linux之 remoteproc 内核实现源码分析
一、什么是 remoteproc 框架?
远程处理器 (RPROC) 框架允许不同的平台/架构控制(开机、加载固件、关机)远程处理器,同时抽象硬件差异。此外,它还提供监控和调试远程协处理器的服务。
1.1 框架通信图
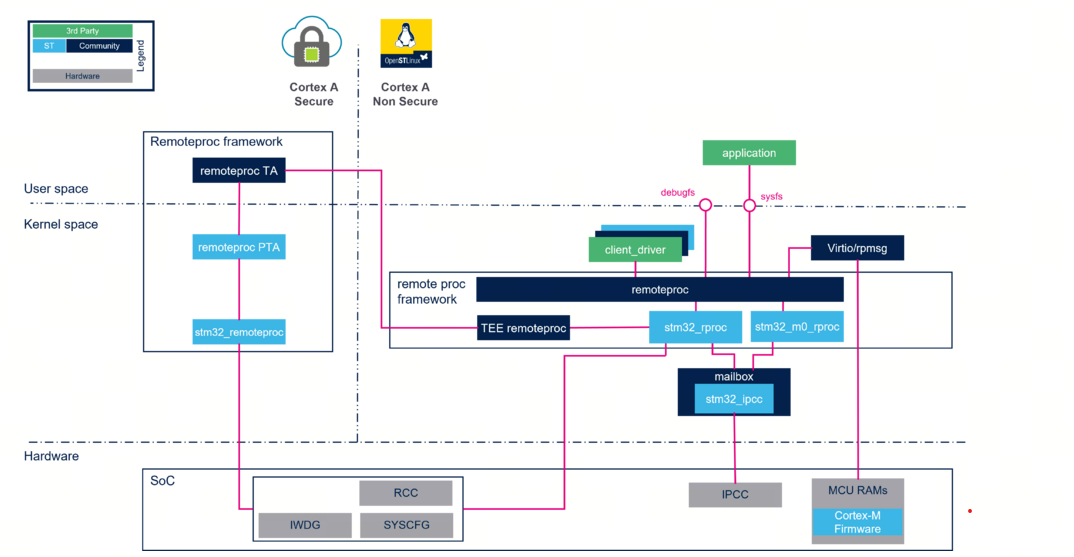
右侧是Linux 的kernel ,左侧是控制的远程处理器。
1.2 加载固件 的格式
remoteproc 框架支持 2 种独占格式:
- ELF 格式:Linux remoteproc 框架支持 ELF 格式
- TEE 格式:OP_TEE remoteproc 框架支持 TEE 格式
看到网友讲到:此外,该框架还为支持该通信类型的远程处理器添加了rpmsg virtio设备,从而使得特定于平台的远程处理器驱动程序只需提供一些低级处理器,而所有rpmsg驱动程序就可以正常工作。
目前还没有明白什么意思。
二、linux 内核中的remoteproc 的源码框架
2.1 remoteproc 在内核中的代码逻辑框架
像内核中很多的其他模块一样, 对上+ core+ 对下。对下层,是需要驱动工程师注册的各个函数接口。
在内核中的路径:drivers/remoteproc/*
打开makefile :
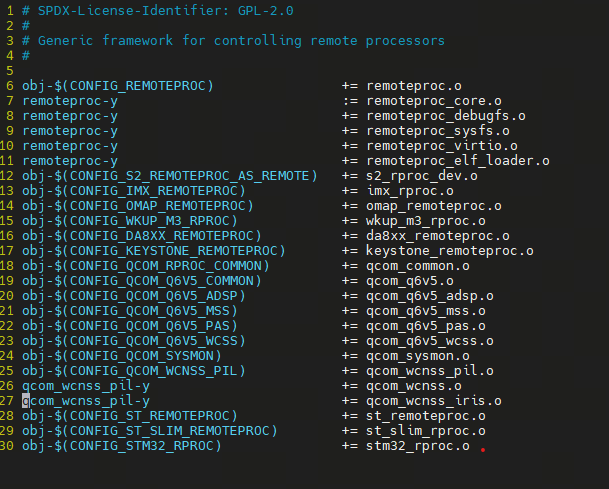
可以发现 remoteproc-y , 是 core 层, 里面包含 remoteproc_debugfs.o, remoteproc_sysfs.o,remoteproc_virtio.o,remoteproc_elf_loader.o , 根据名字可以发现,和第一节描述的功能对应。 分别有debugfs \sysfs 的系统接口,固件加载的elf_loader,还有virtio , 第一节说到 :该框架还为支持该通信类型的远程处理器添加了rpmsg virtio设备,从而使得特定于平台的远程处理器驱动程序只需提供一些低级处理器,而所有rpmsg驱动程序就可以正常工作。难道就是指 这个源码实现的功能。
下面对源码文件进行描述。
drivers/remoteproc/ ├── remoteproc_core.c--remoteproc框架核心。 ├── remoteproc_debugfs.c--创建remoteproc目录,以及为每个remoteproc设备创建调试节点。 ├── remoteproc_elf_loader.c--加载ELF格式固件的接口。 ├── remoteproc_sysfs.c--remoteproc设备属性节点。 ├── remoteproc_virtio.c--创建remoteproc相关的virtio设备。 └── stm32_rproc.c--STM32 remoteproc驱动。
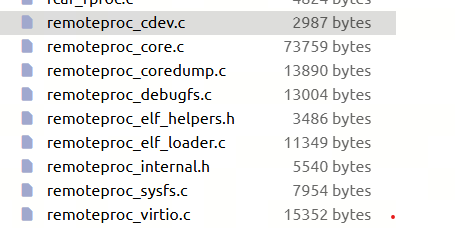
上面的内核版本是5.4.145.*的内核源码, 而对于6.16 的内核源码,remoteproc 核心功能有增加,截图如下,自己去发现。
2.2 remoteproc 初始化
源码:remoteproc_core.c
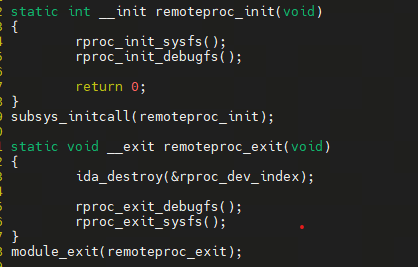
remoteproc_initrproc_init_sysfsclass_register--创建remoteproc类。rproc_init_debugfsdebugfs_initialized--判断debugfs似乎否初始化。debugfs_create_dir--创建/sys/kernel/debug/remoteproc/。
rproc_init_sysfs 对应:remoteproc_sysfs.c ; 在这里注册一个类,并有一些文件被创建:
static struct attribute *rproc_attrs[] = {&dev_attr_firmware.attr,&dev_attr_state.attr,&dev_attr_name.attr,NULL
};
上面的属性文件创建的实例如下:
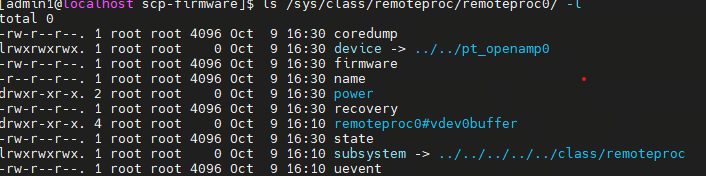
/sys/class/remoteproc/remoteproc0/ |-- firmware--配置/lib/firmware目录下的固件名称。 |-- name--远端处理器名称。 |-- state--仅支持start(rproc_boot)/stop(rproc_shutdown)两个写状态。读状态包括offline/suspended/running/crashed/deleted/invalid。 `-- uevent
rproc_init_debugfs 对应:remoteproc_debugfs.c; 在这个源码中,也有一些文件创建出来:
void rproc_create_debug_dir(struct rproc *rproc)
343 {
344 struct device *dev = &rproc->dev;
345
346 if (!rproc_dbg)
347 return;
348
349 rproc->dbg_dir = debugfs_create_dir(dev_name(dev), rproc_dbg);
350 if (!rproc->dbg_dir)
351 return;
352
353 debugfs_create_file("name", 0400, rproc->dbg_dir,
354 rproc, &rproc_name_ops);
355 debugfs_create_file("recovery", 0400, rproc->dbg_dir,
356 rproc, &rproc_recovery_ops);
357 debugfs_create_file("crash", 0200, rproc->dbg_dir,
358 rproc, &rproc_crash_ops);
359 debugfs_create_file("resource_table", 0400, rproc->dbg_dir,
