项目1:FFMPEG推流器讲解(二):FFMPEG输出模块初始化
一.本章节内容:
FFMPEG输出模块主要用于初始化音视频推流功能,确保RV1126的码流能够通过FFMPEG正常推送。该模块的初始化流程包含以下步骤:
- 使用
avformat_alloc_output_context2分配AVFormatContext - 通过
avformat_new_stream初始化AVStream结构体 - 调用
avcodec_find_encoder获取对应的编码器 - 使用
avcodec_alloc_context3分配AVCodecContext - 配置AVCodecContext结构体参数
- 通过
avcodec_parameters_from_context将编码器参数传递到AVStream - 使用
avio_open初始化FFMPEG的IO结构体 - 调用
avformat_write_header完成AVFormatContext初始化
在RV1126+FFMPEG多路码流推流项目中,输出模块的初始化实现位于rkmedia_ffmpeg_config.cpp文件的init_rkmedia_ffmpeg_context函数中。
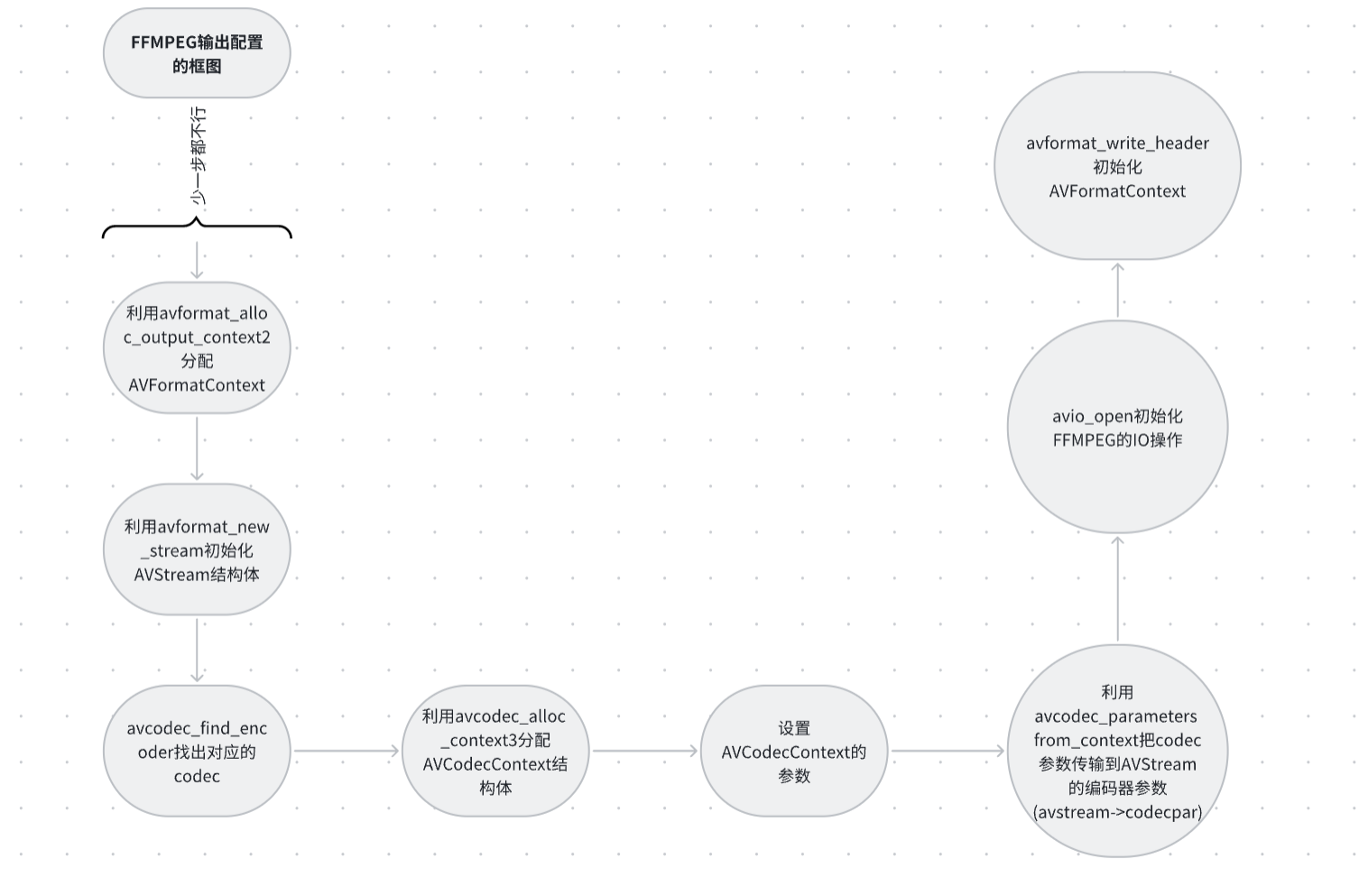
二.FFMPEG输出配置的框图:
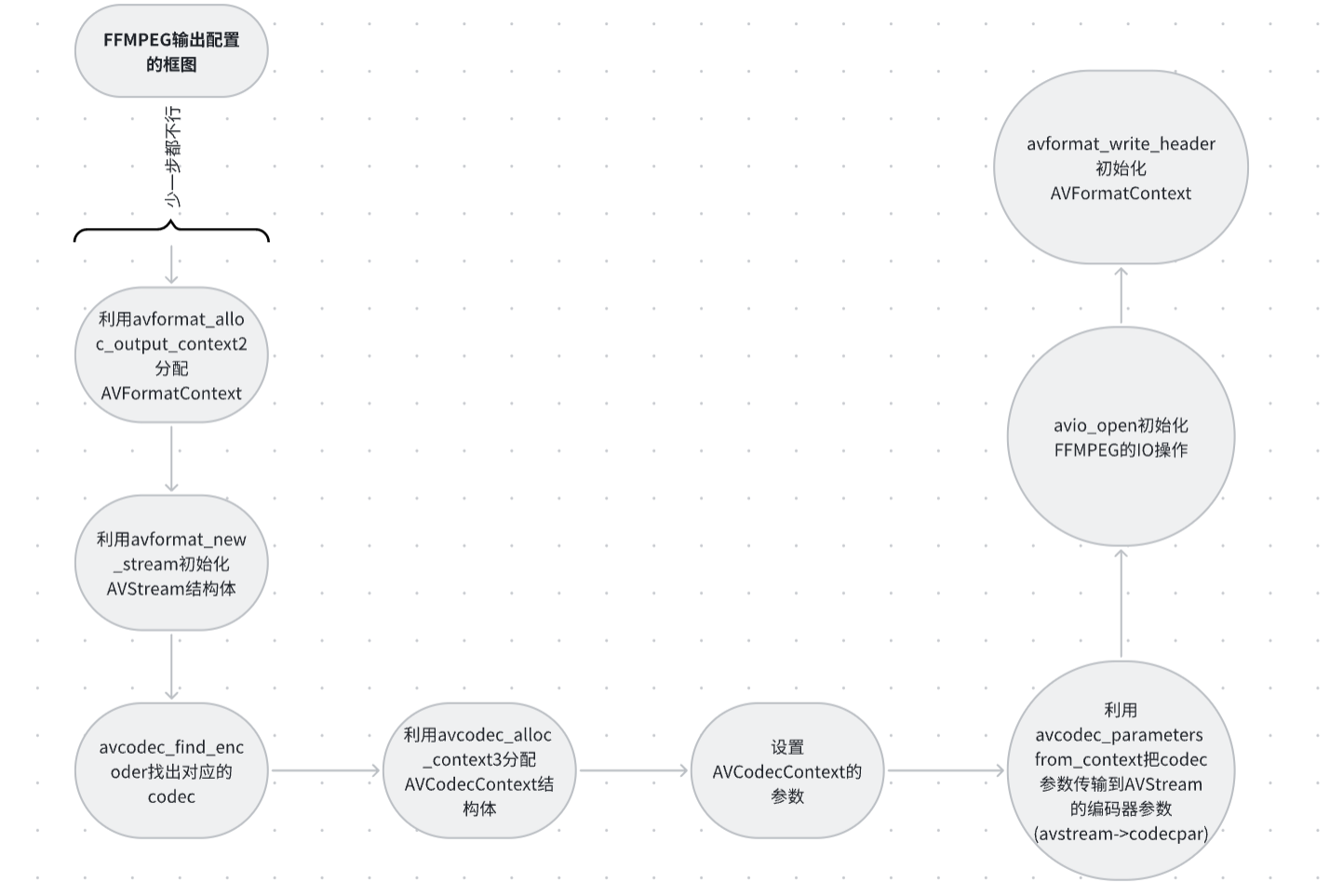
上图是整体的框图,我们具体来看看每个框图的代码实现。
2.1. 分配FFMPEG AVFormatContext输出的上下文结构体指针
//FLV_PROTOCOL is RTMP TCPif (ffmpeg_config->protocol_type == FLV_PROTOCOL){//初始化一个FLV的AVFormatContextret = avformat_alloc_output_context2(&ffmpeg_config->oc, NULL, "flv", ffmpeg_config->network_addr); if (ret < 0){return -1;}}//TS_PROTOCOL is SRT UDP RTSPelse if (ffmpeg_config->protocol_type == TS_PROTOCOL){//初始化一个TS的AVFormatContextret = avformat_alloc_output_context2(&ffmpeg_config->oc, NULL, "mpegts", ffmpeg_config->network_addr);if (ret < 0){return -1;}}
int avformat_alloc_output_context2(AVFormatContext **ctx, AVOutputFormat *oformat, const char *format_name, const char *filename)第一个传输参数:AVFormatContext结构体指针的指针,是存储音视频封装格式中包含的信息的结构体,所有对文件的封装、编码都是从这个结构体开始。
第二个传输参数:AVOutputFormat的结构体指针,它主要存储复合流信息的常规配置,默认为设置NULL。
第三个传输参数:format_name指的是复合流的格式,比方说:flv、ts、mp4等等
