【1.SpringAI】3.SpringAI 聊天模型的介绍
目录
一、ChatClient
1.1 实现简单对话
1.2 角色预设
1.3 结构化输出
1.4 实现流式输出
二、ChatModel
2.1 ChatModel 概述
2.2 实现简单对话
2.3 角色预设
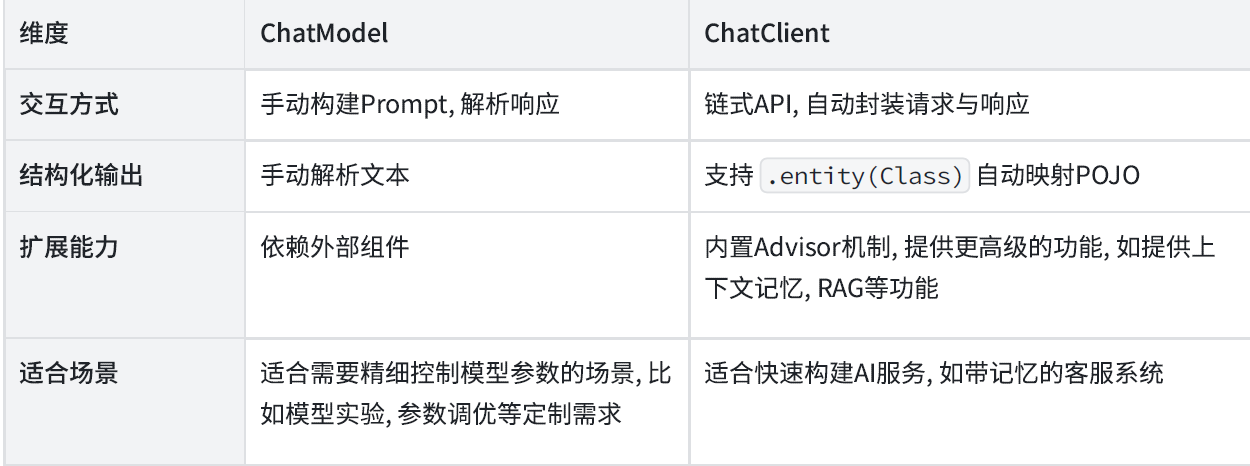
三、ChatClient 和ChatModel区别
一、ChatClient
Spring AI 的聊天模型, 通过标准化的接口设计, 使开发人员可以将AI模型的聊天功能集成到应用程序中。它利用预先训练的语言模型, 例如 GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer), 以自然语言生成类似人类的响应。
API 的工作原理通常是向 AI 模型发送提示或部分对话, 然后 AI 模型根据其训练数据和对自然语言模式的理解生成响应. 然后, 把响应将返回给应用程序, 应用程序可以将其呈现给用户或将其用于进一步处理。
在Spring AI框架中, ChatModel和ChatClient是构建对话式AI应用的两大核心接口。
1.1 实现简单对话
ChatClient 是 Spring AI 框架中封装复杂交互流程的高阶 API 接口 , 旨在简化开发者与大语言模型 (如GPT、通义千问等) 的集成过程. ChatClient 提供了与 AI 模型通信的 Fluent API, 它支持同步和反应式 (Reactive) 编程模型, 将与 LLM 及其他组件交互的复杂性进行封装, 给用户提供开箱即用的服务。
1. 创建ChatClient, 并注入:使用 ChatClient.Builder 来创建ChatClient 对象
private final ChatClient chatClient;
public ChatController(ChatClient.Builder chatClientBuilder) {this.chatClient = chatClientBuilder.build();
}2. 使用ChatClient
@GetMapping("/call")
public String generation(String userInput) {return this.chatClient.prompt()//用户输入的信息.user(userInput)//请求大模型.call()//返回文本.content();
}把用户输入的内容设置为用户消息的内容, call 方法向 AI 模型发送请求, content 方法以字符串
的形式返回 AI 模型的响应。
3. 测试:访问接口: http://127.0.0.1:8080/chat/call?userInput=你是谁

1.2 角色预设
我们应用程序接入DeepSeek之后, 也可以设置自己智能助手的名字, 比如问小白:

1. 配置角色
在Spring AI的ChatClient.Builder 中, defaultSystem() 方法用于设置AI模型的默认系统消息 (System Message) , 它会作为对话的基础角色设定或初始指令. 通过ChatClient.Builder链式调用设置后, 该方法定义的文本会作为系统消息注入到每次对话的上下文中, 用于引导AI的回复风格或身份设定。
private final ChatClient chatClient;
public ChatController(ChatClient.Builder chatClientBuilder) {
this.chatClient = chatClientBuilder.defaultSystem("你叫小白, 是一个智能助手,精通Java和C++, 主要工作是给学员日常答疑").build();
}为了方便在其他地方也可以使用, 可以把chatClient 单独定义:
@Configuration
public class ChatClientConfig {@Bean
public ChatClient chatClient(ChatClient.Builder chatClientBuilder){return chatClientBuilder.defaultSystem("你叫小白, 是一个智能助手,精通Java和C++, 主要工作是给学员日常答疑").build();}
}2. 编写Controller
@RequestMapping("/chat")
@RestController
public class ChatController {@Autowiredprivate ChatClient chatClient;@GetMapping("/call")public String generation(String userInput) {return this.chatClient.prompt()//用户输入的信息.user(userInput)//请求大模型.call()//返回文本.content();}
}3. 测试:访问接口: http://127.0.0.1:8080/chat/call?userInput=你是谁

1.3 结构化输出
如果您想从 LLM 接收结构化输出, Spring AI支持将 ChatModel/ChatClient 方法的返回类型从
String 更改为其他类型。
1. 需求:通过Spring AI 来生成菜单
2. 编写代码:借助JDK16提供的新关键词 record 来定义一个实体类
record Recipe(String dish, List < String > ingredients) {}
@GetMapping("/entity")
public String entity(String userInput) {Recipe recipe = this.chatClient.prompt()//用户输入的信息.user(String.format("请帮我生成%s的食谱", userInput))//请求大模型.call()//返回文本.entity(Recipe.class);return recipe.toString();
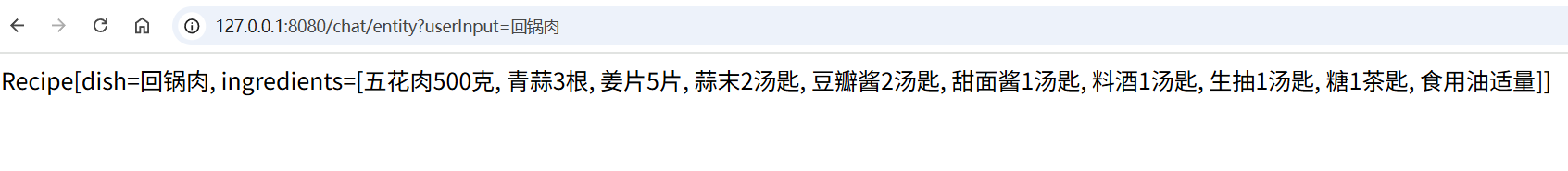
}3. 测试:访问接口: http://127.0.0.1:8080/chat/entity?userInput=回锅肉
 访问接口: http://127.0.0.1:8080/chat/entity?userInput=西红柿炖牛腩:
访问接口: http://127.0.0.1:8080/chat/entity?userInput=西红柿炖牛腩:

1.4 实现流式输出
用户和大模型进行交互时, 由于大模型一次输出内容较多, 等待全部内容生成完毕会导致用户等待时间过长, 这对用户的体验非常不友好. 可以采用流式输出的方式(例如ChatGPT和DeepSeek逐字显示回答)
1. 流式输出介绍
大模型流式输出(Streaming Output)是通过逐步生成内容而非一次性返回完整结果的技术. Spring AI使用 ChatClient 的 stream() 方法生成 Flux<String> 流, 适用于需要更轻量级客户端控制的场景。
2. 代码实现
@GetMapping(value = "/stream", produces = "text/html;charset=utf-8")
public Flux < String > stream(String userInput) {return this.chatClient.prompt()//用户输入的信息.user(userInput)//请求大模型.stream()//返回文本.content();
}3. 测试:访问: http://127.0.0.1:8080/chat/stream?userInput=你是谁
 二、ChatModel
二、ChatModel
2.1 ChatModel 概述
ChatModel 是Spring AI 构建对话应用的核心接口, 它抽象了应用与模型交互的过程, 包括使用
Prompt 作为输入, 使用 ChatResponse 作为输出等. ChatModel 的工作原理是接收 Prompt 或部
分对话作为输入, 将输入发送给后端大模型, 模型根据其训练数据和对自然语言的理解生成对话响应, 应用程序可以将响应呈现给用户或用于进一步处理
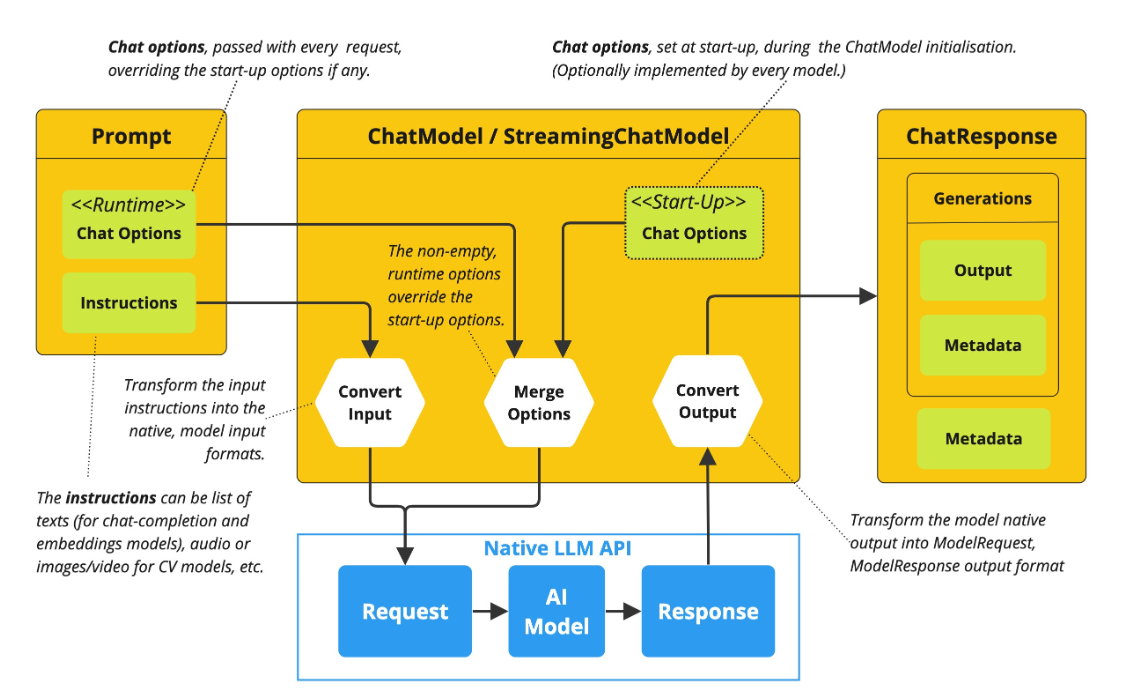
String call(String message) 方法就是对 message进行了封装, 简化了ChatModel 的初始化
使用, 避免了更复杂的Prompt输入和ChatResponse输出, 本质上调用的依然是 ChatResponse
call(Prompt prompt)
default String call(String message) {Prompt prompt = new Prompt(new UserMessage(message));Generation generation = call(prompt).getResult();return (generation != null) ? generation.getOutput().getText() : "";
}ChatClient 本质上也是基于ChatModel 进行的封装和增强:
public interface ChatClient {static ChatClient create(ChatModel chatModel) {return create(chatModel, ObservationRegistry.NOOP);}static ChatClient create(ChatModel chatModel, ObservationRegistry observationRegistry) {return create(chatModel, observationRegistry, null);}static Builder builder(ChatModel chatModel) {return builder(chatModel, ObservationRegistry.NOOP, null);}
}2.2 实现简单对话
1. 编写代码
@GetMapping("/callByPrompt")
public String callByPrompt(String message) {ChatResponse response = openAiChatModel.call(new Prompt(message));return response.getResult().getOutput().getText();
}2. 测试:接口: http://127.0.0.1:8080/ds/callByPrompt?message=祝我拿到满意offer

2.3 角色预设
1. 编写代码:在Prompt 中通过 System Message 明确设定角色身份
@GetMapping(value = "/role")
public String role(String message) {SystemMessage systemMsg = new SystemMessage("你是一名英国人, 只会说英语");UserMessage userMsg = new UserMessage(message);Prompt prompt = new Prompt(List.of(systemMsg, userMsg));ChatResponse response = openAiChatModel.call(prompt);return response.getResult().getOutput().getText();
}2. 测试

三、ChatClient 和ChatModel区别
ChatClient 和ChatModel 是Spring AI 框架提供的与大语言模型(LLM)交互的两大核心接口. 但二者设计理念和适用场景不太一样.
- ChatModel 是Spring AI 框架中的底层接口, 直接与具体的大语言模型 (如通义千问、OpenAI) 交互。提供基础的call 和stream 方法, 开发者需手动处理提示词组装、参数配置和响应解析等细节,在使用上相对更加灵活.
- ChatClient 对ChatModel进行了封装, 相比如ChatModel 原子类API,ChatClient屏蔽了与AI大模型的交互的复杂性, 它自动集成提示词管理、响应格式化、结构化输出映射等能力, 提高了开发效率.