360 rproc, &rproc_rsc_table_ops);
361 debugfs_create_file("carveout_memories", 0400, rproc->dbg_dir,
362 rproc, &rproc_carveouts_ops);
363 }
有些文件没有创建出来, 可能是权限问题。
2.3 举一个操作 state 文件的函数调用流程
源码中实现的函数:
/* Change remote processor state via sysfs */
static ssize_t state_store(struct device *dev,struct device_attribute *attr,const char *buf, size_t count)
{struct rproc *rproc = to_rproc(dev);int ret = 0;if (sysfs_streq(buf, "start")) {if (rproc->state == RPROC_RUNNING)return -EBUSY;ret = rproc_boot(rproc);if (ret)dev_err(&rproc->dev, "Boot failed: %d\n", ret);} else if (sysfs_streq(buf, "stop")) {if (rproc->state != RPROC_RUNNING)return -EINVAL;rproc_shutdown(rproc);} else {dev_err(&rproc->dev, "Unrecognised option: %s\n", buf);ret = -EINVAL;}return ret ? ret : count;
}
static DEVICE_ATTR_RW(state);
当写入 “start” ,调用 rproc_boot
/*** rproc_boot() - boot a remote processor* @rproc: handle of a remote processor** Boot a remote processor (i.e. load its firmware, power it on, ...).** If the remote processor is already powered on, this function immediately* returns (successfully).** Returns 0 on success, and an appropriate error value otherwise.*/
int rproc_boot(struct rproc *rproc)
{const struct firmware *firmware_p = NULL;struct device *dev;int ret;if (!rproc) {pr_err("invalid rproc handle\n");return -EINVAL;}dev = &rproc->dev;ret = mutex_lock_interruptible(&rproc->lock);if (ret) {dev_err(dev, "can't lock rproc %s: %d\n", rproc->name, ret);return ret;}if (rproc->state == RPROC_DELETED) {ret = -ENODEV;dev_err(dev, "can't boot deleted rproc %s\n", rproc->name);goto unlock_mutex;}/* skip the boot process if rproc is already powered up */if (atomic_inc_return(&rproc->power) > 1) {ret = 0;goto unlock_mutex;}dev_info(dev, "powering up %s\n", rproc->name);/* load firmware */if(rproc->is_remote == false) {ret = request_firmware(&firmware_p, rproc->firmware, dev); //加载固件if (ret < 0) {dev_err(dev, "request_firmware failed: %d\n", ret);goto downref_rproc;}ret = rproc_fw_boot(rproc, firmware_p); //重启固件} else {ret = rproc_fw_boot_dev(rproc, NULL);}release_firmware(firmware_p);downref_rproc:if (ret)atomic_dec(&rproc->power);
unlock_mutex:mutex_unlock(&rproc->lock);return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(rproc_boot);
先看加载固件:request_firmware
# drivers/base/firmware_loader/main.c/*** request_firmware() - send firmware request and wait for it* @firmware_p: pointer to firmware image* @name: name of firmware file* @device: device for which firmware is being loaded** @firmware_p will be used to return a firmware image by the name* of @name for device @device.** Should be called from user context where sleeping is allowed.** @name will be used as $FIRMWARE in the uevent environment and* should be distinctive enough not to be confused with any other* firmware image for this or any other device.** Caller must hold the reference count of @device.** The function can be called safely inside device's suspend and* resume callback.**/
int
