深度学习6-激活函数-参数初始化和正则化-搭建神经网络-损失函数
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档
文章目录
- 前言
- 1. 激活函数
- 1.1 Sigmoid函数
- 1.2 Tanh函数
- 1.3 ReLU函数
- 1.4 Softmax函数
- 2. 参数初始化和正则化
- 2.1 全连接层(nn.Linear)--线性层
- 2.2 常数初始化
- 2.3 秩初始化
- 2.4 正态分布初始化
- 2.5 均匀分布初始化
- 2.6 Xavier初始化(Glorot初始化)
- 2.7 He初始化(Kaiming初始化)
- 2.8 Dropout随机失活
- 3. 搭建神经网络
- 3.1 自定义模型
- 3.2 查看模型参数
- 3.3 查看模型结构和参数数量
- 3.4 device设置
- 3.5 使用Sequential构建模型
- 4. 损失函数
- 4.1 二分类任务损失函数
- 4.2 多分类任务损失函数
- 4.3 回归任务损失函数
- 4.4 损失函数综合测试
- 总结
前言
用PyTorch进行深度学习
1. 激活函数
上一节用的线性回归都没有使用激活函数这种
1.1 Sigmoid函数
PyTorch中已经实现了神经网络中可能用到的各种激活函数,我们在代码中只要直接调用即可。
表示二分类概率
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltx = torch.linspace(-10, 10, 1000, requires_grad=True)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2)
fig.set_size_inches(12, 4)ax[0].plot(x.data, torch.sigmoid(x).data, "purple")
ax[0].set_title("sigmoid(x)")
ax[0].spines["top"].set_visible(False)#上边界不可见
ax[0].spines["right"].set_visible(False)
ax[0].spines["left"].set_position("zero")#左边界放在0的位置
ax[0].spines["bottom"].set_position("zero")
ax[0].axhline(0.5, color="gray", alpha=0.7, linewidth=1)#画横线
ax[0].axhline(1, color="gray", alpha=0.7, linewidth=1)torch.sigmoid(x).sum().backward() # 反向传播计算梯度
ax[1].plot(x.data, x.grad, "purple")
ax[1].set_title("sigmoid'(x)")
ax[1].spines["top"].set_visible(False)
ax[1].spines["right"].set_visible(False)
ax[1].spines["left"].set_position("zero")
ax[1].spines["bottom"].set_position("zero")
ax[1].set_ylim(0, 0.3)plt.show()
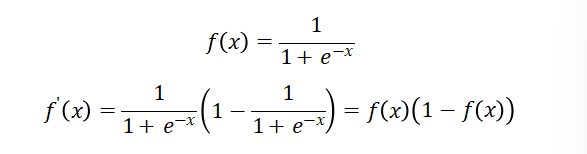
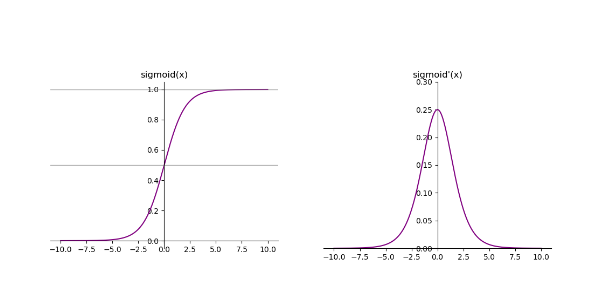
1.2 Tanh函数
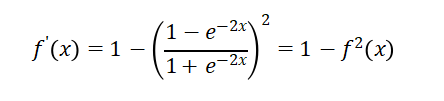
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltx = torch.linspace(-5, 5, 1000, requires_grad=True)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2)
fig.set_size_inches(12, 4)ax[0].plot(x.data, torch.tanh(x).data, "purple")
ax[0].set_title("tanh(x)")
ax[0].spines["top"].set_visible(False)
ax[0].spines["right"].set_visible(False)
ax[0].spines["left"].set_position("zero")
ax[0].spines["bottom"].set_position("zero")
ax[0].axhline(-1, color="gray", alpha=0.7, linewidth=1)
ax[0].axhline(1, color="gray", alpha=0.7, linewidth=1)torch.tanh(x).sum().backward() # 反向传播计算梯度
ax[1].plot(x.data, x.grad, "purple")
ax[1].set_title("tanh'(x)")
ax[1].spines["top"].set_visible(False)
ax[1].spines["right"].set_visible(False)
ax[1].spines["left"].set_position("zero")
ax[1].spines["bottom"].set_position("zero")plt.show()
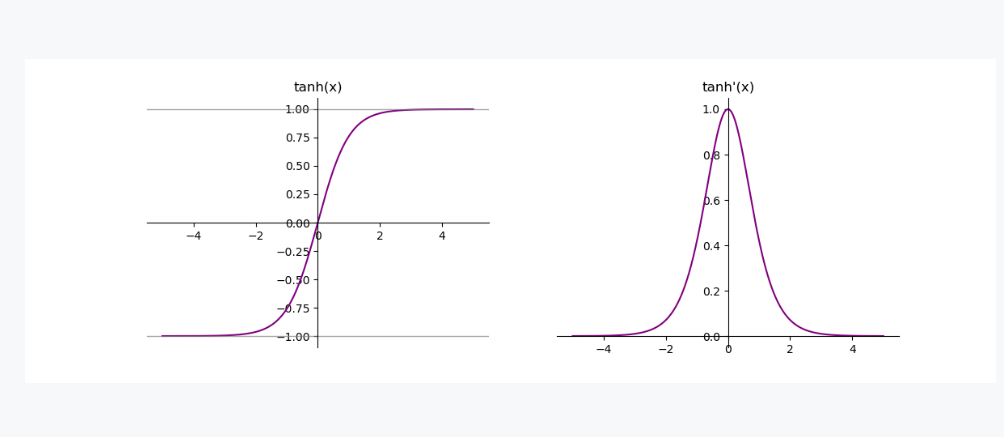
这两个函数在反向传播的时候,都容易出现梯度消失的情况,都是用于二分类
1.3 ReLU函数
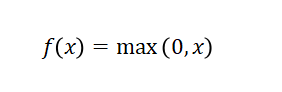

