基于扩散模型的任意尺度磁共振图像超分辨率重建:通过渐进式k空间重建与去噪实现|文献速递-文献分享
Title
题目
Diffusion-based arbitrary-scale magnetic resonance image super-resolutionvia progressive k-space reconstruction and denoising
基于扩散模型的任意尺度磁共振图像超分辨率重建:通过渐进式k空间重建与去噪实现
01
文献速递介绍
磁共振图像超分辨率相关研究内容翻译 磁共振成像(MRI)是一种广泛应用的无创、无电离辐射成像技术,具有出色的软组织对比度,能够提供丰富的解剖学与功能学信息(Fatahi等,2015;de Rooij等,2016)。高分辨率(HR)MRI对于精准临床诊断和详细解剖评估至关重要(Zhao等,2024)。然而,获取高分辨率磁共振(MR)图像通常受限于硬件条件和较长的扫描时间(Feng等,2021;Li等,2021)。更长的采集时间会增加运动伪影的风险,尤其对于儿童患者或神经退行性疾病患者——这类患者在扫描过程中难以保持静止(Havsteen等,2017)。因此,临床迫切需要一种无需增加采集时间即可提升MR图像分辨率与质量的技术。 超分辨率(SR)技术已被广泛用于提升低分辨率(LR)MR图像的空间分辨率,且无需增加扫描时间或改动MRI硬件。传统超分辨率方法包括基于插值的方法(如双三次插值(Keys,1981)、B样条插值(Hou和Andrews,1978))和基于正则化的方法(Rueda等,2013;Shi等,2015;Zhang等,2019),但这些方法的效果欠佳,尤其在大上采样因子下表现更为明显。随着深度学习的发展,基于深度学习的超分辨率方法通过设计各类深度网络(如残差网络(ResNet)(Lyu等,2020;Zhao等,2021)、U型网络(U-Net)(Sui等,2022)、生成对抗网络(GAN)(Ledig等,2017;Li等,2021;You等,2022;Feng等,2024)、Transformer(Liang等,2021;Li等,2022b;Lyu等,2023;Li等,2025;Chen等,2025)、Mamba(Gu和Dao,2023;Ji等,2024)),学习从低分辨率MR图像到高分辨率MR图像的映射关系。尽管这些深度学习方法取得了显著成果,但它们主要依赖固定的整数上采样因子,且针对不同缩放因子需训练独立的网络。近年来,出现了一些基于隐式神经表示(INR)(Wu等,2022;Li等,2023a,b;Zhang等,2023;Wang等,2024)和元上采样模块(Hu等,2019)的任意尺度图像超分辨率方法。然而,这些超分辨率方法多为有监督学习,泛化能力受限于训练数据分布,在真实采集数据和未见过的上采样因子上表现尤为受限。 近年来,扩散模型在自然图像生成领域展现出良好性能(Ho等,2020;Dhariwal和Nichol,2021;Song和Ermon,2019;Song等,2021)。受此启发,已有研究将扩散模型引入MR图像超分辨率领域(Chung和Ye,2022;Chung等,2022;Saharia等,2022;Peng等,2022;Güngör等,2023;Wu等,2023;Wang等,2023;Mao等,2023;Qiu等,2024;Li等,2024;Zhao等,2024;Liu等,2025)。其中一类研究(Chung和Ye,2022;Chung等,2022;Peng等,2022;Chung和Ye,2022;Güngör等,2023;Wu等,2023;Wang等,2023)利用低分辨率图像引导预训练的无条件扩散模型的采样过程,使其向高分辨率图像流形靠拢;另一类研究(Saharia等,2022;Wu等,2023;Mao等,2023;Qiu等,2024;Li等,2024;Zhao等,2024;Liu等,2025)则聚焦于训练特定的条件扩散模型,将低分辨率图像作为条件输入以实现图像超分辨率。所有这些基于扩散的方法均采用向高分辨率图像添加高斯噪声的正向扩散过程。尽管这些方法具有潜力,但它们的正向扩散过程并非基于低分辨率MR图像的退化过程专门设计,可能导致效果欠佳。 近期,一些广义扩散模型对经典扩散模型进行了扩展,融入了多种退化算子,不再局限于添加高斯噪声(Bansal等,2023;Huang等,2023;Fabian等,2024;Delbracio和Milanfar,2023;Liu等,2023;Guan等,2024;Cao等,2024)。例如,DiracDiff(Fabian等,2024)为自然图像恢复设计了含高斯模糊和噪声的正向过程;CDiffMR(Huang等,2023)基于相位编码方向的k空间欠采样,构建了冷扩散先验;此外,HF-SDE(Cao等,2024)采用固定的k空间欠采样掩码保留低频成分,同时向高频区域添加高斯噪声。尽管这些广义扩散模型对正向过程进行了定制,但它们主要聚焦于逆转退化过程以恢复固定分辨率的高分辨率图像,且针对不同目标分辨率需重新训练,这不仅增加了额外的训练成本,也限制了其处理多样化超分辨率任务的灵活性。 为解决上述问题,我们提出一种用于任意尺度面内MR图像超分辨率的统一扩散模型框架(PRDDiff),如图1所示。具体而言,PRDDiff的正向扩散过程在频域中逐步掩盖高频成分并添加高斯噪声,以此模拟MRI的下采样过程。为逆转该过程,我们设计了自适应分辨率恢复网络(ARRNet):该网络将与输入MR图像分辨率对应的“当前步长”和与目标分辨率对应的“终止步长”作为额外输入,从输入MR图像中恢复出目标分辨率的MR图像。随后,超分辨率过程从任意初始分辨率的MR图像开始,基于ARRNet输出的目标分辨率MR图像,通过逐步重建高频成分和去除噪声,将图像分辨率逐步提升至更高水平。此外,我们还提出了多阶段超分辨率策略:通过多个连续阶段逐步提升分辨率,以进一步提高重建精度。每个阶段均采用PRDDiff中设定数量的采样步长(由特定终止步长定制),确保恢复出预定义中间分辨率下的细节信息。在公开脑部和膝关节数据集上开展的大量实验表明,与以往超分辨率方法相比,本文方法在视觉质量和定量精度上均更优。PRDDiff在相位编码方向欠采样、未见过的上采样因子以及自主采集的配对低分辨率-高分辨率脑部数据上均具有良好泛化性,性能优于以往超分辨率方法。此外,PRDDiff在多种场景下均展现出泛化能力,包括不同MR图像对比度、噪声干扰、运动伪影、病灶存在以及采集协议差异等情况。我们还在临床儿童脑性瘫痪(CP)数据集上验证了该方法,结果显示其在重建质量、病灶分割和脑性瘫痪分类方面均优于对比方法。 本文的主要贡献总结如下: 1. 提出PRDDiff——一种专为任意尺度面内MR图像超分辨率设计的新型扩散模型框架,提供了一种灵活、统一的方法,可适应不同的分辨率需求。 2. PRDDiff的正向过程在k空间中逐步掩盖高频成分并添加高斯噪声,以模拟MRI下采样;为逆转该过程,ARRNet将输入图像及其对应的当前步长、终止步长作为输入,训练以重建目标分辨率的MR图像。 3. 超分辨率过程从任意初始分辨率的MR图像开始,逐步将其分辨率提升至更高水平;此外,多阶段超分辨率策略通过多个阶段逐步提升分辨率,每个阶段专注于恢复预定义中间分辨率特有的结构细节。 4. 大量实验表明,在重建质量、泛化能力、下游病灶分割精度及脑性瘫痪分类性能方面,PRDDiff均优于对比超分辨率方法。 本文其余部分结构如下:第2节介绍相关工作,第3节详细阐述PRDDiff,第4节开展实验与消融研究,第5节总结全文。
Aastract
摘要
Acquiring high-resolution Magnetic resonance (MR) images is challenging due to constraints such as hardwarelimitations and acquisition times. Super-resolution (SR) techniques offer a potential solution to enhance MRimage quality without changing the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) hardware. However, typical SR methodsare designed for fixed upsampling scales and often produce over-smoothed images that lack fine texturesand edge details. To address these issues, we propose a unified diffusion-based framework for arbitraryscale in-plane MR image SR, dubbed Progressive Reconstruction and Denoising Diffusion Model (PRDDiff).Specifically, the forward diffusion process of PRDDiff gradually masks out high-frequency components andadds Gaussian noise to simulate the downsampling process in MRI. To reverse this process, we propose anAdaptive Resolution Restoration Network (ARRNet), which introduces a current step corresponding to theresolution of input MR image and an ending step corresponding to the target