【机器学习】基于双向LSTM的IMDb情感分析
【机器学习】基于双向LSTM的IMDb情感分析
简介
在自然语言处理领域,情感分析是入门级经典任务,而 IMDb 电影评论数据集则是验证模型效果的理想选择。本文将基于 TensorFlow 框架,从数据预处理、词汇表构建、模型设计到完整训练流程实现一个基于双向 LSTM 的情感分析模型。
项目目标
利用 IMDb 电影评论数据集(包含 50000 条正负情感标注的评论),构建一个深度学习模型,实现对电影评论的情感二分类(正面 / 负面),最终通过早停策略等优化手段提升模型泛化能力。
技术栈选择
| 核心框架 | TensorFlow 2.x(Keras API) |
|---|---|
| 数据处理 | NumPy、Python 标准库(os、pathlib) |
| 工具辅助 | tqdm(进度条)、logging(日志)、Counter(词频统计) |
| 预训练 | GloVe 6B 50d 词向量(提供初始语义表示) |
环境准备与依赖导入
import os
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import pprint
import logging
import time
from collections import Counter
from pathlib import Path
from tqdm import tqdm
数据预处理
预处理流程主要包括数据加载、词汇映射构建、序列标准化和文件存储四个步骤。
1.加载 IMDb 内置数据集
TensorFlow 内置了预处理后的 IMDb 数据集,可直接通过keras.datasets加载,数据已转换为整数序列(每个整数对应一个单词):
# 加载训练集和测试集,自动分为(特征, 标签)对
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = tf.keras.datasets.imdb.load_data()
- 训练集 / 测试集各 25000 条数据,标签0表示负面评论,1表示正面评论
- 整数序列以标记开头(对应索引 1),未知词以特定索引表示
2.构建词汇映射表
原始数据集的整数序列需要与实际单词对应,同时需补充特殊标记(填充、起始、未知词)
# 获取原始词汇表(单词→原始索引)
_word2idx = tf.keras.datasets.imdb.get_word_index()
# 索引后移3位,预留特殊标记位置
word2idx = {w: i+3 for w, i in _word2idx.items()}
# 添加特殊标记
word2idx['<pad>'] = 0 # 填充标记(统一序列长度)
word2idx['<start>'] = 1 # 起始标记
word2idx['<unk>'] = 2 # 未知词标记
# 构建反向映射(索引→单词,用于文本还原)
idx2word = {i: w for w, i in word2idx.items()}
3.序列标准化与数据存储
不同评论长度差异较大,需按长度排序同统一序列格式,最终写入文本文件便于后续分析
# 按序列长度排序(减少填充冗余)
def sort_by_len(x, y):x, y = np.asarray(x), np.asarray(y)idx = sorted(range(len(x)), key=lambda i: len(x[i]))return x[idx], y[idx]# 排序训练集和测试集
x_train, y_train = sort_by_len(x_train, y_train)
x_test, y_test = sort_by_len(x_test, y_test)# 写入文本文件(格式:标签\t评论文本)
def write_file(f_path, xs, ys):with open(f_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:for x, y in zip(xs, ys):# 去除<start>标记,还原文本text = ' '.join([idx2word[i] for i in x][1:])f.write(f"{y}\t{text}\n")# 创建数据目录并写入文件
Path('../data').mkdir(exist_ok=True)
write_file('../data/train1.txt', x_train, y_train)
write_file('../data/test1.txt', x_test, y_test)
词汇表与预训练词向量准备
深度学习模型需要将文本转换为数值向量,预训练词向量能提供更优的初始语义表示,加速模型收敛。
1.构建过滤后的词汇表
原始词汇表包含大量低频词,过滤低频词可减少模型复杂度
# 统计训练集词频
counter = Counter()
with open('../data/train1.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:for line in f:_, words = line.rstrip().split('\t')counter.update(words.split(' '))# 筛选频率≥10的词,加入<pad>标记
words = ['<pad>'] + [w for w, freq in counter.most_common() if freq >= 10]
vocab_size = len(words)# 保存词汇表
