list的底层实现
list的自主实现
- list的介绍
- 节点的类
- 迭代器的封装(把节点封装成一个迭代器)
- ++ --
- 1. list 的构造
- 1.1官网的构造
- 1.1.1无参构造
- 1.1.2迭代器的区间构造
- 1.1.3现代写法的构造
- 2.插入和删除
- 官网的插入
- 官网删除
- 插入
- 删除
- 头插和头删
- 尾插和尾删
- 析构和清除数据
- 重点:为什么多个模板
- 解决方法
- 当节点是自定义类型应该怎么办
- 总代码(副有注释)
list的介绍
list是链表,只不过官网给它重载一个模板,里面的节点可以满足多种,列如int
如果我们还是跟前面一样vector,string一样把Int重载为迭代器,那么这里iterator,解引用并不能得到节点里面的数据,只能得到节点,所以我们要用类lierator封装节点。
节点的类
先把节点的pre,next,数据,构造给封装好
template<class T>//模板后面没有;struct list_node {list_node<T>* next;//指定类模板,什么类型都可以,如果不加T就只能是intlist_node<T>* pre;T data;//list_node(const T&val=T())//因为不知道node里面是什么类型,所以传参是跟vector一样,用匿名对象:next(nullptr),pre(nullptr),data(val){}};
迭代器的封装(把节点封装成一个迭代器)
++ –
self& operator++() {//返回迭代器前置++的结果,返回指针_node = _node->next;return *this;//this 是指向当前对象的指针,类型是 list_iterator*//*this 是当前对象的引用,类型是 list_iterator&}self operator++(int) {//node* temp(_node);类型与返回类型不匹配,要返回迭代器self temp(_node);_node = _node->next;return temp;}self& operator--() {//返回迭代器前置--的结果,返回指针_node = _node->pre;return *this;//this 对象的成员就是指针.}self operator--(int) {self temp(_node);_node = _node->pre;return temp;}
这里为什么有几个模板,因为后面要用到const,还有指针,下面解释
template<class T,class Ref,class f>//Ref有引用的意思struct list_iterator {using node = list_node<T>;using self = list_iterator<T,Ref,f>;node* _node;//迭代器封装的是一个节点的指针.//迭代器的构造假如用迭代器it去接受一个一个节点的指针,比如d.begin()list_iterator( node*node) {_node = node;}f operator->() {//返回节点的值return &(_node->data);//返回对象的指针}Ref operator*() {//返回节点的值return _node->data;}self& operator++() {//返回迭代器前置++的结果,返回指针_node = _node->next;return *this;//this 是指向当前对象的指针,类型是 list_iterator*//*this 是当前对象的引用,类型是 list_iterator&}self operator++(int) {//node* temp(_node);类型与返回类型不匹配,要返回迭代器self temp(_node);_node = _node->next;return temp;}self& operator--() {//返回迭代器前置--的结果,返回指针_node = _node->pre;return *this;//this 对象的成员就是指针.}self operator--(int) {self temp(_node);_node = _node->pre;return temp;}/*bool operator!=(const node&node) {return _node != node;}*///我开始写迭代器跟节点比较bool operator!=(const self& other) {return _node != other._node;}bool operator==(const self& other) {return _node == other._node;}};
this 就是对象的指针,*this返回对象。
1. list 的构造
1.1官网的构造
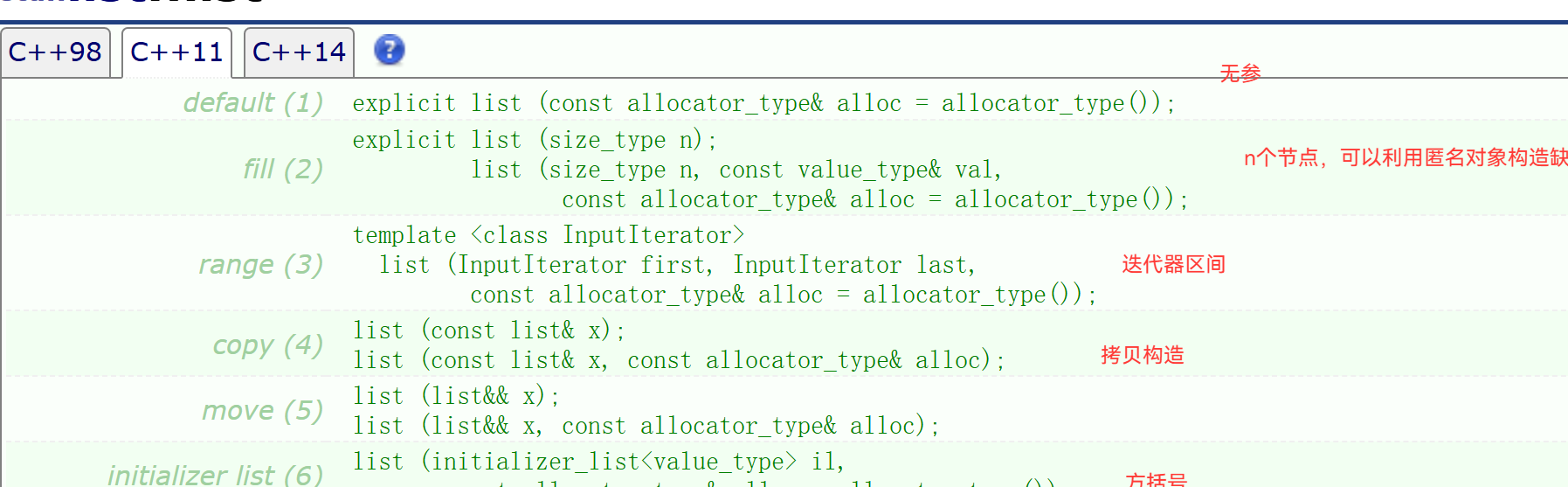
1.1.1无参构造
无参构造就是初始化一个哨兵节点出来
void emptylist() {_head = new Node();_head->next = _head;_head->pre = _head;}list() {emptylist();}先要把begin,和end 实现出来,再来实现其他构造