request_firmware(const struct firmware **firmware_p, const char *name,struct device *device)
{int ret;/* Need to pin this module until return */__module_get(THIS_MODULE);ret = _request_firmware(firmware_p, name, device, NULL, 0,FW_OPT_UEVENT);module_put(THIS_MODULE);return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(request_firmware);
_request_firmware:
# drivers/base/firmware_loader/main.c
static int
_request_firmware(const struct firmware **firmware_p, const char *name,struct device *device, void *buf, size_t size,enum fw_opt opt_flags)
{struct firmware *fw = NULL;int ret;if (!firmware_p)return -EINVAL;if (!name || name[0] == '\0') {ret = -EINVAL;goto out;}ret = _request_firmware_prepare(&fw, name, device, buf, size,opt_flags);if (ret <= 0) /* error or already assigned */goto out;ret = fw_get_filesystem_firmware(device, fw->priv, "", NULL); //根据文件系统路径获取固件
#ifdef CONFIG_FW_LOADER_COMPRESSif (ret == -ENOENT)ret = fw_get_filesystem_firmware(device, fw->priv, ".xz",fw_decompress_xz);
#endifif (ret) {if (!(opt_flags & FW_OPT_NO_WARN))dev_warn(device,"Direct firmware load for %s failed with error %d\n",name, ret);ret = firmware_fallback_sysfs(fw, name, device, opt_flags, ret);} elseret = assign_fw(fw, device, opt_flags);out:if (ret < 0) {fw_abort_batch_reqs(fw);release_firmware(fw);fw = NULL;}*firmware_p = fw;return ret;
}
fw_get_filesystem_firmware: 根据文件系统路径获取固件
/* direct firmware loading support */
static char fw_path_para[256];
static const char * const fw_path[] = {fw_path_para,"/lib/firmware/updates/" UTS_RELEASE,"/lib/firmware/updates","/lib/firmware/" UTS_RELEASE,"/lib/firmware"
};/** Typical usage is that passing 'firmware_class.path=$CUSTOMIZED_PATH'* from kernel command line because firmware_class is generally built in* kernel instead of module.*/
module_param_string(path, fw_path_para, sizeof(fw_path_para), 0644);
MODULE_PARM_DESC(path, "customized firmware image search path with a higher priority than default path");static int
fw_get_filesystem_firmware(struct device *device, struct fw_priv *fw_priv,const char *suffix,int (*decompress)(struct device *dev,struct fw_priv *fw_priv,size_t in_size,const void *in_buffer))
