(四)Gradle 依赖树分析与依赖关系优化

依赖树是 Gradle 项目中所有依赖(包括直接依赖和间接依赖)的层级结构展示,主要包含以下依赖信息:
- GAV 坐标:每个依赖的 GAV 坐标(如
org.springframework:spring-core:5.3.20)。 - 依赖关系:依赖之间的传递关系(如 A 依赖 B,B 依赖 C 则形成嵌套层级)。
- 配置类型:明确依赖所属的作用域(如
implementation编译期依赖、testImplementation测试依赖等)。
一、依赖树符号解读
Gradle 提供了两个核心命令用于生成依赖树:dependencies(全局依赖树)和 dependencyInsight(特定依赖详情),执行命令后,Gradle 会输出结构化的依赖树:
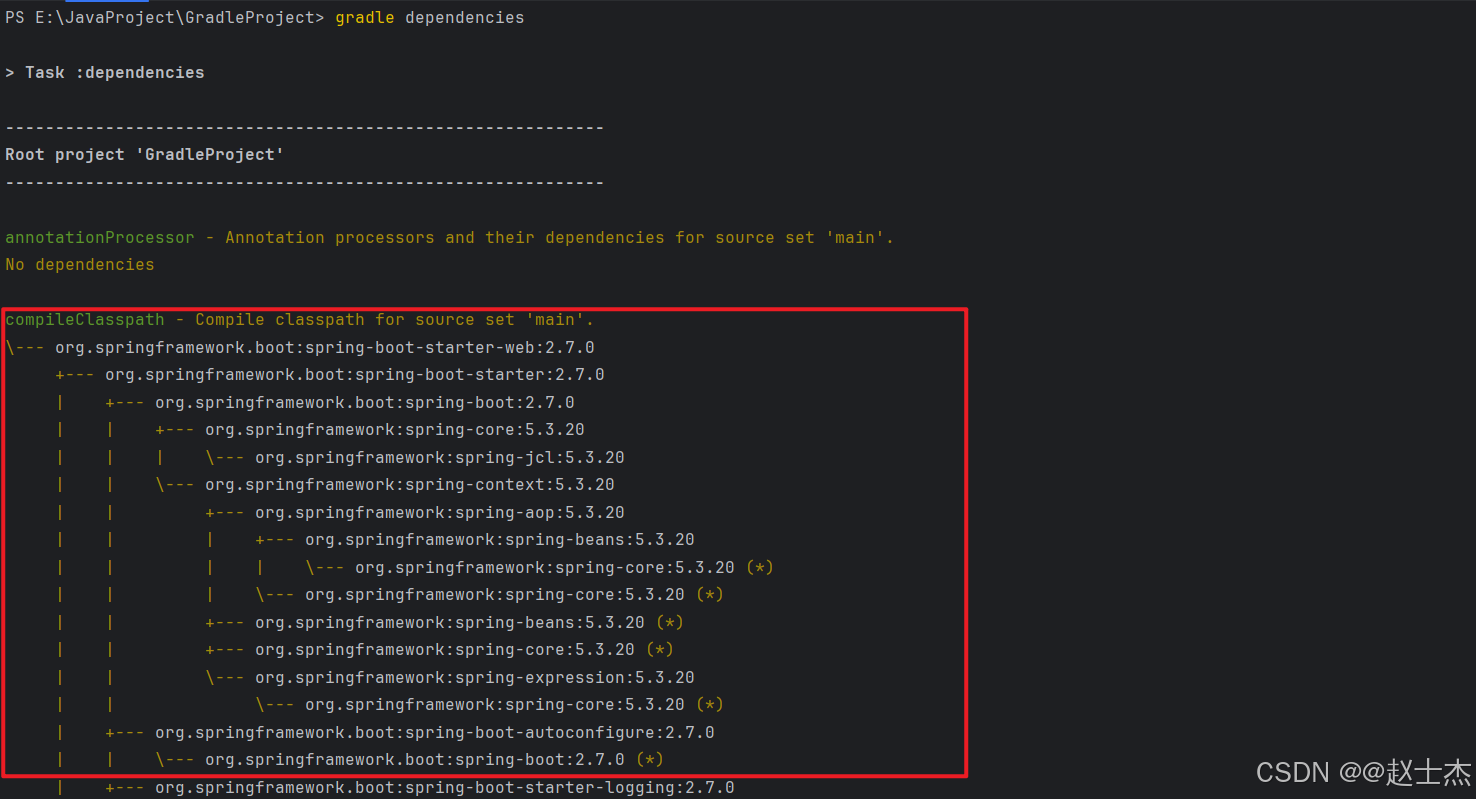
依赖树通过结构化符号展示直接依赖与间接依赖之间的层级关系:
| 符号 | 含义说明 |
|---|---|
+--- | 表示直接依赖(当前模块直接声明的依赖) |
|--- | 表示传递依赖(直接依赖的子依赖,存在嵌套层级) |
\--- | 表示无嵌套的传递依赖(当前层级下的最后一个子依赖) |
(*) | 表示依赖已在其他路径声明,当前路径跳过(避免重复输出,不影响实际依赖) |
(n) | 表示 “未解析”(仅展示结构,未实际下载依赖,需指定配置项解析) |
二、全局依赖树 dependencies
在项目根目录执行 gradle dependencies 命令会输出当前项目(或模块)的完整依赖树,包含所有直接依赖、传递依赖的层级结构和版本信息:
# 输出项目依赖(根目录执行)
gradle dependencies [参数]# 输出项目指定模块的依赖(模块名与 settings.gradle 中声明一致)
gradle :模块名:dependencies [参数]
默认输出包含所有依赖配置(如 implementation、runtimeOnly 等),信息较多,追加参数可以过滤输出内容:
| 参数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
--configuration | 输出指定配置下的依赖(如 implementation、compileOnly) |
--project | 输出指定模块依赖(与 :模块名: 写法等效),默认分析根模块 |
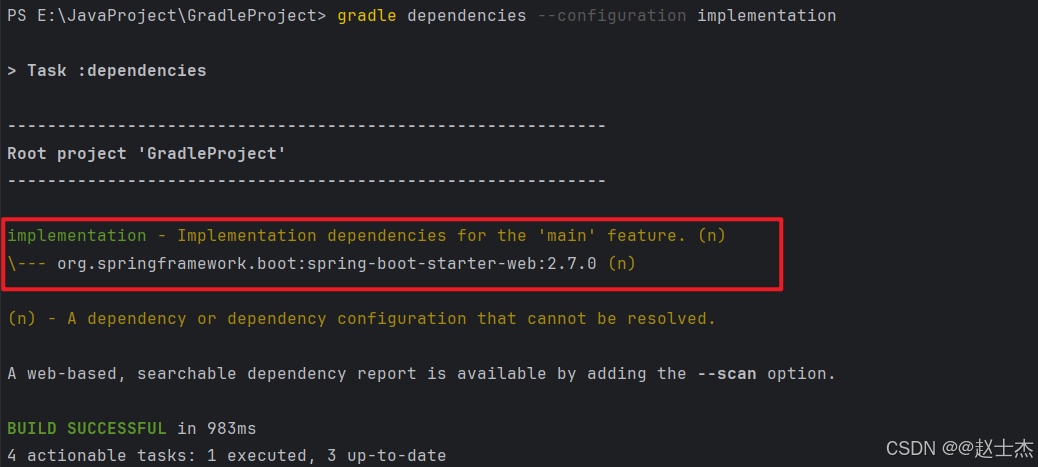
例如,仅查看项目编译期依赖(implementation配置),执行:
gradle dependencies --configuration implementation
输出结果会聚焦于implementation作用域下的依赖:
三、追踪特定依赖 dependencyInsight
当需要深入分析某个依赖(例如排查 “为什么会引入这个版本的依赖?”“它是通过哪个路径被引入的?”),gradle dependencyInsight命令更高效。它能精准展示目标依赖的引入路径、版本来源和匹配的变体属性。
gradle dependencyInsight [参数]gradle :模块名:dependencyInsight [参数]
| 参数 | 作用说明 |
|---|---|
--dependency | 指定目标依赖的标识,格式为 group:artifact(无需版本),也可简化为 artifact |
--configuration | 指定依赖配置(如 implementation、compileOnly) |
--project | 指定模块(与 :模块名: 写法等效),默认分析根模块 |
以分析 spring-context 依赖为例,执行:
gradle dependencyInsight --dependency spring-context
输出结果包含两部分核心信息:
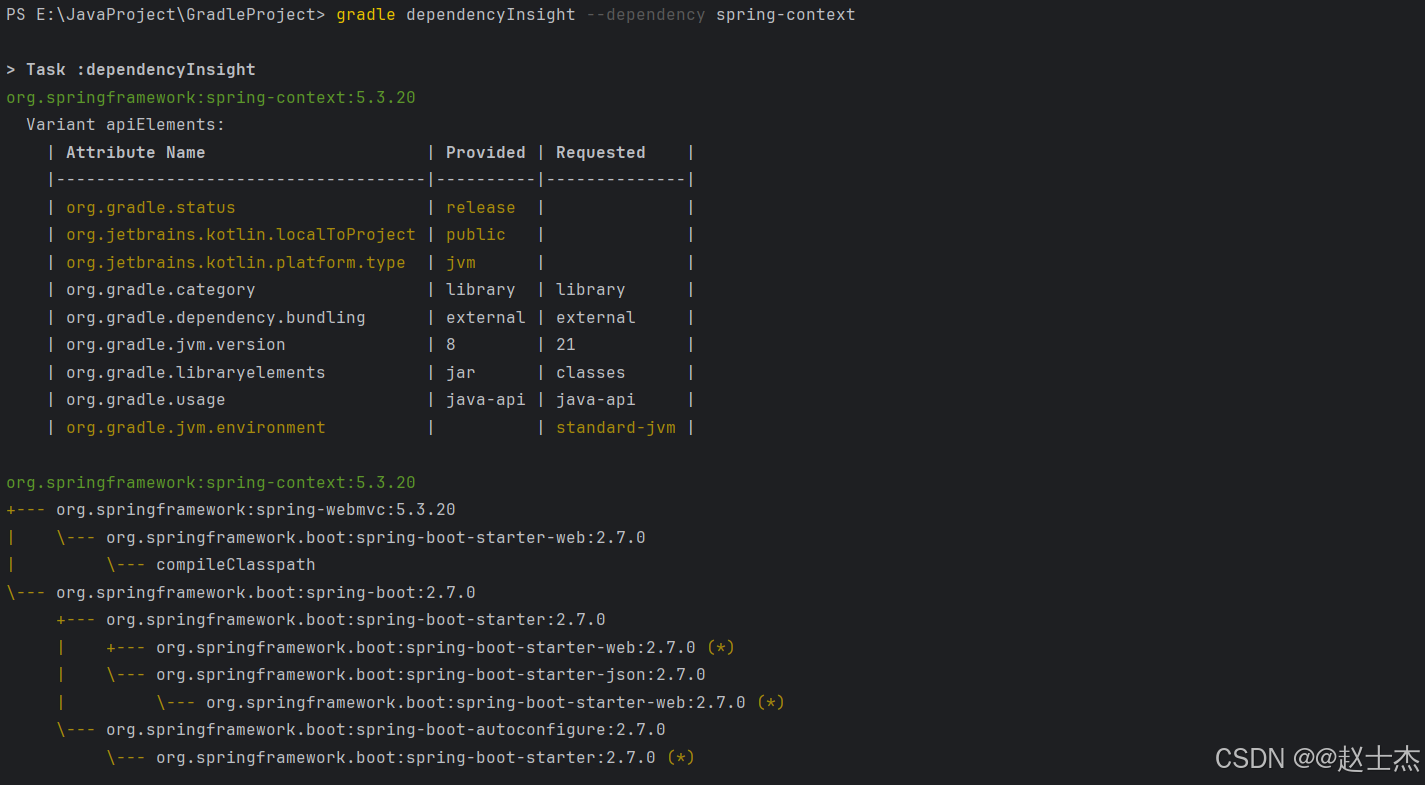
3.1 依赖变体信息
Gradle 会根据项目环境(如 JVM 版本、用途)匹配最适配的依赖变体,结果 “Variant apiElements” 列出了 Gradle 为项目筛选的 spring-context 依赖 “变体” 的元数据:
| 属性名 | 含义与影响 |
|---|---|
org.gradle.status | 依赖的发布状态:release(正式发布版)、snapshot(快照版,开发中) |
org.gradle.category | 依赖的类型:library(库依赖)、platform(平台依赖,如 BOM)、documentation(文档) |
org.gradle.dependency.bundling | 依赖的打包方式:external(外部依赖,需从仓库下载)、embedded(内置代码,无需额外下载)。 |
org.gradle.jvm.version | 依赖编译时使用的 JDK 版本 |
org.gradle.libraryelements | 依赖的形式:jar(完整 JAR 包)、classes(仅 class 文件)、resources(仅资源文件) |
org.gradle.usage | 依赖的场景:java-api(编译期 API 依赖)、java-runtime(运行期依赖) |
3.2 引入路径链
结果的第二部分(树形结构)描述了 spring-context 的两条引入路径,每条路径都能从目标依赖反向追溯至项目直接声明的依赖:
-
路径一:通过