iterator begin() {/*return _head->next;*///这里有隐式转换,如果你不想隐士类型转换,需要在iterator()前面加个explict;return iterator(_head->next);}iterator end() {//return _head;return iterator(_head);//结尾就是头节点。}const_iterator begin()const {/*return _head->next;*///这里有隐式转换,如果你不想隐士类型转换,需要在iterator()前面加个explict;return const_iterator(_head->next);}const_iterator end()const {//return _head;return const_iterator(_head);}
1.1.2迭代器的区间构造
template<class InputIterator>list(InputIterator first, InputIterator last) {emptylist();while (first != last) {push_back(*first);first++;}}
注意我们必须先初始化一个头节点,不然的话,会出错
1.1.3现代写法的构造
list(list<T>& d) {emptylist();list<T> temp(d.begin(), d.end());//先利用迭代器区间构造出一个temp,再交换swap(temp);}list<T>& operator=(list<T> temp) {emptylist();swap(temp);return *this;}void swap(list<T>& temp) {std::swap(this->_head, temp._head);std::swap(this->_size, temp._size);}
2.插入和删除
官网的插入

官网删除

官网这里利用迭代器,erase这个返回要,它返回的是下个节点,很好用
插入
void insert(iterator pos,const T&val) {Node* pre = pos._node->pre;//因为这里迭代器封装的节点,所以对象可以直接访问node。Node* newnode = new Node(val);newnode->pre = pre;newnode->next = pos._node;//原本写成_node->next;导致循环.pre->next = newnode;pos._node->pre = newnode;++_size;}
删除
iterator erase(iterator pos) {Node* pre = pos._node->pre;Node* next = pos._node->next;pre->next = next;next->pre = pre;delete pos._node;//return iterator(pos._node->next)//原来删除了pos,再访问出现了错误。return iterator(next);--_size;}这个千万别用pos访问下个节点,因为pos的节点已经删除,再访问出现错误,先用next保存起来
头插和头删
这里可以直接复用,不用自己实现,复用insert和erase,只需要我们把pos迭代器的位置改变
void push_front(const T&val) {insert(begin(), val);}void pop_front() {erase(begin());}
尾插和尾删
- 要注意尾删,传end的前一个节点,要用前置–,后置–的返回值没有变,直接删除了头节点,然后删除必然出现错误
void push_back(const T& val) {/* Node* newnode = new Node(val);Node* cur = _head->pre;cur->next = newnode;newnode->next = _head;newnode->pre = cur;_head->pre = newnode;*/insert(end(), val);}void pop_back() {/* Node*pre= _head->pre->pre;_head->pre = pre;pre->next = _head;*/erase(--end());//原本写的后置--,导致返回一直是头节点,}析构和清除数据
- clear只是清楚其他节点,除了头节点
- 析构头节点也要清除
~list() {clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}//清除数据void clear() {iterator it = begin();while (it != end()) {it=erase(it);//这里不能用it++,因为这里pos已经删除,再用会出现迭代器失效的问题。}}
重点:为什么多个模板
void print(const jcm::list<T>& d) {for (auto& e : d) {std::cout << e << " ";}
}
- 我们在实现这个const对象的输出时,const对象必须调用const函数,然后范围for,需要迭代器++,–*,还要begin(),end(),d对象的begin()和end()需要const函数
- 然后const 函数,修饰的对象也是const,调用begin(),返回的迭代器也是也应该是const迭代器,const迭代器☞的是其迭代器指向的类容不能修改。