import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltx = torch.linspace(-5, 5, 1000, requires_grad=True)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2)
fig.set_size_inches(12, 4)ax[0].plot(x.data, torch.relu(x).data, "purple")
ax[0].set_title("relu(x)")
ax[0].spines["top"].set_visible(False)
ax[0].spines["right"].set_visible(False)
ax[0].spines["left"].set_position("zero")
ax[0].spines["bottom"].set_position("zero")torch.relu(x).sum().backward() # 反向传播计算梯度
ax[1].plot(x.data, x.grad, "purple")
ax[1].set_title("relu'(x)")
ax[1].spines["top"].set_visible(False)
ax[1].spines["right"].set_visible(False)
ax[1].spines["left"].set_position("zero")
ax[1].spines["bottom"].set_position("zero")plt.show()
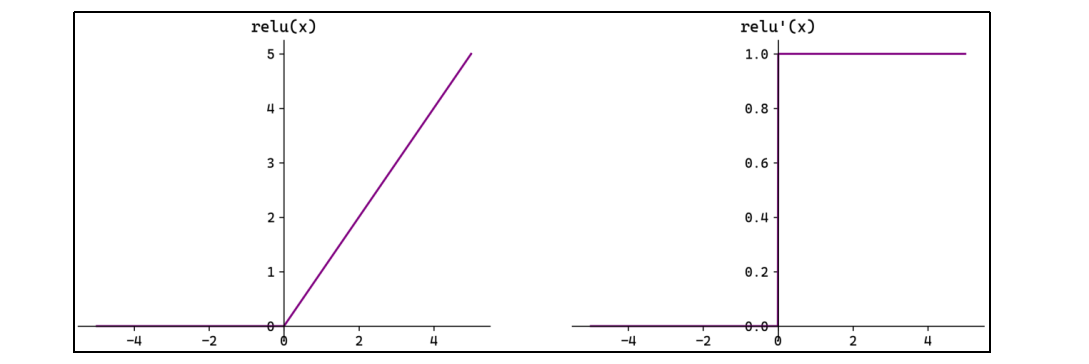
这个是用于回归问题,转换出来不变
1.4 Softmax函数
这个是用于多分类
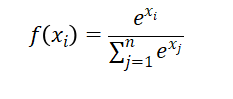
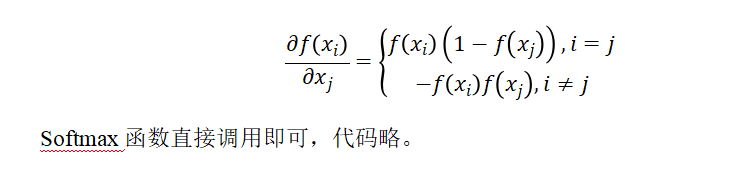
x = torch.randn(3,5)
print(x)

y = torch.softmax(x,dim=1)
print(y)

大的数概率就比较大了
2. 参数初始化和正则化
2.1 全连接层(nn.Linear)–线性层
在神经网络中,参数主要位于全连接层(仿射层Affine)中。
PyTorch提供了torch.nn模块,专门用于神经网络的构建和训练。其中全连接层被实现为Linear类,内部有两个属性:权重 weight和偏置bias;这就是神经网络的主要参数。
权重 weight和偏置bias–》要初始化好,不然一开始就训练不好
import torch.nn as nnlinear = nn.Linear(5, 2)
上面代码定义了一个有5个输入神经元、2个输出神经元的全连接层。
2.2 常数初始化
所有权重参数初始化为一个常数。
#定义一个全连接层
linear = nn.Linear(5,2)
#常数初始化
nn.init.zeros_(linear.weight)
print(linear.weight)

默认打开了requires_grad=True
nn.init.ones_(linear.bias)
print(linear.bias)
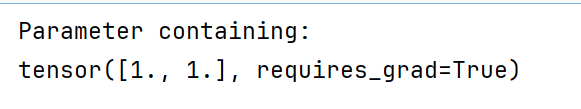
nn.init.constant_(linear.weight,10)
print(linear.weight)

发现变成2*5了
默认转置了,因为反向传播和前向传播的时候就要转置,所以就先转置了
2.3 秩初始化
nn.init.eye_(linear.weight)

2.4 正态分布初始化
nn.init.normal_(linear.weight,mean=0,std=0.1)

2.5 均匀分布初始化
nn.init.uniform_(linear.weight,a=-1,b=1)

