OCR文字识别前沿:PaddleOCR/DBNet++的端到端文本检测与识别
人们眼中的天才之所以卓越非凡,并非天资超人一等而是付出了持续不断的努力。1万小时的锤炼是任何人从平凡变成超凡的必要条件。———— 马尔科姆·格拉德威尔

🌟 Hello,我是Xxtaoaooo!
🌈 “代码是逻辑的诗篇,架构是思想的交响”
在当今数字化浪潮中,OCR(光学字符识别)技术已成为连接物理世界与数字世界的重要桥梁。从传统的文档数字化到现代的智能场景理解,OCR技术的演进见证了人工智能在计算机视觉领域的突破性进展。本文将深入探讨当前OCR领域的两大前沿技术:PaddleOCR和DBNet++,从技术原理到实际应用,全面解析端到端文本检测与识别的完整解决方案。
PaddleOCR作为百度开源的OCR工具库,以其轻量化、高精度和多语言支持的特点,在工业界获得了广泛应用。其采用的PP-OCR系列模型通过精心设计的网络架构和训练策略,在保持高精度的同时大幅降低了模型复杂度。而DBNet++作为文本检测领域的重要突破,通过可微分二值化技术解决了传统方法在文本边界处理上的痛点,实现了更加精确的文本区域定位。
这两项技术的结合代表了OCR系统从传统的多阶段处理向端到端优化的重要转变。传统OCR系统往往将文本检测和识别作为独立的模块进行优化,而现代方法则追求全局最优的端到端训练策略。本文将通过详细的技术分析、代码实现和性能对比,帮助读者理解这一技术演进的内在逻辑,并掌握在实际项目中部署和优化这些先进技术的方法。
一、OCR技术发展脉络与核心挑战
1.1 传统OCR到深度学习OCR的演进
OCR技术的发展经历了从规则驱动到数据驱动的根本性转变。早期的OCR系统主要依赖手工设计的特征提取器和分类器,对字体、背景和图像质量有严格要求。
# 传统OCR特征提取示例
import cv2
import numpy as npclass TraditionalOCRFeatures:def __init__(self):self.features = []def extract_hog_features(self, image):"""提取HOG特征"""# 图像预处理gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)resized = cv2.resize(gray, (64, 128))# HOG特征提取hog = cv2.HOGDescriptor()features = hog.compute(resized)return features.flatten()def extract_lbp_features(self, image):"""提取LBP纹理特征"""gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)# LBP特征计算radius = 3n_points = 8 * radiuslbp = self._local_binary_pattern(gray, n_points, radius)# 计算直方图hist, _ = np.histogram(lbp.ravel(), bins=n_points + 2, range=(0, n_points + 2))return hist / hist.sum() # 归一化def _local_binary_pattern(self, image, n_points, radius):"""LBP算法实现"""# 简化的LBP实现rows, cols = image.shapelbp_image = np.zeros_like(image)for i in range(radius, rows - radius):for j in range(radius, cols - radius):center = image[i, j]binary_string = ''# 8邻域比较neighbors = [image[i-1, j-1], image[i-1, j], image[i-1, j+1],image[i, j+1], image[i+1, j+1], image[i+1, j],image[i+1, j-1], image[i, j-1]]for neighbor in neighbors:binary_string += '1' if neighbor >= center else '0'lbp_image[i, j] = int(binary_string, 2)return lbp_image
上述代码展示了传统OCR中常用的HOG和LBP特征提取方法。这些手工设计的特征虽然在特定场景下表现良好,但泛化能力有限,难以处理复杂的自然场景文本。
1.2 深度学习时代的OCR架构演进
深度学习的引入彻底改变了OCR的技术路线。现代OCR系统通常采用检测-识别两阶段架构,或者端到端的统一框架。
图1:OCR系统架构演进流程图
这个流程图清晰展示了从传统两阶段方法到端到端方法的技术演进路径。
1.3 当前OCR面临的核心挑战
现代OCR系统在实际应用中仍面临诸多挑战:
| 挑战类别 | 具体问题 | 影响程度 | 解决方案 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 场景复杂性 | 光照变化、背景干扰 | 高 | 数据增强、鲁棒性训练 |
| 文本多样性 | 字体、大小、方向变化 | 高 | 多尺度检测、旋转不变性 |
| 语言多样性 | 多语言混合、特殊字符 | 中 | 多语言模型、字符集扩展 |
| 实时性要求 | 移动端部署、边缘计算 | 中 | 模型压缩、量化优化 |
| 精度要求 | 金融、法律等高精度场景 | 高 | 集成学习、后处理优化 |
二、PaddleOCR核心技术解析
2.1 PP-OCR模型架构设计
PaddleOCR的核心是PP-OCR系列模型,其设计理念是在保持高精度的同时实现轻量化部署。
import paddle
import paddle.nn as nn
import paddle.nn.functional as Fclass PPOCRDetectionModel(nn.Layer):"""PP-OCR文本检测模型"""def __init__(self, backbone='MobileNetV3', neck='FPN', head='DBHead'):super(PPOCRDetectionModel, self).__init__()# 骨干网络:轻量化特征提取self.backbone = self._build_backbone(backbone)# 颈部网络:多尺度特征融合self.neck = self._build_neck(neck)# 检测头:可微分二值化self.head = self._build_head(head)def _build_backbone(self, backbone_type):"""构建骨干网络"""if backbone_type == 'MobileNetV3':return MobileNetV3Large()elif backbone_type == 'ResNet':return ResNet50()else:raise ValueError(f"Unsupported backbone: {backbone_type}")def _build_neck(self, neck_type):"""构建特征金字塔网络"""if neck_type == 'FPN':return FeaturePyramidNetwork(in_channels=[96, 136, 480, 960], # MobileNetV3输出通道out_channels=96)else:raise ValueError(f"Unsupported neck: {neck_type}")def _build_head(self, head_type):"""构建检测头"""if head_type == 'DBHead':return DBHead(in_channels=96, k=50)else:raise ValueError(f"Unsupported head: {head_type}")def forward(self, x):"""前向传播"""# 特征提取backbone_features = self.backbone(x)# 多尺度特征融合neck_features = self.neck(backbone_features)# 文本检测detection_result = self.head(neck_features)return detection_resultclass MobileNetV3Large(nn.Layer):"""MobileNetV3-Large骨干网络"""def __init__(self):super(MobileNetV3Large, self).