# 轻量参数以确保快速完成并生成图像
import math, random
from typing import List, Tuple, Dict, Any
import matplotlib, matplotlib.pyplot as plt, pandas as pdmatplotlib.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei', 'Noto Sans CJK SC', 'Arial Unicode MS', 'WenQuanYi Zen Hei']
matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = FalseCity = Tuple[float, float]
Chromosome = List[int]def euclid(a: City, b: City) -> float:return math.hypot(a[0]-b[0], a[1]-b[1])def tour_length(route: Chromosome, coords: List[City]) -> float:return sum(euclid(coords[route[i]], coords[route[(i+1)%len(route)]]) for i in range(len(route)))def init_population(pop_size: int, n_cities: int, seed: int) -> List[Chromosome]:random.seed(seed); base=list(range(n_cities)); pop=[]for _ in range(pop_size):c=base[:]; random.shuffle(c); pop.append(c)return popdef fitness(route, coords): return 1.0/(tour_length(route, coords)+1e-9)def roulette(pop, coords):fit=[fitness(ind, coords) for ind in pop]; s=sum(fit); r=random.random()*s; a=0for ind,f in zip(pop,fit):a+=fif a>=r: return ind[:]return pop[-1][:]def ox(p1, p2):n=len(p1); i,k=sorted(random.sample(range(n),2))c1=[None]*n; c2=[None]*n; c1[i:k+1]=p1[i:k+1]; c2[i:k+1]=p2[i:k+1]def fill(c, d):cur=(k+1)%nfor x in d:if x not in c:c[cur]=x; cur=(cur+1)%nfill(c1,p2); fill(c2,p1); return c1,c2def invert_mut(r, pm):if random.random()<pm:n=len(r); i,k=sorted(random.sample(range(n),2)); r[i:k+1]=reversed(r[i:k+1])return rdef elite(pop, coords, k):return [r[:] for r in sorted(pop, key=lambda x: tour_length(x, coords))[:k]]def diversity(pop):n=len(pop[0]); return sum(len(set(ind[pos] for ind in pop))/n for pos in range(n))/ndef ga(coords, pop_size=100, generations=150, pc=0.95, pm=0.25, elite_k=2, seed=2025):random.seed(seed); n=len(coords); pop=init_population(pop_size,n,seed)best_hist=[]; mean_hist=[]; div_hist=[]; best_route=None; best_len=float('inf')for