2.6 Xavier初始化(Glorot初始化)
Xavier初始化根据输入和输出的神经元数量调整权重的初始范围,确保每一层的输出方差与输入方差相近。适用于Sigmoid和Tanh等激活函数,能有效缓解梯度消失或爆炸问题。

nn.init.xavier_normal_(linear.weight)
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(linear.weight)
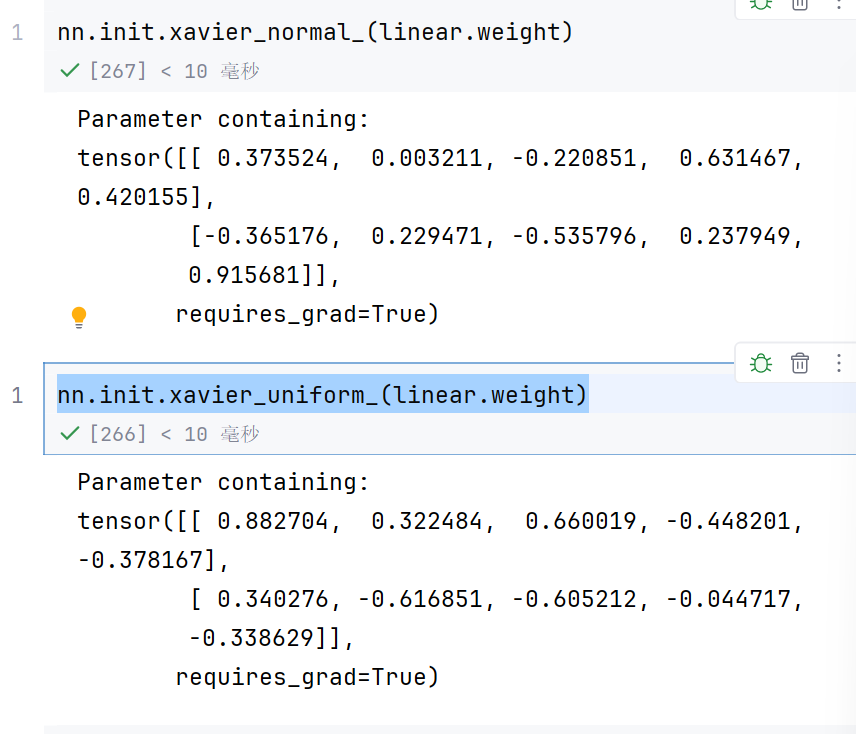
这个用于sigmoid,Ranh
2.7 He初始化(Kaiming初始化)
用于ReLU
He初始化根据输入的神经元数量调整权重的初始范围。主要适用于ReLU及其变体(如Leaky ReLU)激活函数。
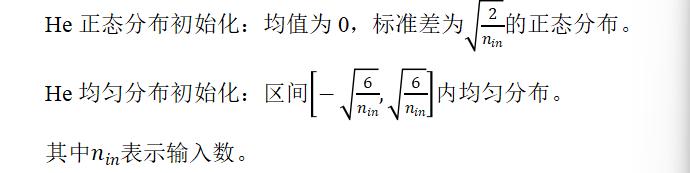
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(linear.weight)
nn.init.kaiming_uniform_(linear.weight)
2.8 Dropout随机失活
Dropout(随机失活,暂退法)是一种在学习的过程中随机关闭神经元的方法。
可以通过torch.nn.Dropout§来使用Dropout,并通过参数p来设置失活概率。
x = torch.randint(1,10,(10,))
#定义一个Dropout层
dropout = nn.Dropout(p=0.5)
y = dropout(x)
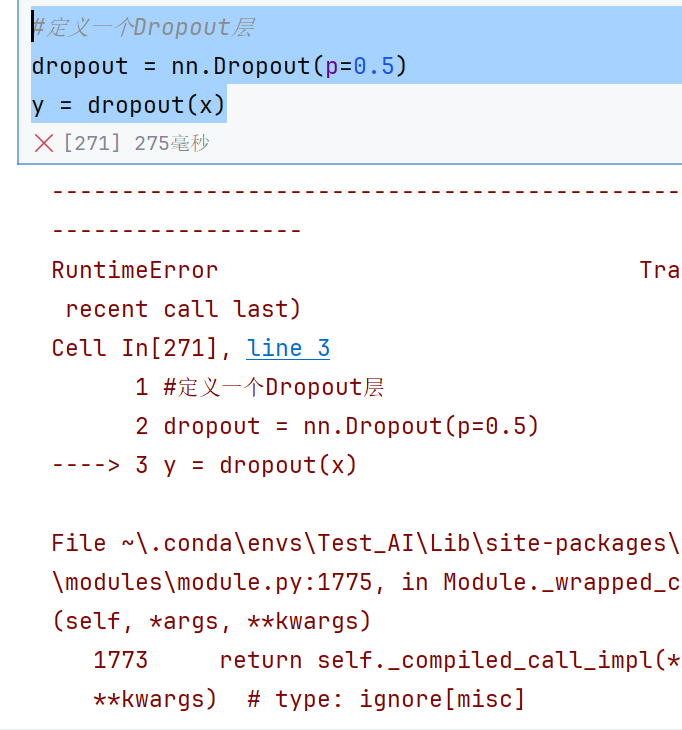
这里报错的原因主要是因为类型不匹配,要用float类型
x = torch.randint(1,10,(10,),dtype=torch.float32)
#定义一个Dropout层
dropout = nn.Dropout(p=0.5)
y = dropout(x)
print(x)
print(y)
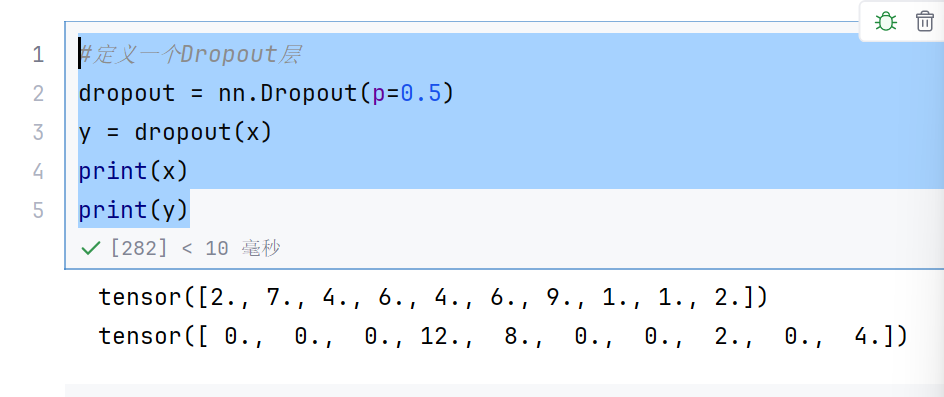
0表示关闭的神经元,没有关闭的神经元就放大为原来的两倍
3. 搭建神经网络
3.1 自定义模型
在神经网络框架中,由多个层组成的组件称之为 模块(Module)。
在PyTorch中模型就是一个Module,各网络层、模块也是Module。Module是所有神经网络的基类。
在定义一个Module时,我们需要继承torch.nn.Module并主要实现两个方法:
__init__:定义网络各层的结构,并初始化参数。
forward:根据输入进行前向传播,并返回输出。计算其输出关于输入的梯度,可通过其反向传播函数进行访问(通常自动发生)。forward方法是每次调用的具体实现。
接下来使用PyTorch实现下图的神经网络:
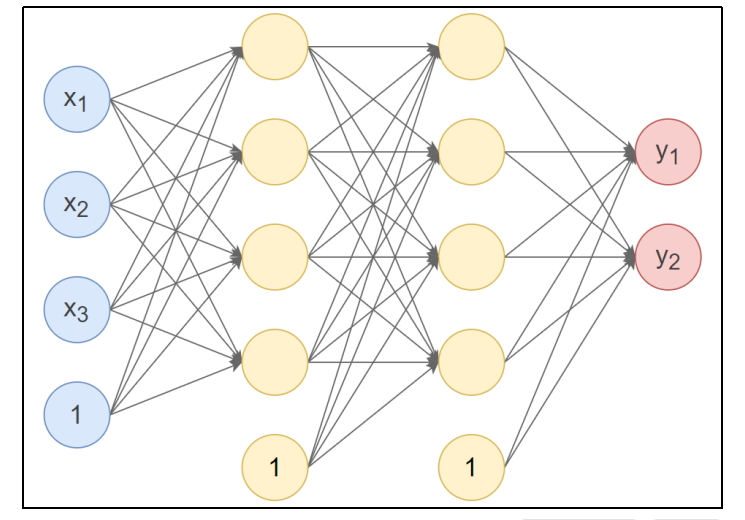
反向传播不需要定义,因为前向弄好了,反向就自动OK了
第1个隐藏层:使用Xavier正态分布初始化权重,激活函数使用Tanh。
第2个隐藏层:使用He正态分布初始化权重,激活函数使用ReLU。
输出层:按默认方式初始化,激活函数使用Softmax。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn#自定义神经网络类class Model(nn.Module):#初始化def __init__(self):super().__init__()#定义三个线性层self.linear1 = nn.Linear(3,4)# 线性层w和b的参数初始化nn.init.xavier_normal_(self.linear1.weight)self.linear2 = nn.Linear(4, 4)nn.init.kaiming_normal_(self.linear2.weight)self.out = nn.Linear(4, 2)# 前向传播def forward(self, x):x = self.linear1(x)x = torch.tanh(x)x = self.linear2(x)x = torch.relu(x)x = self.out(x)x = torch.softmax(x,dim=1)return x#测试,定义数据
model = Model()
x = torch.randn(10,3)
output = model(x)
print("神经网络输出",output)
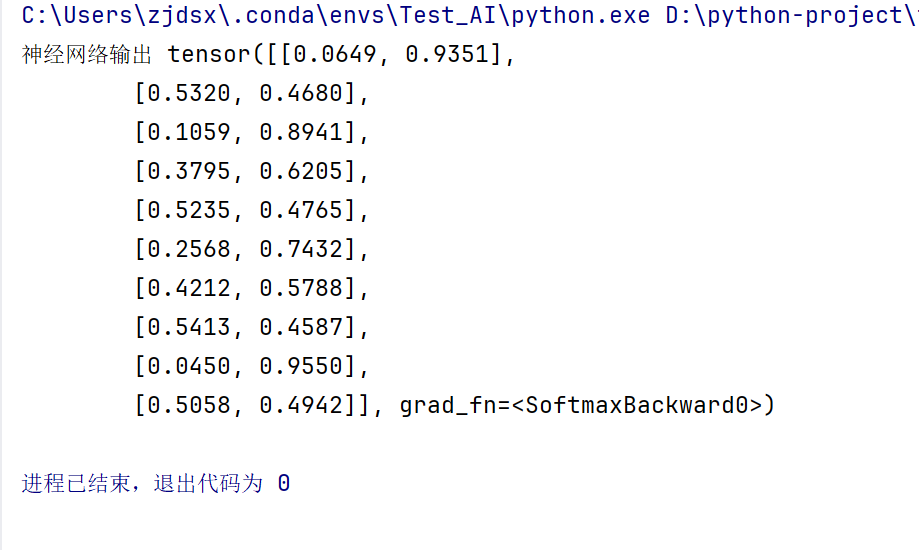
输入103,输出102,表示每个特征的概率
这个神经并没有训练模型的
3.2 查看模型参数
print(model.linear1.weight)
print(model.linear1.bias)
print(model.linear2.weight)
print(model.linear2.bias)
print(model.out.weight)
print(model.out.bias)
但是这样比较麻烦
for param in model.parameters():print(param)

但是还是不知道哪个层是哪个的
for param in model.named_parameters():print(param)
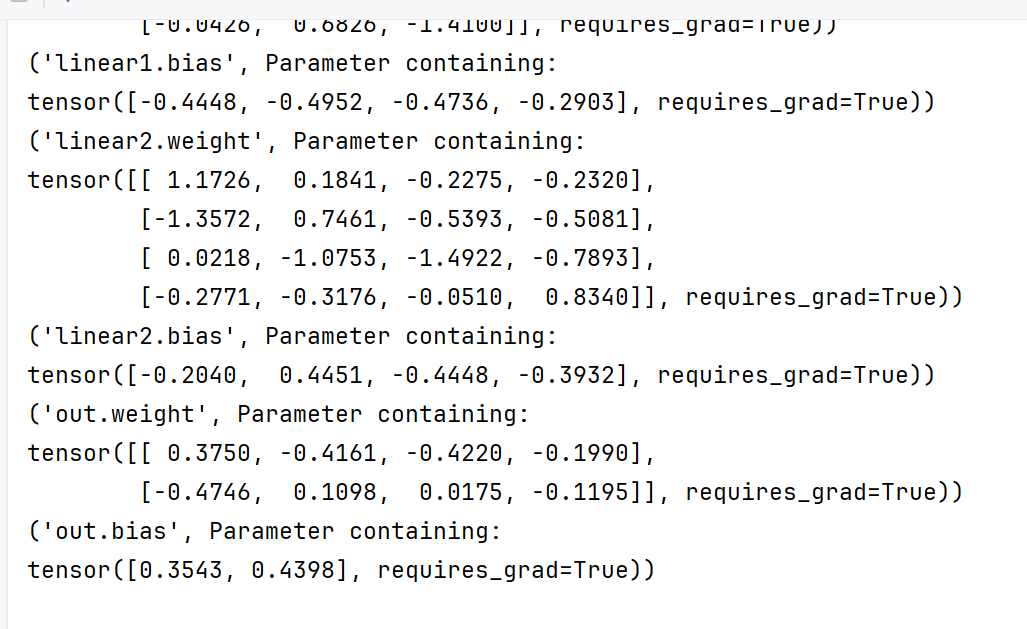
这样就知道谁是谁了
print(model.state_dict())