resolution. This design guide theARRNet to recovering the clean MR image at the target resolution from input MR image. The SR process startsfrom an MR image at the initial resolution and gradually enhances them to higher resolution by progressivelyreconstructing high-frequency components and removing the noise based on the recovered MR image fromARRNet. Furthermore, we design a multi-stage SR strategy that incrementally enhances resolution throughmultiple sequential stages to further improve recovery accuracy. Each stage utilizes a set number of samplingsteps from PRDDiff, guided by a specific ending step, to recover details pertinent to the predefined intermediateresolution. We conduct extensive experiments on fastMRI knee dataset, fastMRI brain dataset, our real-collectedLR-HR brain dataset, and clinical pediatric cerebral palsy (CP) dataset, including T1-weighted and T2-weightedimages for the brain and proton density-weighted images for the knee. The results demonstrate that PRDDiffoutperforms previous MR image super-resolution methods in term of reconstruction accuracy, generalization,and downstream lesion segmentation accuracy and CP classification performance.
磁共振图像超分辨率重建相关研究内容翻译 获取高分辨率磁共振(MR)图像颇具挑战性,这受到硬件限制、采集时间等因素的制约。超分辨率(SR)技术为在不改变磁共振成像(MRI)硬件的前提下提升MR图像质量提供了潜在解决方案。然而,传统SR方法多针对固定上采样尺度设计,且生成的图像往往过度平滑,缺乏精细纹理与边缘细节。 为解决这些问题,我们提出一种用于任意尺度面内MR图像超分辨率重建的统一扩散模型框架,命名为渐进式重建与去噪扩散模型(PRDDiff)。具体而言,PRDDiff的正向扩散过程会逐步掩盖高频成分并添加高斯噪声,以此模拟MRI中的下采样过程。为逆转该过程,我们设计了自适应分辨率恢复网络(ARRNet):该网络引入与输入MR图像分辨率对应的“当前步长”,以及与目标分辨率对应的“终止步长”。此设计可引导ARRNet从输入MR图像出发,恢复出目标分辨率下的清晰MR图像。 超分辨率重建过程始于初始分辨率的MR图像,基于ARRNet恢复的MR图像,通过逐步重建高频成分与去除噪声,将图像分辨率逐步提升至更高水平。此外,我们还设计了多阶段超分辨率策略:通过多个连续阶段逐步提升分辨率,以进一步提高恢复精度。每个阶段均利用PRDDiff中设定数量的采样步长(由特定终止步长引导),恢复与预定义中间分辨率相关的细节信息。 我们在fastMRI膝关节数据集、fastMRI脑部数据集、自主采集的低分辨率-高分辨率(LR-HR)脑部数据集,以及临床儿童脑性瘫痪(CP)数据集上开展了大量实验,涵盖脑部T1加权像、T2加权像与膝关节质子密度加权像。结果表明,在重建精度、泛化能力、下游病灶分割精度及脑性瘫痪分类性能方面,PRDDiff均优于以往的MR图像超分辨率方法。
Conclusion
结论
In this paper, we propose a Progressive Reconstruction and Denoising Diffusion model (PRDDiff) for arbitrary-scale in-plane MR imageSR. We first design a forward diffusion process by gradually maskingout high-frequency components and adding Gaussian noise, whichmimics the downsampling process of MRI. To reverse this process, wedesign an ARRNet to generate the MR image at arbitrary resolutions.The SR process starts from MR images at the initial resolution andprogressively enhances them by reconstructing high-frequency components and removing noise, until the target resolution is achieved.In addition, we introduce a multi-stage SR strategy to incrementallyenhance resolution through multiple stages, each tailored to recover thedetails relevant to the predefined intermediate resolution. Experimentsdemonstrate that our PRDDiff outperforms the previous MR image SRmethods on public T2w images for the brain dataset and proton densityweighted images for the knee dataset, and T2w images for real pairedLR-HR brain dataset. Additionally, to validate the clinical applicability,we evaluate our method on a clinical pediatric cerebral palsy (CP)dataset with T2-weighted MR images. Results show that our method notonly achieves superior reconstruction quality compared to comparedmethods, but also yields higher lesion segmentation accuracy and CPclassification performance, approaching that of HR MR images. Whileour PRDDiff enables the estimation of the uncertainty through stochastic sampling, modeling reconstruction uncertainty under deterministicsettings remains an open and challenging problem. A potential solutionis to explore ensemble-based strategies by training multiple modelswith different initializations to approximate the uncertainty. Anotherpromising direction is to develop network architectures that jointlypredict both the reconstructed image and its associated pixel-wiseuncertainty.In future work, we plan to incorporate the uncertainty analysisunder deterministic settings into PRDDiff. We also plan to extendPRDDiff to through-plane MR image super-resolution. In addition,we will explore the applicability of PRDDiff to multi-modality superresolution tasks, where complementary information from differentimaging modalities (e.g., T1-weighted and T2-weighted MR images)can be leveraged to enhance reconstruction quality.