spring-webmvc引入:org.springframework:spring-context:5.3.20 +--- org.springframework:spring-webmvc:5.3.20\--- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web:2.7.0\--- compileClasspathspring-context被spring-webmvc依赖,而spring-webmvc被spring-boot-starter-web依赖,因此当项目直接声明spring-boot-starter-web作为依赖时,间接引入了spring-webmvc和spring-context依赖。最终,spring-boot-starter-web自身及它的传递依赖都被纳入compileClasspath,在项目运行和编译时提供源代码编译所需的依赖资源。 -
路径二:通过
spring-boot引入:org.springframework:spring-context:5.3.20 \--- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot:2.7.0 // spring-boot 直接依赖 spring-context+--- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter:2.7.0 // starter 依赖 spring-boot| +--- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web:2.7.0 (*) // 已展示,省略重复| \--- ...(其他传递路径)该路径也清晰的展示了
spring-context作为spring-boot的依赖,最终通过spring-boot-starter-web间接引入了spring-context。
从上述路径可知:spring-context并非项目手动声明,而是通过spring-boot-starter-web(直接依赖)间接引入的。
四、快速过滤依赖
当依赖树信息过多时,可结合系统命令(Linux/macOS 用grep,Windows 用findstr)快速定位目标依赖:
# 查找 implementation 配置中包含 "spring" 的依赖(Linux/macOS)
gradle dependencies --configuration implementation | grep spring# Windows 系统
gradle dependencies --configuration implementation | findstr spring
执行后会过滤出所有含 “spring” 关键词的依赖及其层级:

