OkHttp源码解析(一)
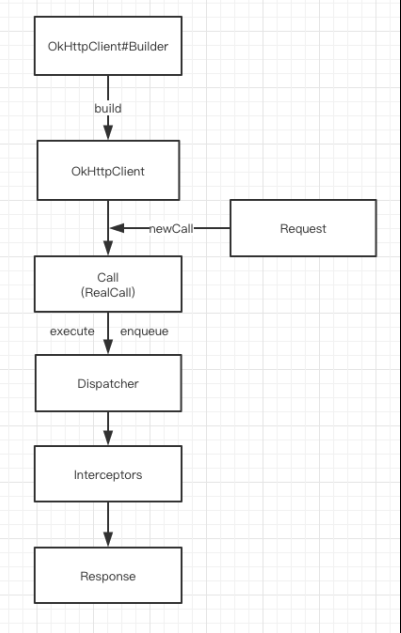
一、使用流程

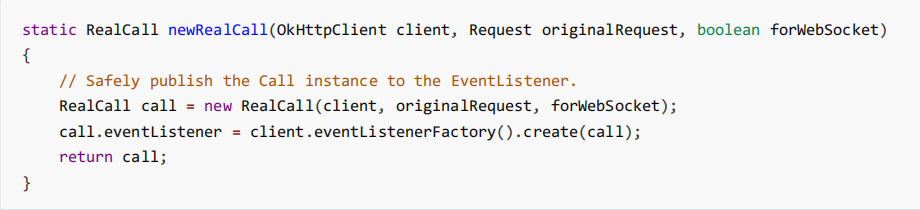

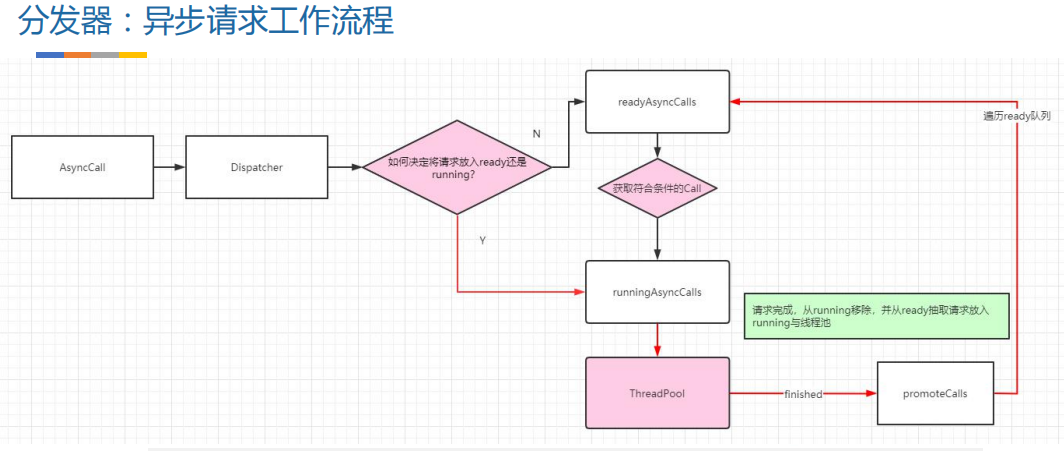
二、分发器

import androidx.annotation.Nullable;import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;// 可根据需要替换/补充 AsyncCall 与 RealCall 的定义
public final class DispatcherLike {// 异步请求同时存在的最大请求private int maxRequests = 64;// 异步请求同一域名同时存在的最大请求private int maxRequestsPerHost = 5;// 闲置任务(没有请求可执行时执行一些任务,由使用者设置)@Nullableprivate Runnable idleCallback;// 异步请求使用的线程池@Nullableprivate ExecutorService executorService;// 异步请求等待执行队列private final Deque<AsyncCall> readyAsyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();// 异步请求正在执行队列private final Deque<AsyncCall> runningAsyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();// 同步请求正在执行队列private final Deque<RealCall> runningSyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();// 根据实际需求添加构造方法、setter/getter、调度逻辑等// ...
}
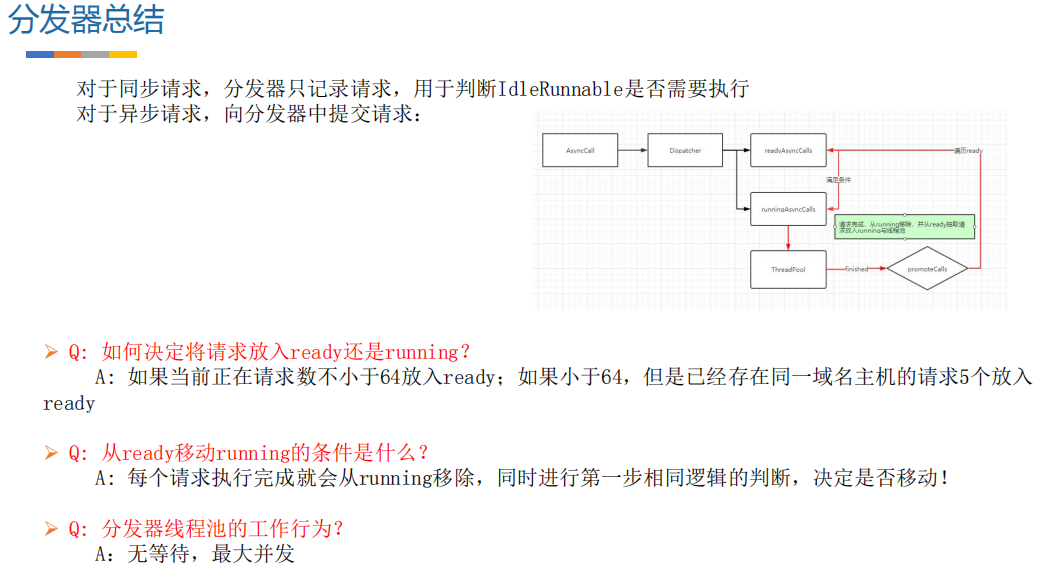
三、同步请求