这个就是把模型参数用一个字典的形式存储,更加方便了
3.3 查看模型结构和参数数量
可使用torchsummary.summary来查看模型结构与参数数量。需要先安装torchsummary库:pip install torchsummary。
from torchsummary import summary
# input_size表示输入神经元个数为3---》特征个数
#batch_size表示个数,有多少个东西
# device表示使用cpu运行
summary(model,input_size=(3,),batch_size=10,device='cpu')
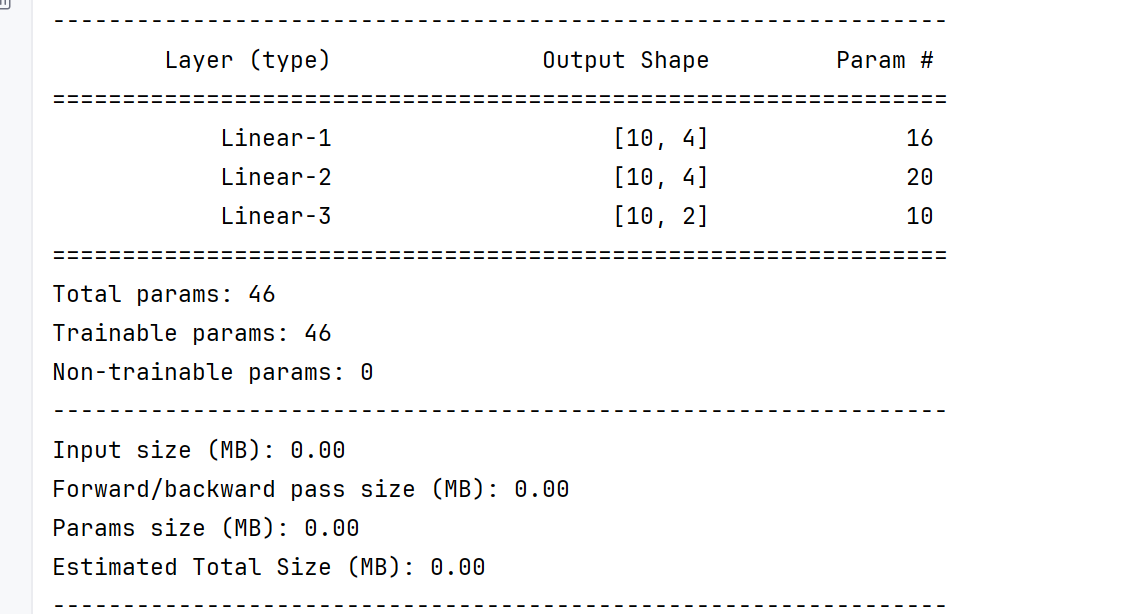
Param #表示每一层的参数个数
比如第一层
w为3*4
b为4
所以就是16个
1B就是10亿个参数
deepseek有671B个参数,满血版
3.4 device设置
cpu计算能力比gpu强
但是gpu对并行运算有架构优化
gpu=1000个小学生
cpu=1个博士生
同时去算10000道十以内数学题—》小学生胜利
gpu做简单任务—》快
cpu做复杂任务
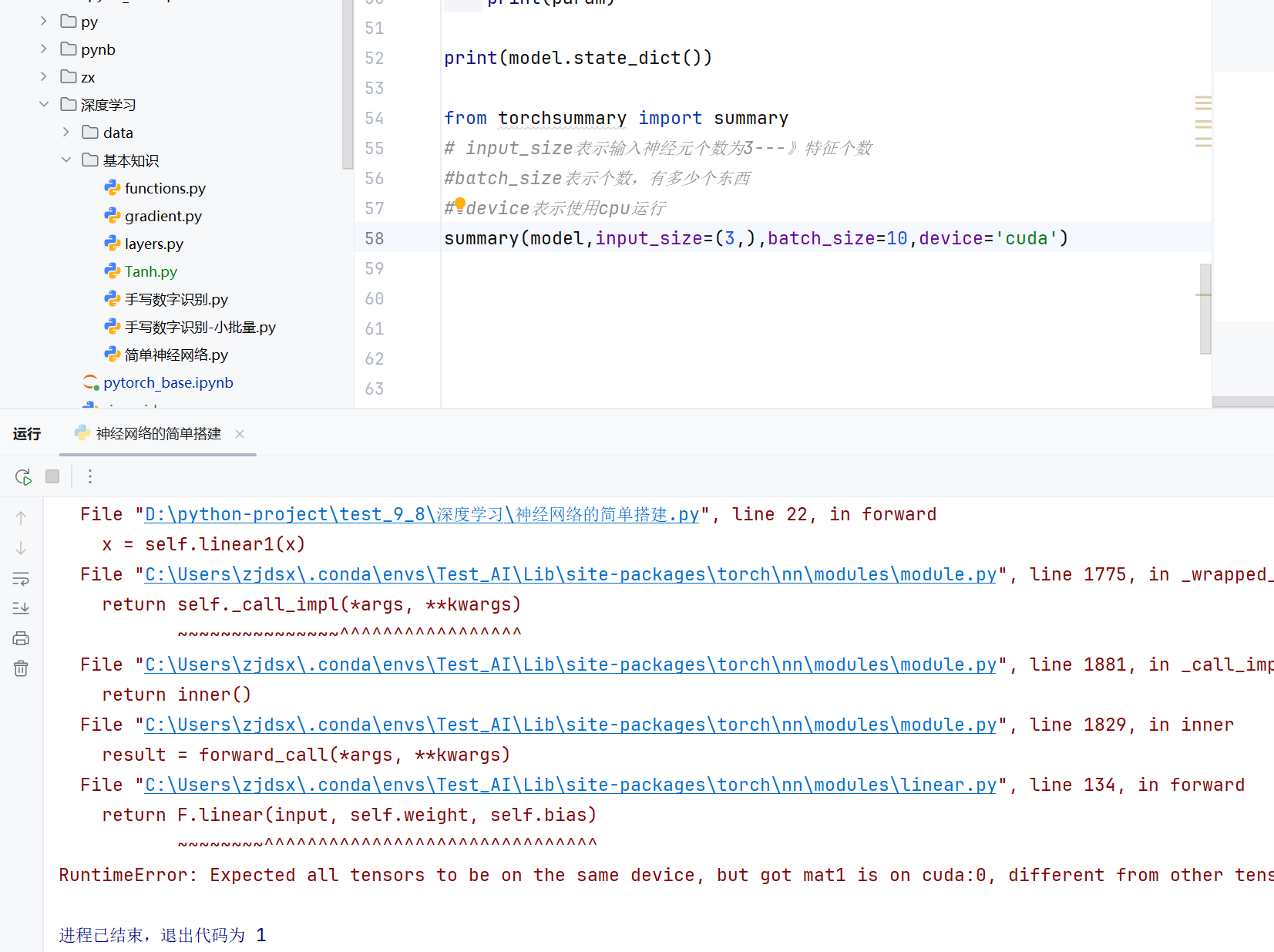
但是直接改为cuda,就报错了
因为前面的张量是在cpu上运行的
现在又在显卡上,gpu上运行—》不行
input = torch.randn(1,5,device='cuda')
print(input.device)