第四个传输参数:filename是输出地址,输出地址可以是本地文件(如:xxx.mp4、xxx.ts等等)。也可以是网络流地址(如:rtmp://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:1935/live/01)
上面这个API是根据我们流媒体类型去分配AVFormatContext结构体。我们传进来的类型会分为FLV_PROTOCOL和TS_PROTOCOL,具体如何配置如下面:
若TS_PROTOCOL类型:avformat_alloc_output_context2(&group->oc, NULL, "mpegts", group->url_addr);
若FLV_PROTOCOL类型:avformat_alloc_output_context2(&group->oc, NULL, "flv", group->url_addr);
注意:TS格式分别可以适配以下流媒体复合流,包括:SRT、UDP、TS本地文件等。flv格式包括:RTMP、FLV本地文件等等。
2.2. 配置推流器编码参数和AVStream结构体
AVStream主要是存储流信息结构体,这个流信息包含音频流和视频流。创建的API是avformat_new_stream
fmt = ffmpeg_config->oc->oformat;//fmt = ffmpeg_config->oc->oformat; 是FFmpeg中获取输出格式描述符的关键操作,其作用是从已创建的输出上下文(AVFormatContext)中提取对应的输出格式元数据,AVFormatContext的成员变量,指向AVOutputFormat结构体。该结构体是FFmpeg对容器格式的抽象定义在avformat_alloc_output_context2(&ffmpeg_config->oc, NULL, "flv", ...)调用后,FFmpeg内部会为oc->oformat自动关联到libavformat/flvenc.c中的ff_flv_muxer(FLV格式)或libavformat/mpegtsenc.c中的ff_ts_muxer(TS格式)/*指定编码器*/fmt->video_codec = ffmpeg_config->video_codec;fmt->audio_codec = ffmpeg_config->audio_codec;if (fmt->video_codec != AV_CODEC_ID_NONE){ret = add_stream(&ffmpeg_config->video_stream, ffmpeg_config->oc, &video_codec, fmt->video_codec,ffmpeg_config->width,ffmpeg_config->height);if (ret < 0){avcodec_free_context(&ffmpeg_config->video_stream.enc);free_stream(ffmpeg_config->oc, &ffmpeg_config->video_stream);avformat_free_context(ffmpeg_config->oc);return -1;}}
int add_stream(OutputStream *ost, AVFormatContext *oc, AVCodec **codec, enum AVCodecID codec_id, int width, int height)
{AVCodecContext *c = NULL;//声明编码器上下文指针,用于后续操作编码器参数//创建输出码流的AVStream, AVStream是存储每一个视频/音频流信息的结构体ost->stream = avformat_new_stream(oc, NULL);if (!ost->stream){printf("Can't not avformat_new_stream\n");return 0;}else{printf("Success avformat_new_stream\n");}
}AVStream * avformat_new_stream(AVFormatContext *s, AVDictionary **options);
第一个传输参数:AVFormatContext的结构体指针
第二个传输参数:AVDictionary结构体指针的指针
返回值:AVStream结构体指针
2.3. 设置对应的推流器编码器参数
int add_stream(OutputStream *ost, AVFormatContext *oc, AVCodec **codec, enum AVCodecID codec_id, int width, int height)
{AVCodecContext *c = NULL;//声明编码器上下文指针,用于后续操作编码器参数//创建输出码流的AVStream, AVStream是存储每一个视频/音频流信息的结构体ost->stream = avformat_new_stream(oc, NULL);if (!ost->stream){printf("Can't not avformat_new_stream\n");return 0;}else{printf("Success avformat_new_stream\n");}//通过codecid找到对应的编码器*codec = avcodec_find_encoder(codec_id);if (!(*codec)){printf("Can't not find any encoder");return 0;}else{printf("Success find encoder");}
}AVCodec *avcodec_find_encoder(enum AVCodecID id); //
第一个传输参数:传递参数AVCodecID
2.4. 根据编码器ID分配AVCodecContext结构体
int add_stream(OutputStream *ost, AVFormatContext *oc, AVCodec **codec, enum AVCodecID codec_id, int width, int height)
{AVCodecContext *c = NULL;//声明编码器上下文指针,用于后续操作编码器参数//创建输出码流的AVStream, AVStream是存储每一个视频/音频流信息的结构体ost->stream = avformat_new_stream(oc, NULL);if (!ost->stream){printf("Can't not avformat_new_stream\n");return 0;}else{printf("Success avformat_new_stream\n");}//通过codecid找到对应的编码器*codec = avcodec_find_encoder(codec_id);if (!