MYSQL之内置函数
内置函数
日期函数
不作特殊的说明, 对于日期(date) 对应 年-月-日, 时间(time) 对应 时:分:秒, 日期时间(datetime) 对应年-月-日 时:分:秒, 而对于 时间戳 mysql会自动把它转换为 年-月-日 时:分:秒.
明确 MYSQL 中关于时间的概念, 下面的函数就很好理解:
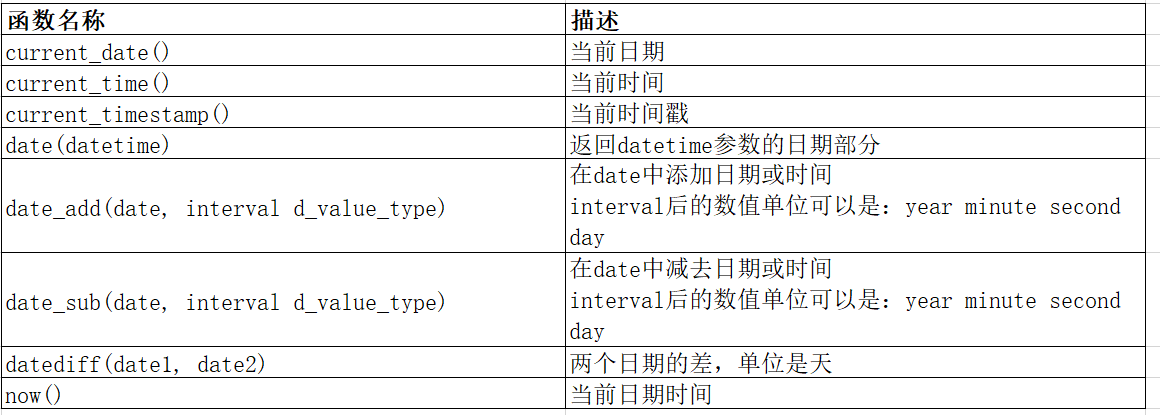
- current 系列简单展示:
其中注意, current_timestamp 和 now 的功能一模一样, 只是 now 更简洁, 而 current_timestamp 更正式.
select current_time();
+----------------+
| current_time() |
+----------------+
| 11:51:49 |
+----------------+
select current_date();
+----------------+
| current_date() |
+----------------+
| 2025-05-15 |
+----------------+
select current_timestamp();
+---------------------+
| current_timestamp() |
+---------------------+
| 2025-05-15 11:52:11 |
+---------------------+
本质上三者调用的都是同一个系统时间源, 只是根据你调用的函数(current_time, date, timestamp )不同, 截取或格式化显示不同的部分, 从而最后显示的内容和格式不同.
date 可以截取datetime格式的左半部分(date):
select date("1949-10-01 00:00:00")
+-----------------------------+
| date("1949-10-01 00:00:00") |
+-----------------------------+
| 1949-10-01 |
+-----------------------------+//效果和date()一样:
select date(now())
+-------------+
| date(now()) |
+-------------+
| 2025-10-24 |
+-------------+
- date_add 和 data_sub, 语法都一样, 最终结果都是
参数1 +/- 参数2:
select data_add(now(), interval 常数 year/month/day/hour/minute/second)
select data_sub(now(), interval 常数 year/month/day/hour/minute/second)

将当前时间分别增加30天和减少30天, 发现它会自动帮我们进行月份的转换:
select now();
+---------------------+
| now() |
+---------------------+
| 2025-10-24 11:16:52 |
+---------------------+select date_add(now(), interval 30 day);
+----------------------------------+
| date_add(now(), interval 30 day) |
+----------------------------------+
| 2025-11-23 11:16:56 |
+----------------------------------+select date_sub(now(), interval 30 day);
+----------------------------------+
| date_sub(now(), interval 30 day) |
+----------------------------------+
| 2025-09-24 11:17:09 |
+----------------------------------+- datediff: 计算两个日期之间相差多少天(date1-date2)
select datediff(now(), '1949-10-1');
+------------------------------+
| datediff(now(), '1949-10-1') |
+------------------------------+
| 27620 |
+------------------------------+
比如"当前时间" - "入学时间"就是入学时长
案例1:
先创建一个表, 它的birthday字段是date类型的:
create table tmp(
id int primary key auto_increment,
birthday date
);
现在分别用 current_date, current_time, current_timestamp 插入日期, 发现最终都会被转换为 date 类型, 可以类比理解成一种 “隐式类型转换”.