{loff_t size;int i, len;int rc = -ENOENT;char *path;enum kernel_read_file_id id = READING_FIRMWARE;size_t msize = INT_MAX;void *buffer = NULL;/* Already populated data member means we're loading into a buffer */if (!decompress && fw_priv->data) {buffer = fw_priv->data;id = READING_FIRMWARE_PREALLOC_BUFFER;msize = fw_priv->allocated_size;}path = __getname();if (!path)return -ENOMEM;for (i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE(fw_path); i++) {/* skip the unset customized path */if (!fw_path[i][0])continue;len = snprintf(path, PATH_MAX, "%s/%s%s",fw_path[i], fw_priv->fw_name, suffix);if (len >= PATH_MAX) {rc = -ENAMETOOLONG;break;}fw_priv->size = 0;rc = kernel_read_file_from_path(path, &buffer, &size,msize, id);if (rc) {if (rc != -ENOENT)dev_warn(device, "loading %s failed with error %d\n",path, rc);elsedev_dbg(device, "loading %s failed for no such file or directory.\n",path);continue;}if (decompress) {dev_dbg(device, "f/w decompressing %s\n",fw_priv->fw_name);rc = decompress(device, fw_priv, size, buffer);/* discard the superfluous original content */vfree(buffer);buffer = NULL;if (rc) {fw_free_paged_buf(fw_priv);continue;}} else {dev_dbg(device, "direct-loading %s\n",fw_priv->fw_name);if (!fw_priv->data)fw_priv->data = buffer;fw_priv->size = size;}fw_state_done(fw_priv);break;}__putname(path);return rc;
}
总结rproc_boot 的调用流程
rproc_bootrequest_firmware--根据rproc->firmware名称,到fw_path目录下查找固件并加载。参考《Linux下固件加载器Firmware Loader》。rproc_fw_bootrproc_fw_sanity_check--调用rproc_ops的sanity_check对固件进行基本检查。对于ELF文件则是调用rproc_elf_sanity_check()进行检查。rproc_enable_iommu--如果存在IOMMU的话,使能IOMMU。rproc_get_boot_addr--调用rproc_ops的get_boot_addr函数获取启动地址。对于ELF文件则是调用rproc_elf_get_boot_addr()。rproc_parse_fw--调用rproc_ops的parse_fw函数。rproc_handle_resources--遍历resource_table,处理rproc的resource_table中资源。rproc_alloc_registered_carveouts--分配rproc所有注册的carveouts。rproc_startrproc_load_segments--调用rproc_ops的load函数。对于ELF文件则是调用rproc_elf_load_segments(),加载ELF的Segment到内存中。rproc_find_loaded_rsc_table--调用rproc_ops的find_loaded_src_table,从固件中加载resource table。rproc_prepare_subdevices--遍历rproc的subdevs并调用prepare函数。rproc->ops->start--给远程处理器上电。rproc_start_subdevices--调用subdevs的start函数。release_firmware--释放固件相关资源。
三、remoteproc 的重要的数据结构
3.1 struct rproc是remoteproc框架中对一个Remote Processor的抽象:
struct rproc {struct list_head node;struct iommu_domain *domain;const char *name;char *firmware;--对应固件名称。void *priv;struct rproc_ops *ops;struct device dev;atomic_t power;unsigned int state;struct mutex lock;struct dentry *dbg_dir;struct list_head traces;int num_traces;struct list_head carveouts;struct list_head mappings;u32 bootaddr;--rproc执行的第一条指令地址。struct list_head rvdevs;struct list_head subdevs;struct idr notifyids;int index;struct work_struct crash_handler;unsigned int crash_cnt;bool recovery_disabled;int max_notifyid;struct resource_table *table_ptr;struct resource_table *cached_table;size_t table_sz;bool has_iommu;bool auto_boot;struct list_head dump_segments;int nb_vdev;bool early_boot;