(*codec)){printf("Can't not find any encoder");return 0;}else{printf("Success find encoder");}//nb_streams 输入视频的AVStream 个数 就是当前有几种Stream,比如视频流、音频流、字幕,这样就算三种了,// oc->nb_streams - 1其实对应的应是AVStream 中的 indexost->stream->id = oc->nb_streams - 1;//通过CODEC分配编码器上下文,关联到ost->enc供后续操作使用c = avcodec_alloc_context3(*codec);if (!c){printf("Can't not allocate context3\n");return 0;}else{printf("Success allocate context3");}ost->enc = c;
}
`AVCodecContext *avcodec_alloc_context3(const AVCodec *codec);`参数说明:
- 传入参数:指向AVCodec结构体的指针功能说明:
`avcodec_find_encoder`函数通过codec_id(编码器ID)查找对应的AVCodec结构体。在RV1126推流项目中,我们使用两种编码器ID:`AV_CODEC_ID_H264`和`AV_CODEC_ID_H265`。获取到AVCodec结构体后,即可调用`avcodec_alloc_context3`来创建AVCodecContext上下文环境。初始化完AVStream和编码上下文结构体之后,我们就需要对这些参数进行配置。重点:推流编码器参数和RV1126编码器的参数要完全一样,否则可能会出问题,具体的如下图:
1920 * 1080编码器以及1280* 720编码器和FFMPEG推流器的配置
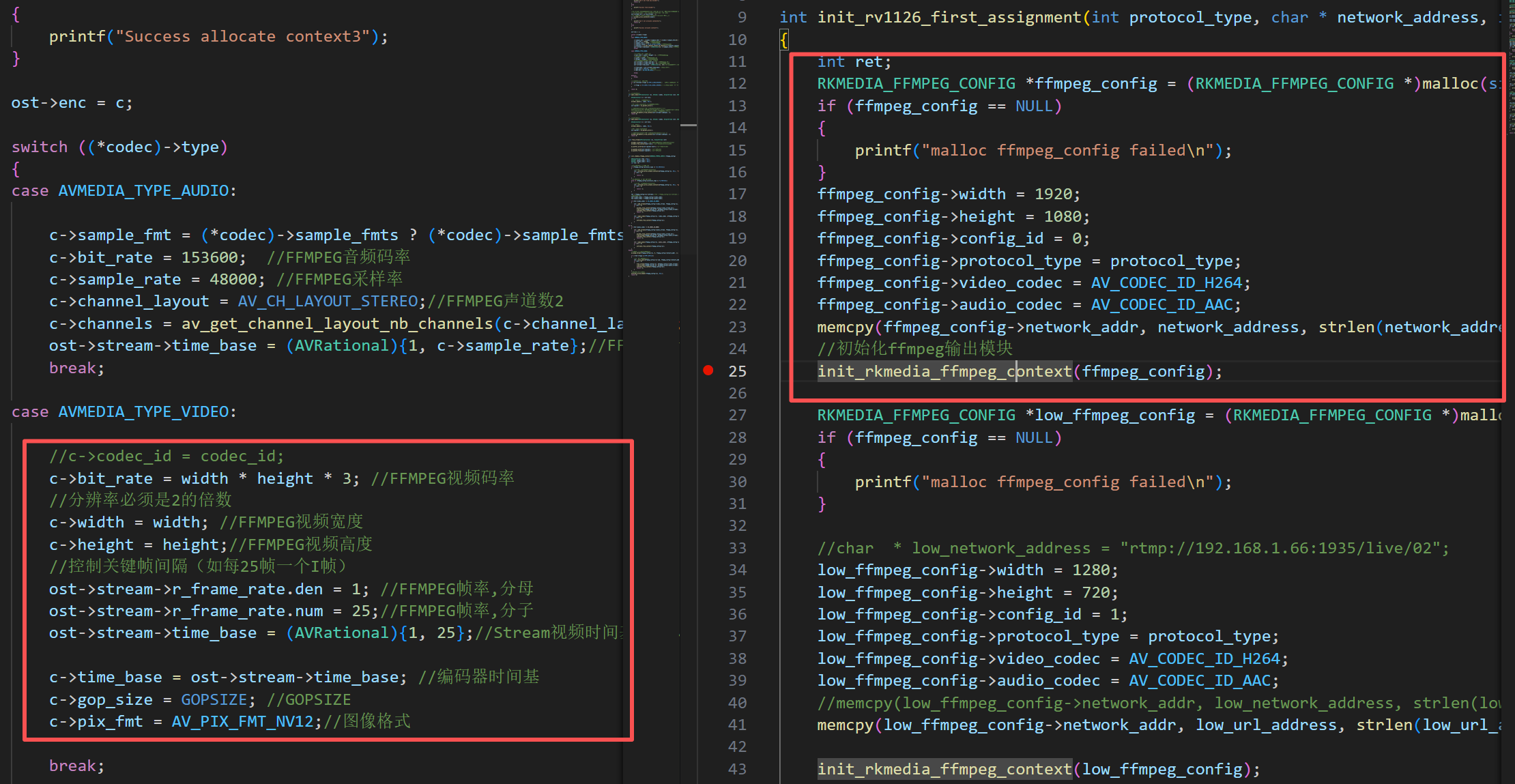
为确保视频编码的一致性,FFMPEG的参数设置须与右侧VENC编码器完全匹配。关键参数包括:
分辨率参数(WIDTH/HEIGHT)必须对应:
- 当RV1126编码器设为1920×1080时,FFMPEG的WIDTH=1920,HEIGHT=1080
- 当RV1126编码器设为1280×720时,FFMPEG的WIDTH=1280,HEIGHT=720
GOP_SIZE参数需保持相同:
- 若RV1126的GOP值为25,则FFMPEG的gop_size同样设为25
时间基(time_base)必须与视频帧率完全一
//在h264头部添加SPS,PPSif (oc->oformat->flags & AVFMT_GLOBALHEADER)// 检查容器是否支持全局头{c->flags |= AV_CODEC_FLAG_GLOBAL_HEADER;// 启用编码器的全局头标志}AV_CODEC_FLAG_GLOBAL_HEADER:发送视频数据的时候都会在关键帧前面添加SPS/PPS,这个标识符在FFMPEG初始化的时候都需要添加。
2.5. 设置完上述参数之后,拷贝参数到AVStream编解码器,具体的操作如下:
拷贝参数到AVStream,我们封装到open_video自定义函数里面,要先调用avcodec_open2打开编码器,然后再调用avcodec_parameters_from_context把编码器参数传输到AVStream里面
//使能video编码器