所以可以说明三者底层调用的都是同一个函数去获取同一个系统时间源, 只不过显示出来的格式不同.
insert into tmp (birthday) values(current_date());
insert into tmp (birthday) values(current_time());
insert into tmp (birthday) values(current_timestamp());
//查询
select * from tmp;
+----+------------+
| id | birthday |
+----+------------+
| 1 | 2025-05-15 |
| 2 | 2025-05-15 |
| 3 | 2025-05-15 |
+----+------------+
但是建议不要让它去转换, 是什么类型就插入什么类型:
insert into tmp (birthday) values(current_date());
insert into tmp (birthday) values(date(current_time()));
insert into tmp (birthday) values(date(current_timestamp()));
案例2, 创建一个留言板, 顺便介绍 date 的使用:
create table msg (
id int primary key auto_increment,
content varchar(30) not null,
sendtime datetime
);
insert into msg (content, sendtime) values ("第一条消息", now());
insert into msg (content, sendtime) values ("第二条消息", now());
显示所有留言信息, 发布日期只显示日期, 不用显示时间:
select content, date(sendtime) from msg;
+------------+----------------+
| content | date(sendtime) |
+------------+----------------+
| 第一条消息 | 2025-05-15 |
| 第二条消息 | 2025-05-15 |
+------------+----------------+
查询在2分钟内发布的帖子(date_sub):
select * from msg
where date_sub(now(), interval 2 minute) < sendtime;
+----+------------+---------------------+
| id | content | sendtime |
+----+------------+---------------------+
| 3 | 第三条消息 | 2025-05-15 19:59:37 |
+----+------------+---------------------+
字符串函数
mysql 内置了很多字符串函数, 其中一些和C语言string.h里的函数很像
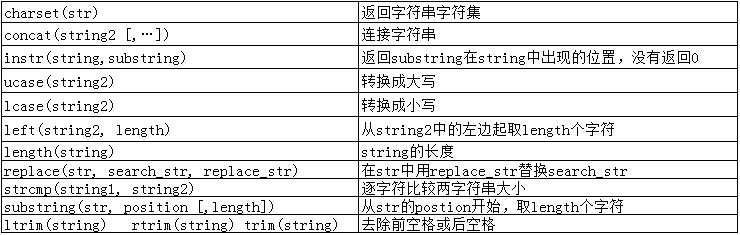
- charset(str)
功能: 可以查看字符串的字符集, 对于字符串字面量, 默认用的是客户端连接的字符集:
select charSet("你好")
+-----------------+
| charSet("你好") |
+-----------------+
| utf8mb3 |
+-----------------+
可以查看一个表中字段的字符集. MySQL配置过后一般就两种编码, 一种是utf-8编码针对字符的, 一种是binary的针对整数浮点数.
select charset(ename) from emp
+----------------+
| charset(ename) |
+----------------+
| utf8mb3 |
| utf8mb3 |
| utf8mb3 |
| utf8mb3 |
| utf8mb3 |
| utf8mb3 |
| utf8mb3 |
| utf8mb3 |
| utf8mb3 |
| utf8mb3 |
| utf8mb3 |
| utf8mb3 |
+----------------+select charset(sal) from emp
+--------------+
| charset(sal) |
+--------------+
| binary |
| binary |
| binary |
| binary |
| binary |
| binary |
| binary |
| binary |
| binary |
| binary |
| binary |
| binary |
+--------------+
我们什么时候用这个函数呢? 如果在查询过程中发现表中某些部分乱码了, 那就要查一下字段的编码看看是否是哪些部分编码不同.
- concat(string, […])
concat可以把参数都连接起来, 如果是整型也会转为字符串:
select concat("hello", "world") as res
+------------+
| res |
+------------+
| helloworld |
+------------+select concat("hello", "world", 1, 2) as res
+--------------+
| res |
+--------------+
| helloworld12 |
+--------------+
要求显示exam_result表中的信息,显示格式:“XXX的语文是XXX分,数学是XXX分,英语XXX分”
select concat(name,"的语文是", chinese, "分, 数学是", math, "分, 英语是", english, "分") as 成绩 from exam_result
+--------------------------------------------+
| 成绩 |
+--------------------------------------------+
| 唐三藏的语文是67分, 数学是98分, 英语是56分 |
| 孙悟空的语文是87分, 数学是78分, 英语是77分 |
| 猪悟能的语文是88分, 数学是98分, 英语是90分 |
| 曹孟德的语文是82分, 数学是84分, 英语是67分 |
| 刘玄德的语文是55分, 数学是85分, 英语是45分 |
| 孙权的语文是70分, 数学是73分, 英语是78分 |
| 宋公明的语文是75分, 数学是65分, 英语是30分 |
+--------------------------------------------+
- instr(string, substring)
判断 参数2字符串 是否在 参数1字符串 中, 在的话返回所在的位置(下标从1开始), 不在返回0
select instr("helloworld", "world")
+------------------------------+
| instr("helloworld", "world") |
+------------------------------+
| 6 |
+------------------------------+select instr("helloworld", "123")
+----------------------------+
| instr("helloworld", "123") |
+----------------------------+
| 0 |
+----------------------------+
- ucase(str) 和 lcase(str)
分别为转换大/小写:
select ucase("HELLOWORLD1234")
+-------------------------+
| ucase("HELLOWORLD1234") |
+-------------------------+
| HELLOWORLD1234 |
+-------------------------+select lcase("HELLOWORLD1234")
+-------------------------+
| lcase("HELLOWORLD1234") |
+-------------------------+
| helloworld1234 |
+-------------------------+
- left(str, length), right(str, length) 和 substring(str, position, [,length])
left 和 right 是从参数1字符串 左/右边起, 取 参数2长度个字符
select left("helloworld1234", 10)
+----------------------------+
| left("helloworld1234", 10) |
+----------------------------+
| helloworld |
+----------------------------+select right("helloworld1234", 5)
+----------------------------+
| right("helloworld1234", 5) |
+----------------------------+
| d1234 |
+----------------------------+
而 substring 是从 参数1字符串 的 参数2 个位置起, 取 参数3 长度个字符, 如果参数3省略就是读到尾. 也就是说可以从任意位置开始截取字符串.