};struct rproc_ops是特定remoteproc设备的操作函数:
struct rproc_ops {int (*start)(struct rproc *rproc);--给remoteproc上电并且启动。int (*stop)(struct rproc *rproc);--给remoteproc下电。void (*kick)(struct rproc *rproc, int vqid);void * (*da_to_va)(struct rproc *rproc, u64 da, int len);int (*parse_fw)(struct rproc *rproc, const struct firmware *fw);int (*handle_rsc)(struct rproc *rproc, u32 rsc_type, void *rsc,int offset, int avail);struct resource_table *(*find_loaded_rsc_table)(struct rproc *rproc, const struct firmware *fw);int (*load)(struct rproc *rproc, const struct firmware *fw);--加载固件到内存,给remoteproc使用。int (*sanity_check)(struct rproc *rproc, const struct firmware *fw);--对固件进行合理性检查。u32 (*get_boot_addr)(struct rproc *rproc, const struct firmware *fw);--获取启动地址。
};remoteproc创建者相关API:
struct rproc *rproc_alloc(struct device *dev, const char *name,const struct rproc_ops *ops,const char *firmware, int len);--分配一个struct rproc,并对其进行初始化。
void rproc_put(struct rproc *rproc);--减小remoteproc引用计数。
int rproc_add(struct rproc *rproc);--将struct rproc注册到remoteproc框架中,创建remoteproc相关设备。
int rproc_del(struct rproc *rproc);--移除remoteproc设备。
void rproc_free(struct rproc *rproc);--释放struct rproc。rproc_alloc:
/*** rproc_alloc() - allocate a remote processor handle* @dev: the underlying device* @name: name of this remote processor* @ops: platform-specific handlers (mainly start/stop)* @firmware: name of firmware file to load, can be NULL* @len: length of private data needed by the rproc driver (in bytes)** Allocates a new remote processor handle, but does not register* it yet. if @firmware is NULL, a default name is used.** This function should be used by rproc implementations during initialization* of the remote processor.** After creating an rproc handle using this function, and when ready,* implementations should then call rproc_add() to complete* the registration of the remote processor.** On success the new rproc is returned, and on failure, NULL.** Note: _never_ directly deallocate @rproc, even if it was not registered* yet. Instead, when you need to unroll rproc_alloc(), use rproc_free().*/
struct rproc *rproc_alloc(struct device *dev, const char *name,const struct rproc_ops *ops,const char *firmware, int len)
{struct rproc *rproc;char *p, *template = "rproc-%s-fw";int name_len;if (!dev || !name || !ops)return NULL;if (!firmware) {/** If the caller didn't pass in a firmware name then* construct a default name.