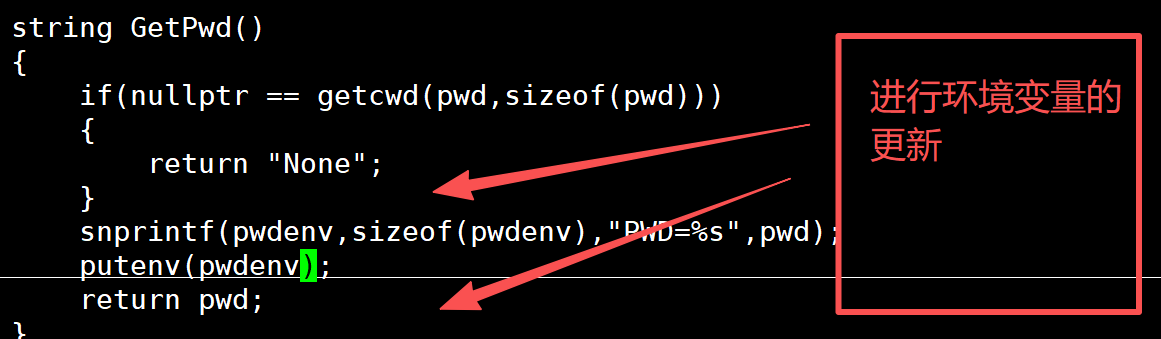
string GetPwd()
{if(nullptr == getcwd(pwd,sizeof(pwd))){return "None";}snprintf(pwdenv,sizeof(pwdenv),"PWD=%s",pwd);putenv(pwdenv);return pwd;
}
4.增加自己的环境变量表
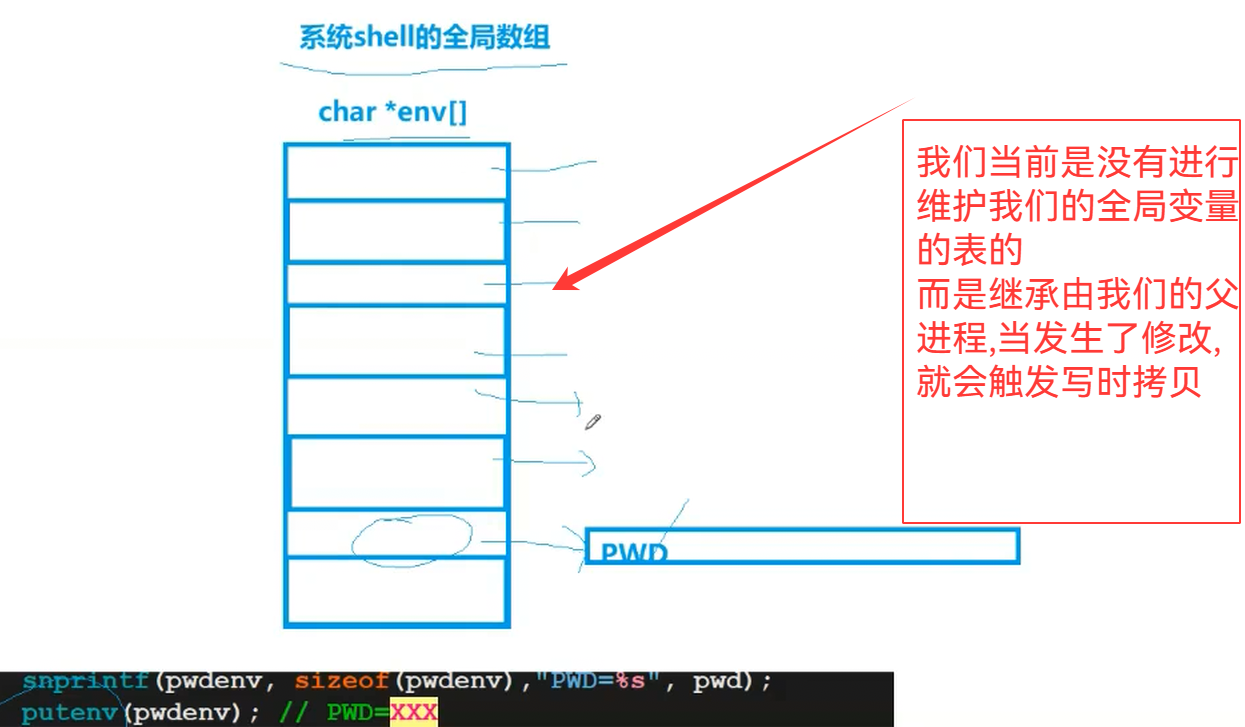
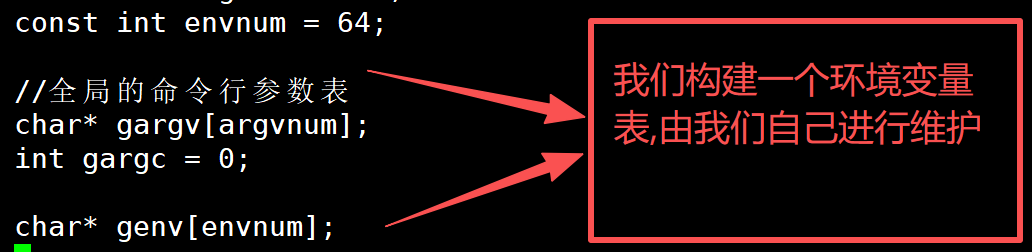
如果我们自己维护了一张表,那么我们要是直接 export(导入环境变量) 或者 echo PATH等命令,就都不需要我们自己创建子进程来维护了
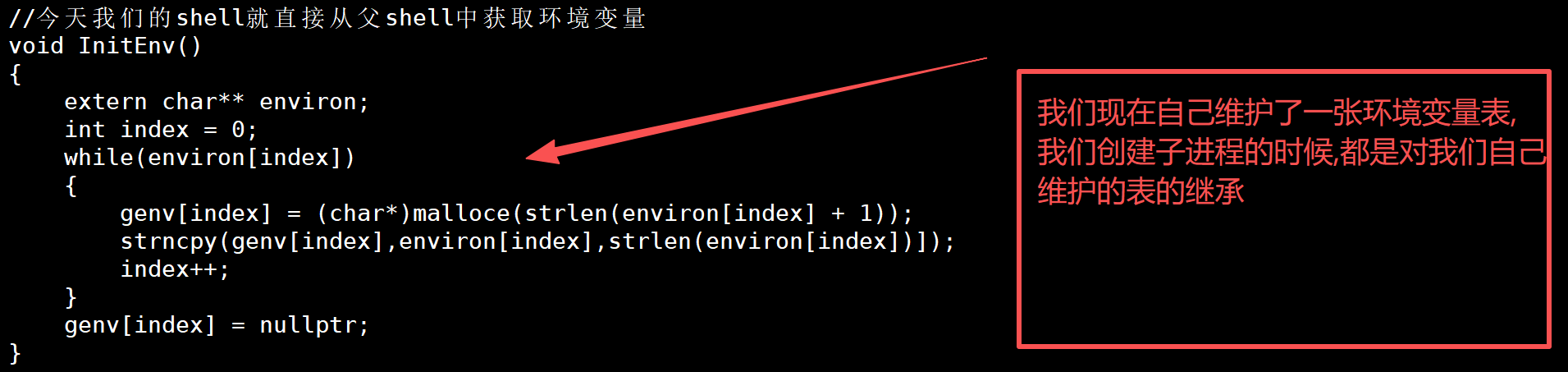
//今天我们的shell就直接从父shell中获取环境变量
void InitEnv()
{extern char** environ;int index = 0;while(environ[index]){genv[index] = (char*)malloce(strlen(environ[index] + 1));strncpy(genv[index],environ[index],strlen(environ[index])]);index++;}genv[index] = nullptr;
}5.增加内建命令
a.cd
已经写了,所以就不讲了
b.export
我们添加了自己的环境变量表,所以export导入环境变量的时候,要我们自己(主进程)添加到自己的环境变量中
// shell自己执行命令,本质上是shell调用自己的函数
bool CheckAndExecBuiltCommand()
{if(strcmp(gargv[0],"cd") == 0){if(gargc == 2){chdir(gargv[1]);}return true;}else if(strcmp(gargv[0],"export") == 0){if(gargc == 2){AddEnv(gargv[1]);}return true;}return false;
}c.env
// shell自己执行命令,本质上是shell调用自己的函数
bool CheckAndExecBuiltCommand()