在本文中,我们提出了一种用于任意尺度面内磁共振(MR)图像超分辨率(SR) 的渐进式重建与去噪扩散模型(Progressive Reconstruction and Denoising Diffusion model, PRDDiff)。首先,我们通过逐步掩盖高频成分并添加高斯噪声,设计了一个正向扩散过程,该过程可模拟磁共振成像(MRI)的下采样过程。为逆转这一过程,我们设计了逆向重建网络(ARRNet),用于生成任意分辨率的磁共振图像。超分辨率过程从初始分辨率的磁共振图像开始,通过重建高频成分和去除噪声逐步提升图像质量,直至达到目标分辨率。 此外,我们引入了多阶段超分辨率策略,通过多个阶段逐步提升分辨率,每个阶段均针对预定义中间分辨率进行定制,以恢复该分辨率下的相关细节。实验表明,在公开的脑部T2加权(T2w)图像数据集、膝关节质子密度加权图像数据集,以及真实配对低分辨率-高分辨率(LR-HR)脑部T2加权图像数据集上,我们提出的PRDDiff模型性能均优于以往的磁共振图像超分辨率方法。 为验证临床适用性,我们在含T2加权磁共振图像的临床儿童脑性瘫痪(CP)数据集上对该方法进行了评估。结果显示,与对比方法相比,我们的方法不仅能实现更优的重建质量,还能获得更高的病灶分割精度和脑性瘫痪分类性能,且接近高分辨率(HR)磁共振图像的分析效果。尽管我们的PRDDiff模型可通过随机采样实现不确定性估计,但在确定性设置下对重建不确定性进行建模仍是一个尚未解决的挑战性问题。潜在的解决方案包括:探索基于集成学习的策略,通过训练具有不同初始化参数的多个模型来近似不确定性;另一个有前景的方向是开发能够联合预测重建图像及其相关像素级不确定性的网络架构。 在未来的工作中,我们计划将确定性设置下的不确定性分析整合到PRDDiff模型中;还计划将PRDDiff扩展至面外磁共振图像超分辨率任务;此外,我们将探索PRDDiff在多模态超分辨率任务中的适用性——在这类任务中,可利用不同成像模态(如T1加权和T2加权磁共振图像)的互补信息来提升重建质量。
Results
结果
In this section, we first provide a detailed description of the experimental setting. Then, we evaluate the performance of our methodon the public fastMRI brain dataset, fastMRI knee dataset, and ourcollected paired LR-HR brain dataset by comparing it with existingSR methods. Finally, we perform the ablation studies to verify theeffectiveness of the core components in our method.
本节内容概述 本节首先详细介绍实验设置;随后,通过在公开的fastMRI脑部数据集、fastMRI膝关节数据集以及自主采集的配对低分辨率-高分辨率(LR-HR)脑部数据集上,将本文方法与现有超分辨率(SR)方法进行对比,评估本文方法的性能;最后,通过消融实验验证本文方法中核心组件的有效性。
Figure
图
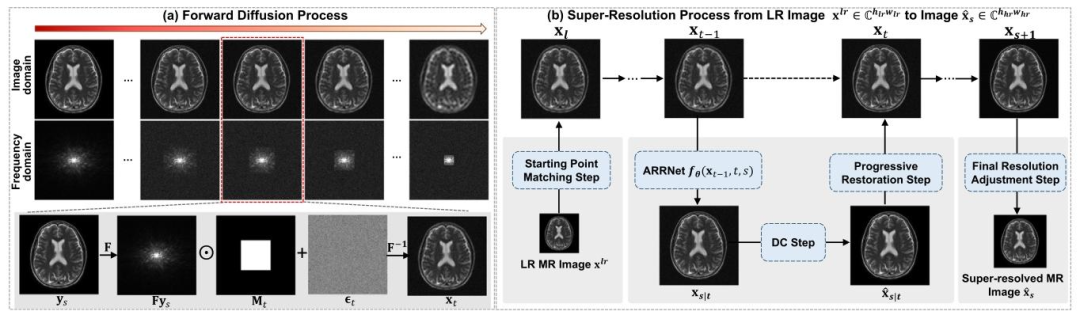
Fig. 1. Illustration of the proposed Progressive Reconstruction and Denoising Diffusion Model (PRDDiff). (a) The forward diffusion process of the PRDDiff graduallymasks out high-frequency components and adds Gaussian noise in the frequency domain. (b) The SR process of the proposed PRDDiff. Specifically, given a LRMR image 𝐱 𝑙𝑟 , we determine the corresponding starting point 𝐱𝑙 by the starting point matching step. Then, we alternately execute ARRNet, Data Consistency (DC)steps, and progressive restoration steps from step 𝑙 to step 𝑠 + 1. Finally, we use final resolution adjustment step to adjust the resolution of the recovered MRimage to obtain the super-resolved MR image 𝐱̂ 𝑠 .