g in range(generations):lens=[tour_length(ind, coords) for ind in pop]gb=min(lens); gm=sum(lens)/len(lens)best_hist.append(gb); mean_hist.append(gm); div_hist.append(diversity(pop))if gb<best_len: best_len=gb; best_route=pop[lens.index(gb)][:]newp=elite(pop, coords, elite_k)while len(newp)<pop_size:p1=roulette(pop, coords); p2=roulette(pop, coords)c1,c2=ox(p1,p2) if random.random()<pc else (p1[:],p2[:])newp.append(c1);if len(newp)<pop_size: newp.append(c2)for i in range(elite_k, pop_size): newp[i]=invert_mut(newp[i], pm)pop=newpreturn {"best_route":best_route,"best_len":best_len,"best_hist":best_hist,"mean_hist":mean_hist,"div_hist":div_hist,"params":dict(pop_size=pop_size,generations=generations,pc=pc,pm=pm,elite_k=elite_k,seed=seed)}# 运行
random.seed(8); N=40
coords=[(random.uniform(0,100), random.uniform(0,100)) for _ in range(N)]
res=ga(coords)best_route=res["best_route"]; best_len=res["best_len"]
best_hist=res["best_hist"]; mean_hist=res["mean_hist"]; div_hist=res["div_hist"]; params=res["params"]df_coords=pd.DataFrame(coords, columns=["X坐标","Y坐标"]); df_coords.index.name="城市编号"df_route=pd.DataFrame({"次序":list(range(len(best_route))),"城市编号":best_route})
df_route["X坐标"]=df_route["城市编号"].map(df_coords["X坐标"]); df_route["Y坐标"]=df_route["城市编号"].map(df_coords["Y坐标"])def add_param_box(ax, params, extra=""):txt=("可调参数:\n"f"• 种群规模 = {params['pop_size']}\n"f"• 代数 = {params['generations']}\n"f"• 交叉概率 pc = {params['pc']}\n"f"• 变异概率 pm = {params['pm']}\n"f"• 精英数 = {params['elite_k']}\n"f"• 随机种子 = {params['seed']}\n""• 交叉:顺序交叉(OX)\n""• 变异:片段反转(类似 2-opt)")if extra: txt+="\n"+extraax.text(1.02,0.5,txt,transform=ax.transAxes,va="center",ha="left",fontsize=10,bbox=dict(boxstyle="round",alpha=0.15))# 图1 最终路线
