Easysearch 索引别名(Index Alias)详解
在 Easysearch 中,索引别名(Index Alias) 是一种逻辑名称,它可以指向一个或多个真实索引。
使用别名的好处在于:
- 让应用层无需感知底层索引名变化;
- 方便进行索引切换、版本升级和数据迁移;
- 支持查询、写入、过滤、路由等控制;
- 实现读写分离或权限隔离。
简而言之,别名是索引的抽象层,就像数据库中的“视图(View)”或操作系统中的“符号链接(symlink)”。
创建索引别名
别名可以在创建索引时定义,也可以在已有索引上添加。
在创建索引时定义别名
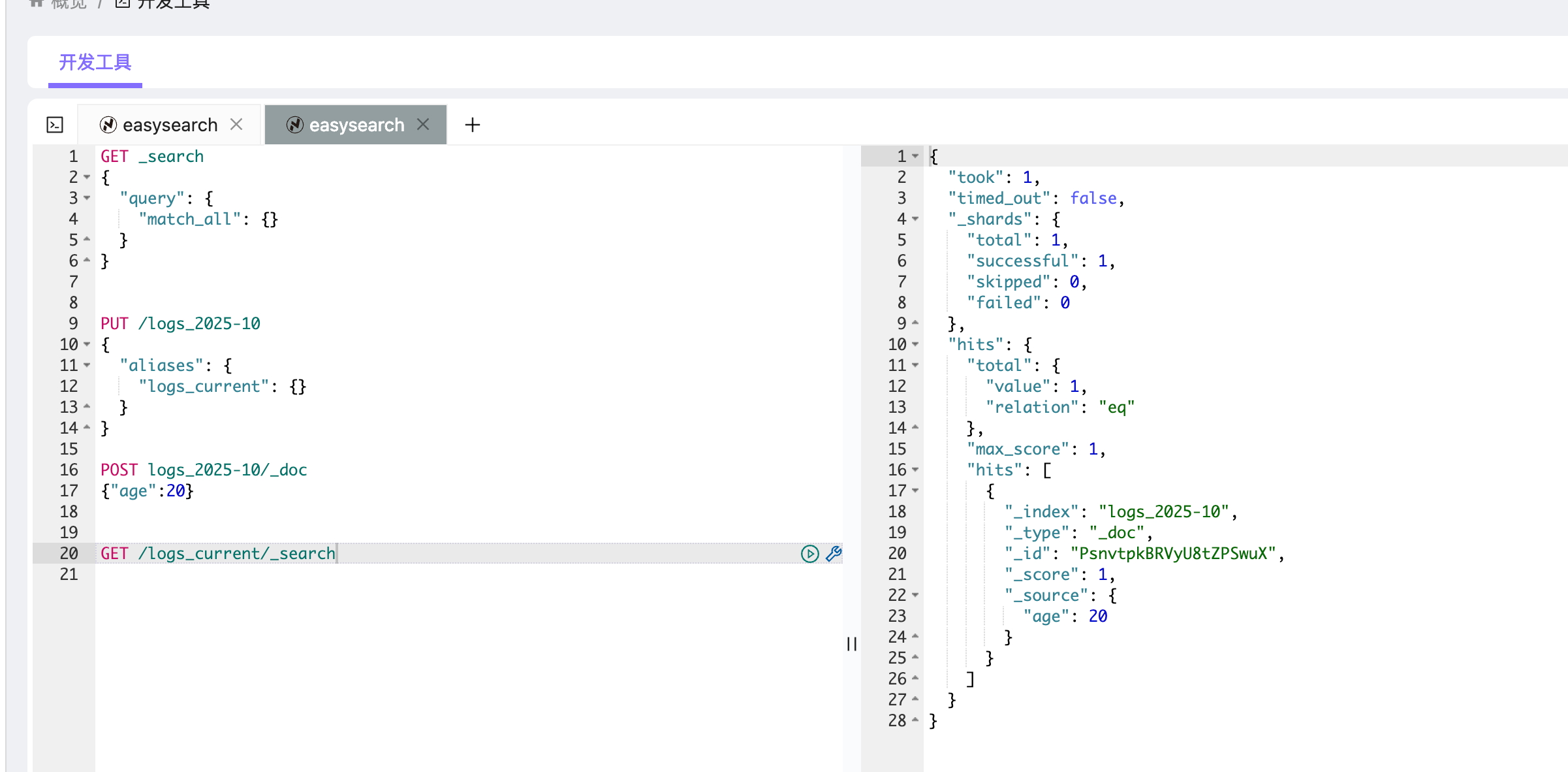
PUT /logs_2025-10
{"aliases": {"logs_current": {}}
}
该操作创建索引 logs_2025-10,并同时定义一个别名 logs_current。
之后,所有针对 logs_current 的查询都会路由到 logs_2025-10:
POST logs_2025-10/_doc
{"age":20}GET /logs_current/_search
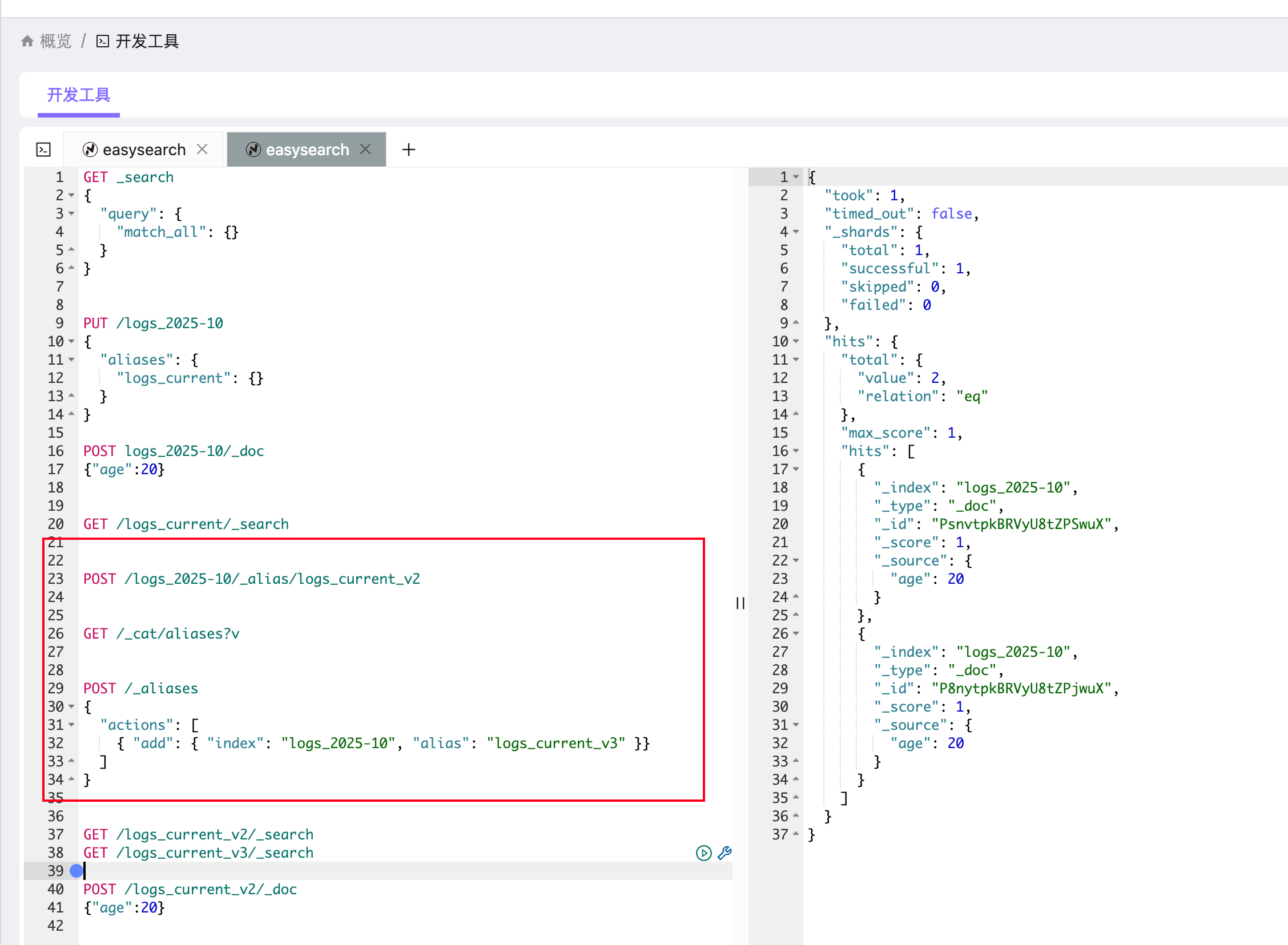
给现有索引添加别名
POST /logs_2025-10/_alias/logs_current_v2
或者使用 _aliases 批量操作:
POST /_aliases
{"actions": [{ "add": { "index": "logs_2025-10", "alias": "logs_current_v3" }}]
}
查询与写入的区别
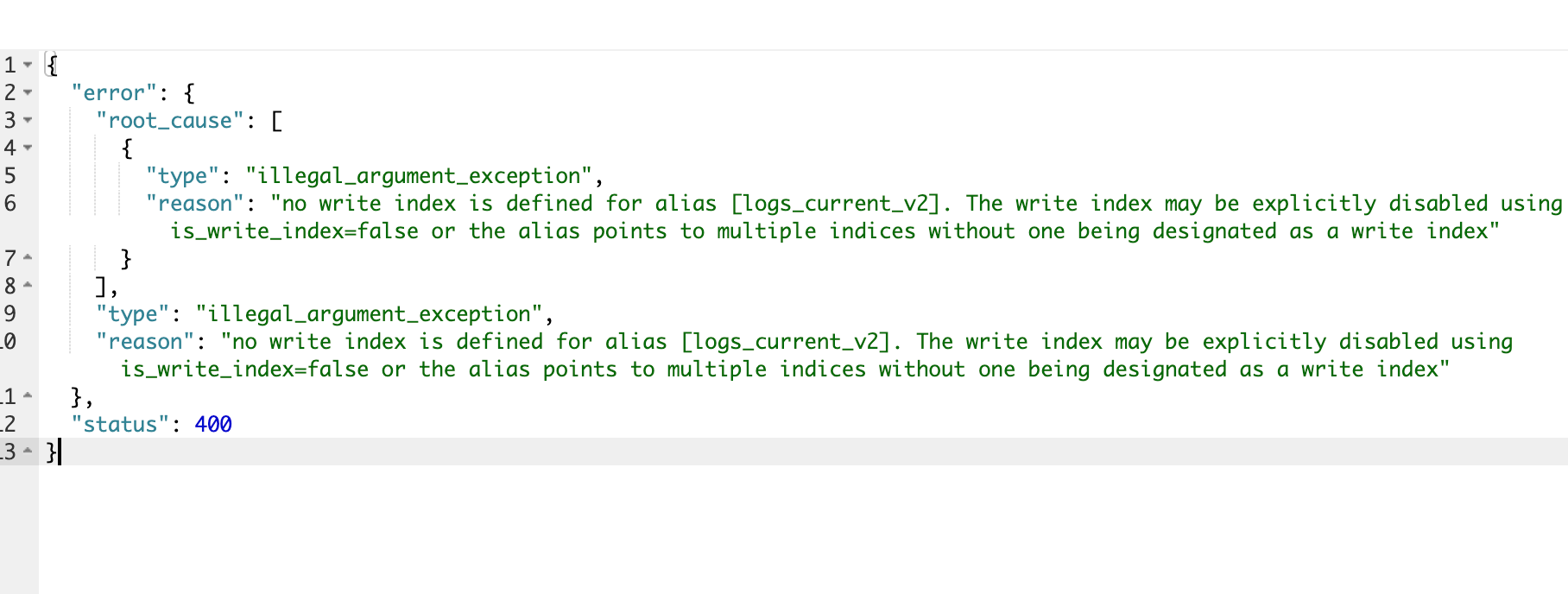
默认情况下,别名仅支持查询。
如果一个别名指向多个索引,那么写入(POST /alias/_doc)操作会报错。