图1 所提渐进式重建与去噪扩散模型(PRDDiff)示意图 (a)PRDDiff的正向扩散过程:在频域中逐步掩盖高频成分并添加高斯噪声。 (b)PRDDiff的超分辨率(SR)过程:具体而言,给定低分辨率磁共振(LR MR)图像𝐱ₗᵣ,通过起始点匹配步骤确定其对应的起始点𝐱ₗ;随后从步骤𝑙到步骤𝑠+1,交替执行自适应分辨率恢复网络(ARRNet)、数据一致性(DC)步骤与渐进式恢复步骤;最后通过最终分辨率调整步骤,对恢复出的MR图像分辨率进行调整,得到超分辨率MR图像𝐱̂ₛ。
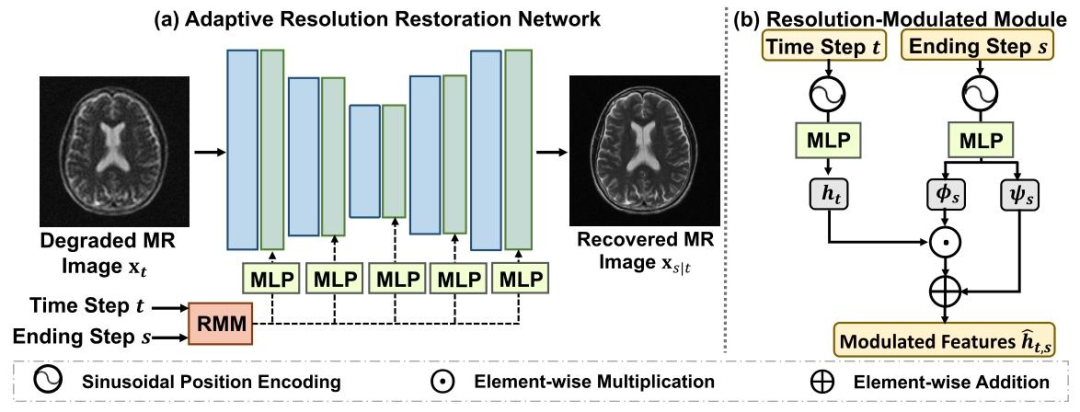
Fig. 2. (a) Overview of the Adaptive Resolution Restoration Network (ARRNet). (b) The architecture of Resolution-Modulated Module(RMM)
图2 (a)自适应分辨率恢复网络(ARRNet)整体结构示意图。 (b)分辨率调制模块(RMM)的架构示意图。
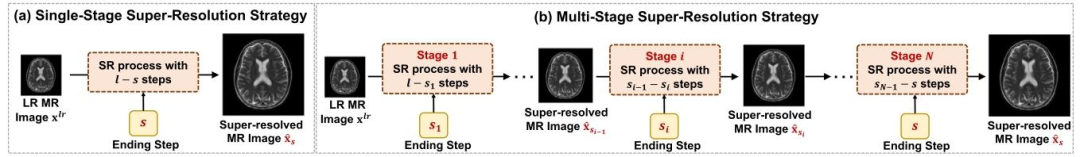
Fig. 3. Illustration of single-stage and multi-stage Super-Resolution (SR) strategies. (a) Single-stage SR strategy enhances a LR MR image to a super-resolved MRimage through a SR process involving 𝑠 − 𝑙 sampling steps guided by the ending step 𝑠. (b) Multi-stage SR strategy incrementally enhances the MR image at thetarget resolution through 𝑁 stages. Each stage uses a SR process to recover the MR images at a predefined intermediate resolution, guided by a specific endingstep.
图3 单阶段与多阶段超分辨率(SR)策略示意图 (a)单阶段超分辨率策略:以终止步长(s)为引导,通过包含(s-l)个采样步长的超分辨率过程,将低分辨率(LR)磁共振(MR)图像直接提升为超分辨率MR图像。 (b)多阶段超分辨率策略:通过(N)个阶段逐步将MR图像提升至目标分辨率。每个阶段均以特定终止步长为引导,采用超分辨率过程恢复预定义中间分辨率下的MR图像。
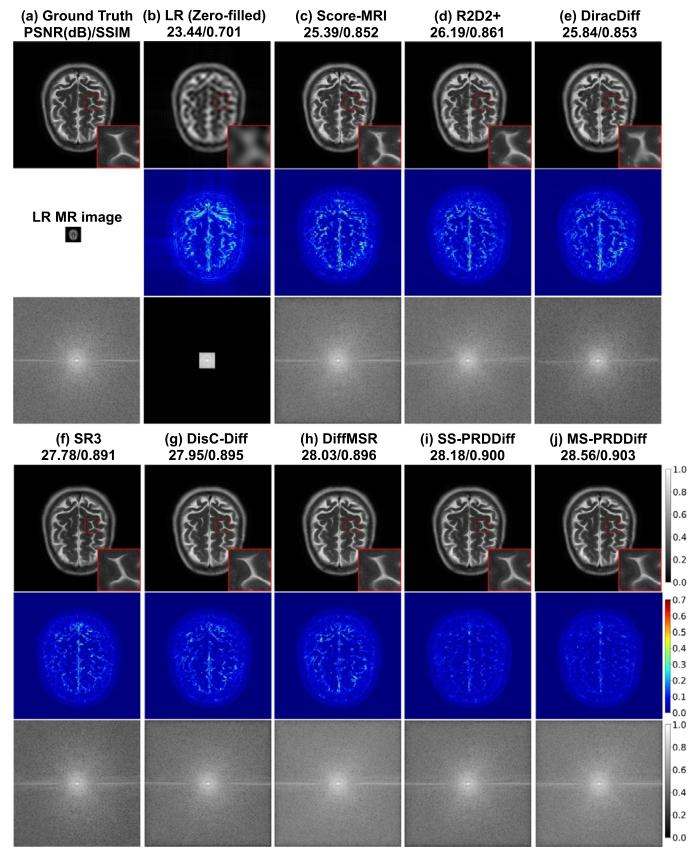
Fig. 4. Qualitative comparison with compared diffusion-based SR methods onfastMRI healthy brain dataset for 8× SR tasks. We show the recovered MR images, error maps, and zoomed-in details and 𝑘-space data with correspondingevaluation metrics in PSNR(dB)/SSIM.
图4 fastMRI健康脑部数据集上8倍超分辨率(8× SR)任务中,本文方法与对比扩散型超分辨率方法的定性对比 图中展示了各方法的重建MR图像、误差图、放大细节图及对应的k空间数据,并标注了峰值信噪比(PSNR,单位:dB)与结构相似性指数(SSIM)作为定量评估指标。
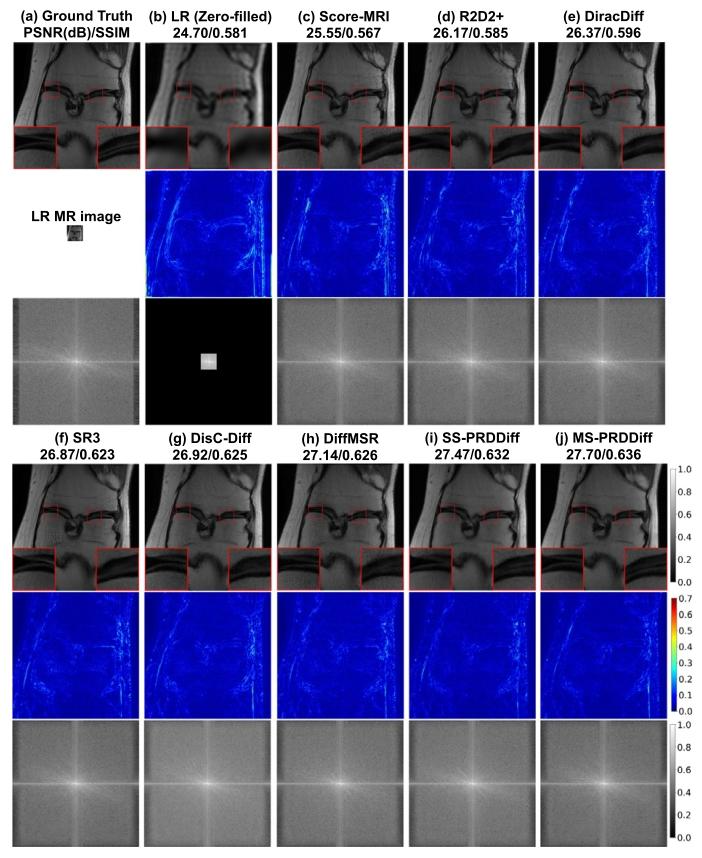
Fig. 5. Qualitative comparison with compared diffusion-based SR methods onfastMRI knee dataset for 8× SR tasks. We show the recovered MR images,error maps, zoomed-in details, and 𝑘-space data with corresponding evaluationmetrics in PSNR(dB)/SSIM
图5 fastMRI膝关节数据集上8倍超分辨率(8× SR)任务中,本文方法与对比扩散型超分辨率方法的定性对比 图中展示了各方法的重建磁共振(MR)图像、误差图、放大细节图及对应的k空间数据,并标注了峰值信噪比(PSNR,单位:dB)与结构相似性指数(SSIM)作为定量评估指标。
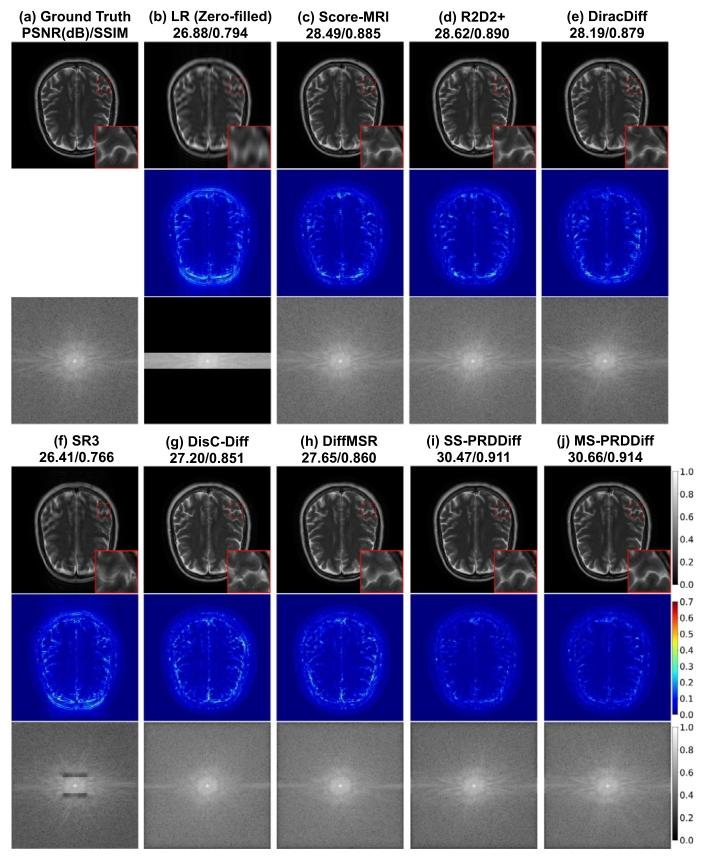
Fig. 6. Qualitative comparison with the diffusion-based SR methods for the8× SR task on fastMRI healthy brain MR images. The test MR images areundersampled in the phase-encoding direction, while the models are trainedon brain MR images undersampled in both the phase-encoding and readoutdirections. We show the recovered MR images, error maps, zoomed-in details,and 𝑘-space data with corresponding evaluation metrics in PSNR(dB)/SSIM.
图6 fastMRI健康脑部磁共振(MR)图像8倍超分辨率(8× SR)任务中,本文方法与扩散型超分辨率方法的定性对比 测试所用MR图像为仅在相位编码方向欠采样的图像,而所有模型均在“相位编码与读出方向均欠采样”的脑部MR图像上完成训练。图中展示了各方法的重建MR图像、误差图、放大细节图及对应的k空间数据,并标注了峰值信噪比(PSNR,单位:dB)与结构相似性指数(SSIM)作为定量评估指标。
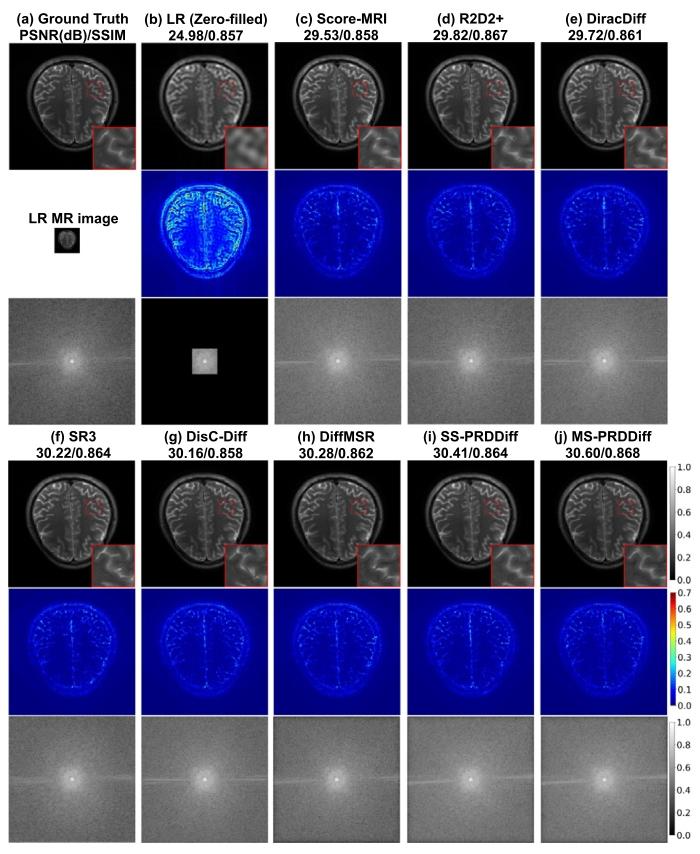
Fig. 7. Qualitative comparison with compared diffusion-based SR methods onthe real-paired LR-HR dataset for 5× SR using the models trained on fastMRIhealthy brain dataset. We show the recovered MR images, error maps, zoomedin details, and 𝑘-space data with evaluation metrics in PSNR(dB)/SSIM.