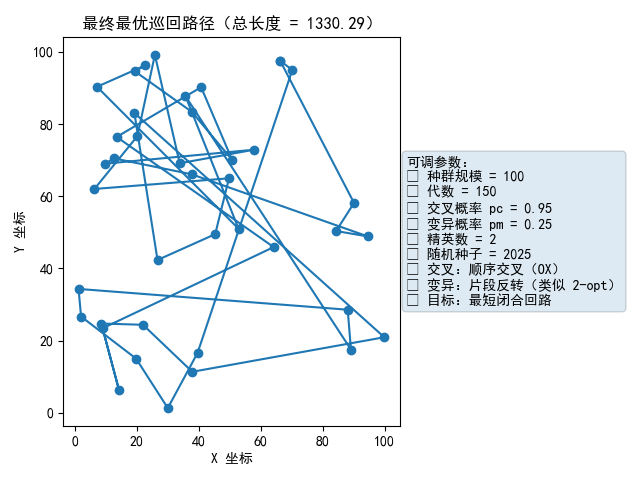
plt.figure()
xs=[coords[i][0] for i in best_route]+[coords[best_route[0]][0]]
ys=[coords[i][1] for i in best_route]+[coords[best_route[0]][1]]
plt.plot(xs, ys, marker="o")
plt.title(f"最终最优巡回路径(总长度 = {best_len:.2f})")
plt.xlabel("X 坐标"); plt.ylabel("Y 坐标")
ax=plt.gca(); add_param_box(ax, params, extra="• 目标:最短闭合回路")
plt.tight_layout(); plt.show()# 图2 代际最优
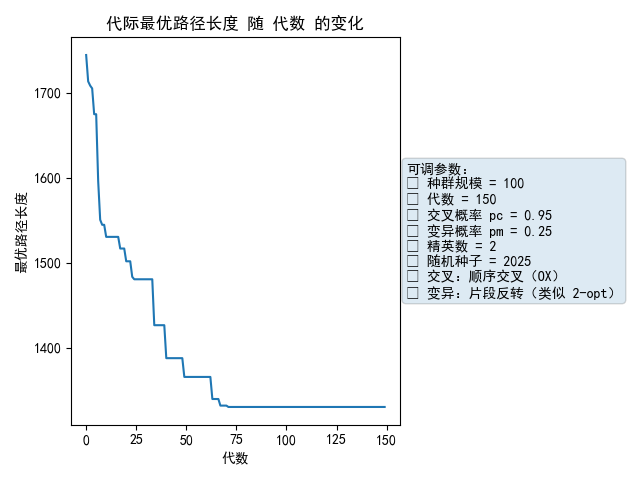
plt.figure(); plt.plot(range(len(best_hist)), best_hist)
plt.title("代际最优路径长度 随 代数 的变化"); plt.xlabel("代数"); plt.ylabel("最优路径长度")
ax=plt.gca(); add_param_box(ax, params); plt.tight_layout(); plt.show()# 图3 平均路径长度
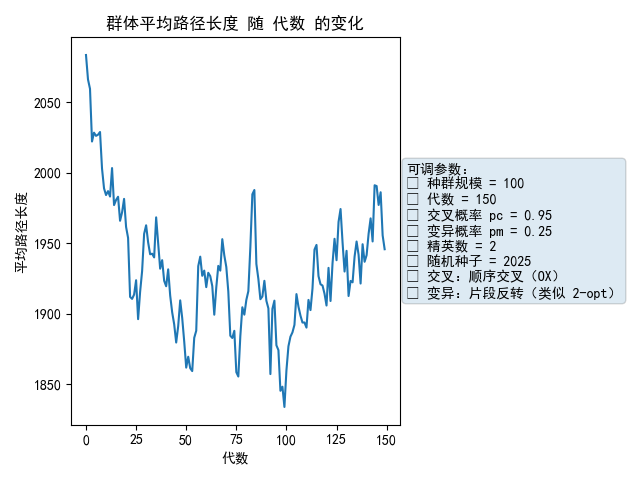
plt.figure(); plt.plot(range(len(mean_hist)), mean_hist)
plt.title("群体平均路径长度 随 代数 的变化"); plt.xlabel("代数"); plt.ylabel("平均路径长度")
ax=plt.gca(); add_param_box(ax, params); plt.tight_layout(); plt.show()# 图4 多样性
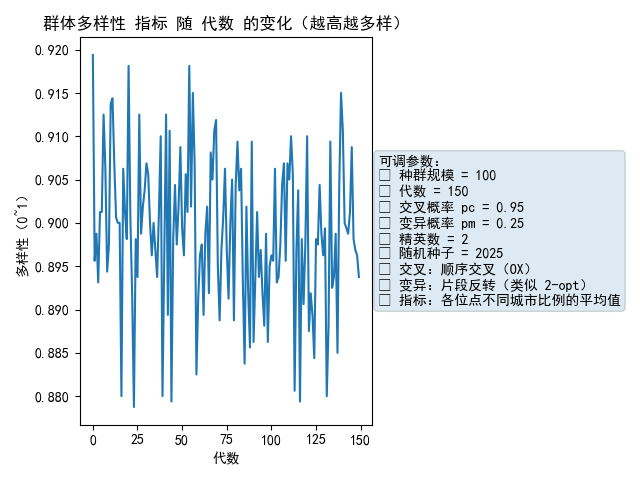
plt.figure(); plt.plot(range(len(div_hist)), div_hist)
plt.title("群体多样性 指标 随 代数 的变化(越高越多样)"); plt.xlabel("代数"); plt.ylabel("多样性(0~1)")
ax=plt.gca(); add_param_box(ax, params, extra="• 指标:各位点不同城市比例的平均值")
plt.tight_layout(); plt.show()# 文字示意图
plt.figure(); ax=plt.gca()
txt=("生成新解的方法:\n""1) 顺序交叉(OX):复制父代1的一个区段,其余按父代2出现顺序填入。\n""2) 片段反转变异:随机 i<k,将 route[i:k+1] 反转,常用于消除交叉、缩短路径。\n""调参提示:pc↑→重组更频繁;pm↑→探索更强;精英数↑→保留好解更稳但多样性下降。")
ax.text(0.05,0.5,txt,transform=ax.transAxes,fontsize=12,va="center",ha="left",bbox=dict(boxstyle="round",alpha=0.15))
ax.axis("off"); plt.title("遗传算法新解产生(中文说明)"); plt.tight_layout(); plt.show()# 保存最终路线图
plt.figure(); plt.plot(xs, ys, marker="o"); plt.title(f"最终最优巡回路径(总长度 = {best_len:.2f})")
plt.xlabel("X 坐标"); plt.ylabel("Y 坐标"); ax=plt.gca(); add_param_box(ax, params)
plt.tight_layout(); savepath="/mnt/data/GA_TSP_最终最优路径.png"; plt.savefig(savepath); savepath