【文献分享】空间互近邻关系在空间转录组学数据中的应用
文章目录
- 介绍
- 代码
- 参考
介绍
互最近邻(MNN)是一种广泛使用的计算工具,用于对单细胞 RNA 测序数据进行批量校正。然而,在诸如空间转录组学等应用中,它未能考虑二维空间信息。
在此,我们介绍了空间MNN 这一算法,该算法能够整合多个空间转录组样本,并识别出空间区域。我们的方法首先基于空间坐标构建一个 k 近邻(kNN)图,剔除噪声边,并确定每个样本的生态位作为锚点。接下来,我们在样本之间构建一个 MNN 图以识别相似的生态位。最后,可以使用现有的算法(如 Louvain 算法)对空间MNN 图进行分区,以预测整个组织样本中的空间区域。我们使用大型数据集(包括一个包含 N = 31 个 10x Genomics Visium 样本的数据集)来展示空间MNN 的性能。我们还评估了空间MNN 的计算性能与其他流行的空间聚类方法相比的情况。
Motivation: Mutual nearest neighbors (MNN) is a widely used computational tool to perform batch correction for single-cell RNA-sequencing data. However, in applications such as spatial transcriptomics, it fails to take into account the 2D spatial information.
Results: Here, we present spatialMNN, an algorithm that integrates multiple spatial transcriptomic samples and identifies spatial domains. Our approach begins by building a k-nearest neighbors (kNN) graph based on the spatial coordinates, prunes noisy edges, and identifies niches to act as anchor points for each sample. Next, we construct a MNN graph across the samples to identify similar niches. Finally, the spatialMNN graph can be partitioned using existing algorithms, such as the Louvain algorithm to predict spatial domains across the tissue samples. We demonstrate the performance of spatialMNN using large datasets, including one with N = 31 10x Genomics Visium samples. We also evaluate the computing performance of spatialMNN to other popular spatial clustering methods.

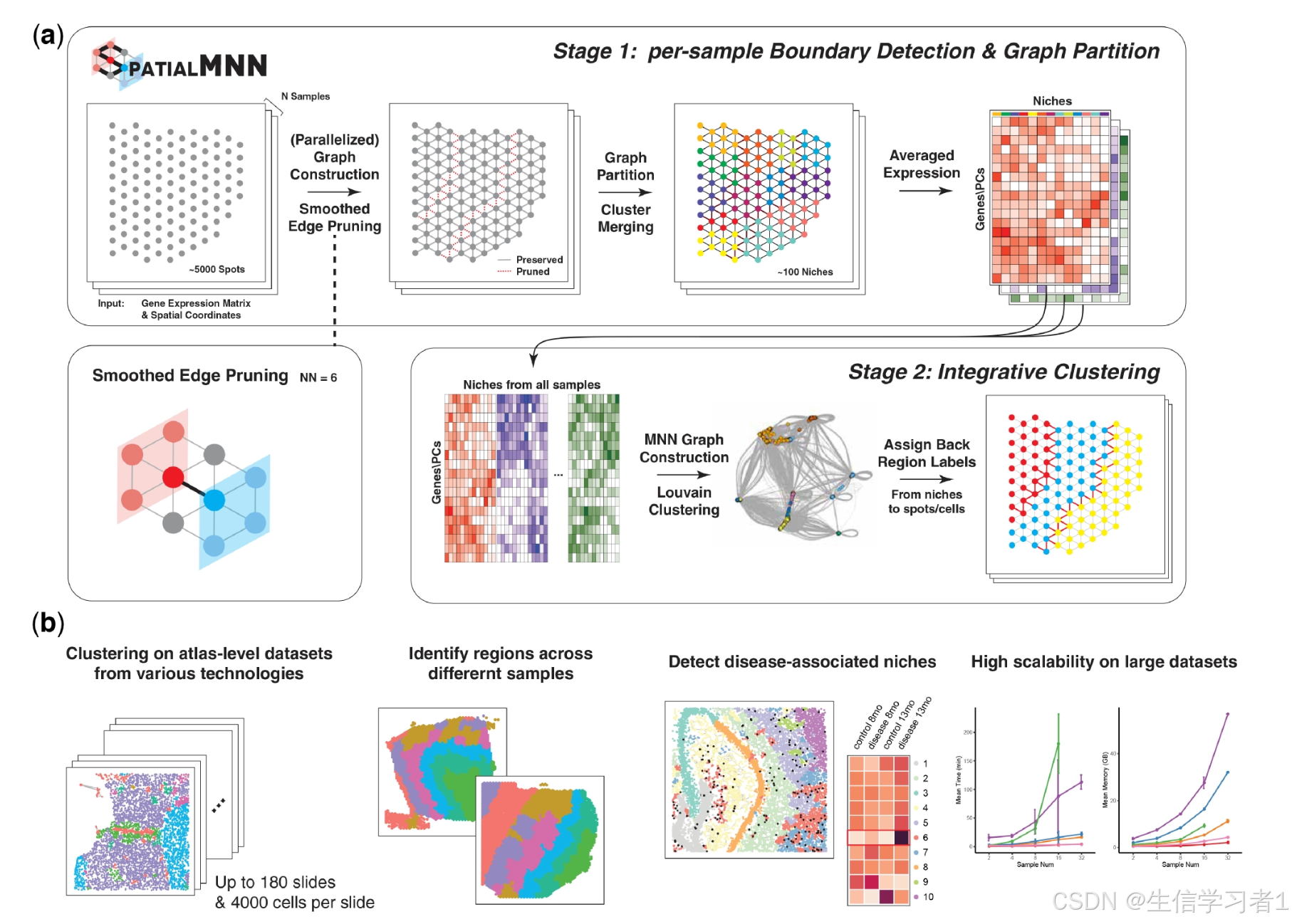