Path('../vocab').mkdir(exist_ok=True)
with open('../vocab/word1.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:for w in words:f.write(f"{w}\n")# 重建单词→索引映射
word2idx = {}
with open('../vocab/word1.txt', encoding='utf-8') as f:for i, line in enumerate(f):word2idx[line.rstrip()] = i
2. 加载 GloVe 预训练词向量
GloVe(Global Vectors for Word Representation)是常用的预训练词向量,我们加载 50 维的词向量并构建嵌入矩阵:
# 初始化嵌入矩阵(词汇表大小+1, 词向量维度)
embedding_dim = 50
embedding = np.zeros((vocab_size + 1, embedding_dim))# 加载GloVe词向量并填充矩阵
count = 0 # 统计匹配到的词向量数量
with open('../data/glove.6B.50d.txt', encoding='utf-8') as f:for i, line in enumerate(f):if i % 100000 == 0:print(f"-处理到第{i}行")line = line.rstrip()word, vec = line.split(' ')[0], line.split(' ')[1:]if word in word2idx:count += 1embedding[word2idx[word]] = np.asarray(vec, dtype='float32')# 输出匹配率
print(f"[{count} / {vocab_size}] 个单词匹配到预训练词向量")
# 保存嵌入矩阵
np.save('../vocab/word1.npy', embedding)
- 预训练词向量匹配率越高,模型初始语义表示越准确
- 未匹配的单词保持零向量,训练中可自主学习
数据生成器
大型数据集直接加载会占用大量内存,使用生成器逐行加载数据,结合 TensorFlow 的tf.dataAPI 优化数据管道:
- tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(tensor):将tensor沿其第一个维度切片,返回一个含有N个样本的数据集,这样做的问题就是需要将整个数据集整体传入,然后切片建立数据集类对象,比较占内存。
- tf.data.Dataset.from_generator(data_generator,output_data_type,output_data_shape):从一个生成器中不断读取样本
1.自定义数据生成器
将文本转换为模型可接受的固定长度整数序列
def data_generator(f_path, params):with open(f_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:print(f'读取文件: {f_path}')for line in f:line = line.rstrip()label, text = line.split('\t')words = text.split(' ')# 单词→索引,未知词用vocab_size标记x = [params['word2idx'].get(w, len(params['word2idx'])) for w in words]# 截断或填充至max_lenif len(x) >= params['max_len']:x = x[:params['max_len']]else:x += [0] * (params['max_len'] - len(x))y = int(label)yield x, y
2.构建 TensorFlow 数据集
通过tf.data.Dataset.from_generator转换生成器,添加分批、打乱、预加载等优化:
def data_generator(f_path, params):with open(f_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:print(f'读取文件: {f_path}')for line in f:line = line.rstrip()label, text = line.split('\t')words = text.split(' ')# 单词→索引,未知词用vocab_size标记x = [params['word2idx'].get(w, len(params['word2idx'])) for w in words]# 截断或填充至max_lenif len(x) >= params['max_len']:x = x[:params['max_len']]else:x += [0] * (params['max_len'] - len(x))y = int(label)yield x, y
模型设计:层次化双向 LSTM
针对文本序列的时序特性,采用双向 LSTM 捕捉上下文信息,结合层次化结构和正则化手段提升模型性能。
1. 模型结构定义
继承tf.keras.Model自定义模型,包含嵌入层、多层双向 LSTM、全连接层:
class Model(tf.keras.Model):def __init__(self, params):super().__init__()# 加载预训练嵌入层(不更新权重)self.embedding = tf.Variable(np.load('../vocab/word1.npy'),dtype=tf.float32,name='pretrained_embedding',trainable=False,)# Dropout层(防止过拟合)self.drop1 = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(params['dropout_rate'])self.drop2 = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(params['dropout_rate'])self.drop3 = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(params['dropout_rate'])self.drop_fc = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(params['dropout_rate'])# 三层双向LSTM(捕捉正反序上下文)self.rnn1 = tf.keras.layers.Bidirectional(tf.keras.layers.LSTM(params['rnn_units'], return_sequences=True))self.rnn2 = tf.keras.layers.Bidirectional(tf.keras.layers.LSTM(params['rnn_units'], return_sequences=True))self.rnn3 = tf.keras.layers.Bidirectional(tf.keras.layers.LSTM(params['rnn_units'], return_sequences=True))# 全连接层(特征融合)self.fc = tf.keras.layers.Dense(2*params['rnn_units'], tf.nn.elu)# 输出层(二分类)self.out_linear = tf.keras.layers.Dense(2)def call(self, inputs, training=False):# 输入类型转换if inputs.dtype != tf.int32:inputs = tf.cast(inputs, tf.int32)batch_sz = tf.shape(inputs)[0]rnn_units = 2 * params['rnn_units'] # 双向LSTM输出维度翻倍# 1. 词嵌入 lookupx = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(self.embedding, inputs)# 2. 层次化LSTM处理(分粒度捕捉上下文)# 第一层:细粒度处理x = tf.reshape(x, (batch_sz*10*10, 10, 50))x = self.drop1(x, training=training)x = self.rnn1(x)x = tf.reduce_max(x, 1) # 时序最大池化# 第二层:中粒度处理x = tf.reshape(x, (batch_sz*10, 10, rnn_units))x = self.drop2(x, training=training)x = self.rnn2(x)x = tf.reduce_max(x, 1)# 第三层:粗粒度处理x = tf.reshape(x, (batch_sz, 10, rnn_units))x = self.drop3(x, training=training)x = self.rnn3(x)x = tf.reduce_max(x, 1)# 3. 输出层x = self.drop_fc(x, training=training)x = self.fc(x)x = self.out_linear(x)return x
- 双向LSTM:同时学习文本的正向和反向语义,比单向LSTM更全面
- 层次化结构:通过reshape将序列分粒度处理,捕捉不同长度的上下文
- 最大池化:提取时序维度的关键特征,降低计算复杂度
模型训练与优化:从配置到早停
合理的训练配置和优化策略是模型收敛的关键,本项目采用学习率衰减、梯度裁剪和早停策略提升训练效果。
1. 训练参数配置
统一管理超参数和路径配置,便于后续调优:
params = {'vocab_path': '../vocab/word1.txt', # 词汇表文件路径'train_path': '../data/train1.txt', # 训练数据集文件路径'test_path': '../data/test1.txt', # 测试数据集文件路径'num_samples':25000, #样本数量'num_labels':2, # 标签数量,表明这是一个二分类任务'batch_size':32, # 批处理大小,每次训练模型时输入的样本数量 'max_len':1000, #文本序列的最大长度,用于对文本进行截断或补全'rnn_units':200, # RNN层的单元数量,这里用于配置LSTM层的大小'dropout_rate':0.2, # dropout比率,用于防止过拟合'clip_norm':10., #梯度裁剪的阈值,用于防止梯度爆炸问题'num_patience':3, # 早停策略的耐心值,当验证集连续3次没有提升时停止训练'lr': 3e-4, # 学习率,优化器更新参数的步长