int open_video(AVFormatContext *oc, AVCodec *codec, OutputStream *ost, AVDictionary *opt_arg)
{AVCodecContext *c = ost->enc;//打开编码器(激活视频编码器)avcodec_open2(c, codec, NULL);//分配video avpacket包,创建视频数据包容器ost->packet = av_packet_alloc();/* 将AVCodecContext参数复制AVCodecParameters复用器 将AVCodecContext的参数(如width/height/pix_fmt)复制到AVStream->codecpar复用器(avformat_write_header)依赖这些参数生成容器头部*/avcodec_parameters_from_context(ost->stream->codecpar, c);return 0;
}2.5.1.int avcodec_open2(AVCodecContext *avctx, const AVCodec *codec, AVDictionary **options);
这个函数的具体作用是,打开编解码器
第一个参数:AVCodecContext结构体指针
第二个参数:AVCodec结构体指针
第三个参数:AVDictionary二级指针
2.5.2. int avcodec_parameters_from_context(AVCodecParameters *par, const AVCodecContext *codec);
这个函数的具体作用是,把AVCodecContext的参数拷贝到AVCodecParameters里面。
第一个参数:AVCodecParameters结构体指针
第二个参数:AVCodecContext结构体指针
2.6. 打开IO文件操作
//打印输出格式的详细调试信息av_dump_format(ffmpeg_config->oc, 0, ffmpeg_config->network_addr, 1);if (!(fmt->flags & AVFMT_NOFILE)){//打开输出文件或网络流ret = avio_open(&ffmpeg_config->oc->pb, ffmpeg_config->network_addr, AVIO_FLAG_WRITE);if (ret < 0){free_stream(ffmpeg_config->oc, &ffmpeg_config->video_stream);free_stream(ffmpeg_config->oc, &ffmpeg_config->audio_stream);avformat_free_context(ffmpeg_config->oc);return -1;}}使用avio_open打开对应的文件,注意这里的文件不仅是指本地的文件也指的是网络流媒体文件,下面是avio_open的定义。
/*** Create and initialize a AVIOContext for accessing the* resource indicated by url.* @note When the resource indicated by url has been opened in* read+write mode, the AVIOContext can be used only for writing.