Overview of spatialMNN to integrate multiple SRT samples and perform downstream analyses including spatial domain detection. (a) Given a set
of N multi-sample SRT datasets, the spatialMNN algorithm builds a k-nearest neighbor (kNN) graph based on the spatial coordinates and gene expression
within each tissue sample. Next, edge weights are smoothed (considering neighboring spots/cells) and pruned to identify a set of anchor points for each
sample. Then, spatialMNN constructs a MNN graph across the samples, followed by Louvain clustering to identify similar niches across the samples using
gene expression that has been averaged across spots/cells within a niche. The resulting clusters are assigned back to the original spatial coordinates. (b)
spatialMNN can be used in downstream analyses, including detecting spatial domains in large-scale atlas datasets, identifying regions across different
samples, and detecting disease-associated niches. We demonstrate how spatialMNN is highly scalable and accurate on large datasets.
空间MNN 的概述:用于整合多个 SRT 样本并执行下游分析,包括空间域检测。(a)给定一组 N 个多样本 SRT 数据集,空间MNN 算法基于每个组织样本中的空间坐标和基因表达构建一个 k 近邻(kNN)图。接下来,对边权重进行平滑处理(考虑相邻的点/细胞),并进行修剪以确定每个样本的一组锚点。然后,空间MNN 在样本之间构建一个 MNN 图,随后通过使用在某个生态位内的点/细胞上平均计算得到的基因表达来执行 Louvain 聚类,以识别样本之间的相似生态位。所得的聚类再根据原始的空间坐标进行重新分配。(b)
空间MNN 可用于后续分析,包括在大规模图谱数据集中检测空间区域、识别不同样本中的区域以及检测与疾病相关的生态位。我们展示了空间MNN 在大型数据集上的高扩展性和准确性。
代码
https://github.com/Pixel-Dream/spatialMNN
参考
- Spatial mutual nearest neighbors for spatial transcriptomics data
- https://github.com/Pixel-Dream/spatialMNN