{"error": {"root_cause": [{"type": "illegal_argument_exception","reason": "no write index is defined for alias [logs_current_v2]. The write index may be explicitly disabled using is_write_index=false or the alias points to multiple indices without one being designated as a write index"}],"type": "illegal_argument_exception","reason": "no write index is defined for alias [logs_current_v2]. The write index may be explicitly disabled using is_write_index=false or the alias points to multiple indices without one being designated as a write index"},"status": 400
}
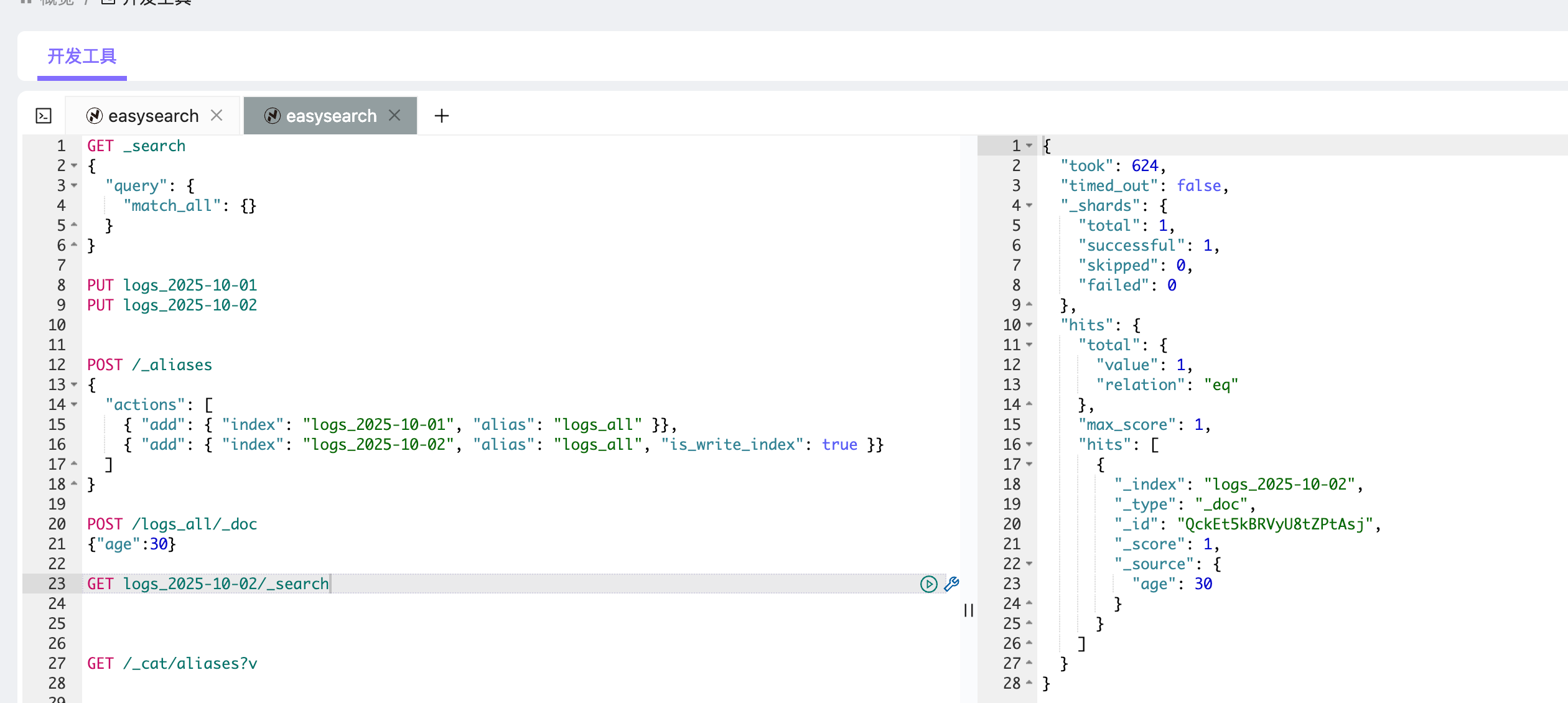
为了解决这一问题,可以通过 is_write_index 参数指定某个索引作为写入目标。
POST /_aliases
{"actions": [{ "add": { "index": "logs_2025-10-01", "alias": "logs_all" }},{ "add": { "index": "logs_2025-10-02", "alias": "logs_all", "is_write_index": true }}]
