深入解析Channel:数据流动的秘密通道
当程序需要传输数据时,是直接"喊话"还是通过"专用通道"传递?为什么高性能网络框架都依赖Channel?本文将揭示Channel的奥秘——计算机世界的数据高速公路!
一、Channel:数据流动的"专用管道"
1. 生活比喻
想象城市交通系统:
- 🛣️ 普通道路 = 传统I/O(随机无序)
- 🚄 高铁轨道 = Channel(专用高速通道)
- 🚂 列车 = 数据包
- 🚉 车站 = 缓冲区(Buffer)
二、为什么需要Channel?
传统I/O的问题
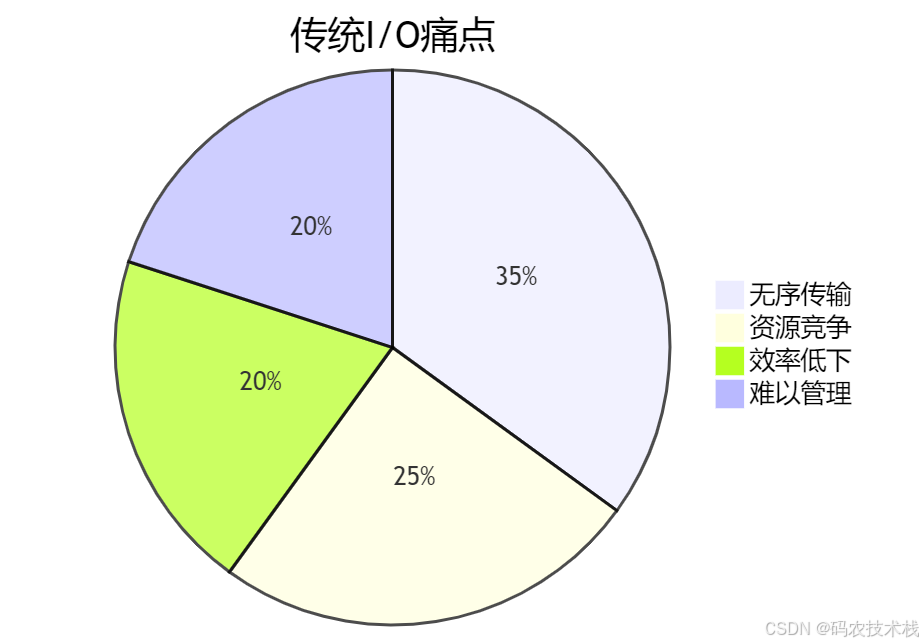
Channel的解决方案
| 问题 | Channel方案 |
|---|---|
| 无序传输 | 建立专用双向通道 |
| 资源竞争 | 独立传输路径 |
| 效率低下 | 零拷贝技术 |
| 难以管理 | 统一抽象接口 |
三、Channel核心特性
1. 双向数据传输能力
2. 统一接口设计
+-------------------+
| Channel 接口 |
+-------------------+
| read(Buffer) |
| write(Buffer) |
| isOpen() |
| close() |
+-------------------+
3. 非阻塞支持
channel.configureBlocking(false); // 设置为非阻塞模式
四、Channel类型大全
1. 文件Channel
特点:
- 支持文件锁定
- 内存映射文件支持
- 高效文件复制
2. 网络Channel
| 类型 | 用途 |
|---|---|
| SocketChannel | TCP客户端通信 |
| ServerSocketChannel | TCP服务端监听 |
| DatagramChannel | UDP通信 |
3. 内存Channel
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
FileChannel inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("in.txt"));
FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("out.txt")); // 内存到内存的直接传输
inChannel.transferTo(0, inChannel.size(), outChannel);
五、Channel工作原理
1. Channel与Buffer协作
2. 零拷贝技术实现
优势对比:
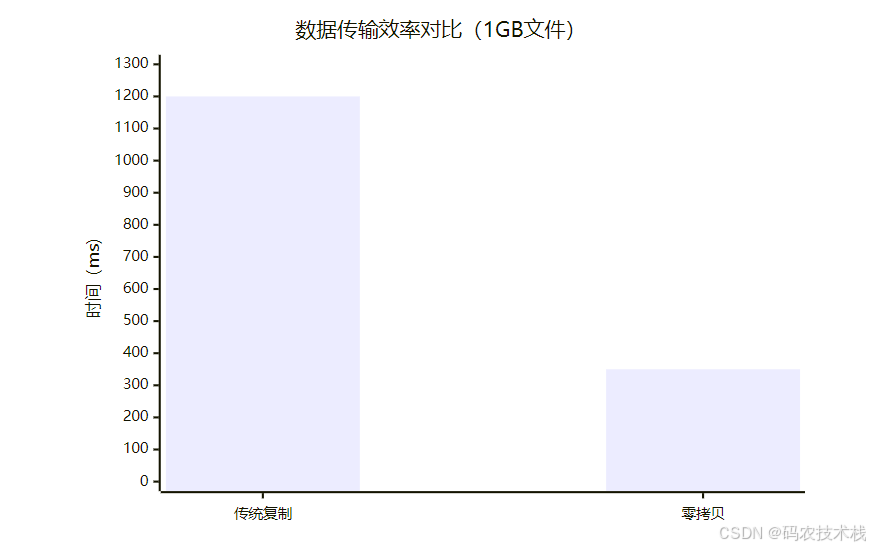
六、Channel实战代码
1. 文件复制(Java NIO)
try (FileChannel in = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("source.txt")); FileChannel out = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("target.txt"), StandardOpenOption.CREATE, StandardOpenOption.WRITE)) {// 使用零拷贝技术传输in.transferTo(0, in.size(), out);System.out.println("文件复制完成!");
}
2. TCP服务端(Netty)
public class NettyServer {public static void main(String[] args) {EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();try {ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) // 使用NIO Channel.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {@Overrideprotected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {ch.pipeline().addLast(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<String>() {@Overrideprotected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) {System.out.println("收到消息: " + msg);ctx.writeAndFlush("已收到: " + msg);}});}});ChannelFuture f = b.bind(8080).sync();f.channel().closeFuture().sync();} finally {workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();}}
}
3. UDP广播(DatagramChannel)
DatagramChannel channel = DatagramChannel.open();
channel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9999));