** @param s Used to return the pointer to the created AVIOContext.* In case of failure the pointed to value is set to NULL.* @param url resource to access* @param flags flags which control how the resource indicated by url* is to be opened* @return >= 0 in case of success, a negative value corresponding to an* AVERROR code in case of failure*/
int avio_open(AVIOContext **s, const char *url, int flags);int avio_open(AVIOContext **s, const char *url, int flags);
第一个参数:AVIOContext的结构体指针,它主要是管理数据输入输出的结构体
第二个参数: url地址,这个URL地址既包括本地文件如(xxx.ts、xxx.mp4),也可以是网络流媒体地址,如(rtmp://192.168.22.22:1935/live/01)等
第三个参数:flags标识符
#define AVIO_FLAG_READ 1 /**< read-only */
#define AVIO_FLAG_WRITE 2 /**< write-only */
#define AVIO_FLAG_READ_WRITE (AVIO_FLAG_READ|AVIO_FLAG_WRITE) /**< read-write pseudo flag */
2.7. avformat_write_header对头部进行初始化,输出模块头部进行初始化
//写入容器头部元数据avformat_write_header(ffmpeg_config->oc, NULL);int avformat_write_header(AVFormatContext *s, AVDictionary **options);
第一个参数:传递AVFormatContext结构体指针
第二个参数:传递AVDictionary结构体指针的指针
疑问:为什么一定要在h264头部添加SPS,PPS
if (oc->oformat->flags & AVFMT_GLOBALHEADER)// 检查容器是否支持全局头{c->flags |= AV_CODEC_FLAG_GLOBAL_HEADER;// 启用编码器的全局头标志}全局头模式:说明书贴在包装盒外面(类似MP4容器)。打开盒子前就能看到,一次阅读,全程通用,省纸又方便。
非全局头模式:说明书塞在每个零件袋里(类似MPEG-TS容器)。每个袋子都有说明书,但重复印刷浪费纸,还可能看混。
FFmpeg的全局头配置就是帮你选“说明书放哪里”,让播放器快速找到参数,避免播放失败或浪费流量。
SPS和PPS就是“玩具说明书”的内容
SPS(序列参数集):相当于玩具的“总说明书”,规定整体规格。比如:玩具尺寸(视频分辨率)、颜色模式(色彩格式)、最大承重(码率上限)等。没有它,播放器根本不知道该怎么“组装”视频。
PPS(图像参数集):相当于每个零件的“小说明书”,规定具体细节。比如:螺丝型号(量化参数)、弹簧长度(帧率)、是否防锈(去块滤波)等。没有它,每一帧视频都可能“装错”或“卡住”。
为什么需要全局头配置?