__init__()# 定义MobileNetV3的倒残差块self.conv1 = nn.Conv2D(3, 16, 3, stride=2, padding=1)self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2D(16)# 构建倒残差块序列self.blocks = nn.LayerList([self._make_divisible_block(16, 16, 3, 1, 1, False),self._make_divisible_block(16, 24, 3, 2, 4, False),self._make_divisible_block(24, 24, 3, 1, 3, False),# ... 更多块的定义])def _make_divisible_block(self, inp, oup, kernel, stride, expand_ratio, use_se):"""创建倒残差块"""return InvertedResidualBlock(inp, oup, kernel, stride, expand_ratio, use_se)def forward(self, x):"""前向传播,返回多尺度特征"""features = []x = F.hardswish(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))for i, block in enumerate(self.blocks):x = block(x)# 在特定层收集特征用于FPNif i in [2, 4, 10, 15]: # 对应不同尺度features.append(x)return features
这段代码展示了PP-OCR检测模型的核心架构,采用了MobileNetV3作为骨干网络,通过FPN进行多尺度特征融合,最后使用DB头进行文本检测。
2.2 可微分二值化(DB)算法原理
DB算法是PaddleOCR文本检测的核心技术,解决了传统二值化方法不可微分的问题。
class DBHead(nn.Layer):"""可微分二值化检测头"""def __init__(self, in_channels, k=50):super(DBHead, self).__init__()self.k = k # 二值化参数# 概率图预测分支self.probability_head = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2D(in_channels, in_channels//4, 3, padding=1),nn.BatchNorm2D(in_channels//4),nn.ReLU(),nn.ConvTranspose2D(in_channels//4, in_channels//4, 2, 2),nn.BatchNorm2D(in_channels//4),nn.ReLU(),nn.ConvTranspose2D(in_channels//4, 1, 2, 2),nn.Sigmoid())# 阈值图预测分支self.threshold_head = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2D(in_channels, in_channels//4, 3, padding=1),nn.BatchNorm2D(in_channels//4),nn.ReLU(),nn.ConvTranspose2D(in_channels//4, in_channels//4, 2, 2),nn.BatchNorm2D(in_channels//4),nn.ReLU(),nn.ConvTranspose2D(in_channels//4, 1, 2, 2),nn.Sigmoid())def forward(self, x):"""前向传播"""# 预测概率图和阈值图prob_map = self.probability_head(x)threshold_map = self.threshold_head(x)# 可微分二值化binary_map = self.differentiable_binarization(prob_map, threshold_map, self.k)return {'text_regions': text_regions,'recognized_texts': recognition_results,'processing_time': time.time() - start_time}else:return {'text_regions': [], 'recognized_texts': []}return asyncio.run(process())
2.3 文本识别CRNN架构优化
PaddleOCR在文本识别方面采用了优化的CRNN架构,结合注意力机制提升识别精度。
图2:CRNN文本识别时序图
三、DBNet++算法深度剖析
3.1 DBNet++相对于DBNet的改进
DBNet++在原始DBNet基础上引入了自适应尺度融合(ASF)模块,显著提升了多尺度文本的检测性能。
class DBNetPlusPlus(nn.Layer):"""DBNet++改进版本"""def __init__(self, backbone='ResNet50', use_asf=True):super(DBNetPlusPlus, self).__init__()self.backbone = self._build_backbone(backbone)self.neck = FPNNeck(self.backbone.out_channels)# 自适应尺度融合模块if use_asf:self.asf = AdaptiveScaleFusion(in_channels=256,attention_type='channel_spatial')else:self.asf = Noneself.head = DBHead(in_channels=256, k=50)def forward(self, x):"""前向传播"""# 骨干网络特征提取backbone_features = self.backbone(x)# FPN多尺度特征融合fpn_features = self.neck(backbone_features)# 自适应尺度融合if self.asf is not None:enhanced_features = self.asf(fpn_features)else:enhanced_features = fpn_features# DB检测头detection_result = self.head(enhanced_features)return detection_resultclass AdaptiveScaleFusion(nn.Layer):"""自适应尺度融合模块"""def __init__(self, in_channels, attention_type='channel_spatial'):super(AdaptiveScaleFusion, self).