*/name_len = strlen(name) + strlen(template) - 2 + 1;p = kmalloc(name_len, GFP_KERNEL);if (!p)return NULL;snprintf(p, name_len, template, name);} else {p = kstrdup(firmware, GFP_KERNEL);if (!p)return NULL;}rproc = kzalloc(sizeof(struct rproc) + len, GFP_KERNEL);if (!rproc) {kfree(p);return NULL;}rproc->ops = kmemdup(ops, sizeof(*ops), GFP_KERNEL);if (!rproc->ops) {kfree(p);kfree(rproc);return NULL;}rproc->firmware = p;rproc->name = name;rproc->priv = &rproc[1];rproc->auto_boot = true;device_initialize(&rproc->dev); //初始化设备。rproc->dev.parent = dev;rproc->dev.type = &rproc_type;rproc->dev.class = &rproc_class;rproc->dev.driver_data = rproc;idr_init(&rproc->notifyids);/* Assign a unique device index and name */rproc->index = ida_simple_get(&rproc_dev_index, 0, 0, GFP_KERNEL);if (rproc->index < 0) {dev_err(dev, "ida_simple_get failed: %d\n", rproc->index);put_device(&rproc->dev);return NULL;}dev_set_name(&rproc->dev, "remoteproc%d", rproc->index); //设置设备名称。atomic_set(&rproc->power, 0);/* Default to ELF loader if no load function is specified */if (!rproc->ops->load) {rproc->ops->load = rproc_elf_load_segments;rproc->ops->parse_fw = rproc_elf_load_rsc_table;rproc->ops->find_loaded_rsc_table = rproc_elf_find_loaded_rsc_table;rproc->ops->sanity_check = rproc_elf_sanity_check;rproc->ops->get_boot_addr = rproc_elf_get_boot_addr;}mutex_init(&rproc->lock);INIT_LIST_HEAD(&rproc->carveouts);INIT_LIST_HEAD(&rproc->mappings);INIT_LIST_HEAD(&rproc->traces);INIT_LIST_HEAD(&rproc->rvdevs);INIT_LIST_HEAD(&rproc->subdevs);INIT_LIST_HEAD(&rproc->dump_segments);INIT_WORK(&rproc->crash_handler, rproc_crash_handler_work); //设置crash_handlerrproc->state = RPROC_OFFLINE;return rproc;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(rproc_alloc);
rproc_add:
/*** rproc_add() - register a remote processor* @rproc: the remote processor handle to register** Registers @rproc with the remoteproc framework, after it has been* allocated with rproc_alloc().** This is called by the platform-specific rproc implementation, whenever* a new remote processor device is probed.** Returns 0 on success and an appropriate error code otherwise.** Note: this function initiates an asynchronous firmware loading* context, which will look for virtio devices supported by the rproc's* firmware.** If found, those virtio devices will be created and added, so as a result* of registering this remote processor, additional virtio drivers might be* probed.*/
int rproc_add(struct rproc *rproc)
{struct device *dev = &rproc->dev;int ret;ret = device_add(dev); //创建rproc设备。if (ret < 0)return ret;dev_info(dev, "%s is available\n", rproc->name);/* create debugfs entries */rproc_create_debug_dir(rproc); //创建特定remoteproc的调试节点。/* if rproc is marked always-on, request it to boot */if (rproc->auto_boot) {ret = rproc_trigger_auto_boot(rproc); //支持autoboot的情况下调用。if (ret < 0)return ret;}/* expose to rproc_get_by_phandle users */mutex_lock(&rproc_list_mutex);list_add(&rproc->node, &rproc_list); // 把节点注册到remoteproc 核心中mutex_unlock(&rproc_list_mutex);return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(rproc_add);