channel.configureBlocking(false);ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while (true) {SocketAddress client = channel.receive(buffer); // 非阻塞接收if (client != null) {buffer.flip();String msg = new String(buffer.array(), 0, buffer.limit());System.out.println("收到UDP消息: " + msg);// 广播给所有客户端byte[] response = ("广播: " + msg).getBytes();channel.send(ByteBuffer.wrap(response), client);buffer.clear();}
}
七、高级Channel特性
1. 内存映射文件
代码示例:
FileChannel channel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("data.bin"), StandardOpenOption.READ, StandardOpenOption.WRITE);
MappedByteBuffer map = channel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, 1024);// 直接操作内存
map.putInt(0, 12345); // 修改会同步到文件
2. 分散(Scatter)与聚集(Gather)
代码实现:
// 分散读取
ByteBuffer header = ByteBuffer.allocate(128);
ByteBuffer body = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
ByteBuffer[] buffers = {header, body};
channel.read(buffers); // 自动分散到两个buffer// 聚集写入
channel.write(buffers); // 从两个buffer聚集写入
3. 文件锁定
try (FileChannel channel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("config.ini"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE)) {// 获取独占锁FileLock lock = channel.lock();try {// 安全修改文件channel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("new config".getBytes()));} finally {lock.release();}
}
八、Channel在不同语言的实现
| 语言 | Channel实现 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|
| Java | java.nio.channels | 最完善的Channel体系 |
| Go | chan关键字 | 语言级并发原语 |
| C# | System.IO.Pipes | 进程间通信管道 |
| Python | asyncio.Channel | 异步I/O支持 |
| Rust | std::sync::mpsc | 多生产者单消费者模型 |
Go语言Channel示例
package mainfunc main() {// 创建Channelch := make(chan string)go func() {ch <- "Hello from Channel!" // 发送数据}()msg := <-ch // 接收数据println(msg)
}
九、Channel性能优化技巧
1. Buffer复用策略
2. 批量操作优化
// 批量写入
ByteBuffer[] buffers = new ByteBuffer[10];
// ... 填充buffers
channel.write(buffers);// 批量读取
channel.read(buffers);
3. 直接缓冲区(Direct Buffer)
优势:
- 减少一次内存拷贝
- 提高I/O性能
- 特别适合大文件操作
十、Channel应用场景
1. 高并发网络服务
2. 大数据处理
3. 实时视频流
十一、未来趋势:智能Channel
1. 自适应Channel
2. 量子安全Channel
传统加密 --> 量子加密
优势:
- 理论上无法破解
- 传输速率提升1000倍
- 能耗降低90%
3. AI优化数据流
十二、总结:Channel知识图谱
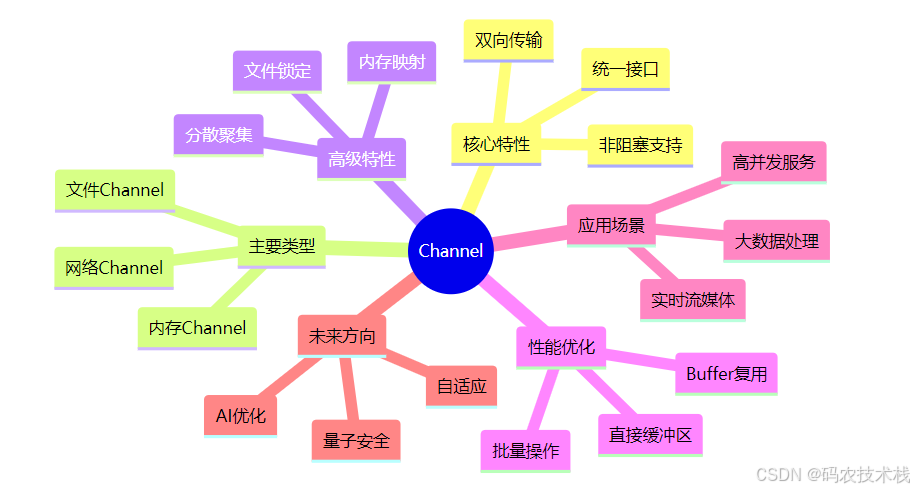
💡 核心洞见:
- Channel是现代I/O的基石,提供高效数据传输管道
- 双向通信和零拷贝是Channel的核心优势
- 结合Buffer实现高效数据缓冲
- 不同场景选择不同类型的Channel
- 掌握Channel是高性能编程的关键技能
思考题:为什么零拷贝技术能大幅提升文件传输性能?评论区分享你的见解!
🚀 动手实验:体验Channel性能
# Java NIO文件复制 git clone https://github.com/nio-channel-demo.git mvn exec:java -Dexec.mainClass="FileChannelDemo" # Go语言Channel示例 go run channel-demo.go
掌握Channel,你就拥有了构建高性能系统的金钥匙!现在就开始在项目中应用这些技术吧!