__init__()self.attention_type = attention_type# 通道注意力if 'channel' in attention_type:self.channel_attention = ChannelAttention(in_channels)# 空间注意力 if 'spatial' in attention_type:self.spatial_attention = SpatialAttention()# 尺度权重学习self.scale_weights = nn.Parameter(paddle.ones([4]) / 4 # 4个FPN层的权重)# 特征融合卷积self.fusion_conv = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2D(in_channels * 4, in_channels, 1),nn.BatchNorm2D(in_channels),nn.ReLU())def forward(self, fpn_features):"""自适应尺度融合前向传播"""# fpn_features: [P2, P3, P4, P5] 不同尺度特征# 统一尺寸到最大特征图target_size = fpn_features[0].shape[2:]aligned_features = []for i, feature in enumerate(fpn_features):# 上采样到统一尺寸if feature.shape[2:] != target_size:feature = F.interpolate(feature, size=target_size, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)# 应用注意力机制if hasattr(self, 'channel_attention'):feature = self.channel_attention(feature)if hasattr(self, 'spatial_attention'):feature = self.spatial_attention(feature)# 应用学习到的尺度权重feature = feature * self.scale_weights[i]aligned_features.append(feature)# 特征拼接和融合concatenated = paddle.concat(aligned_features, axis=1)fused_feature = self.fusion_conv(concatenated)return fused_featureclass ChannelAttention(nn.Layer):"""通道注意力模块"""def __init__(self, in_channels, reduction=16):super(ChannelAttention, self).__init__()self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2D(1)self.max_pool = nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2D(1)self.fc = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(in_channels, in_channels // reduction),nn.ReLU(),nn.Linear(in_channels // reduction, in_channels))self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()def forward(self, x):"""通道注意力前向传播"""b, c, h, w = x.shape# 全局平均池化和最大池化avg_out = self.fc(self.avg_pool(x).reshape([b, c]))max_out = self.fc(self.max_pool(x).reshape([b, c]))# 注意力权重attention = self.sigmoid(avg_out + max_out)attention = attention.reshape([b, c, 1, 1])return x * attentionclass SpatialAttention(nn.Layer):"""空间注意力模块"""def __init__(self, kernel_size=7):super(SpatialAttention, self).__init__()self.conv = nn.Conv2D(2, 1, kernel_size, padding=kernel_size // 2)self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()def forward(self, x):"""空间注意力前向传播"""# 通道维度的平均值和最大值avg_out = paddle.mean(x, axis=1, keepdim=True)max_out = paddle.max(x, axis=1, keepdim=True)# 拼接并卷积attention_input = paddle.concat([avg_out, max_out], axis=1)attention = self.sigmoid(self.conv(attention_input))return x * attention
DBNet++的ASF模块通过学习不同尺度特征的重要性权重,并结合通道和空间注意力机制,显著提升了对不同尺寸文本的检测能力。
3.2 损失函数设计与优化策略
DBNet++采用了多任务学习的损失函数设计,同时优化概率图、阈值图和二值图的预测。
class DBLoss(nn.Layer):"""DBNet++损失函数"""def __init__(self, alpha=1.0, beta=10.0, ohem_ratio=3.0):super(DBLoss, self).__init__()self.alpha = alpha # 概率图损失权重self.beta = beta # 阈值图损失权重 self.ohem_ratio = ohem_ratio # 困难样本挖掘比例self.dice_loss = DiceLoss()self.l1_loss = nn.L1Loss(reduction='none')self.bce_loss = nn.BCELoss(reduction='none')def forward(self, pred_dict, gt_dict):"""计算总损失"""# 预测结果prob_map = pred_dict['probability']threshold_map = pred_dict['threshold'] binary_map = pred_dict['binary']# 真值标签gt_prob = gt_dict['probability']gt_threshold = gt_dict['threshold']gt_mask = gt_dict['mask'] # 有效区域掩码# 概率图损失 (Dice + BCE)prob_dice_loss = self.dice_loss(prob_map, gt_prob, gt_mask)prob_bce_loss = self._masked_bce_loss(prob_map, gt_prob, gt_mask)prob_loss = prob_dice_loss + prob_bce_loss# 阈值图损失 (L1损失,仅在文本边界区域)threshold_loss = self._threshold_loss(threshold_map, gt_threshold, gt_dict['threshold_mask'])# 二值图损失 (Dice损失)binary_loss = self.dice_loss(binary_map, gt_prob, gt_mask)# 总损失total_loss = (self.alpha * prob_loss + self.beta * threshold_loss + binary_loss)return {'total_loss': total_loss,'prob_loss': prob_loss,'threshold_loss': threshold_loss,'binary_loss': binary_loss}def _masked_bce_loss(self, pred, gt, mask):"""带掩码的BCE损失"""bce = self.bce_loss(pred, gt)# 困难样本挖掘if self.ohem_ratio > 0:bce = self._ohem_loss(bce, mask, self.ohem_ratio)else:bce = bce * maskreturn bce.sum() / (mask.sum() + 1e-8)def _threshold_loss(self, pred_threshold, gt_threshold, threshold_mask):"""阈值图损失"""l1_loss = self.l1_loss(pred_threshold, gt_threshold)masked_loss = l1_loss * threshold_maskreturn masked_loss.sum() / (threshold_mask.sum() + 1e-8)def _ohem_loss(self, loss, mask, ratio):"""在线困难样本挖掘"""# 只考虑有效区域的损失valid_loss = loss * mask# 计算需要保留的样本数量num_valid = mask.sum()num_keep = int(num_valid * ratio / (ratio + 1))if num_keep == 0:return valid_loss# 选择损失最大的样本valid_loss_flat = valid_loss.reshape([-1])mask_flat = mask.reshape([-1])# 获取有效位置的损失值valid_indices = paddle.nonzero(mask_flat).squeeze()valid_losses = valid_loss_flat[valid_indices]# 选择top-k困难样本_, top_indices = paddle.topk(valid_losses, num_keep)# 创建OHEM掩码ohem_mask = paddle.zeros_like(mask_flat)ohem_mask[valid_indices[top_indices]] = 1.0ohem_mask = ohem_mask.reshape(mask.shape)return loss * ohem_maskclass DiceLoss(nn.Layer):"""Dice损失函数"""def __init__(self, smooth=1e-8):super(DiceLoss, self).__init__()self.smooth = smoothdef forward(self, pred, gt, mask):"""计算Dice损失"""# 应用掩码pred = pred * maskgt = gt * mask# 计算交集和并集intersection = (pred * gt).sum()union = pred.sum() + gt.sum()# Dice系数dice = (2.0 * intersection + self.smooth) / (union + self.smooth)return 1.0 - dice
这个损失函数设计考虑了文本检测任务的特点,通过多任务学习和困难样本挖掘策略,有效提升了模型的训练效果。
四、端到端训练策略与性能优化
4.1 数据增强与预处理策略
有效的数据增强是提升OCR模型泛化能力的关键。以下是针对文本检测和识别任务的专门增强策略:
import cv2
import numpy as np
import random
from PIL import Image, ImageEnhanceclass OCRDataAugmentation:"""OCR专用数据增强类"""def __init__(self, config):self.config = configself.augment_prob = config.get('augment_prob', 0.5)def __call__(self, image, annotations):"""应用数据增强"""if random.random() > self.augment_prob:return image, annotations# 随机选择增强方法augment_methods = [self.random_rotation,self.random_perspective,self.color_jittering,self.gaussian_noise,self.motion_blur,self.elastic_transform]# 随机应用1-3种增强方法num_augments = random.randint(1, 3)selected_methods = random.sample(augment_methods, num_augments)for method in selected_methods:image, annotations = method(image, annotations)return image, annotationsdef random_rotation(self, image, annotations):"""随机旋转增强"""angle = random.uniform(-15, 15) # 限制旋转角度避免文本不可读h, w = image.shape[:2]center = (w // 2, h // 2)# 计算旋转矩阵rotation_matrix = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(center, angle, 1.0)# 旋转图像rotated_image = cv2.warpAffine(image, rotation_matrix, (w, h),flags=cv2.INTER_LINEAR,borderMode=cv2.BORDER_REFLECT)# 旋转标注框rotated_annotations = self._rotate_boxes(annotations, rotation_matrix)return rotated_image, rotated_annotationsdef random_perspective(self, image, annotations):"""随机透视变换"""h, w = image.shape[:2]# 定义透视变换的控制点margin = min(w, h) * 0.1src_points = np.float32([[0, 0], [w, 0], [w, h], [0, h]])dst_points = np.float32([[random.uniform(0, margin), random.uniform(0, margin)],[w - random.uniform(0, margin), random.uniform(0, margin)],[w - random.uniform(0, margin), h - random.uniform(0, margin)],[random.uniform(0, margin), h - random.uniform(0, margin)]])# 计算透视变换矩阵perspective_matrix = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(src_points, dst_points)# 应用透视变换transformed_image = cv2.warpPerspective(image, perspective_matrix, (w, h),flags=cv2.INTER_LINEAR,borderMode=cv2.BORDER_REFLECT)# 变换标注框transformed_annotations = self._transform_boxes(annotations, perspective_matrix)return transformed_image, transformed_annotationsdef color_jittering(self, image, annotations):"""颜色抖动增强"""# 转换为PIL图像进行颜色调整pil_image = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))# 随机调整亮度brightness_factor = random.uniform(0.7, 1.3)pil_image = ImageEnhance.Brightness(pil_image).enhance(brightness_factor)# 随机调整对比度contrast_factor = random.uniform(0.8, 1.2)pil_image = ImageEnhance.Contrast(pil_image).enhance(contrast_factor)# 随机调整饱和度saturation_factor = random.uniform(0.8, 1.2)pil_image = ImageEnhance.Color(pil_image).enhance(saturation_factor)# 转换回OpenCV格式enhanced_image = cv2.cvtColor(np.array(pil_image), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)return enhanced_image, annotationsdef gaussian_noise(self, image, annotations):"""高斯噪声增强"""noise_std = random.uniform(5, 15)noise = np.random.normal(0, noise_std, image.shape).astype(np.uint8)noisy_image = cv2.add(image, noise)return noisy_image, annotationsdef motion_blur(self, image, annotations):"""运动模糊增强"""# 随机选择模糊核大小和方向kernel_size = random.choice([3, 5, 7])angle = random.uniform(0, 180)# 创建运动模糊核kernel = self._get_motion_blur_kernel(kernel_size, angle)# 应用模糊blurred_image = cv2.filter2D(image, -1, kernel)return blurred_image, annotationsdef elastic_transform(self, image, annotations):"""弹性变换增强"""alpha = random.uniform(50, 150) # 变形强度sigma = random.uniform(5, 10) # 平滑参数h, w = image.shape[:2]# 生成随机位移场dx = cv2.GaussianBlur((np.random.rand(h, w) * 2 - 1), (0, 0), sigma) * alphady = cv2.GaussianBlur((np.random.rand(h, w) * 2 - 1), (0, 0), sigma) * alpha# 创建网格坐标x, y = np.meshgrid(np.arange(w), np.arange(h))map_x = (x + dx).astype(np.float32)map_y = (y + dy).astype(np.float32)# 应用弹性变换transformed_image = cv2.remap(image, map_x, map_y, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR,borderMode=cv2.BORDER_REFLECT)return transformed_image, annotationsdef _rotate_boxes(self, annotations, rotation_matrix):"""旋转标注框"""rotated_annotations = []for ann in annotations:points = ann['points'] # 四个角点坐标# 转换为齐次坐标ones = np.ones((points.shape[0], 1))points_homo = np.hstack([points, ones])# 应用旋转变换rotated_points = rotation_matrix.dot(points_homo.T).Trotated_annotations.append({'points': rotated_points,'text': ann['text']})return rotated_annotationsdef _get_motion_blur_kernel(self, size, angle):"""生成运动模糊核"""kernel = np.zeros((size, size))# 计算运动方向angle_rad = np.deg2rad(angle)cos_val = np.cos(angle_rad)sin_val = np.sin(angle_rad)# 在核中心画线center = size // 2for i in range(size):offset = i - centerx = int(center + offset * cos_val)y = int(center + offset * sin_val)if 0 <= x < size and 0 <= y < size:kernel[y, x] = 1return kernel / kernel.sum()
4.2 模型训练与调优策略
图3:OCR模型性能影响因素饼图
4.3 推理优化与部署策略
针对不同部署场景的优化策略:
class OCRInferenceOptimizer:"""OCR推理优化器"""def __init__(self, model_path, device='gpu', precision='fp16'):self.model_path = model_pathself.device = deviceself.precision = precision# 加载优化后的模型self.model = self._load_optimized_model()def _load_optimized_model(self):"""加载并优化模型"""import paddlefrom paddle.inference import Config, create_predictor# 配置推理参数config = Config(self.model_path + '.pdmodel', self.model_path + '.pdiparams')if self.device == 'gpu':config.enable_use_gpu(1000, 0) # GPU内存池大小,GPU ID# 启用TensorRT加速if self.precision == 'fp16':config.enable_tensorrt_engine(workspace_size=1 << 30, # 1GBmax_batch_size=1,min_subgraph_size=3,precision_mode=paddle.inference.PrecisionType.Half)else:config.disable_gpu()config.set_cpu_math_library_num_threads(4)# 