对于vdev(a virtio device)资源,调用rproc_handle_vdev进行处理:
先介绍rproc_handle_vdev 函数的定义和调用者是哪个函数:
/*** A lookup table for resource handlers. The indices are defined in* enum fw_resource_type.*/
static rproc_handle_resource_t rproc_loading_handlers[RSC_LAST] = {[RSC_CARVEOUT] = (rproc_handle_resource_t)rproc_handle_carveout,[RSC_DEVMEM] = (rproc_handle_resource_t)rproc_handle_devmem,[RSC_TRACE] = (rproc_handle_resource_t)rproc_handle_trace,[RSC_VDEV] = (rproc_handle_resource_t)rproc_handle_vdev,
};
定义了不同的resource,对应不同的回调函数。
rproc_handle_vdev:
/*** rproc_handle_vdev() - handle a vdev fw resource* @rproc: the remote processor* @rsc: the vring resource descriptor* @avail: size of available data (for sanity checking the image)** This resource entry requests the host to statically register a virtio* device (vdev), and setup everything needed to support it. It contains* everything needed to make it possible: the virtio device id, virtio* device features, vrings information, virtio config space, etc...** Before registering the vdev, the vrings are allocated from non-cacheable* physically contiguous memory. Currently we only support two vrings per* remote processor (temporary limitation). We might also want to consider* doing the vring allocation only later when ->find_vqs() is invoked, and* then release them upon ->del_vqs().** Note: @da is currently not really handled correctly: we dynamically* allocate it using the DMA API, ignoring requested hard coded addresses,* and we don't take care of any required IOMMU programming. This is all* going to be taken care of when the generic iommu-based DMA API will be* merged. Meanwhile, statically-addressed iommu-based firmware images should* use RSC_DEVMEM resource entries to map their required @da to the physical* address of their base CMA region (ouch, hacky!).** Returns 0 on success, or an appropriate error code otherwise*/
static int rproc_handle_vdev(struct rproc *rproc, struct fw_rsc_vdev *rsc,int offset, int avail)
{struct device *dev = &rproc->dev;struct rproc_vdev *rvdev;int i, ret;char name[16];/* make sure resource isn't truncated */if (sizeof(*rsc) + rsc->num_of_vrings * sizeof(struct fw_rsc_vdev_vring)+ rsc->config_len > avail) {dev_err(dev, "vdev rsc is truncated\n");return -EINVAL;}/* make sure reserved bytes are zeroes */if (rsc->reserved[0] || rsc->reserved[1]) {dev_err(dev, "vdev rsc has non zero reserved bytes\n");return -EINVAL;}dev_dbg(dev, "vdev rsc: id %d, dfeatures 0x%x, cfg len %d, %d vrings\n",rsc->id, rsc->dfeatures, rsc->config_len, rsc->num_of_vrings);/* we