【C++】set map 的使用
目录
一. set
二. map
operator[ ]
一. set
底层是搜索树中的红黑树,key 模型
 查找成功,返回节点的迭代器;查找失败返回 end()
查找成功,返回节点的迭代器;查找失败返回 end()

返回 key 这个值出现了几次,由于所有元素唯一,有就返回 1,没有就返回 0
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
using namespace std;void test_set1()
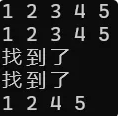
{// 排序+去重// 去重原理:一个值已经有了,我们就不插入set<int> s;s.insert(3); s.insert(2); s.insert(4);s.insert(5); s.insert(1); s.insert(5);s.insert(2); s.insert(5);set<int>::iterator it = s.begin();while (it != s.end()){// *it = 10; 报错: “it”: 不能给常量赋值cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;for (auto e : s) { cout << e << " "; }cout << endl;if (s.find(5) != s.end()) { cout << "找到了" << endl; }if (s.count(5)) { cout << "找到了" << endl; }auto pos = s.find(3); // O(logN)//auto pos = find(s.begin(), s.end(), 3); // O(N)if (pos != s.end())s.erase(pos);s.erase(30);for (auto e : s) { cout << e << " "; }cout << endl;
}
第 17 行,set 不允许修改:iterator 和 const_iterator 都是 const_iterator
typedef typename rep_type::const_iterator iterator;typedef typename rep_type::const_iterator const_iterator;第 30 行是 set 自己的 find
第 31 行是算法库里的 find,用迭代器区间遍例,暴力查找,效率低下
找边界区间

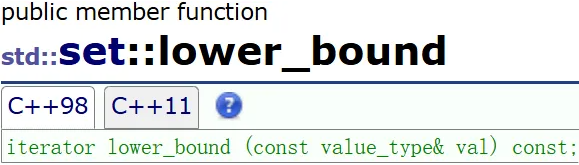 找 >= 的(找下界)
找 >= 的(找下界)
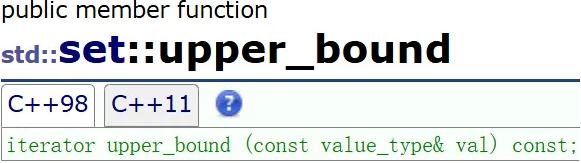 找 > 的(找上界)
找 > 的(找上界)
void test_set1()
{std::set<int> myset;std::set<int>::iterator itlow, itup;for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) myset.insert(i * 10); // 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90// 删除[30, 60]itlow = myset.lower_bound(30); // 找 >=30 的最小数itup = myset.upper_bound(60); // 找 >60 的最小数cout << *itlow << endl; // 30cout << *itup << endl; // 70myset.erase(itlow, itup); // 因为这里是[itlow, itup)for (auto e : myset) { cout << e << " "; }cout << endl; // 10 20 70 80 90
}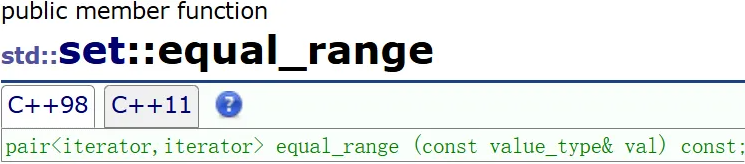 找相等值的 [ ) 区间
找相等值的 [ ) 区间
count 和 equal_range 是专门为 multiset 设计的
void test_set2()