图7 模型在fastMRI健康脑部数据集上训练后,于真实配对低分辨率-高分辨率(LR-HR)数据集5倍超分辨率(5× SR)任务中与对比扩散型超分辨率方法的定性对比 图中展示了各方法的重建磁共振(MR)图像、误差图、放大细节图及对应的k空间数据,并标注了峰值信噪比(PSNR,单位:dB)与结构相似性指数(SSIM)作为评价指标。
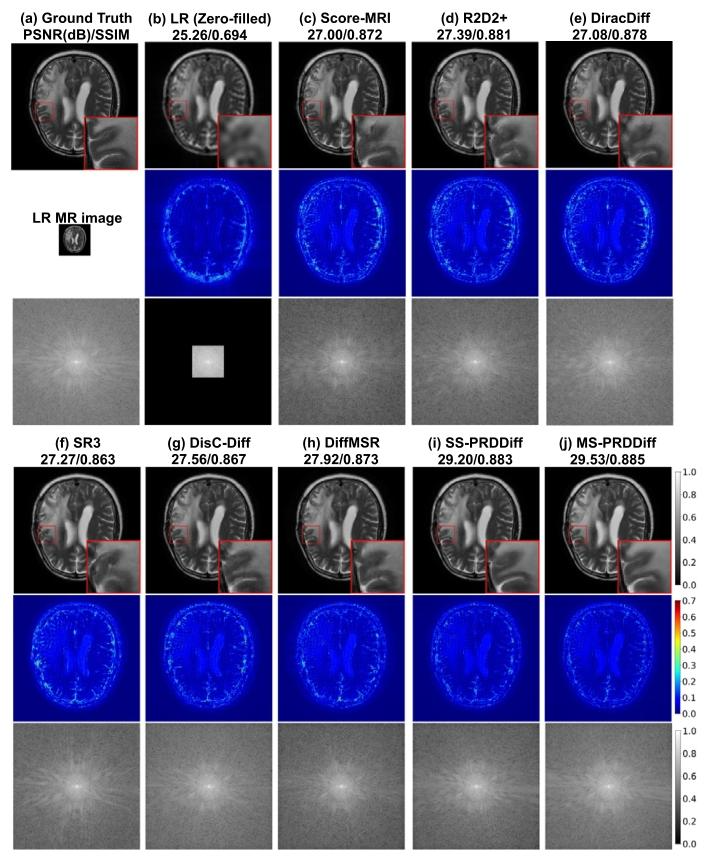
Fig. 8. Qualitative comparison with compared diffusion-based SR methodson fastMRI patient brain dataset for 4× SR task using the models trainedon fastMRI healthy brain dataset. We show the recovered MR images, error maps, zoomed-in details, and 𝑘-space data with evaluation metrics inPSNR(dB)/SSIM.
图8 模型在fastMRI健康脑部数据集上训练后,于fastMRI患者脑部数据集4倍超分辨率(4× SR)任务中与对比扩散型超分辨率方法的定性对比 图中展示了各方法的重建磁共振(MR)图像、误差图、放大细节图及对应的k空间数据,并标注了峰值信噪比(PSNR,单位:dB)与结构相似性指数(SSIM)作为评价指标。
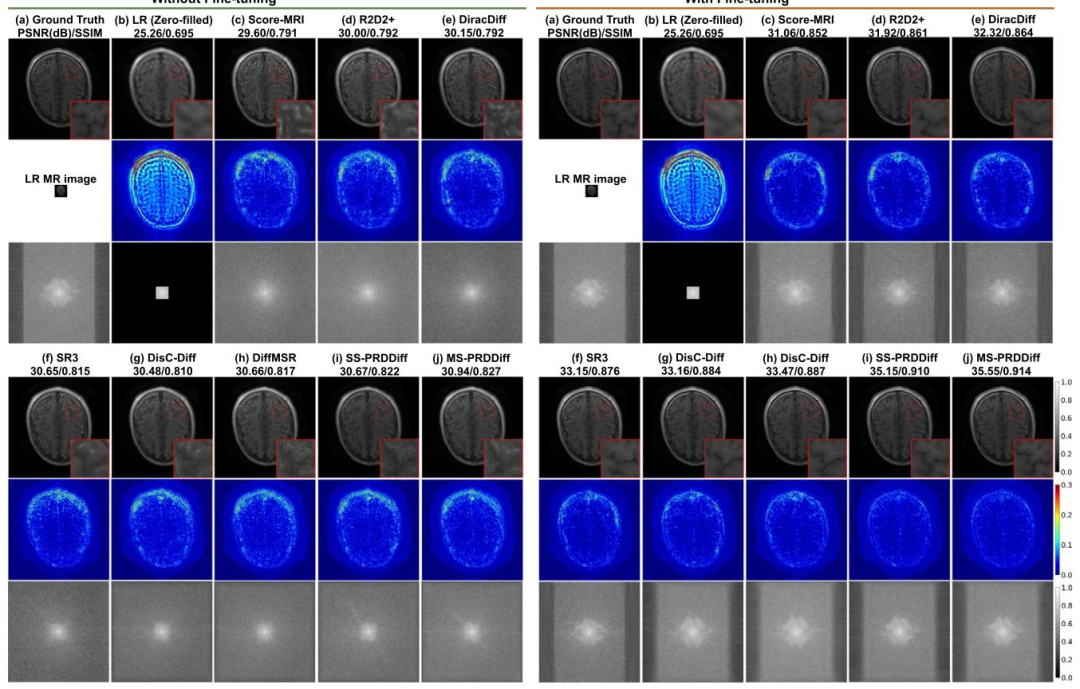
Fig. 9. Qualitative comparison of diffusion-based 8× SR methods tested on T1-weighted MR images, using models trained on T2-weighted MR images, with finetuning and without fine-tuning. We show the recovered MR images, error maps, zoomed-in details, and 𝑘-space data with evaluation metrics in PSNR(dB)/SSIM.