解决方法
- 我们可以还是一个迭代器模板,但是两个一样的iterator类,只是里面重载的operator返回值不一样在operator,一个返回T&,一个返回const T&.但是这样代码太冗杂了。
- 就跟上面代码一样迭代器类有两个模板,ref意思引用模板,
迭代器类里面
using node = list_node<T>;using self = list_iterator<T,Ref,f>;
list的对迭代器的使用,它控制上面迭代器模板的类型,我们这里需要什么,是T,还是constT,上面就是什么类型
using iterator = list_iterator<T,T&,T*>; using const_iterator = list_iterator<T, const T&,const T*>;
就拿迭代器遍历疏通一遍
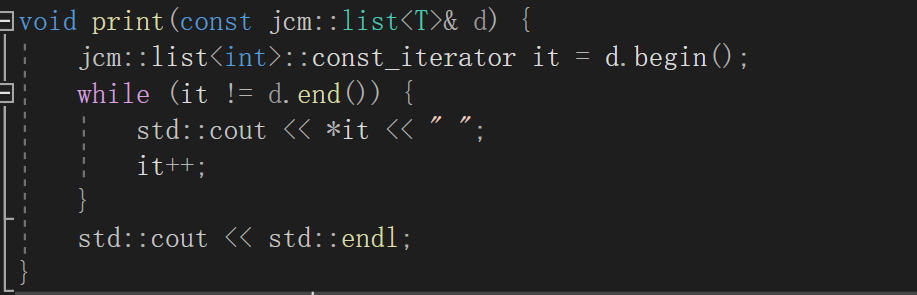
const对象d需要调用const函数,返回const_iterator迭代器,const 迭代器不是迭代器本身不能修改,而是指向的内容不能修改,返回的operator*不能修改所以就是const T&
当节点是自定义类型应该怎么办
void list_test05() {struct A {int _a1;int _a2;};jcm::list<A> d1;d1.push_back({ 1,2 });d1.push_back({ 2,3 });d1.push_back({ 3,4 });//for (auto& e : d1) {// //std::cout << e << std::endl;因为编译器不知道怎么A类对象的节点输出,struct没有重载流插入// std::cout << e._a1 << " " << e._a2 << std::endl;//}jcm::list<A>::iterator it = d1.begin();//it是迭代器,所以调用迭代器里面的->while (it != d1.end()) {std::cout << it->_a1 << " :" << it->_a2;//这里it.operator()->->a1_a1;为了方便可以可以读性。it++;}
}
由于自定义这种没有重载<<,所以不能直接读取,除了通过对象访问,我们还可以通过迭代器,迭代器的底层是指针
f operator->() {return &(_node->data);//返回对象的指针}
由于要返回指针,所以我们需要多出第三个模板,using iterator = list_iterator<T,T&,T*>; 所以迭代器是T*,f返回类型就是对应数据类型的指针,因为节点是自定义节点。这里显示的是it,operator()->->_a1,先调用,返回数据类型的指针,再通过指针指向数据输出
总代码(副有注释)
.h
#include<iostream>
#include<initializer_list>namespace jcm {template<class T>//模板后面没有;struct list_node {list_node<T>* next;//指定类模板,什么类型都可以,如果不加T就只能是intlist_node<T>* pre;T data;//list_node(const T&val=T())//因为不知道node里面是什么类型,所以传参是跟vector一样,用匿名对象:next(nullptr),pre(nullptr),data(val){}};template<class T,class Ref,class f>//Ref有引用的意思struct list_iterator {using node = list_node<T>;using self = list_iterator<T,Ref,f>;node* _node;//迭代器封装的是一个节点的指针.//迭代器的构造假如用迭代器it去接受一个一个节点的指针,比如d.begin()list_iterator( node*node) {_node = node;}f operator->() {return &(_node->data);//返回对象的指针}Ref operator*() {//返回节点的值return _node->data;}self& operator++() {//返回迭代器前置++的结果,返回指针_node = _node->next;return *this;//this 是指向当前对象的指针,类型是 list_iterator*//*this 是当前对象的引用,类型是 list_iterator&}self operator++(int) {//node* temp(_node);类型与返回类型不匹配,要返回迭代器self temp(_node);_node = _node->next;return temp;}self& operator--() {//返回迭代器前置--的结果,返回指针_node = _node->pre;return *this;//this 对象的成员就是指针.}self operator--(int) {self temp(_node);_node = _node->pre;return temp;}/*bool operator!