而 left(str1, 1) 就相当于 substring(str1, 1, 1)
select substring("helloworld", 6, 5)
+-------------------------------+
| substring("helloworld", 6, 5) |
+-------------------------------+
| world |
+-------------------------------+
案例: 以首字母小写的方式显示所有员工的姓名
select ename, concat(lcase(left(ename, 1)), right(ename, length(ename)-1)) as res from emp
+--------+--------+
| ename | res |
+--------+--------+
| WARD | wARD |
| JONES | jONES |
| MARTIN | mARTIN |
| BLAKE | bLAKE |
| CLARK | cLARK |
| SCOTT | sCOTT |
| KING | kING |
| TURNER | tURNER |
| ADAMS | aDAMS |
| JAMES | jAMES |
| FORD | fORD |
| MILLER | mILLER |
+--------+--------+
- length(str)
length函数返回字符串长度, 以字节为单位. 如果是多字节字符则计算多个字节数; 如果是单字节字符则算作一个字节. 比如:字母, 数字算作一个字节, 中文表示多个字节数(与字符集编码有关, utf-8是1个汉字占用3个字节)
select length("helloworld")
+----------------------+
| length("helloworld") |
+----------------------+
| 10 |
+----------------------+
想查看 exam_result 表中学生姓名占用的字节数:
select name, length(name) from exam_result
+--------+--------------+
| name | length(name) |
+--------+--------------+
| 唐三藏 | 9 |
| 孙悟空 | 9 |
| 猪悟能 | 9 |
| 曹孟德 | 9 |
| 刘玄德 | 9 |
| 孙权 | 6 |
| 宋公明 | 9 |
+--------+--------------+
- replace(str, from_str, to_str)
功能: 将参数1中所有的参数2替换为参数3
案例: 把所有邮箱的域名从 gmail.com 改成 example.com
//现在email字段都是gmail的邮箱
select * from users2
+----+-------------------+
| id | email |
+----+-------------------+
| 1 | alice@gmail.com |
| 2 | bob@gmail.com |
| 3 | charlie@gmail.com |
+----+-------------------+
//替换
update users2 set email=replace (email, "gmail.com", "qq.com")
//替换成功
select * from users2
+----+----------------+
| id | email |
+----+----------------+
| 1 | alice@qq.com |
| 2 | bob@qq.com |
| 3 | charlie@qq.com |
+----+----------------+
-
strcmp(string1, string2)
-
ltrim(string), rtrim(string), trim(string)
select ltrim(' 你好 世界 ') as res
+---------------+
| res |
+---------------+
| 你好 世界 |
+---------------+
select rtrim(' 你好 世界 ') as res
+---------------+
| res |
+---------------+
| 你好 世界 |
+---------------+
select trim(' 你好 世界 ') as res
+------------+
| res |
+------------+
| 你好 世界 |
+------------+
在实际场景中, 用户复制粘贴、接口传输、文件导入、不同操作系统或编码差异等都可能引入不可见的空格或制表符. 这些空白字符会导致查询匹配失败、唯一约束失效或统计结果错误. 使用 TRIM() 可以有效清除这些隐性空格, 确保数据在存储、比较和分析时保持一致与可靠.
数学函数
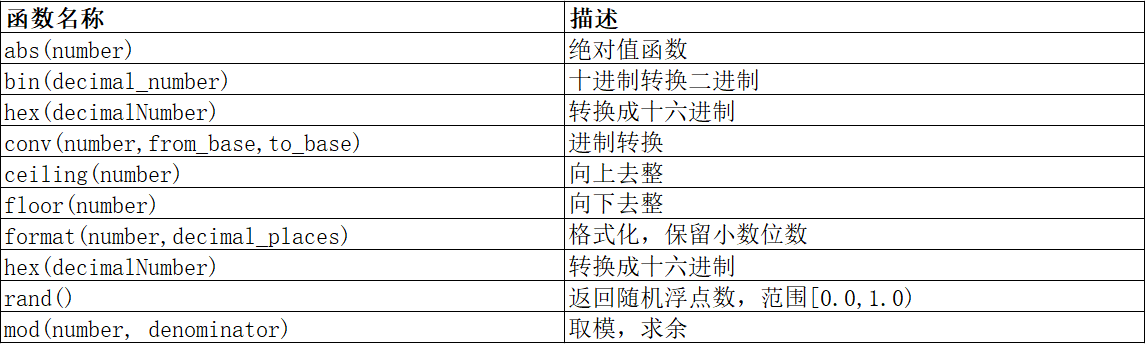
// 绝对值
select abs(-12.3)
+------------+
| abs(-12.3) |
+------------+
| 12.3 |
+------------+// 二进制
select bin(10);
+---------+
| bin(10) |
+---------+
| 1010 |
+---------+
select bin(3.14);
+-----------+
| bin(3.14) |
+-----------+
| 11 |
+-----------+//十六进制
select hex(16)
+---------+
| hex(16) |
+---------+
| 10 |
+---------+// 转换任意进制
select conv(10, 10, 2)
+-----------------+
| conv(10, 10, 2) |
+-----------------+
| 1010 |
+-----------------+
select conv(10, 10, 4)
+-----------------+
| conv(10, 10, 4) |
+-----------------+
| 22 |
+-----------------+//不管对于正数还是负数, 四舍五入都是向远离0的方向取整. 而向上取整是向大的方向取整, 向下取整是向小的方向取整
scott> select round(-11.9), ceil(-11.9)
+--------------+-------------+
| round(-11.9) | ceil(-11.9) |
+--------------+-------------+
| -12 | -11 |
+--------------+-------------+
select round(-11.1), floor(-11.1)
+--------------+--------------+
| round(-11.1) | floor(-11.1) |
+--------------+--------------+
| -11 | -12 |
+--------------+--------------+//保留n位小数
select round(-11.1), floor(-11.1)
+--------------+--------------+
| round(-11.1) | floor(-11.1) |
+--------------+--------------+
| -11 | -12 |
+--------------+--------------+//mysql的mod和c是一样的, 准确来说是"取余", 商是向 0 取整, 余数符号和被除数相同
select mod(10,-3), mod(-10,3), 10%-3, -10%3
+------------+------------+-------+-------+
| mod(10,-3) | mod(-10,3) | 10%-3 | -10%3 |
+------------+------------+-------+-------+
| 1 | -1 | 1 | -1 |
+------------+------------+-------+-------+//rand 生成[0.0,10.0)的数据
select rand()
+--------------------+
| rand() |
+--------------------+
| 0.9501509535593455 |
+--------------------+select format(rand()*100,0)
+----------------------+
| format(rand()*100,0) |
+----------------------+
| 50 |
+----------------------+
select format(rand()*100,1)
+----------------------+
| format(rand()*100,1) |
+----------------------+
| 27.2 |
+----------------------+
其它函数
- user()
功能: 查询当前用户
select user()
+----------------+
| user() |
+----------------+
| root@localhost |
+----------------+
- database()
功能: 显示当前正在使用的数据库
select database();
+------------+
| database() |
+------------+
| scott |
+------------+
- md5(str)
功能:对一个字符串进行md5摘要, 摘要后得到一个 32 位字符串
select md5("admin")
+----------------------------------+
| md5("admin") |
+----------------------------------+
| 21232f297a57a5a743894a0e4a801fc3 |
+----------------------------------+
由于每个用户的密码长度都不固定, 因此可以将密码统一设置为md5加密后的格式, 固定 32 个字符:
//创建一个表, password是
create table accounts(
id int auto_increment primary key,
username varchar(50) not null,
passwaord char(32) not null
);//插入两个用户, 密码用md5哈希
insert into accounts (username, password) values("张三", md5(123456))
insert into accounts (username, password) values("李四", md5(123))//查看
select * from accounts
+----+----------+----------------------------------+
| id | username | password |
+----+----------+----------------------------------+
| 1 | 张三 | e10adc3949ba59abbe56e057f20f883e |
| 2 | 李四 | 202cb962ac59075b964b07152d234b70 |
+----+----------+----------------------------------+
MD5 是单向哈希, 虽然不能通过算法逆向解密, 但是仍可以通过穷举的方式被解密, 所以不安全, 但攻击者无法直接看到用户的真实密码(至少不是立即可用的明文)
- ifnull (val1, val2)
功能: 如果val1为null,返回val2,否则返回val1的值. 等价于 val1==null ? val2 : val1