省流量:全局头模式下,参数只存一次(像说明书贴盒外),不用每帧重复,减少视频体积,直播更流畅。
防卡顿:播放器一开始就能读到参数,快速启动播放;非全局头模式下,每遇到关键帧(如I帧)都要重新读参数,可能卡顿。
避错误:如果容器需要全局头但没配置(比如MP4没贴说明书),播放器会报错“找不到说明书”,直接罢工;如果容器不支持全局头却强行配置(比如MPEG-TS贴说明书),参数反而会丢失,播放异常。
举个实际例子
你看直播时,如果主播用MP4格式(支持全局头),视频参数一开始就加载好,播放丝滑;如果用MPEG-TS格式(不支持全局头),每切换一个画面(关键帧)都要重新加载参数,可能卡一下。而SPS/PPS就是这些参数的“核心内容”,没有它们,视频就像没说明书的玩具,根本玩不了。
简单来说,全局头配置是“选对放说明书的位置”,SPS/PPS是“说明书的内容”,两者配合,才能让视频流畅播放。
全部代码:
int add_stream(OutputStream *ost, AVFormatContext *oc, AVCodec **codec, enum AVCodecID codec_id, int width, int height)
{AVCodecContext *c = NULL;//声明编码器上下文指针,用于后续操作编码器参数//创建输出码流的AVStream, AVStream是存储每一个视频/音频流信息的结构体ost->stream = avformat_new_stream(oc, NULL);if (!ost->stream){printf("Can't not avformat_new_stream\n");return 0;}else{printf("Success avformat_new_stream\n");}//通过codecid找到对应的编码器*codec = avcodec_find_encoder(codec_id);if (!(*codec)){printf("Can't not find any encoder");return 0;}else{printf("Success find encoder");}//nb_streams 输入视频的AVStream 个数 就是当前有几种Stream,比如视频流、音频流、字幕,这样就算三种了,// oc->nb_streams - 1其实对应的应是AVStream 中的 indexost->stream->id = oc->nb_streams - 1;//通过CODEC分配编码器上下文,关联到ost->enc供后续操作使用c = avcodec_alloc_context3(*codec);if (!c){printf("Can't not allocate context3\n");return 0;}else{printf("Success allocate context3");}ost->enc = c;switch ((*codec)->type){case AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO:c->sample_fmt = (*codec)->sample_fmts ? (*codec)->sample_fmts[0] : AV_SAMPLE_FMT_FLTP; //FFMPEG采样格式c->bit_rate = 153600; //FFMPEG音频码率c->sample_rate = 48000; //FFMPEG采样率c->channel_layout = AV_CH_LAYOUT_STEREO;//FFMPEG声道数2c->channels = av_get_channel_layout_nb_channels(c->channel_layout); //FFMPEG采样通道ost->stream->time_base = (AVRational){1, c->sample_rate};//FFMPEG音频时间基break;case AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO://c->codec_id = codec_id;c->bit_rate = width * height * 3; //FFMPEG视频码率//分辨率必须是2的倍数c->width = width; //FFMPEG视频宽度c->height = height;//FFMPEG视频高度//控制关键帧间隔(如每25帧一个I帧)ost->stream->r_frame_rate.den = 1; //FFMPEG帧率,分母ost->stream->r_frame_rate.num = 25;//FFMPEG帧率,分子ost->stream->time_base = (AVRational){1, 25};//Stream视频时间基,默认情况下等于帧率c->time_base = ost->stream->time_base; //编码器时间基c->gop_size = GOPSIZE; //GOPSIZEc->pix_fmt = AV_PIX_FMT_NV12;//图像格式break;default:break;}//在h264头部添加SPS,PPSif (oc->oformat->flags & AVFMT_GLOBALHEADER)// 检查容器是否支持全局头{c->flags |= AV_CODEC_FLAG_GLOBAL_HEADER;// 启用编码器的全局头标志}return 0;
}//使能video编码器
int open_video(AVFormatContext *oc, AVCodec *codec, OutputStream *ost, AVDictionary *opt_arg)
{AVCodecContext *c = ost->enc;//打开编码器(激活视频编码器)avcodec_open2(c, codec, NULL);//分配video avpacket包,创建视频数据包容器ost->packet = av_packet_alloc();/* 将AVCodecContext参数复制AVCodecParameters复用器 将AVCodecContext的参数(如width/height/pix_fmt)复制到AVStream->codecpar复用器(avformat_write_header)依赖这些参数生成容器头部*/avcodec_parameters_from_context(ost->stream->codecpar, c);return 0;