=(const node&node) {return _node != node;}*///我开始写迭代器跟节点比较bool operator!=(const self& other) {return _node != other._node;}bool operator==(const self& other) {return _node == other._node;}};template<class T>class list {size_t _size=0;public:using Node = list_node<T>;using iterator = list_iterator<T,T&,T*>; using const_iterator = list_iterator<T, const T&,const T*>;Node* _head;//用public因为外面还要访问node;void emptylist() {_head = new Node();_head->next = _head;_head->pre = _head;}list() {emptylist();}//list(list<T>& d) {//可以不要T,在类里面这是一种简便方法传统方法// emptylist();// for (auto& e : d) {// push_back(e);// }//}list(std::initializer_list<T> il) {//这个还有stdemptylist();//先必须搞一个哨兵节点出来for (auto& e : il) {push_back(e);}}template<class InputIterator>list(InputIterator first, InputIterator last) {emptylist();while (first != last) {push_back(*first);first++;}}list(size_t n,const T&val=T()) {emptylist();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {push_back(val);}}list(int n, const T& val = T()) {emptylist();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {push_back(val);}}list(list<T>& d) {emptylist();list<T> temp(d.begin(), d.end());swap(temp);}list<T>& operator=(list temp) {//类里面可以直接写类名,不用写模板。emptylist();swap(temp);return *this;}void swap(list<T>& temp) {std::swap(this->_head, temp._head);std::swap(this->_size, temp._size);}~list() {clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}//清除数据void clear() {iterator it = begin();while (it != end()) {it=erase(it);//这里不能用it++,因为这里pos已经删除,再用会出现迭代器失效的问题。}}void push_back(const T& val) {/* Node* newnode = new Node(val);Node* cur = _head->pre;cur->next = newnode;newnode->next = _head;newnode->pre = cur;_head->pre = newnode;*/insert(end(), val);}void pop_back() {/* Node*pre= _head->pre->pre;_head->pre = pre;pre->next = _head;*/erase(--end());//原本写的后置--,导致返回一直是头节点,}void push_front(const T&val) {insert(begin(), val);}void pop_front() {erase(begin());}void insert(iterator pos,const T&val) {Node* pre = pos._node->pre;Node* newnode = new Node(val);newnode->pre = pre;newnode->next = pos._node;//原本写成_node->next;导致循环.pre->next = newnode;pos._node->pre = newnode;++_size;}iterator erase(iterator pos) {Node* pre = pos._node->pre;Node* next = pos._node->next;pre->next = next;next->pre = pre;delete pos._node;//return iterator(pos._node->next)//原来删除了pos,再访问出现了错误。