{if(strcmp(gargv[0],"cd") == 0){if(gargc == 2){chdir(gargv[1]);}return true;}else if(strcmp(gargv[0],"export") == 0){if(gargc == 2){AddEnv(gargv[1]);}return true;}else if(strcmp(gargv[0],"env") == 0){for(int i = 0;genv[i]; i++){printf("%s\n",genv[i]);}return true;}return false;
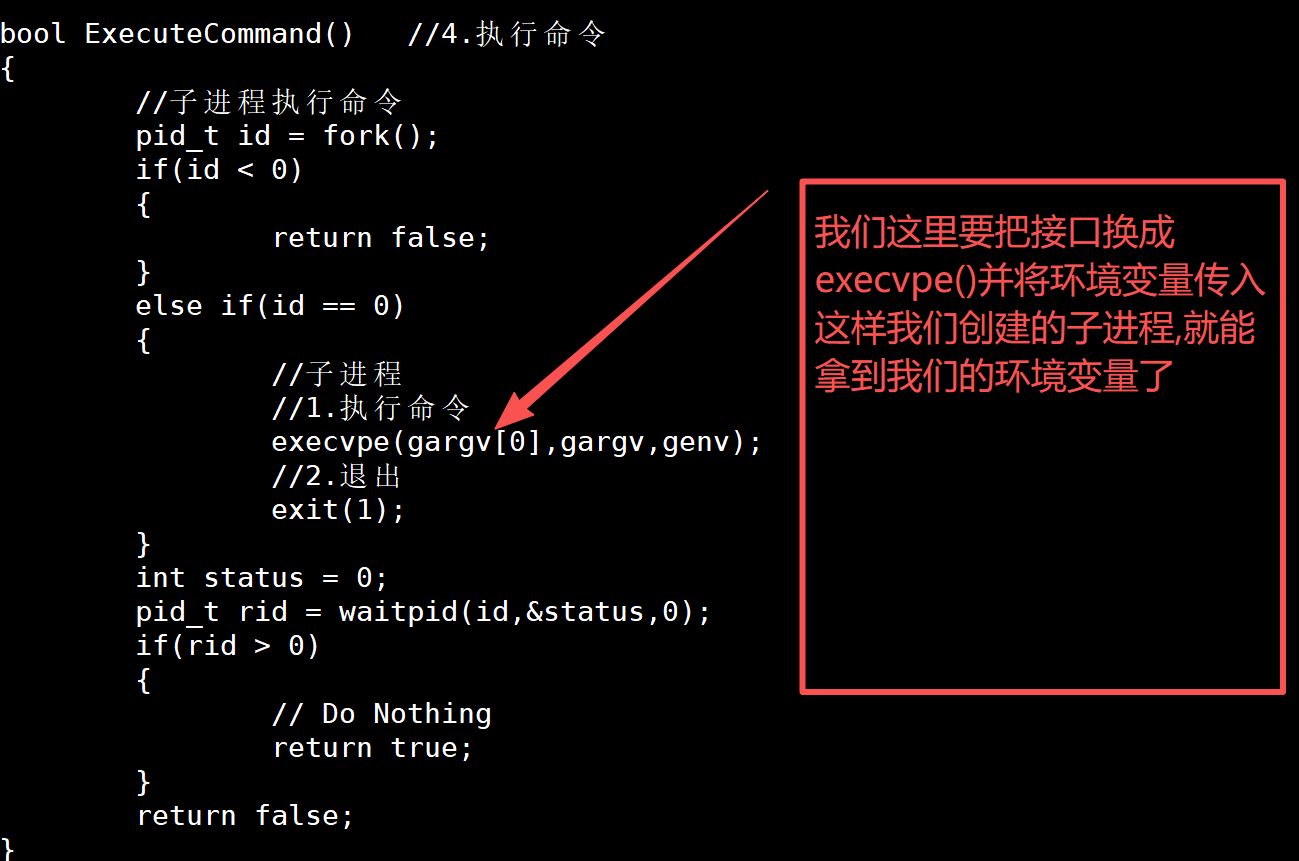
}d.将环境变量传递给子进程
bool ExecuteCommand() //4.执行命令
{//子进程执行命令pid_t id = fork();if(id < 0){return false;}else if(id == 0){//子进程//1.执行命令execvpe(gargv[0],gargv,genv);//2.退出exit(1);}int status = 0;pid_t rid = waitpid(id,&status,0);if(rid > 0){// Do Nothingreturn true;}return false;
}
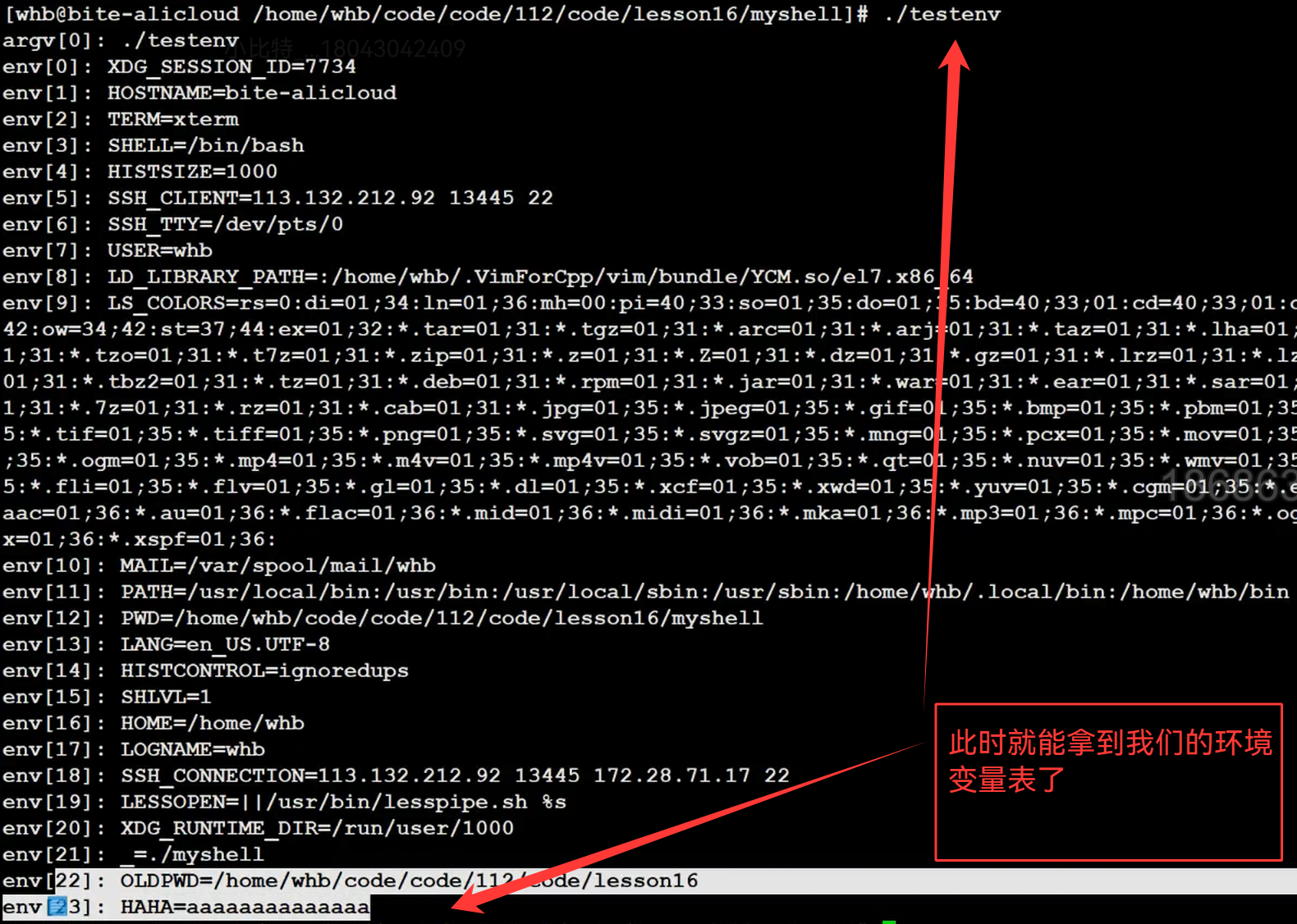
6.测试环境变量导入是否成功
我们写了一个测试文件,用于检测环境变量
/*************************************************************************> File Name: testenv.c> Author: ma6174> Mail: ma6174@163.com > Created Time: Fri 31 Oct 2025 02:08:08 PM CST************************************************************************/#include<stdio.h>int main(int argc,char* argv[],char* env[])
{for(int i = 0;i < argc;i++){printf("argv[%d]: %s\n",i,argv[i]);}for(int i = 0; env[i]; i++){printf("env[%d]: %s\n",i,env[i]);}return 0;
}
7.获取内建命令和子进程的退出信息
补充知识: 快速定位函数 ctrl + #
a.内建命令
// shell自己执行命令,本质上是shell调用自己的函数