}int init_rkmedia_ffmpeg_context(RKMEDIA_FFMPEG_CONFIG *ffmpeg_config)
{AVOutputFormat *fmt = NULL;AVCodec *audio_codec = NULL;AVCodec *video_codec = NULL;int ret = 0;//FLV_PROTOCOL is RTMP TCPif (ffmpeg_config->protocol_type == FLV_PROTOCOL){//初始化一个FLV的AVFormatContextret = avformat_alloc_output_context2(&ffmpeg_config->oc, NULL, "flv", ffmpeg_config->network_addr); if (ret < 0){return -1;}}//TS_PROTOCOL is SRT UDP RTSPelse if (ffmpeg_config->protocol_type == TS_PROTOCOL){//初始化一个TS的AVFormatContextret = avformat_alloc_output_context2(&ffmpeg_config->oc, NULL, "mpegts", ffmpeg_config->network_addr);if (ret < 0){return -1;}}fmt = ffmpeg_config->oc->oformat;//fmt = ffmpeg_config->oc->oformat; 是FFmpeg中获取输出格式描述符的关键操作,其作用是从已创建的输出上下文(AVFormatContext)中提取对应的输出格式元数据,AVFormatContext的成员变量,指向AVOutputFormat结构体。该结构体是FFmpeg对容器格式的抽象定义在avformat_alloc_output_context2(&ffmpeg_config->oc, NULL, "flv", ...)调用后,FFmpeg内部会为oc->oformat自动关联到libavformat/flvenc.c中的ff_flv_muxer(FLV格式)或libavformat/mpegtsenc.c中的ff_ts_muxer(TS格式)/*指定编码器*/fmt->video_codec = ffmpeg_config->video_codec;fmt->audio_codec = ffmpeg_config->audio_codec;if (fmt->video_codec != AV_CODEC_ID_NONE){ret = add_stream(&ffmpeg_config->video_stream, ffmpeg_config->oc, &video_codec, fmt->video_codec,ffmpeg_config->width,ffmpeg_config->height);if (ret < 0){avcodec_free_context(&ffmpeg_config->video_stream.enc);free_stream(ffmpeg_config->oc, &ffmpeg_config->video_stream);avformat_free_context(ffmpeg_config->oc);return -1;}ret = open_video(ffmpeg_config->oc, video_codec, &ffmpeg_config->video_stream, NULL);if (ret < 0){avformat_free_context(ffmpeg_config->oc);}}#if 0if (fmt->audio_codec != AV_CODEC_ID_NONE){ret = add_stream(&ffmpeg_config->audio_stream, ffmpeg_config->oc, &audio_codec, fmt->audio_codec);if (ret < 0){avcodec_free_context(&ffmpeg_config->audio_stream.enc);free_stream(ffmpeg_config->oc, &ffmpeg_config->audio_stream);avformat_free_context(ffmpeg_config->oc);return -1;}ret = open_audio(ffmpeg_config->oc, audio_codec, &ffmpeg_config->audio_stream, NULL);if (ret < 0){avformat_free_context(ffmpeg_config->oc);}}
#endif//打印输出格式的详细调试信息av_dump_format(ffmpeg_config->oc, 0, ffmpeg_config->network_addr, 1);if (!(fmt->flags & AVFMT_NOFILE)){//打开输出文件或网络流ret = avio_open(&ffmpeg_config->oc->pb, ffmpeg_config->network_addr, AVIO_FLAG_WRITE);if (ret < 0){free_stream(ffmpeg_config->oc, &ffmpeg_config->video_stream);free_stream(ffmpeg_config->oc, &ffmpeg_config->audio_stream);avformat_free_context(ffmpeg_config->oc);return -1;}}//写入容器头部元数据avformat_write_header(ffmpeg_config->oc, NULL);return 0;
}注:还是要注意一点 这里的FFMPEG的输出配置一步都不能少 否则就启动不了