{// 排序multiset<int> s;s.insert(3); s.insert(5); s.insert(8);s.insert(7); s.insert(7); s.insert(9);s.insert(7);for (auto e : s) { cout << e << " "; }cout << endl; // 3 5 7 7 7 8 9// 返回中序第一个7auto pos = s.find(7);while (pos != s.end()){cout << *pos << " ";++pos;}cout << endl; // 7 7 7 8 9cout << s.count(7) << endl; // 3auto ret = s.equal_range(7); // 想删掉所有7auto itlow = ret.first; // 返回7auto itup = ret.second; // 返回比7大的值// [itlow, itup)// [7,8)cout << *itlow << endl; // 7cout << *itup << endl; // 8s.erase(itlow, itup);for (auto e : s) { cout << e << " "; }cout << endl; // 3 5 8 9
}二. map
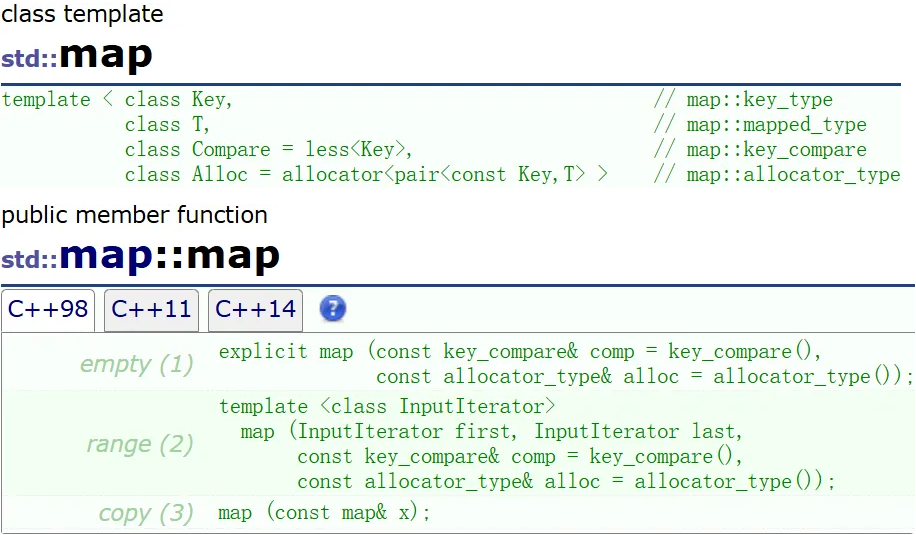
不能修改 key,可以修改 value
pair 是类模板的结构,map 节点里存数据使用 pair 存的

key 是任意类型都可以,树里面要进行比较大小
如果该类型支持比较大小最好;不支持我们可以自己写仿函数控制
为什么要搞 pair?
namespace key_value
{template<class K, class V>struct BSTreeNode{BSTreeNode<K, V>* _left;BSTreeNode<K, V>* _right;//K _key;//V _value;pair<K, V> _kv;BSTreeNode(const K& key, const V& value):_left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _key(key), _value(value){ }};pair<K, V>& operator*(){return _node->_kv;}pair<K, V>* operator->(){return &_node->_kv;}
}迭代器最终要重载 operator*,对迭代器解引用,迭代器里面包含节点的指针;C++ 不支持返回俩值
如果是 _key 和 _value,无法返回
要返回多个值,得返回结构
插入的是一个结构对象
5-7 行:调构造函数,构造一个对象
不用把 key 写成 const,自己内部会转换
第 10 行:类 pair 提供了函数模板 make_pair,等价于第 7 行的写法:自动调 pair 的构造
 没有效率问题,会被定义为 inline
没有效率问题,会被定义为 inline
重点掌握 10.13 行
void test_map1()
{map<string, string> dict;pair<string, string> kv1("insert", "插入");dict.insert(kv1);dict.insert(pair<string, string> ("sort", "排序")); // 匿名对象// C++98dict.insert(make_pair("string", "字符串"));// C++11 多参数的构造函数隐式类型转换dict.insert({ "string", "字符串" });// 隐式类型的转换string str1 = "hello";A aa1 = { 1, 2 };pair<string, string> kv2 = { "string", "字符串" };
}class A // 应该写到上面,这里是嫌挡视野
{
public:A(int a1, int a2):_a1(a1), _a2(a2){ }
private:int _a1;int _a2;
};void test_map2()
{map<string, string> dict;dict.insert(make_pair("string", "字符串"));dict.insert(make_pair("sort", "排序"));dict.insert(make_pair("insert", "插入"));// 不插入,不覆盖;插入过程中,只比较key,value是相同无所谓// key已经有了就不插入了// 查找、删除都只看keydict.insert(make_pair("insert", "xxxx"));//map<string, string>::iterator it = dict.begin();auto it = dict.begin();while (it != dict.end()){//it->first = "xxx"; 报错,_key是const不能修改//it->second = "xxx"; 正确//cout << *it << " "; 报错//cout << (*it).first << ":" << (*it).second << endl;cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;++it;}cout << endl;for (const auto& kv : dict) // 把 *it 给kv{cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;}