}
2. 训练流程实现
包含模型初始化、优化器配置、训练循环和早停判断:
# 初始化模型
model = Model(params)
model.build(input_shape=(None, None)) # 动态输入形状# 学习率指数衰减(随步数衰减)
decay_lr = tf.optimizers.schedules.ExponentialDecay(params['lr'],1000, # 衰减步数0.95 # 衰减率
)
# Adam优化器
optim = tf.optimizers.Adam(params['lr'])# 训练跟踪变量
global_step = 0
history_acc = [] # 准确率历史
best_acc = 0.0 # 最佳准确率# 日志配置
logging.getLogger('tensorflow').setLevel(logging.INFO)
t0 = time.time()# 早停判断函数(检查是否连续下降)
def is_descending(history: list):history = history[-(params['num_patience']+1):]for i in range(1, len(history)):if history[i-1] <= history[i]:return Falsereturn True# 训练主循环
while True:# 训练阶段:遍历训练集for texts, labels in dataset(is_training=True, params=params):with tf.GradientTape() as tape:logits = model(texts, training=True)# 计算交叉熵损失loss = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=labels, logits=logits)loss = tf.reduce_mean(loss)# 更新学习率optim.lr.assign(decay_lr(global_step))# 计算梯度并裁剪grads = tape.gradient(loss, model.trainable_variables)grads, _ = tf.clip_by_global_norm(grads, params['clip_norm'])# 应用梯度更新参数optim.apply_gradients(zip(grads, model.trainable_variables))# 每50步输出日志if global_step % 50 == 0:logging.info(f"Step {global_step} | Loss: {loss.numpy():.4f} | "f"Spent: {time.time()-t0:.1f}s | LR: {optim.lr.numpy():.6f}")t0 = time.time()global_step += 1# 验证阶段:评估测试集准确率acc_metric = tf.keras.metrics.Accuracy()for texts, labels in dataset(is_training=False, params=params):logits = model(texts, training=False)y_pred = tf.argmax(logits, axis=-1) # 取概率最大的类别acc_metric.update_state(labels, y_pred)acc = acc_metric.result().numpy()logging.info(f"Evaluation: Testing Accuracy: {acc:.3f}")history_acc.append(acc)# 更新最佳准确率if acc > best_acc:best_acc = acclogging.info(f"Best Accuracy: {best_acc:.3f}")# 早停判断if len(history_acc) > params['num_patience'] and is_descending(history_acc):logging.info(f"Testing Accuracy not improved over {params['num_patience']} epochs, Early Stop")break
运行结果
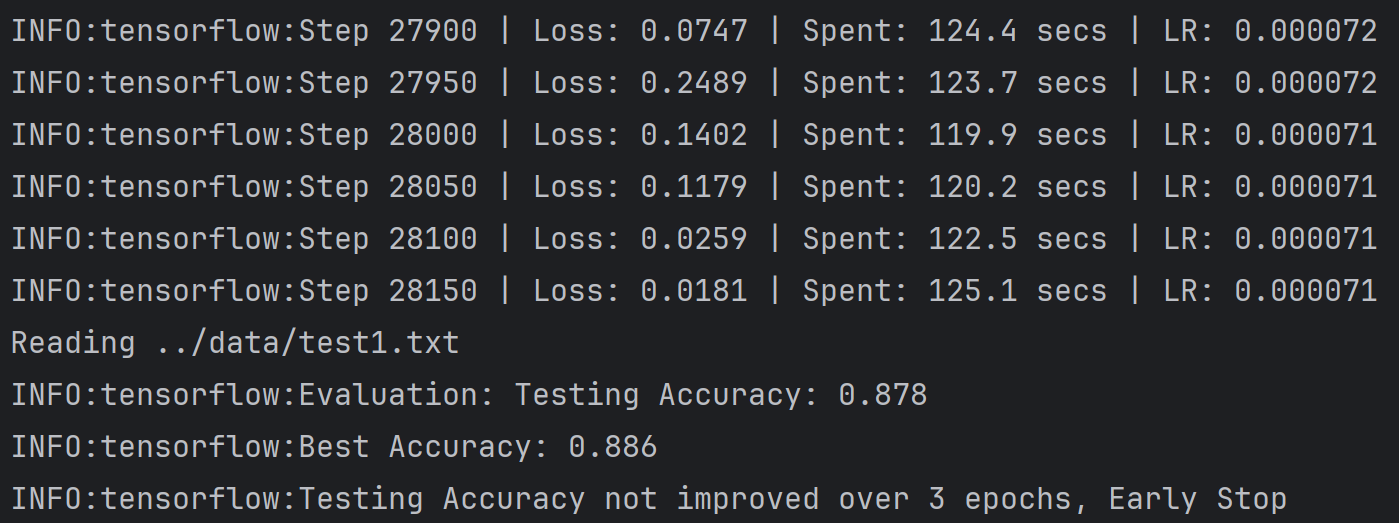
训练结果核心指标
| 指标 | 最终数值/状态 | 核心含义 |
|---|---|---|
| 最终训练步数 | 28150步 | 模型共经过 28150 次参数更新,覆盖多轮训练集迭代 |
| 最终训练损失(Loss) | 0.0181 | 模型在最后一批训练数据上的预测误差极低,拟合程度很高 |
| 最终学习率 | 0.000071(7.1e-5) | 经过指数衰减后,学习率已从初始 3e-4 降至极低水平,接近训练尾声 |
| 测试集准确率 | 0.878 | 模型在未见过的测试数据上分类正确率为 87.8%,泛化能力中等偏上 |
| 最佳测试准确率 | 0.886 | 训练过程中模型达到的最高泛化性能为 88.6%,早停前出现性能回落 |
| 早停触发条件 | 连续3轮测试准确率未提升 | 符合预设的早停策略,避免模型进一步过拟合 |