四、异步请求


// 异步请求调用
public void finished(AsyncCall call) {finished(runningAsyncCalls, call, true);
}// 同步请求调用
public void finished(RealCall call) {finished(runningSyncCalls, call, false);
}private <T> void finished(Deque<T> calls, T call, boolean promoteCalls) {int runningCallsCount;Runnable idleCallback;synchronized (this) {// 不管异步还是同步,执行完后都要从队列移除if (!calls.remove(call)) {throw new AssertionError("Call wasn't in-flight!");}if (promoteCalls) {promoteCalls();}// 异步任务和同步任务正在执行的和runningCallsCount = runningCallsCount();idleCallback = this.idleCallback;}// 没有任务执行时执行闲置回调if (runningCallsCount == 0 && idleCallback != null) {idleCallback.run();}
}
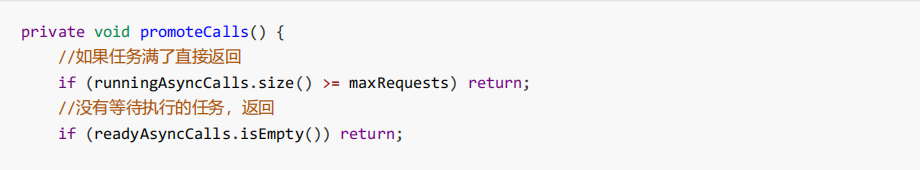


五、请求流程
用户是不需要直接操作任务分发器的,获得的 RealCall 中就分别提供了 execute 与 enqueue 来开始同步请求或异 步请求。
@Override
public Response execute() throws IOException {synchronized (this) {if (executed) throw new IllegalStateException("Already Executed");executed = true;}captureCallStackTrace();eventListener.callStart(this);try {// 调用分发器client.dispatcher().executed(this);// 执行请求Response result = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();if (result == null) throw new IOException("Canceled");return result;} catch (IOException e) {eventListener.callFailed(this, e);throw e;} finally {// 请求完成client.dispatcher().finished(this);}
}![]()

import java.io.IOException;final class AsyncCall extends NamedRunnable {private final Callback responseCallback;AsyncCall(Callback responseCallback) {super("OkHttp %s", redactedUrl());this.responseCallback = responseCallback;}// 线程池执行@Overrideprotected void execute() {boolean signalledCallback = false;try {Response response = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();// ......} catch (IOException e) {// ......} finally {// 请求完成client.dispatcher().finished(this);}}private static String redactedUrl() { return "url"; }private Response getResponseWithInterceptorChain() throws IOException { return new Response(); }private final OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
}public abstract class NamedRunnable implements Runnable {protected final String name;public NamedRunnable(String format, Object... args) {this.name = Util.format(format, args);}@Overridepublic final void run() {String oldName = Thread.currentThread().getName();Thread.currentThread().setName(name);try {execute();} finally {Thread.currentThread().setName(oldName);}}protected abstract void execute();
}

六、分发器线程池
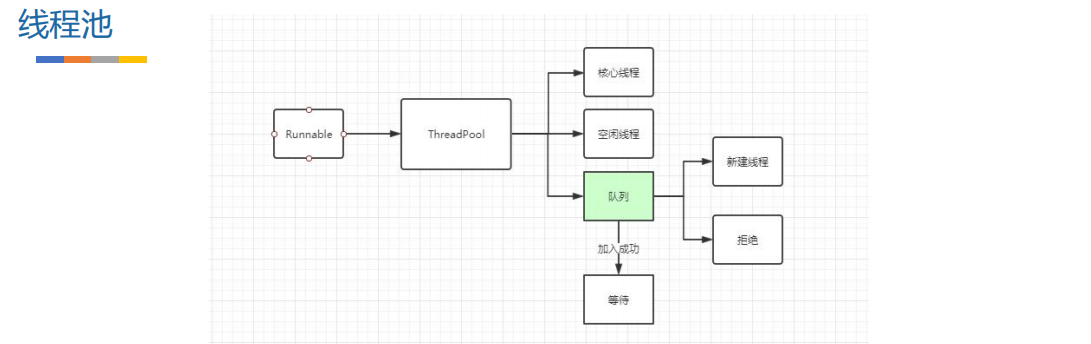

前面我们提过,分发器就是来调配请求任务的,内部会包含一个线程池。当异步请求时,会将请求任务交给线程池 来执行。那分发器中默认的线程池是如何定义的呢?为什么要这么定义?
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;private ExecutorService executorService;public synchronized ExecutorService executorService() {if (executorService == null) {executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, // 核心线程Integer.MAX_VALUE, // 最大线程60L, // 空闲线程闲置时间TimeUnit.SECONDS, // 闲置时间单位new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(), // 线程等待队列Util.threadFactory("OkHttp Dispatcher", false) // 线程创建工厂);}return executorService;
}


七、拦截器责任链
OkHttp最核心的工作是在 getResponseWithInterceptorChain() 中进行,在进入这个方法分析之前,我们先来了 解什么是责任链模式,因为此方法就是利用的责任链模式完成一步步的请求。
责任链模式
为请求创建了一个接收者对象的链。这种模式给予请求的类型,对请求的发送者和接收者进行解耦。在这种模式 中,通常每个接收者都包含对另一个接收者的引用。如果一个对象不能处理该请求,那么它会把相同的请求传给下 一个接收者,依此类推。比如:

八、拦截器流程
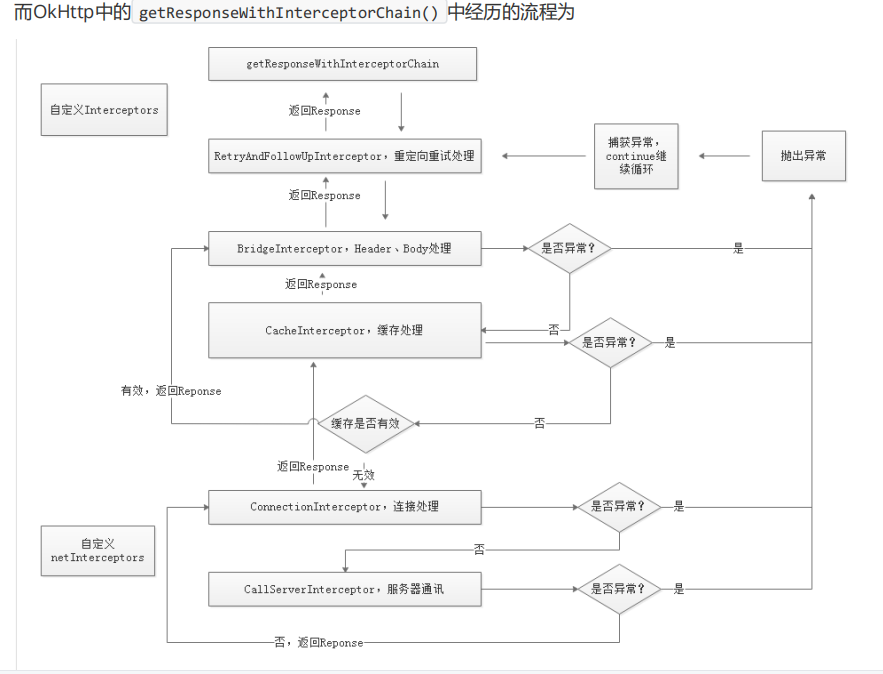
请求会被交给责任链中的一个个拦截器。默认情况下有五大拦截器:1. RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor第一个接触到请求,最后接触到响应;负责判断是否需要重新发起整个请求2. BridgeInterceptor补全请求,并对响应进行额外处理3. CacheInterceptor请求前查询缓存,获得响应并判断是否需要缓存4. ConnectInterceptor与服务器完成TCP连接5. CallServerInterceptor与服务器通信;封装请求数据与解析响应数据(如:HTTP报文)