图9 模型在T2加权磁共振(MR)图像上训练后,分别采用微调与不微调方式,在T1加权MR图像8倍超分辨率(8× SR)任务中与其他扩散型超分辨率方法的定性对比 图中展示了各方法的重建MR图像、误差图、放大细节图及对应的k空间数据,并标注了峰值信噪比(PSNR,单位:dB)与结构相似性指数(SSIM)作为评价指标。
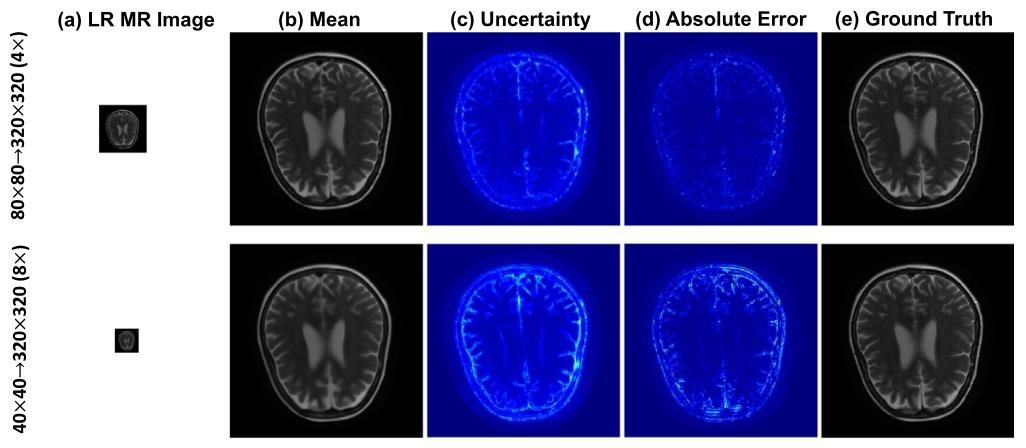
Fig. 10. Visualization of uncertainty estimation results for (top) 4× SR task and (bottle) 8× SR task. From left to right: LR MR image, mean (i.e., the pixel-wisemean of the reconstructed images), uncertainty (i.e., pixel-wise standard deviation), absolute error (i.e., the corresponding absolute error between ground truthand pixel-wise mean of the reconstructed images), and ground truth. Note that the range of the absolute error is [0, 0.4], and the range of the uncertainty is [0,0.15]
图10 (上方)4倍超分辨率(4× SR)任务与(下方)8倍超分辨率(8× SR)任务的不确定性估计结果可视化 从左至右依次为:低分辨率(LR)磁共振(MR)图像、均值图(即重建图像的像素级均值)、不确定性图(即像素级标准差)、绝对误差图(即真实高分辨率图像与重建图像像素级均值的对应绝对误差)、真实高分辨率图像(Ground Truth)。
Table
表
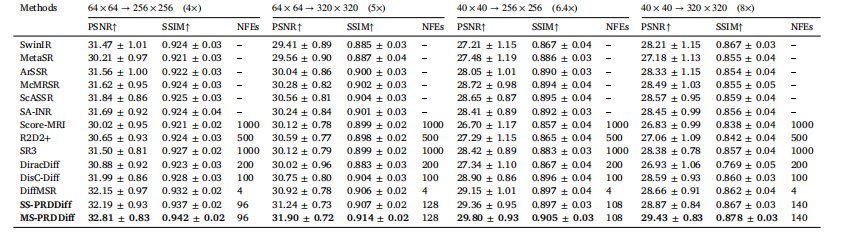
Table 1Quantitative comparison on the fastMRI healthy brain dataset for different SR tasks, in terms of PSNR (dB) and SSIM.
表1 fastMRI健康脑部数据集上不同超分辨率(SR)任务的定量对比(以峰值信噪比(PSNR,单位:dB)和结构相似性指数(SSIM)为评价指标)
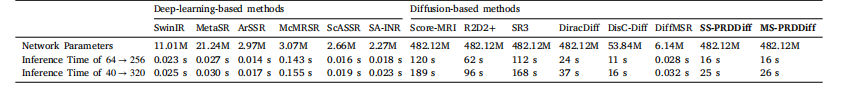
Table 2Computational complexity of different methods. ‘‘M’’ denotes the number of parameters in millions. ‘‘s’’ denotes inference time in seconds
表2 不同方法的计算复杂度 “M”表示参数数量(单位:百万),“s”表示推理时间(单位:秒)
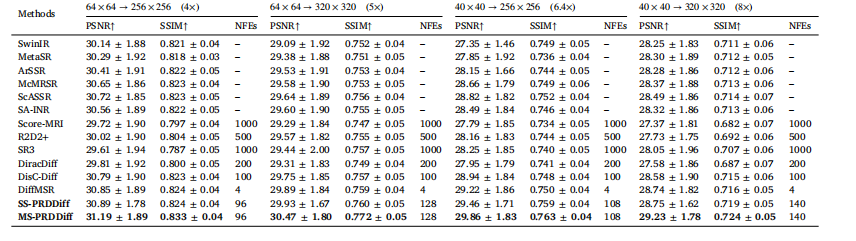
Table 3Quantitative comparison on the fastMRI knee dataset for different SR tasks, in terms of PSNR (dB) and SSIM
表3 fastMRI膝关节数据集上不同超分辨率(SR)任务的定量对比(以峰值信噪比(PSNR,单位:分贝)和结构相似性指数(SSIM)为评价指标)
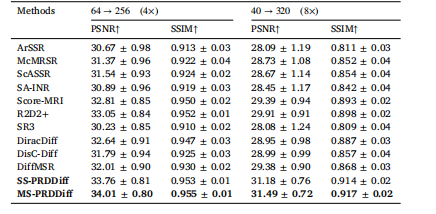
Table 4Quantitative comparison on the fastMRI healthy brain dataset for SR tasks withundersampling in phase-encoding direction.
表4 针对“相位编码方向欠采样”的超分辨率(SR)任务,在fastMRI健康脑部数据集上的定量对比
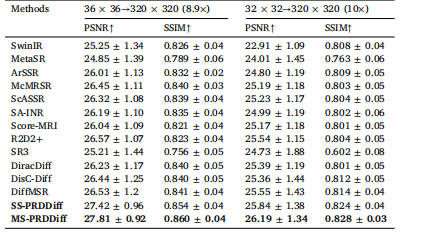
Table 5Quantitative comparison on the fastMRI healthy brain dataset with unseenupsampling scales
表5 针对“未见过的上采样尺度”,在fastMRI健康脑部数据集上的定量对比
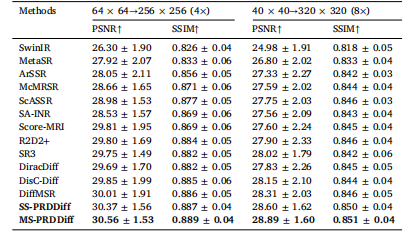
Table 6Quantitative comparison of different methods trained on fastMRI healthy braindataset and tested on real LR-HR dataset.
表6 各方法在fastMRI健康脑部数据集上训练、在真实低分辨率-高分辨率(LR-HR)数据集上测试的定量对比
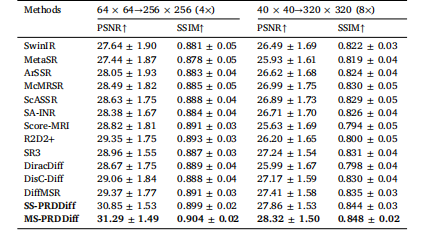
Table 7Quantitative comparison of different methods trained on fastMRI healthy braindataset and tested on the fastMRI patient brain dataset
表7 各方法在fastMRI健康脑部数据集上训练、在fastMRI患者脑部数据集上测试的定量对比
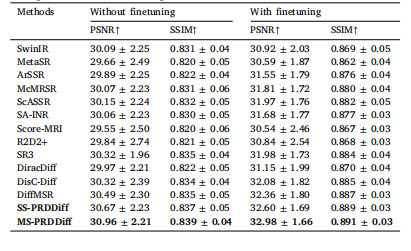
Table 8Quantitative comparison of different methods on T1w MR images with finetuning and without fine-tuning for 8× SR task.
表8 针对8倍超分辨率(8× SR)任务,各方法在T1加权(T1w)磁共振(MR)图像上(含微调与无微调两种设置)的定量对比
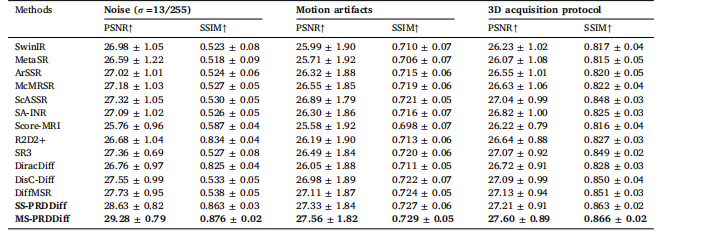
Table 9Quantitative comparison for 8× SR tasks under various challenges, including noise, motion artifacts, and different MRI acquisitionprotocols, in terms of PSNR (dB) and SSIM.
表9 针对8倍超分辨率(8× SR)任务,在多种挑战场景(包括噪声、运动伪影及不同磁共振(MRI)采集协议)下的定量对比(以峰值信噪比(PSNR,单位:dB)和结构相似性指数(SSIM)为评价指标)
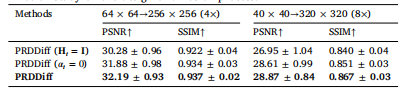
Table 10Ablation study on the design of diffusion process.
表10 关于扩散过程设计的消融实验
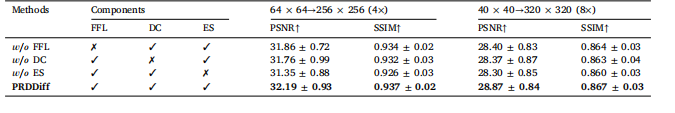
Table 11Ablation study of the effectiveness of key components.
表11 核心组件有效性的消融实验
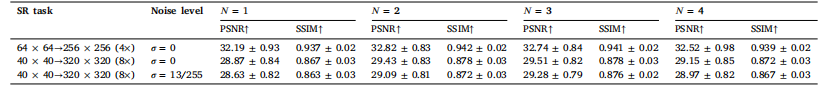
Table 12Quantitative evaluation of different numbers of stages (i.e., 𝑁) for 4×and 8× SR tasks under Gaussian noise with 𝜎 = 13∕255.
表12 在标准差(\boldsymbol{\sigma = 13/255})的高斯噪声下,针对4倍和8倍超分辨率(SR)任务,不同阶段数(即(\boldsymbol{N}))的定量评估
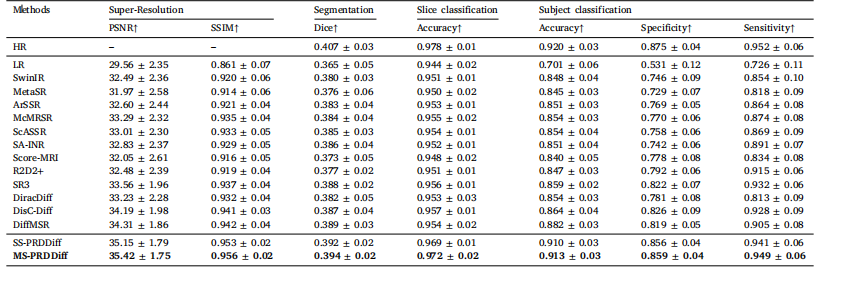
Table 13Quantitative comparison of different methods on clinical pediatric CP dataset for the 4×super-resolution task, PWMI lesion segmentation and CP classificationperformance at both slice and subject levels
表13 各方法在临床儿童脑性瘫痪(CP)数据集上的定量对比,涵盖4倍超分辨率(4× SR)任务、脑室周围白质损伤(PWMI)分割任务,以及在切片层面与受试者层面的脑性瘫痪(CP)分类性能
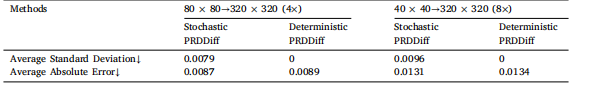
Table 14Quantitative evaluation in average standard deviation and average absolute error, computed over multiple samplesper image and averaged across the fastMRI healthy brain dataset for the 4x and 8x SR tasks.
表14 4倍和8倍超分辨率(SR)任务的平均标准差与平均绝对误差定量评估 (计算方式:对每幅图像的多个样本分别计算,再在fastMRI健康脑部数据集上取平均值)