}库里没有重载 pair 这个类的流插入、留提取
*it 返回的是 pair
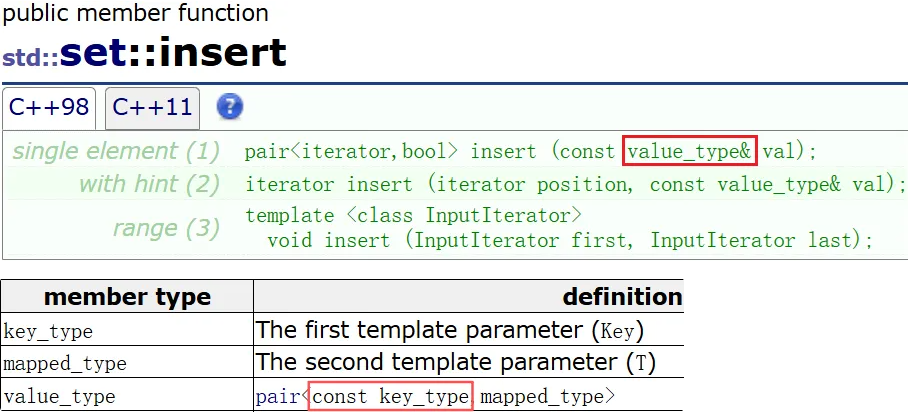
只要 T(里面的数据) 是结构时,要用迭代器重载的->。恰好 map 里面的数据是结构
operator[ ]
void test_map3()
{// 统计次数string arr[] = { "西瓜", "西瓜", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉" };map<string, int> countMap;//for (auto e : arr)//{// auto it = countMap.find(e);// if (it == countMap.end())// {// countMap.insert(make_pair(e, 1));// }// else// {// it->second++;// }//}for (auto e : arr){countMap[e]++;}for (const auto& kv : countMap){cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;}
}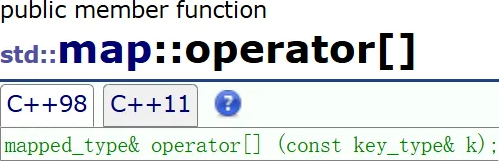
以前 string vector deque 的 [ ] 都是用下标,直接返回第 i 个数据的引用(可读可写)
map 的 [ ] 不常规,给 key 返回对应 value 的引用
上面的例子 countMap[e]++,如果 countMap 里面有对应水果,出现一次就++
那第一次是怎么实现的呢?库里面给了
![]()
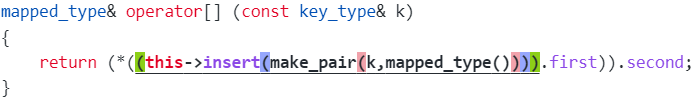
[ ] 通过 insert 实现,借助了 insert 的返回值
![]()

1. key 已经在树里面:返回 pair<树里面 key 所在节点的 iterator,false>
2. key 不在树里:返回 pair<新插入 key 所在节点的 iterator,true>
可以看出,insert 还有查找的价值
根据这个模拟实现 operator[ ]V& operator[](const K& key)
{pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make(key, V()));return ret.first->second;
}
// countMap[e]++;若 key 没在树里,调 V 的默认构造,插入成功返回 pair 类型的 ret,拿到 key 迭代器,通过迭代器取到 value 的引用,并返回
第一次:[ ] 是插入,++是修改返回值
若 key 在树里,插入失败返回 pair 类型的 ret,拿到 key 迭代器,通过迭代器取到 value 的引用,并返回
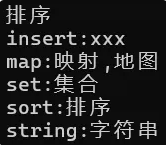
void test_map4()
{map<string, string> dict;dict.insert(make_pair("string", "字符串"));dict.insert(make_pair("sort", "排序"));dict.insert(make_pair("insert", "插入"));cout << dict["sort"] << endl; // 查找和读dict["map"]; // 插入dict["map"] = "映射,地图"; // 修改dict["insert"] = "xxx"; // 修改dict["set"] = "集合"; // 插入+修改for (const auto& kv : dict) // 把 *it 给kv{cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;}
}
nultimap 没有提供 [ ],不知道映射哪一个
insert 也不一样,multmap 插入永远成功
哈希用迭代器走不有序,有序是搜索树特有的
本篇的分享就到这里了,感谢观看,如果对你有帮助,别忘了点赞+收藏+关注。
小编会以自己学习过程中遇到的问题为素材,持续为您推送文章