bool CheckAndExecBuiltCommand()
{if(strcmp(gargv[0],"cd") == 0){if(gargc == 2){chdir(gargv[1]);lastcode = 0;}else{lastcode = 1;}return true;}else if(strcmp(gargv[0],"export") == 0){if(gargc == 2){AddEnv(gargv[1]);lastcode = 0;}else{lastcode = 2;}return true;}else if(strcmp(gargv[0],"env") == 0){for(int i = 0;genv[i]; i++){printf("%s\n",genv[i]);}lastcode = 0;return true;}else if(strcmp(gargv[0],"echo") == 0){if(gargc == 2){//echo $?//echo helloif(gargv[1][0] == '$'){if(gargv[1][1] == '?'){printf("%d\n",lastcode);lastcode = 0;}}else{printf("%s\n",gargv[1]);lastcode = 0;}}else{lastcode = 3;}return true;}return false;
}我们要将lastcode存储进程退出的信息
b.子进程退出信息获取
bool ExecuteCommand() //4.执行命令
{//子进程执行命令pid_t id = fork();if(id < 0){return false;}else if(id == 0){//子进程//1.执行命令execvpe(gargv[0],gargv,genv);//2.退出exit(1);}int status = 0;pid_t rid = waitpid(id,&status,0);if(rid > 0){if(WIFEXITED(status)){lastcode = WEXITSTATUS(status);}else{lastcode = 100;}return true;}return false;
}8.获取最后一个目录
string LastDir()
{string curr = GetPwd();if(curr == "/" || curr == "None"){return curr;}string lastdir = curr.substr(curr.rfind("/") + 1);return lastdir;
}四.myshell总代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>using namespace std;const int basesize = 1024;
const int argvnum = 64;
const int envnum = 64;//全局的命令行参数表
char* gargv[argvnum];
int gargc = 0;//全局的变量
int lastcode = 0;//我的系统的环境变量
char* genv[envnum];//全局的当前shell工作路径
char pwd[basesize];
char pwdenv[basesize + 4];string GetUserName()
{string name = getenv("USER");return name.empty() ? "None" : name;
}string GetPwd()
{if(nullptr == getcwd(pwd,sizeof(pwd))){return "None";}snprintf(pwdenv,sizeof(pwdenv),"PWD=%s",pwd);putenv(pwdenv);return pwd;
}string LastDir()
{string curr = GetPwd();if(curr == "/" || curr == "None"){return curr;}string lastdir = curr.substr(curr.rfind("/") + 1);return lastdir;
}string MakeCommandLine()
{// [ltw@alicloud myshell]$char command_line[basesize];snprintf(command_line,basesize,"[%s@ %s]# ",\GetUserName().c_str(),LastDir().c_str());return command_line;
}void PrintCommandLine()
{printf("%s",MakeCommandLine().c_str());fflush(stdout);
}bool GetCommandLine(char command_buffer[],int size)
{//我们认为:我们要将用户输入的命令行,当做一个完整的字符串//"ls -a -l -n"char* result = fgets(command_buffer,size,stdin);if(!result){return false;}command_buffer[strlen(command_buffer) - 1] = 0;if(strlen(command_buffer) == 0){return false;}return true;
}void ParseCommandLine(char command_buffer[],int len) //3.分析命令
{memset(gargv,0,sizeof(gargv));gargc = 0;// "ls -a -l -n"const char *sep = " ";gargv[gargc++] = strtok(command_buffer,sep);//这里直接就能写完while(gargv[gargc++] = strtok(nullptr,sep));gargc--;
}void debug()
{printf("argc: %d\n",gargc);for(int i = 0;gargv[i];i++){printf("argv[%d]: %s\n",i,gargv[i]);}
}bool ExecuteCommand() //4.执行命令
{//子进程执行命令pid_t id = fork();if(id < 0){return false;}else if(id == 0){//子进程//1.执行命令execvpe(gargv[0],gargv,genv);//2.退出exit(1);}int status = 0;pid_t rid = waitpid(id,&status,0);if(rid > 0){if(WIFEXITED(status)){lastcode = WEXITSTATUS(status);}else{lastcode = 100;}return true;}return false;
}void AddEnv(const char* item)
{int index = 0;while(genv[index]){index++;}genv[index] = (char*)malloc(strlen(item) + 1);strncpy(genv[index],item,strlen(item) + 1);genv[++index] = nullptr;
}// shell自己执行命令,本质上是shell调用自己的函数
bool CheckAndExecBuiltCommand()
{if(strcmp(gargv[0],"cd") == 0){if(gargc == 2){chdir(gargv[1]);lastcode = 0;}else{lastcode = 1;}return true;}else if(strcmp(gargv[0],"export") == 0){if(gargc == 2){AddEnv(gargv[1]);lastcode = 0;}else{lastcode = 2;}return true;}else if(strcmp(gargv[0],"env") == 0){for(int i = 0;genv[i]; i++){printf("%s\n",genv[i]);}lastcode = 0;return true;}else if(strcmp(gargv[0],"echo") == 0){if(gargc == 2){//echo $?//echo helloif(gargv[1][0] == '$'){if(gargv[1][1] == '?'){printf("%d\n",lastcode);lastcode = 0;}}else{printf("%s\n",gargv[1]);lastcode = 0;}}else{lastcode = 3;}return true;}return false;
}//今天我们的shell就直接从父shell中获取环境变量
void InitEnv()
{extern char** environ;int index = 0;while(environ[index]){genv[index] = (char*)malloc(strlen(environ[index] + 1));strncpy(genv[index],environ[index],strlen(environ[index]) + 1);index++;}genv[index] = nullptr;
}int main()
{InitEnv();char command_buffer[basesize];while(true){PrintCommandLine(); //1.命令行提示符if(!GetCommandLine(command_buffer,basesize)) //2.获取用户输入{continue;}//printf("%s\n",command_buffer);ParseCommandLine(command_buffer,strlen(command_buffer)); //3.分析命令//debug();if(CheckAndExecBuiltCommand()){continue;}ExecuteCommand(); //4.执行命令}return 0;
}