}
此时:
- 查询
GET /logs_all/_search会同时检索两个索引; - 写入
POST /logs_all/_doc时,数据会写入logs_2025-10。
动态切换索引(零停机升级)
别名的最大优势之一是实现索引的无缝切换。
例如,应用程序始终通过 logs_all 查询数据,而底层实际索引会按天数变化。
切换示例:
POST /_aliases
{"actions": [{ "remove": { "index": "logs_2025-10-01", "alias": "logs_all" }},{ "add": { "index": "logs_2025-10-03", "alias": "logs_all" }}]
}
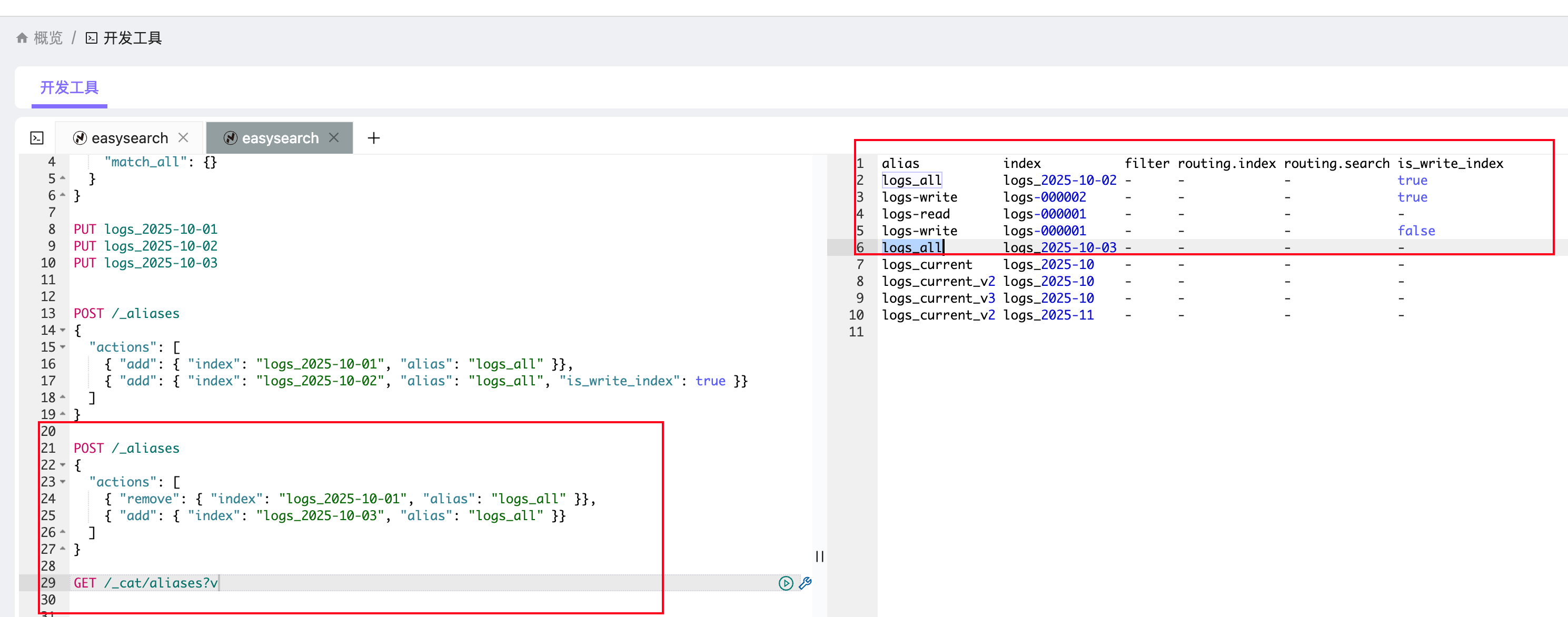
这里我移除了logs_2025-10-01,然后添加了logs_2025-10-03。
可以使用GET /_cat/aliases?v查看。
过滤别名(Filtered Alias)
别名还可以定义过滤条件,控制用户只能看到部分数据。
这是实现数据分区视图或权限隔离的常见方式。
它展示如何让一个别名只返回 region=china 的文档,而不暴露其他地区的数据。
1. 创建一个示例索引并插入数据
PUT /transactions
{"mappings": {"properties": {"region": { "type": "keyword" },"user": { "type": "keyword" },"amount": { "type": "float" }}}
}POST /transactions/_bulk
{ "index": { "_id": 1 } }
{ "region": "china", "user": "alice", "amount": 100.0 }