input = torch.randn(1,5,device='cuda').to(device='cpu')
print(input.device)
发现设备还可以转换的
import torch
import torch.nn as nn#自定义神经网络类class Model(nn.Module):#初始化def __init__(self):super().__init__()#定义三个线性层self.linear1 = nn.Linear(3,4,device='cuda')# 线性层w和b的参数初始化nn.init.xavier_normal_(self.linear1.weight)self.linear2 = nn.Linear(4, 4,device='cuda')nn.init.kaiming_normal_(self.linear2.weight)self.out = nn.Linear(4, 2,device='cuda')# 前向传播def forward(self, x):x = self.linear1(x)x = torch.tanh(x)x = self.linear2(x)x = torch.relu(x)x = self.out(x)x = torch.softmax(x,dim=1)return x#测试,定义数据
model = Model()
x = torch.randn(10,3,device='cuda')
output = model(x)
print("神经网络输出",output)print(model.linear1.weight)
print(model.linear1.bias)
print(model.linear2.weight)
print(model.linear2.bias)
print(model.out.weight)
print(model.out.bias)for param in model.parameters():print(param)for param in model.named_parameters():print(param)print(model.state_dict())from torchsummary import summary
# input_size表示输入神经元个数为3---》特征个数
#batch_size表示个数,有多少个东西
# device表示使用cpu运行
summary(model,input_size=(3,),batch_size=10,device='cuda')
这样给每一个类都弄上device就没有问题了—》张量和线性层
—》张量麻烦,因为有很多层
class Model(nn.Module):#初始化def __init__(self,device='cpu'):super().__init__()#定义三个线性层self.linear1 = nn.Linear(3,4,device=device)# 线性层w和b的参数初始化nn.init.xavier_normal_(self.linear1.weight)self.linear2 = nn.Linear(4, 4,device=device)nn.init.kaiming_normal_(self.linear2.weight)self.out = nn.Linear(4, 2,device=device)
#测试,定义数据
model = Model(device='cuda')
可以在构造函数那里指定device
#自定义神经网络类class Model(nn.Module):#初始化def __init__(self,device='cpu'):super().__init__()#定义三个线性层self.linear1 = nn.Linear(3,4,device=device)# 线性层w和b的参数初始化nn.init.xavier_normal_(self.linear1.weight)self.linear2 = nn.Linear(4, 4,device=device)nn.init.kaiming_normal_(self.linear2.weight)self.out = nn.Linear(4, 2,device=device)# 前向传播def forward(self, x):x = self.linear1(x)x = torch.tanh(x)x = self.linear2(x)x = torch.relu(x)x = self.out(x)x = torch.softmax(x,dim=1)return x#统一定义全景变量device
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'#测试,定义数据
model = Model(device=device)
x = torch.randn(10,3,device=device)
output = model(x)
print("神经网络输出",output)print(model.linear1.weight)
print(model.linear1.bias)
print(model.linear2.weight)
print(model.linear2.bias)
print(model.out.weight)
print(model.out.bias)for param in model.parameters():print(param)for param in model.named_parameters():print(param)print(model.state_dict())from torchsummary import summary
# input_size表示输入神经元个数为3---》特征个数
#batch_size表示个数,有多少个东西
# device表示使用cpu运行
summary(model,input_size=(3,),batch_size=10,device=device)
这样也是一样的,给一个全局变量
3.5 使用Sequential构建模型
可以通过torch.nn.Sequential来构建模型,将各层按顺序传入。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torchsummary import summary#定义数据
x = torch.randn(10,3)
#构建模型
model = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(3,4),nn.Tanh(),nn.Linear(4,4),nn.ReLU(),nn.Linear(4,2),nn.Softmax(dim=1),
)
#定义一个参数初始化函数
def init_params(layer):if isinstance(layer, nn.Linear):nn.init.xavier_uniform_(layer.weight)nn.init.constant_(layer.bias,0.1)#参数初始化
model.apply(init_params)#前向传播
output = model(x)
print(output)
summary(model,input_size=(3,),batch_size=10,device='cpu')
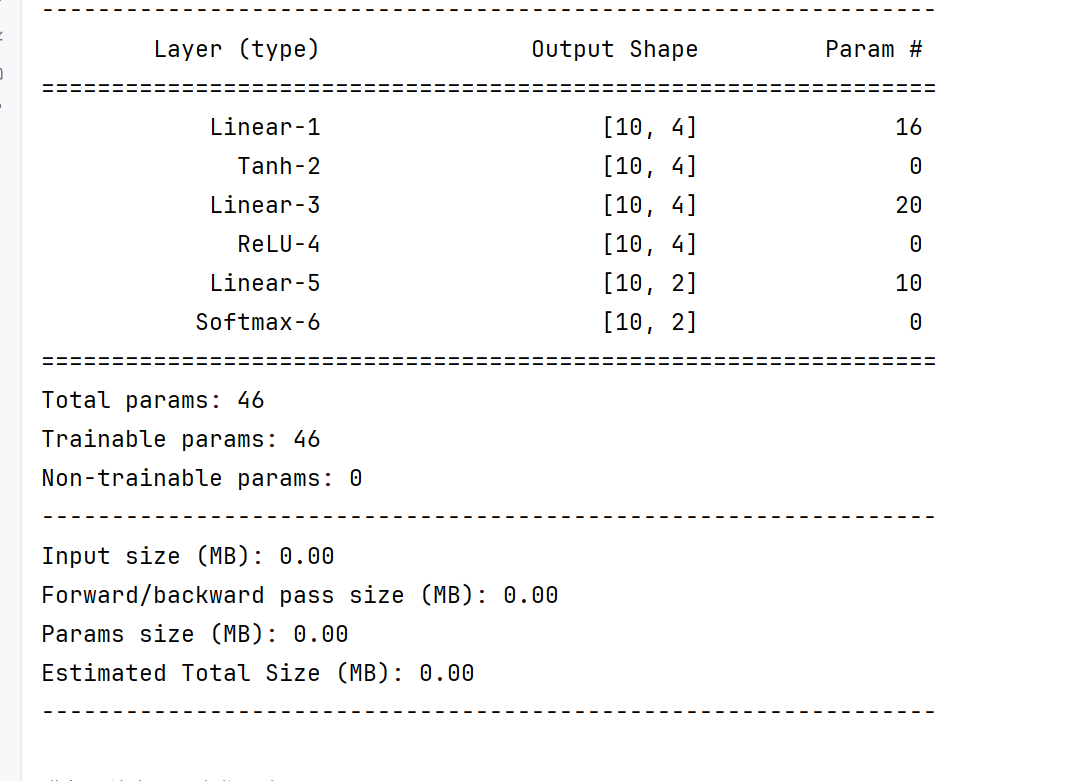
这样就把激活层都当做线性层了–》也可以
4. 损失函数
4.1 二分类任务损失函数

1)二分类任务损失函数
在PyTorch中可使用torch.nn.BCELoss实现:
#%%
#输入数据
input = torch.randn(3,2)
print(input)

#目标值
target = torch.tensor([[0,1],[1,0],[0,1]],dtype=torch.float)
因为后面会进行运算,所以要用浮点数
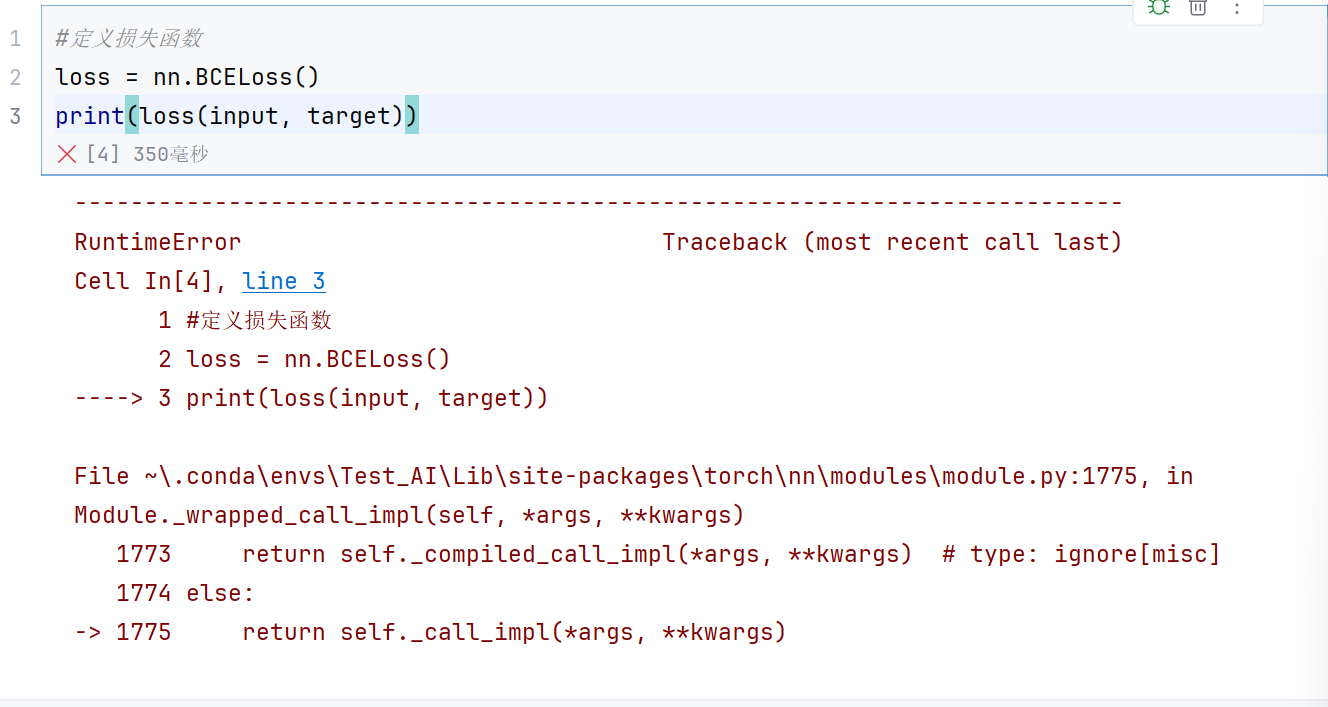
这样肯定是不行的,因为input不是预测1的概率值
#输入数据
input = torch.randn(3,2)
print(input)
pred = torch.sigmoid(input)
print(pred)

因为sigmoid生成的就是0~1,所以可以用它来生成预测值
#定义损失函数
loss = nn.BCELoss()
print(loss(pred, target))

4.2 多分类任务损失函数
2)多分类任务损失函数
多分类任务常用多类交叉熵损失函数(Categorical Cross-Entropy Loss)。它是对每个类别的预测概率与真实标签之间差异的加权平均。

在PyTorch中可使用torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss 实现:
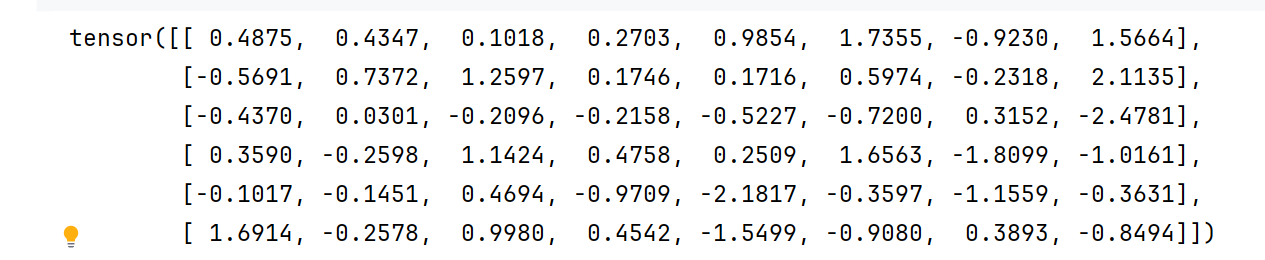
input = torch.randn(6,8)
print(input)
#目标值,6个数据的类别标签
target = torch.tensor([1,0,3,7,5,2])
pred = torch.softmax(input,dim=1)
print(pred)
#定义损失函数
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
print(loss(pred, target))

#定义损失函数
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
print(loss(input, target))

我们还可以直接传入input—》因为这个函数进行处理的了
注意:调用torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss相当于调用了torch.nn.LogSoftmax之后再调用torch.nn.NLLLoss。即使用CrossEntropyLoss时上一层的输出不需要Softmax激活函数,因为该损失函数内会自动处理。
8指的是8个类别
pred是预测的每个类别的概率
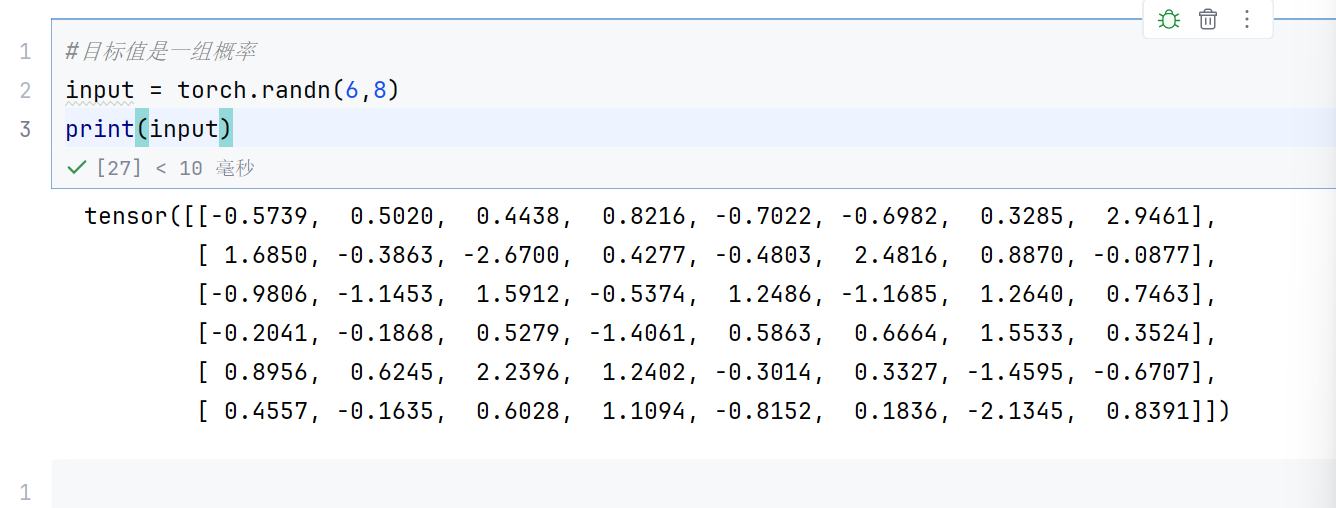
目标值是一组概率
target = torch.randn(6,8).softmax(dim=1)
print(input)
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
print(loss(input, target))
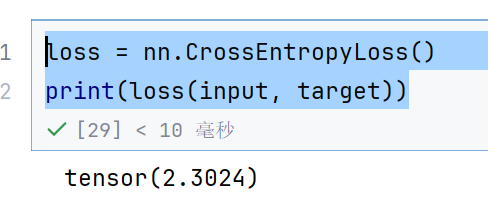
所以目标值是概率值还是类别标签都是可以计算的
4.3 回归任务损失函数
1)MAE
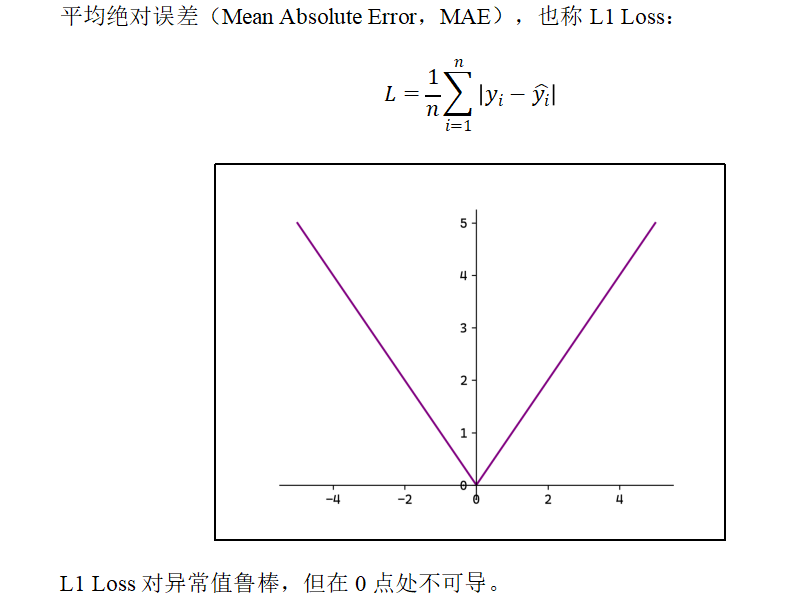
2)MSE
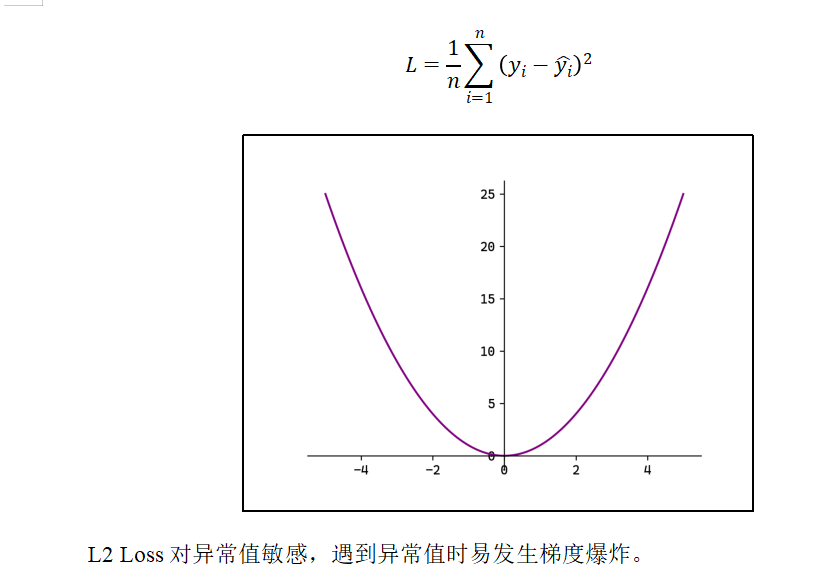
3)Smooth L1
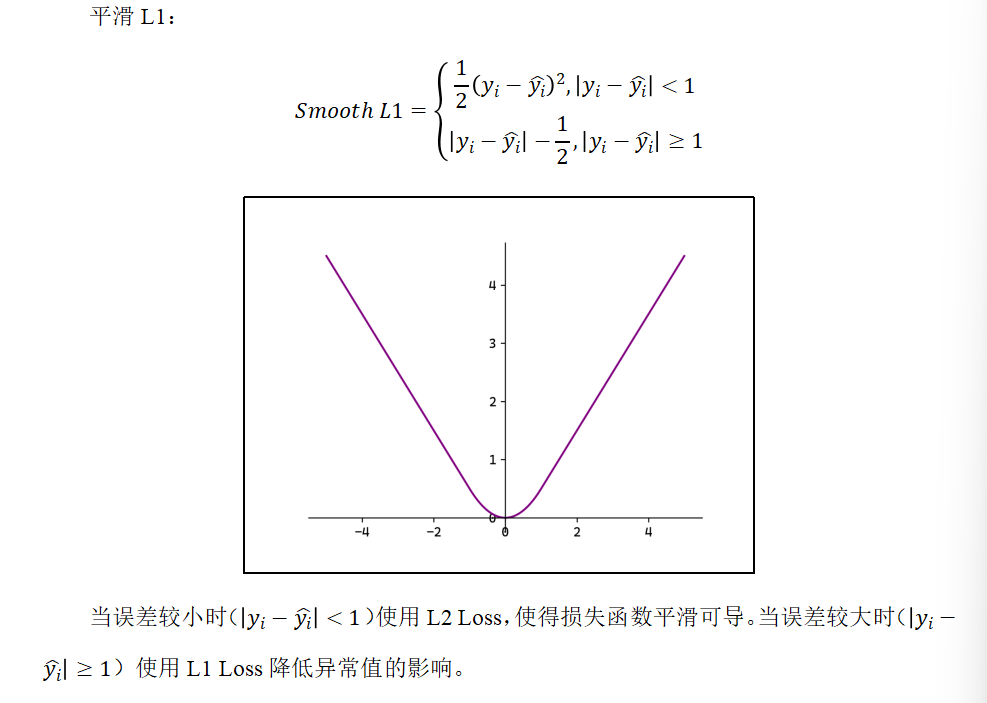
#回归
input = torch.randn(3,5)
target = torch.randn(3,5)
mse_loss = nn.MSELoss()
mse_loss = mse_loss(input, target)
print(mse_loss)
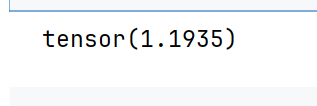
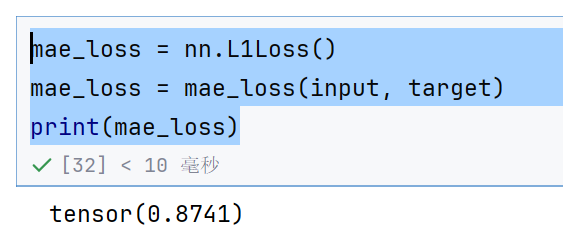
mae_loss = nn.L1Loss()
mae_loss = mae_loss(input, target)
print(mae_loss)
smooth_l1_loss = nn.SmoothL1Loss()
loss = smooth_l1_loss(input, target)
print(loss)

4.4 损失函数综合测试
import torch
from torch import nn,optim#定义模型
class Model(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super().__init__()#只定义一个全连接层---》线性层self.linear = nn.Linear(5,3)#权值初始化self.linear.weight.data = torch.tensor([[0.1,0.2,0.3],[0.4,0.5,0.6],[0.7,0.8,0.9],[1.0,1.1,1.2],[1.3,1.4,1.5],]).Tself.linear.bias.data = torch.tensor([1.0,2.0,3.0])def forward(self, x):return self.linear(x)return x#输入数据2*5
X = torch.tensor([[1,2,3,4,5],[6,7,8,9,10]],dtype=torch.float32)
#目标值2*3
target = torch.tensor([[0,0,0],[0,0,0]],dtype=torch.float32)
#创建模型
model = Model()
#前向传播
output = model(X)
#定义损失函数
loss = nn.MSELoss()
loss_value = loss(output, target)#反向传播计算梯度
loss_value.backward()# 定义优化器
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
#更新参数w和b
optimizer.step()
# 清除梯度,再次迭代
optimizer.zero_grad()#打印模型参数
for param in model.state_dict():print(param)print(model.state_dict()[param])

