数据结构——哈希(自定义hashMap实现、解决哈希冲突、拉链寻址Java实现)
文章目录
- 数据结构——哈希
- 核心思想
- 哈希冲突
- 哈希冲突解决
- 拉链寻址 (最常用)
- Java中的哈希实现
- 1. HashMap
- 2. HashSet
- 3. ConcurrentHashMap(线程安全)
数据结构——哈希
哈希是一种非常重要的数据结构,它通过哈希函数将键映射到存储位置,实现高效的数据访问。
核心思想
- 键值对存储:通过键(Key)快速访问值(Value)
- 哈希函数:将任意大小的数据映射到固定大小的值(哈希值)
- 数组存储:使用哈希值作为数组索引来存储数据
基本结构:键(Key) → 哈希函数 → 哈希值 → 数组索引 → 存储值(Value)
理想哈希函数的特性:
- 确定性:相同输入总是产生相同输出
- 高效性:计算速度快
- 均匀分布:将键均匀分布到整个地址空间
- 最小冲突:不同输入产生相同输出的概率低
常见Hash函数:
// 简单取模哈希
int hash(int key, int tableSize) {return key % tableSize;
}// 字符串哈希(Java String的hashCode实现原理)
int stringHash(String key, int tableSize) {int hash = 0;for (int i = 0; i < key.length(); i++) {hash = 31 * hash + key.charAt(i);}return Math.abs(hash) % tableSize;
}// DJB2哈希(流行的字符串哈希算法)
int djb2Hash(String key, int tableSize) {int hash = 5381;for (int i = 0; i < key.length(); i++) {hash = ((hash << 5) + hash) + key.charAt(i);}return Math.abs(hash) % tableSize;
}
哈希冲突
理想情况下,每个Key对应一个哈希值,但是因为随着元素的增多,很可能发生哈希冲突,或者哈希值波动不大导致索引计算相同,也就是一个索引位置出现多个元素情况。
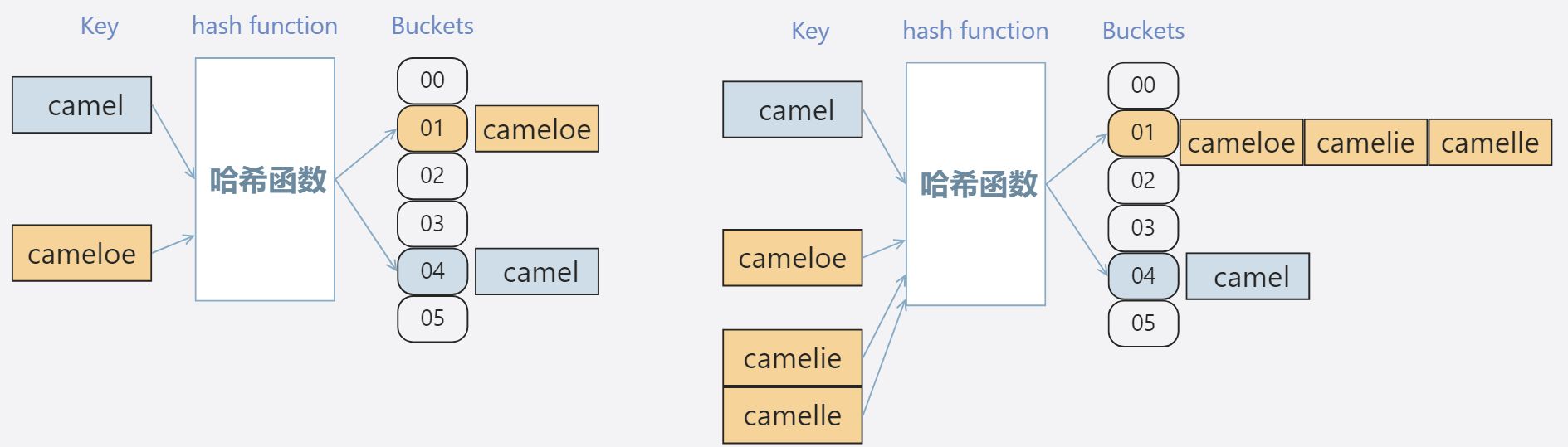
哈希冲突解决
解决哈希冲突的方法有很多,HashMap 中的拉链寻址 + 红黑树、扰动函数、负载因子、ThreadLocal 的开放寻址、合并散列、杜鹃散列、跳房子哈希、罗宾汉哈希等各类数据结构设计。让元素在发生哈希冲突时,也可以存放到新的槽位,并尽可能保证索引的时间复杂度小于O(n)。
拉链寻址 (最常用)
为避免不同关键字会被映射到同一个地址空间中,便将所有同义词存储在同一个线性链表中,这个线性表由其散列地址唯一标识。将非同义词标记在数组中的不同位置,数组中的不同下标对应的元素将会指向不同的同义词线性表的起始地址。
每个数组位置存储一个链表,冲突元素添加到链表中。
🖊️Java实现:
public class MyHashMap<K, V> {private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 16;private static final double LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75;private HashNode<K, V>[] table;private int size;@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public MyHashMap() {table = new HashNode[DEFAULT_CAPACITY];size = 0;}// 哈希函数private int hash(K key) {return Math.abs(key.hashCode()) % table.length;}// 插入键值对public void put(K key, V value) {if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Key cannot be null");int index = hash(key);HashNode<K, V> current = table[index];// 检查键是否已存在while (current != null) {if (current.key.equals(key)) {current.value = value; // 更新值return;}current = current.next;}// 插入新节点到链表头部HashNode<K, V> newNode = new HashNode<>(key, value);newNode.next = table[index];table[index] = newNode;size++;// 检查是否需要扩容if ((double)size / table.length > LOAD_FACTOR) {resize();}}// 获取值public V get(K key) {int index = hash(key);HashNode<K, V> current = table[index];while (current != null) {if (current.key.equals(key)) {return current.value;}current = current.next;}return null; // 键不存在}// 扩容@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")private void resize() {HashNode<K, V>[] oldTable = table;table = new HashNode[oldTable.length * 2];size = 0;for (HashNode<K, V> head : oldTable) {HashNode<K, V> current = head;while (current != null) {put(current.key, current.value);current = current.next;}}}public int size() { return size; }public boolean isEmpty() { return size == 0; }/*** @author: Camel* @description: 链地址法,每个数组位置存储一个链表,冲突元素添加到链表中.* @date: 2025/10/14 14:46*/public class HashNode<K, V> {K key;V value;HashNode<K, V> next;public HashNode(K key, V value) {this.key = key;this.value = value;}}
}
Java中的哈希实现
1. HashMap
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("apple", 1);
map.put("banana", 2);// 遍历
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) {System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ": " + entry.getValue());
}
2. HashSet
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add("hello");
set.add("world");// 检查存在性
boolean contains = set.contains("hello");
3. ConcurrentHashMap(线程安全)
Map<String, Integer> concurrentMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