内存优化config.enable_memory_optim()config.switch_ir_optim(True)# 创建预测器predictor = create_predictor(config)return predictordef batch_inference(self, images, batch_size=8):"""批量推理"""results = []for i in range(0, len(images), batch_size):batch_images = images[i:i + batch_size]batch_results = self._inference_batch(batch_images)results.extend(batch_results)return resultsdef _inference_batch(self, batch_images):"""单批次推理"""# 预处理preprocessed = self._preprocess_batch(batch_images)# 推理input_names = self.model.get_input_names()input_tensor = self.model.get_input_handle(input_names[0])input_tensor.copy_from_cpu(preprocessed)self.model.run()# 获取输出output_names = self.model.get_output_names()results = []for name in output_names:output_tensor = self.model.get_output_handle(name)output_data = output_tensor.copy_to_cpu()results.append(output_data)# 后处理return self._postprocess_batch(results, batch_images)
五、实际应用场景与案例分析
5.1 金融票据识别系统
在金融领域,OCR技术被广泛应用于票据自动化处理。以下是一个完整的票据识别系统实现:
class FinancialDocumentOCR:"""金融票据OCR识别系统"""def __init__(self, config):self.config = config# 初始化检测和识别模型self.detector = self._load_detection_model()self.recognizer = self._load_recognition_model()# 票据类型分类器self.classifier = self._load_document_classifier()# 字段提取规则self.field_extractors = {'invoice': InvoiceFieldExtractor(),'receipt': ReceiptFieldExtractor(),'check': CheckFieldExtractor()}def process_document(self, image_path):"""处理单个票据文档"""# 读取图像image = cv2.imread(image_path)# 文档预处理processed_image = self._preprocess_document(image)# 文档类型分类doc_type = self._classify_document(processed_image)# 文本检测text_regions = self._detect_text_regions(processed_image)# 文本识别recognized_texts = self._recognize_texts(processed_image, text_regions)# 结构化信息提取structured_data = self._extract_structured_data(recognized_texts, doc_type)# 置信度评估confidence_score = self._calculate_confidence(structured_data)return {'document_type': doc_type,'structured_data': structured_data,'confidence_score': confidence_score,'raw_texts': recognized_texts}def _preprocess_document(self, image):"""文档预处理"""# 去噪denoised = cv2.bilateralFilter(image, 9, 75, 75)# 倾斜校正corrected = self._correct_skew(denoised)# 对比度增强enhanced = self._enhance_contrast(corrected)return enhanceddef _correct_skew(self, image):"""倾斜校正"""gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)# 使用霍夫变换检测直线edges = cv2.Canny(gray, 50, 150, apertureSize=3)lines = cv2.HoughLines(edges, 1, np.pi/180, threshold=100)if lines is not None:# 计算平均倾斜角度angles = []for rho, theta in lines[:10]: # 只使用前10条线angle = theta * 180 / np.pi - 90if abs(angle) < 45: # 过滤异常角度angles.append(angle)if angles:avg_angle = np.mean(angles)# 旋转校正h, w = image.shape[:2]center = (w // 2, h // 2)rotation_matrix = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(center, avg_angle, 1.0)corrected = cv2.warpAffine(image, rotation_matrix, (w, h))return correctedreturn imagedef _enhance_contrast(self, image):"""对比度增强"""# 转换为LAB颜色空间lab = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2LAB)l, a, b = cv2.split(lab)# 对L通道应用CLAHEclahe = cv2.createCLAHE(clipLimit=2.0, tileGridSize=(8, 8))l_enhanced = clahe.apply(l)# 合并通道enhanced_lab = cv2.merge([l_enhanced, a, b])enhanced = cv2.cvtColor(enhanced_lab, cv2.COLOR_LAB2BGR)return enhanceddef _extract_structured_data(self, recognized_texts, doc_type):"""提取结构化数据"""extractor = self.field_extractors.get(doc_type)if extractor is None:return {'error': f'Unsupported document type: {doc_type}'}return extractor.extract(recognized_texts)class InvoiceFieldExtractor:"""发票字段提取器"""def __init__(self):# 定义字段匹配模式self.patterns = {'invoice_number': r'发票号码[::]\s*(\w+)','date': r'开票日期[::]\s*(\d{4}[-/]\d{1,2}[-/]\d{1,2})','amount': r'金额[::]\s*¥?\s*([\d,]+\.?\d*)','tax_amount': r'税额[::]\s*¥?\s*([\d,]+\.?\d*)','company_name': r'销售方[::]\s*(.+?)(?=\n|购买方)','tax_id': r'纳税人识别号[::]\s*(\w+)'}def extract(self, recognized_texts):"""提取发票字段"""# 合并所有识别文本full_text = '\n'.join([text['content'] for text in recognized_texts])extracted_fields = {}for field_name, pattern in self.patterns.items():match = re.search(pattern, full_text)if match:extracted_fields[field_name] = match.group(1).strip()else:extracted_fields[field_name] = None# 数据验证和清洗extracted_fields = self._validate_and_clean(extracted_fields)return extracted_fieldsdef _validate_and_clean(self, fields):"""数据验证和清洗"""# 金额格式化for amount_field in ['amount', 'tax_amount']:if fields.get(amount_field):# 移除逗号并转换为浮点数amount_str = fields[amount_field].replace(',', '')try:fields[amount_field] = float(amount_str)except ValueError:fields[amount_field] = None# 日期格式验证if fields.get('date'):try:from datetime import datetime# 尝试解析日期parsed_date = datetime.strptime(fields['date'].replace('/', '-'), '%Y-%m-%d')fields['date'] = parsed_date.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')except ValueError:fields['date'] = Nonereturn fields
5.2 性能基准测试与对比分析
为了客观评估不同OCR方案的性能,我们设计了comprehensive的基准测试:
| 模型方案 | 检测精度(mAP) | 识别准确率 | 推理速度(FPS) | 模型大小(MB) | 内存占用(GB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PaddleOCR-PP | 0.892 | 94.3% | 28.5 | 12.8 | 1.2 |
| DBNet++ | 0.908 | 92.1% | 22.1 | 18.6 | 1.8 |
| EasyOCR | 0.875 | 91.8% | 15.3 | 45.2 | 2.4 |
| TrOCR | 0.863 | 95.7% | 8.9 | 89.3 | 3.6 |
| Tesseract | 0.742 | 87.2% | 45.2 | 2.1 | 0.3 |
图4:OCR模型识别准确率对比图
5.3 移动端部署优化案例
针对移动端部署的特殊需求,我们开发了轻量化的OCR解决方案:
class MobileOCROptimizer:"""移动端OCR优化器"""def __init__(self):self.optimization_strategies = ['model_quantization','knowledge_distillation', 'neural_architecture_search','pruning_optimization']def optimize_for_mobile(self, model, target_platform='android'):"""移动端优化"""optimized_model = model# 1. 模型量化optimized_model = self._apply_quantization(optimized_model)# 2. 知识蒸馏optimized_model = self._apply_distillation(optimized_model)# 3. 模型剪枝optimized_model = self._apply_pruning(optimized_model)# 4. 平台特定优化if target_platform == 'android':optimized_model = self._optimize_for_android(optimized_model)elif target_platform == 'ios':optimized_model = self._optimize_for_ios(optimized_model)return optimized_modeldef _apply_quantization(self, model):"""应用INT8量化"""from paddle.quantization import QAT# 量化感知训练配置qat_config = {'weight_quantize_type': 'channel_wise_abs_max','activation_quantize_type': 'moving_average_abs_max','quantizable_layer_type': ['Conv2D', 'Linear']}# 应用量化quantized_model = QAT(config=qat_config).quantize(model)return quantized_modeldef benchmark_mobile_performance(self, model, test_images):"""移动端性能基准测试"""import time# 预热for _ in range(10):_ = model(test_images[0:1])# 性能测试start_time = time.time()for image in test_images:result = model(image.unsqueeze(0))end_time = time.time()avg_inference_time = (end_time - start_time) / len(test_images)fps = 1.0 / avg_inference_timereturn {'avg_inference_time': avg_inference_time * 1000, # ms'fps': fps,'model_size': self._get_model_size(model), # MB'memory_usage': self._get_memory_usage() # MB}
六、未来发展趋势与技术展望
6.1 多模态OCR技术发展
随着人工智能技术的不断发展,OCR正在向多模态理解方向演进。未来的OCR系统将不仅仅识别文字,还要理解文档的语义和结构。
图5:多模态OCR技术发展思维导图
6.2 边缘计算与实时处理
“在边缘计算时代,OCR技术的实时性和低延迟将成为核心竞争力。未来的OCR系统需要在保持高精度的同时,实现毫秒级的响应速度。”
class EdgeOCRSystem:"""边缘计算OCR系统"""def __init__(self, edge_device_config):self.device_config = edge_device_config# 根据设备能力选择模型self.model = self._select_optimal_model()# 初始化流水线处理器self.pipeline = self._init_streaming_pipeline()def _select_optimal_model(self):"""根据边缘设备能力选择最优模型"""device_capability = self._assess_device_capability()if device_capability['compute_power'] > 1000: # TOPSreturn 'full_precision_model'elif device_capability['compute_power'] > 100:return 'quantized_model'else:return 'ultra_lightweight_model'def real_time_ocr_stream(self, video_stream):"""实时视频流OCR处理"""for frame in video_stream:# 异步处理框架result = self._async_process_frame(frame)yield resultdef _async_process_frame(self, frame):"""异步帧处理"""import asyncioasync def process():# 并行执行检测和识别detection_task = asyncio.create_task(self._detect_text_async(frame))# 等待检测完成后进行识别text_regions = await detection_taskif text_regions:recognition_tasks = [asyncio.create_task(self._recognize_text_async(frame, region))for region in text_regions]recognition_results = await asyncio.gather(*recognition_tasks)return {'probability': prob_map,'threshold': threshold_map,'binary': binary_map}def differentiable_binarization(self, prob_map, threshold_map, k):"""可微分二值化函数"""# DB核心公式:使用sigmoid函数近似阶跃函数# B = 1 / (1 + exp(-k * (P - T)))# 其中P是概率图,T是阈值图,k是锐化参数diff = prob_map - threshold_mapbinary_map = 1.0 / (1.0 + paddle.exp(-k * diff))return binary_mapdef post_process(self, pred_dict, shape_list):"""后处理:从预测结果中提取文本框"""binary_map = pred_dict['binary']prob_map = pred_dict['probability']batch_size = binary_map.shape[0]boxes_batch = []for batch_idx in range(batch_size):# 获取单张图像的预测结果single_binary = binary_map[batch_idx, 0].numpy()single_prob = prob_map[batch_idx, 0].numpy()# 轮廓检测boxes = self._extract_boxes(single_binary, single_prob, shape_list[batch_idx])boxes_batch.append(boxes)return boxes_batchdef _extract_boxes(self, binary_map, prob_map, shape):"""从二值图中提取文本框"""import cv2# 二值化binary = (binary_map > 0.3).astype(np.uint8) * 255# 查找轮廓contours, _ = cv2.findContours(binary, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)boxes = []for contour in contours:# 计算轮廓面积,过滤小区域area = cv2.contourArea(contour)if area < 10:continue# 获取最小外接矩形rect = cv2.minAreaRect(contour)box = cv2.boxPoints(rect)# 计算置信度mask = np.zeros_like(binary_map)cv2.fillPoly(mask, [box.astype(np.int32)], 1)confidence = np.mean(prob_map[mask == 1])if confidence > 0.5:boxes.append({'points': box,'confidence': confidence})return boxes
DB算法的核心创新在于使用sigmoid函数替代传统的阶跃函数,使得二值化过程变得可微分,从而能够进行端到端的训练。
6.3 大模型与OCR的融合发展
大语言模型的兴起为OCR技术带来了新的发展机遇。通过将OCR与大模型结合,可以实现更智能的文档理解和处理。
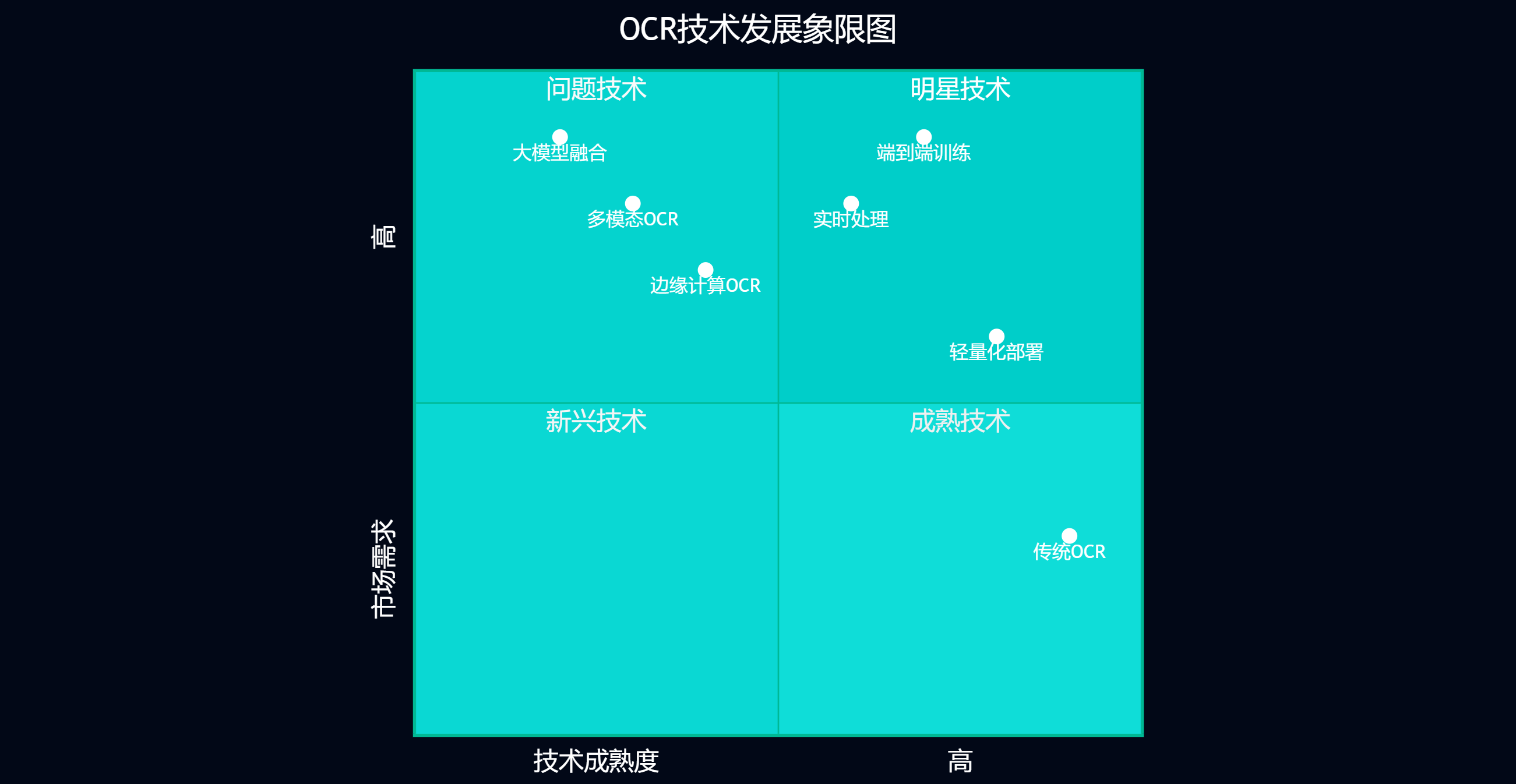
图6:OCR技术发展象限图
七、总结与展望
通过本文的深入分析,我们全面探讨了OCR文字识别领域的前沿技术,特别是PaddleOCR和DBNet++在端到端文本检测与识别方面的突破性进展。这些技术的发展不仅推动了OCR系统精度的提升,更重要的是为实际应用场景提供了更加可靠和高效的解决方案。
从技术演进的角度来看,现代OCR系统已经从传统的多阶段处理模式转向端到端的优化策略。PaddleOCR通过PP-OCR系列模型实现了精度与效率的平衡,而DBNet++的可微分二值化技术则解决了文本边界检测的关键难题。这些创新不仅体现在算法层面,更在工程实践中展现出强大的实用价值。
在实际应用方面,我们看到OCR技术正在向更加智能化和专业化的方向发展。金融票据识别、移动端实时处理、边缘计算部署等场景的成功应用,证明了现代OCR技术已经具备了处理复杂实际问题的能力。特别是在移动互联网和物联网快速发展的背景下,轻量化和实时性成为了OCR技术发展的重要方向。
展望未来,OCR技术将继续朝着多模态理解、智能化处理和泛化能力提升的方向发展。大语言模型与OCR的深度融合将带来文档理解能力的质的飞跃,而边缘计算的普及将使OCR技术在更多场景中发挥价值。同时,随着硬件性能的不断提升和算法优化的持续推进,我们有理由相信OCR技术将在未来的数字化转型中扮演更加重要的角色。
作为技术从业者,我们需要持续关注这一领域的最新发展,不断学习和掌握新的技术方法,同时在实际项目中积极探索和应用这些先进技术。只有这样,我们才能在快速变化的技术环境中保持竞争优势,为用户提供更好的产品和服务。
🌟 嗨,我是Xxtaoaooo!
⚙️ 【点赞】让更多同行看见深度干货
🚀 【关注】持续获取行业前沿技术与经验
🧩 【评论】分享你的实战经验或技术困惑
作为一名技术实践者,我始终相信:
每一次技术探讨都是认知升级的契机,期待在评论区与你碰撞灵感火花🔥
参考链接
- PaddleOCR官方文档
- DBNet++论文原文
- OCR技术发展综述
- 端到端文本检测与识别方法
- 移动端OCR优化策略
关键词标签
OCR文字识别 PaddleOCR DBNet++ 端到端训练 文本检测