{ "index": { "_id": 2 } }
{ "region": "usa", "user": "bob", "amount": 200.0 }
{ "index": { "_id": 3 } }
{ "region": "china", "user": "cindy", "amount": 150.0 }
{ "index": { "_id": 4 } }
{ "region": "japan", "user": "daisuke", "amount": 300.0 }
刷新索引:
POST /transactions/_refresh
创建过滤别名
定义一个只允许访问中国区数据的别名:
POST /_aliases
{"actions": [{"add": {"index": "transactions","alias": "transactions_cn","filter": {"term": { "region": "china" }}}}]
}
使用过滤别名查询
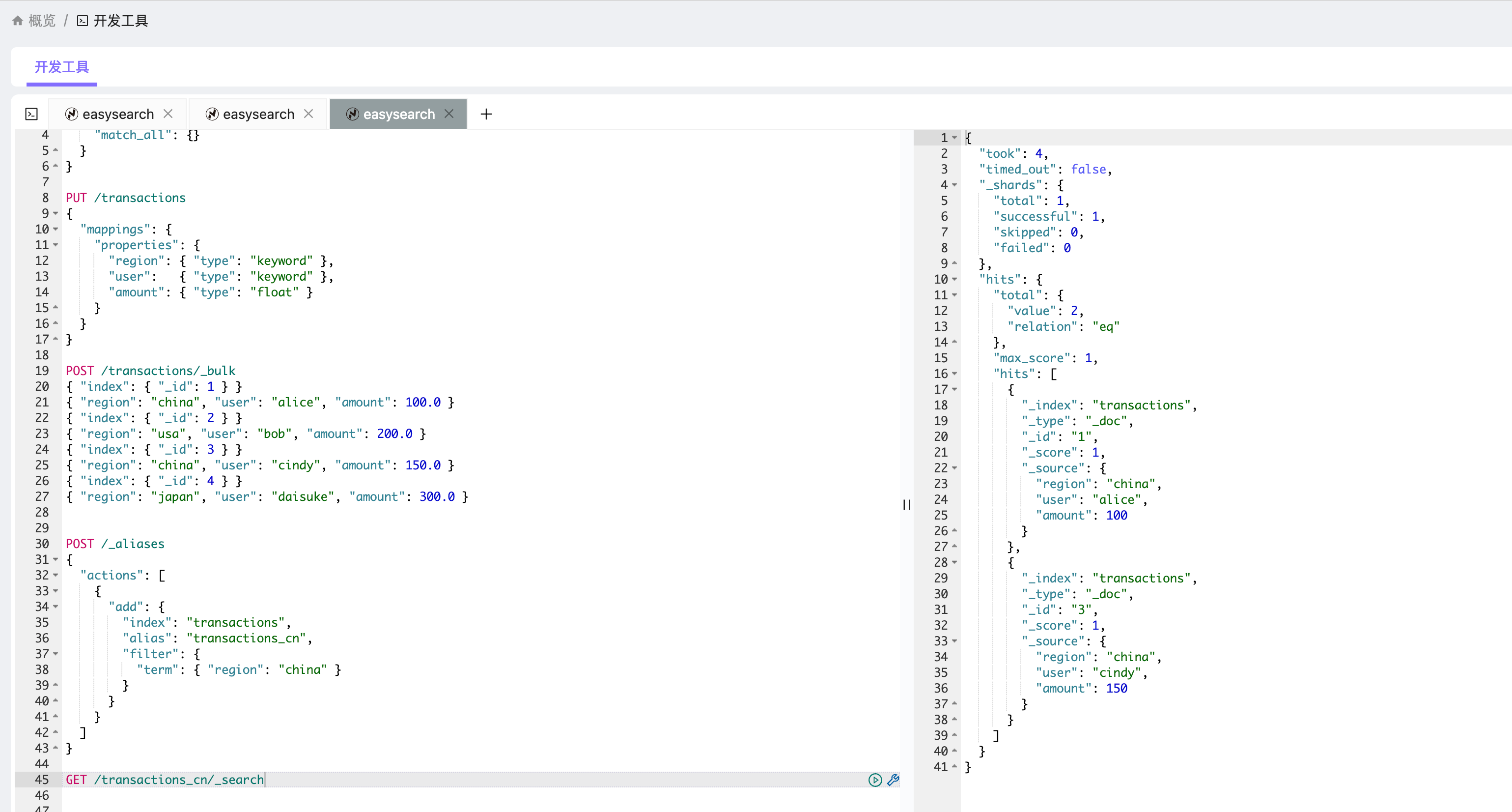
GET /transactions_cn/_search
返回结果类似:
{"hits": {"hits": [{"_id": "1","_source": { "region": "china", "user": "alice", "amount": 100.0 }},{"_id": "3","_source": { "region": "china", "user": "cindy", "amount": 150.0 }}]}
}
可以看到:
- 来自
usa和japan的记录不会出现在结果中; - 别名层面自动做了过滤;
- 应用层调用时完全不需要在查询语句中加
term条件。
路由别名(Routing Alias)
Elasticsearch 的数据分片(sharding)是通过一个公式决定的:
shard = hash(routing) % number_of_primary_shards
- 默认情况下,routing =
_id - 但如果你有多租户、分国家、分部门的场景,可以用业务逻辑字段当作 routing。
- routing 相同的数据会落在同一个分片上,提高写入和查询的性能。
因此:
把别名和 routing 绑定起来,可以实现“逻辑分区 + 性能优化 + 查询隔离”。
下面通过一个完整的数据例子演示。
创建索引
PUT users
{"settings": {"number_of_shards": 4,"number_of_replicas": 0},"mappings": {"properties": {"name": { "type": "keyword" },"country": { "type": "keyword" },"age": { "type": "integer" }}}
}
创建带 routing 的别名
POST /_aliases
{"actions": [{"add": {"index": "users","alias": "users_cn","routing": "china"}},{"add": {"index": "users","alias": "users_us","routing": "usa"}}]
}
✅ 我们现在有两个逻辑视图:
| Alias | Routing | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
users_cn | "china" | 代表中国用户 |
users_us | "usa" | 代表美国用户 |
通过别名写入数据
POST users_cn/_doc
{"name": "张伟","country": "CN","age": 29
}POST users_cn/_doc
{"name": "王芳","country": "CN","age": 34
}POST users_us/_doc
{"name": "John","country": "US","age": 42
}POST users_us/_doc
{"name": "Emily","country": "US","age": 31
}
✅ 实际都写入到同一个物理索引 users,
但数据被根据 routing(china / usa)分到了不同分片。
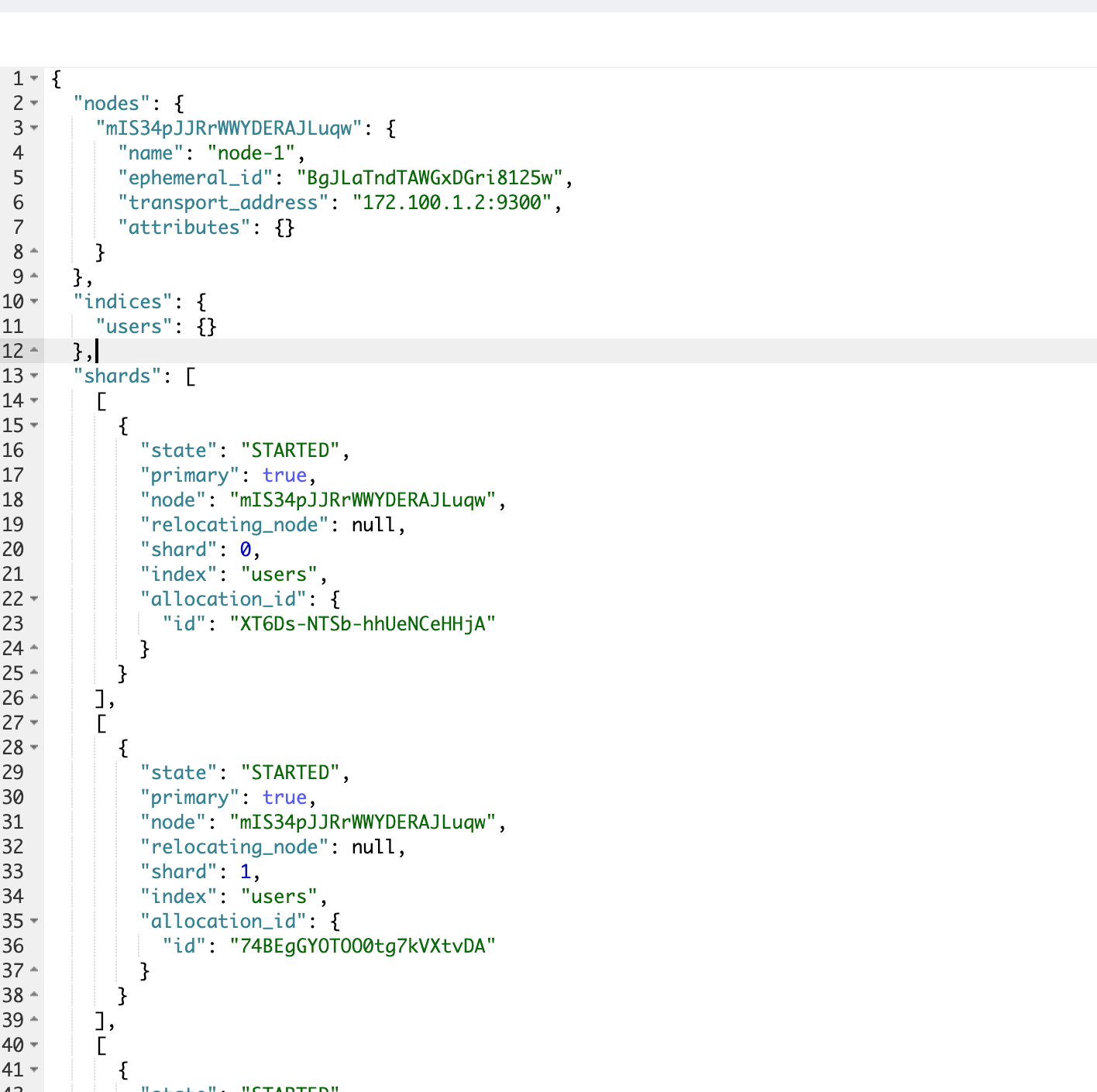
4️⃣ 验证分片路由情况
GET users/_search_shards
返回示例:
{"nodes": {"mIS34pJJRrWWYDERAJLuqw": {"name": "node-1","ephemeral_id": "BgJLaTndTAWGxDGri8125w","transport_address": "172.100.1.2:9300","attributes": {}}},"indices": {"users": {}},"shards": [[{"state": "STARTED","primary": true,"node": "mIS34pJJRrWWYDERAJLuqw","relocating_node": null,"shard": 0,"index": "users","allocation_id": {"id": "XT6Ds-NTSb-hhUeNCeHHjA"}}],[{"state": "STARTED","primary": true,"node": "mIS34pJJRrWWYDERAJLuqw","relocating_node": null,"shard": 