return iterator(next);--_size;}iterator begin() {/*return _head->next;*///这里有隐式转换,如果你不想隐士类型转换,需要在iterator()前面加个explict;return iterator(_head->next);}iterator end() {//return _head;return iterator(_head);}const_iterator begin()const {/*return _head->next;*///这里有隐式转换,如果你不想隐士类型转换,需要在iterator()前面加个explict;return const_iterator(_head->next);}const_iterator end()const {//return _head;return const_iterator(_head);}size_t size() {return _size;}
};}.test
#include"list.h"
template<class T>
void print(const jcm::list<T>& d) {jcm::list<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin();while (it != d.end()) {std::cout << *it << " ";it++;}std::cout << std::endl;
}
void list_test01() {jcm::list<int> d1;d1.push_back(1);d1.push_back(2);d1.push_back(3);d1.push_back(4);for (auto& e :d1) {std::cout << e << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;d1.pop_back();d1.pop_back();d1.pop_back();for (auto& e : d1) {std::cout << e << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;d1.push_front(-2);d1.push_front(-3);d1.push_front(-1);for (auto& e : d1) {std::cout << e << " ";}d1.clear();for (auto& e : d1) {std::cout << e << " ";}
}void list_test02() {jcm::list<int> d1={ 1,2,3,4,5 };for (auto& e : d1) {std::cout << e << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;jcm::list<int> d2(d1.begin(), d1.end());for (auto& e : d2) {std::cout << e << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;jcm::list<int > d3(5, 3);for (auto& e : d3) {std::cout << e << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;jcm::list<int> d4(d3);for (auto& e : d4) {std::cout << e << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;std::cout << d4.size() << std::endl;
}void list_test04() {jcm::list<int> d1 = { 1,2,3,4 };jcm::list<int> d2(d1);for (auto& e : d2) {std::cout << e << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;jcm::list<int> d3 = { 4,5,6,7 };d1 = d3;for (auto& e : d1) {std::cout << e << " ";}print(d3);
}
void list_test05() {struct A {int _a1;int _a2;};jcm::list<A> d1;d1.push_back({ 1,2 });d1.push_back({ 2,3 });d1.push_back({ 3,4 });//for (auto& e : d1) {// //std::cout << e << std::endl;因为编译器不知道怎么A类对象的节点输出,struct没有重载流插入// std::cout << e._a1 << " " << e._a2 << std::endl;//}jcm::list<A>::iterator it = d1.begin();//it是迭代器,所以调用迭代器里面的->while (it != d1.end()) {std::cout << it->_a1 << " :" << it->_a2;//这里it.operator()->->a1_a1;为了方便可以可以读性。it++;}
}int main() {//list_test01();list_test04();
}