currently support only two vrings per rvdev */if (rsc->num_of_vrings > ARRAY_SIZE(rvdev->vring)) {dev_err(dev, "too many vrings: %d\n", rsc->num_of_vrings);return -EINVAL;}rvdev = kzalloc(sizeof(*rvdev), GFP_KERNEL);if (!rvdev)return -ENOMEM;kref_init(&rvdev->refcount);rvdev->id = rsc->id;rvdev->rproc = rproc;rvdev->index = rproc->nb_vdev++;/* Initialise vdev subdevice */snprintf(name, sizeof(name), "vdev%dbuffer", rvdev->index); //这个在/sys是/sys/class/remoteproc/remoteproc0/remoteproc0#vdev0buffer.rvdev->dev.parent = &rproc->dev;rvdev->dev.dma_pfn_offset = rproc->dev.parent->dma_pfn_offset;rvdev->dev.release = rproc_rvdev_release;dev_set_name(&rvdev->dev, "%s#%s", dev_name(rvdev->dev.parent), name);// 最终形成remoteproc0#vdev0buffer。dev_set_drvdata(&rvdev->dev, rvdev);ret = device_register(&rvdev->dev);if (ret) {put_device(&rvdev->dev);return ret;}/* Make device dma capable by inheriting from parent's capabilities */set_dma_ops(&rvdev->dev, get_dma_ops(rproc->dev.parent));ret = dma_coerce_mask_and_coherent(&rvdev->dev,dma_get_mask(rproc->dev.parent));if (ret) {dev_warn(dev,"Failed to set DMA mask %llx. Trying to continue... %x\n",dma_get_mask(rproc->dev.parent), ret);}/* parse the vrings */for (i = 0; i < rsc->num_of_vrings; i++) {ret = rproc_parse_vring(rvdev, rsc, i);if (ret)goto free_rvdev;}/* remember the resource offset*/rvdev->rsc_offset = offset;/* allocate the vring resources */for (i = 0; i < rsc->num_of_vrings; i++) {if(rvdev->rproc->is_remote == true)ret = rproc_associate_vring_dev(rvdev, i);elseret = rproc_alloc_vring(rvdev, i);if (ret)goto unwind_vring_allocations;}list_add_tail(&rvdev->node, &rproc->rvdevs);if(rvdev->rproc->is_remote == true)rvdev->subdev.start = rproc_vdev_device_do_start;elservdev->subdev.start = rproc_vdev_do_start;rvdev->subdev.stop = rproc_vdev_do_stop;rproc_add_subdev(rproc, &rvdev->subdev);return 0;unwind_vring_allocations:for (i--; i >= 0; i--)rproc_free_vring(&rvdev->vring[i]);
free_rvdev:device_unregister(&rvdev->dev);return ret;
}
![]()
![]()
留一个问题: virtio0 目录下,virtio0.cm3_cmd.-1.1024 virtio0.cm3_report.-1.1025 virtio0.rpmsg_ctrl.0.0 virtio0.rpmsg_ns.53.53 这些是如何创建的以及代表什么意思?
哪个函数会调用到rproc_handle_vdev函数?
rproc_boot-> rproc_fw_boot ->rproc_handle_resources->rproc_handle_vdev (这是上面加载固件的流程)
rproc_handle_resourcesrproc_handle_rsc--对于vendor自定义资源,调用rproc_ops的handle_rsc处理。rproc_handle_vdev--适用于vdev类型资源。device_register--注册vdev设备。dma_coerce_mask_and_coherentrproc_parse_vringrproc_alloc_vringrproc_add_subdev--添加subdev到remoteproc。rproc_vdev_do_start--subdev的start函数。rproc_add_virtio_devregister_virtio_device--注册virtio_device。 rproc_vdev_do_stoprproc_handle_tracerproc_handle_devmemrproc_handle_carveout
四、