1,"index": "users","allocation_id": {"id": "74BEgGYOTOO0tg7kVXtvDA"}}],[{"state": "STARTED","primary": true,"node": "mIS34pJJRrWWYDERAJLuqw","relocating_node": null,"shard": 2,"index": "users","allocation_id": {"id": "9hdcuoz5TbWql3kipudCxA"}}],[{"state": "STARTED","primary": true,"node": "mIS34pJJRrWWYDERAJLuqw","relocating_node": null,"shard": 3,"index": "users","allocation_id": {"id": "h0esaYy8QJmvfiGLjn3Zwg"}}]]
}
查询数据
查询中国区用户:
GET users_cn/_search
输出:
{"hits": {"total": 2,"hits": [{"_source": {"name": "张伟", "age": 29}},{"_source": {"name": "王芳", "age": 34}}]}
}
查询美国区用户:
GET users_us/_search
输出:
{"hits": {"total": 2,"hits": [{"_source": {"name": "John", "age": 42}},{"_source": {"name": "Emily", "age": 31}}]}
}
如果直接查物理索引
GET users/_search
返回所有 4 条记录,因为没带 routing。
再加一个过滤型 alias(可选)
POST /_aliases
{"actions": [{"add": {"index": "users","alias": "users_adults","filter": { "range": { "age": { "gte": 30 } } }}}]
}
然后查询:
GET users_adults/_search
→ 只返回 王芳(34岁)和 John(42岁)和Emily(31岁)。

。
| 场景 | routing 带来的好处 |
|---|---|
| 写入 | 相同 routing 的文档总是写入同一分片,减少 shard 跳转 |
| 查询 | 查询时只访问一个 shard,速度可提升数倍 |
| 多租户 | 每个租户 routing 不同,实现物理隔离 |
| 地域分区 | 中国区、美国区等逻辑分区共享同一个索引 |
查看与删除别名
查看当前集群中所有别名:
GET /_cat/aliases?v
输出结果:
alias index filter routing.index routing.search is_write_index
logs_current logs_2025-10 - - - -
logs_all logs_2025-10 - - - true
删除别名:
DELETE /logs_2025-10/_alias/logs_current
或:
POST /_aliases
{"actions": [{ "remove": { "index": "logs_2025-10", "alias": "logs_current" }}]
}
总结
Easysearch 的索引别名是一个轻量、强大且几乎“零成本”的机制,它在索引生命周期管理中起着核心作用。
合理使用别名,可以实现:
- 热切换(零停机索引迁移);
- 分片控制(按租户或地理位置隔离);
- 安全访问(按条件过滤可见数据);
- 持续演进(读写分离 + 版本平滑过渡)。
对于任何生产环境的 Easysearch 集群来说,别名是不可或缺的基础能力。
